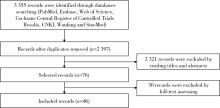
北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (2): 304-314. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.02.018
显微外科手术与血管内栓塞治疗硬脊膜动静脉瘘临床疗效比较的meta分析
- 北京大学第一医院神经外科,北京 100034
Clinical outcomes following microsurgery and endovascular embolization in the management of spinal dural arteriovenous fistula: A meta-analysis study
YUAN Chang-wei,WANG Ying-jin,ZHANG Shu-jie,SHEN Sheng-li,DUAN Hong-zhou( )
)
- Department of Neurosurgery, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
摘要:
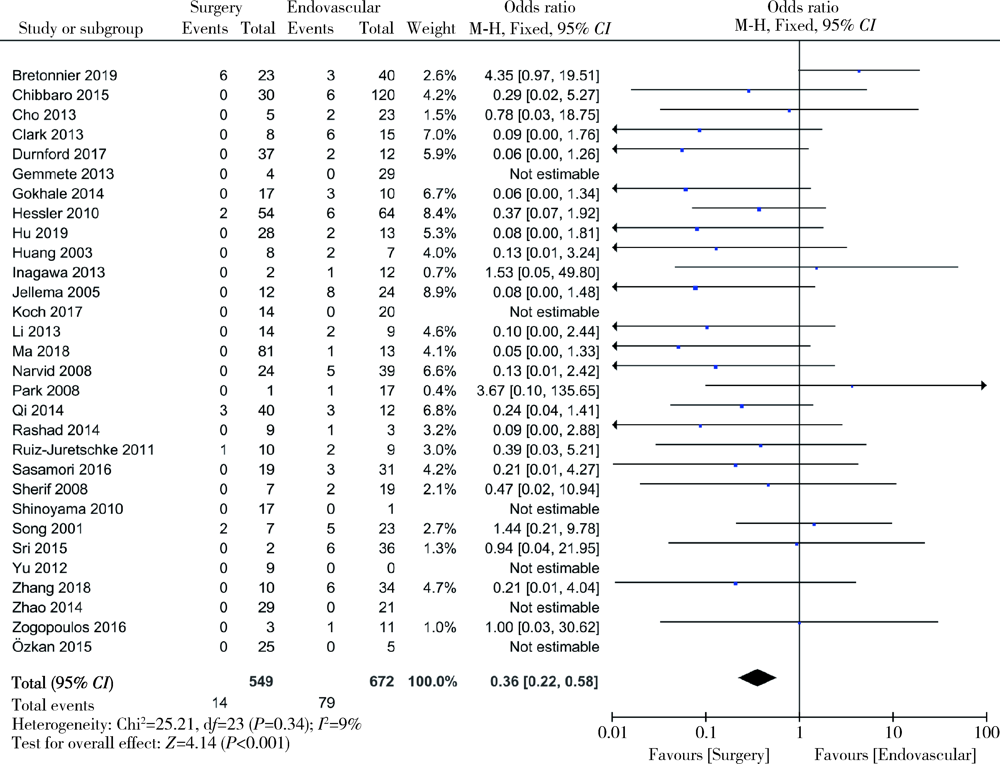
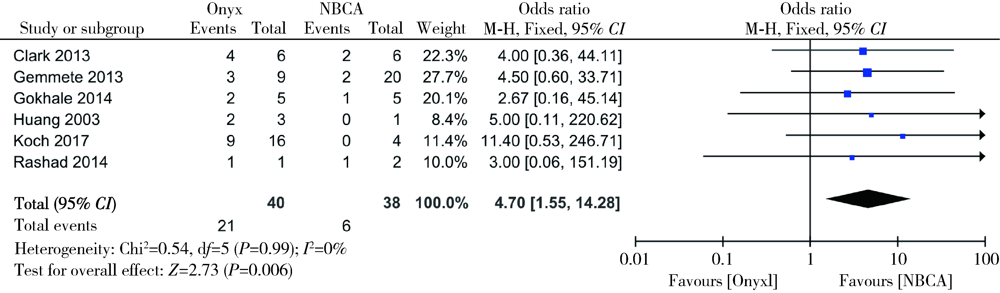
目的: 通过meta分析比较显微外科手术与血管内栓塞治疗硬脊膜动静脉瘘的临床疗效。方法: 计算机检索PubMed、Embase、Web of Science、Cochrane临床试验数据库、中国知网、万方数据库、中国生物医学文献数据库(Chinese BioMedical Literature Database,CBM),检索时间从数据库建库至2019年12月,纳入采用显微外科手术和血管内栓塞治疗硬脊膜动静脉瘘的所有中英文文献。使用RevMan 5.3软件进行统计学分析,评估术后早期失败率、远期复发、神经功能恢复程度、并发症情况,比较两种治疗方式对硬脊膜动静脉瘘的临床疗效,并对血管内栓塞治疗进行亚组分析。结果: 纳入文献46篇,共1 958例硬脊膜动静脉瘘患者,其中935例采用显微外科手术治疗,1 023例采用血管内栓塞治疗,漏斗图显示未见明显发表偏倚。经meta分析结果显示,显微外科手术早期治疗失败的发生率低于血管内栓塞治疗(OR=0.20, 95%CI: 0.13~0.30, P<0.05),远期复发率也低于血管内栓塞治疗(OR=0.36, 95%CI: 0.22~0.58, P<0.05),显微外科手术治疗后患者神经功能改善情况优于血管内栓塞治疗的患者(OR=2.86, 95%CI: 1.36~5.99, P<0.05),两种治疗方式患者并发症的发生率差异无统计学意义(OR=1.52, 95%CI: 0.88~2.64, P=0.14)。血管内栓塞治疗的患者中,使用Onyx胶进行栓塞比使用α-氰基丙烯酸正丁酯(n-butyl 2-cyanoacrylate,NBCA胶)有更高的治疗失败或复发风险,差异有统计学意义(OR=4.70, 95%CI: 1.55~14.28, P<0.05)。结论: 虽然血管内栓塞治疗硬脊膜动静脉瘘的应用日趋广泛,但显微外科手术所获得的临床疗效仍明显优于血管内栓塞治疗。
中图分类号:
- R744.1
| [1] | 马廉亭, 龚杰, 樊光辉, 等. 脊髓静脉高压综合征的诊断治疗策略与方法[J]. 中华神经外科志, 2010, 26(11):1007-1009. |
| [2] | 王刚, 佟志勇, 刘源, 等. 硬脊膜动静脉瘘的临床特点和治疗现状[J]. 医学综述, 2018, 24(3):527-532. |
| [3] |
Brinjikji W, Nasr DM, Morris JM, et al. Clinical outcomes of patients with delayed diagnosis of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas[J]. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 2016, 37(2):380-386.
doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4504 |
| [4] |
Aminoff MJ, Logue V. The prognosis of patients with spinal vascular malformations[J]. Brain, 1974, 97(1):211-218.
pmid: 4434169 |
| [5] |
Ushikoshi S, Hida K, Kikuchi Y, et al. Functional prognosis after treatment of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas[J]. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo), 1999, 39(3):206-213.
doi: 10.2176/nmc.39.206 |
| [6] |
Song JK, Vinuela F, Gobin YP, et al. Surgical and endovascular treatment of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: Long-term disability assessment and prognostic factors[J]. J Neurosurg, 2001, 94(2 Suppl):199-204.
pmid: 11302620 |
| [7] |
Jellema K, Sluzewski M, van Rooij WJ, et al. Embolization of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: Importance of occlusion of the draining vein[J]. J Neurosurg Spine, 2005, 2(5):580-583.
doi: 10.3171/spi.2005.2.5.0580 |
| [8] | Andres RH, Barth A, Guzman R, et al. Endovascular and surgical treatment of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas[J]. Neuro-radiology, 2008, 50(10):869-876. |
| [9] | Narvid J, Hetts SW, Larsen D, et al. Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulae: Clinical features and long-term results[J]. Neurosurge-ry, 2008, 62(1):159-167. |
| [10] |
Park SB, Han MH, Jahng TA, et al. Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: Clinical experience with endovascular treatment as a primary therapeutic modality[J]. J Korean Neurosurg Soc, 2008, 44(6):364-369.
doi: 10.3340/jkns.2008.44.6.364 |
| [11] |
Sherif C, Gruber A, Bavinzski G, et al. Long-term outcome of a multidisciplinary concept of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulae treatment[J]. Neuroradiology, 2008, 50(1):67-74.
doi: 10.1007/s00234-007-0303-4 |
| [12] |
Hessler C, Regelsberger J, Grzyska U, et al. Therapeutic clues in spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: A 30 year experience of 156 cases[J]. Cent Eur Neurosurg, 2010, 71(1):8-12.
doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1224195 pmid: 19784910 |
| [13] |
Shinoyama M, Endo T, Takahash T, et al. Long-term outcome of cervical and thoracolumbar dural arteriovenous fistulas with emphasis on sensory disturbance and neuropathic pain[J]. World Neurosurg, 2010, 73(4):401-408.
doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2010.01.003 pmid: 20849800 |
| [14] |
Kaufmann TJ, Morris JM, Saladino A, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging findings in treated spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: lack of correlation with clinical outcomes[J]. J Neurosurg Spine, 2011, 14(4):548-554.
doi: 10.3171/2010.11.SPINE10178 |
| [15] |
Ruiz-Juretschke F, Perez-Calvo JM, Castro E, et al. A single-center, long-term study of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas with multidisciplinary treatment[J]. J Clin Neurosci, 2011, 18(12):1662-1666.
doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2011.03.008 pmid: 22019434 |
| [16] | Cenzato M, Debernardi A, Stefini R, et al. Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: Outcome and prognostic factors[J]. Neurosurg Focus, 2012, 32(5):E11. |
| [17] |
Cho WS, Kim KJ, Kwon OK, et al. Clinical features and treatment outcomes of the spinal arteriovenous fistulas and malformation: Clinical article[J]. J Neurosurg Spine, 2013, 19(2):207-216.
doi: 10.3171/2013.4.SPINE12732 |
| [18] |
Clark S, Powell G, Kandasamy J, et al. Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: Presentation, management and outcome in a single neurosurgical institution[J]. Br J Neurosurg, 2013, 27(4):465-470.
doi: 10.3109/02688697.2012.752433 |
| [19] |
Gemmete JJ, Chaudhary N, Elias AE, et al. Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: Clinical experience with endovascular treatment as a primary therapy at 2 academic referral centers[J]. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 2013, 34(10):1974-1979.
doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A3522 |
| [20] |
Inagawa S, Yamashita S, Hiramatsu H, et al. Clinical results after the multidisciplinary treatment of spinal arteriovenous fistulas[J]. Jpn J Radiol, 2013, 31(7):455-464.
doi: 10.1007/s11604-013-0216-6 |
| [21] |
Kirsch M, Berg-Dammer E, Musahl C, et al. Endovascular management of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas in 78 patients[J]. Neuroradiology, 2013, 55(3):337-343.
doi: 10.1007/s00234-013-1134-0 pmid: 23334434 |
| [22] |
Takai K, Kin T, Oyama H, et al. Three-dimensional angioarchitecture of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas, with special reference to the intradural retrograde venous drainage system[J]. J Neurosurg Spine, 2013, 18(4):398-408.
doi: 10.3171/2013.1.SPINE12305 |
| [23] | Gokhale S, Khan SA, McDonagh DL, et al. Comparison of surgical and endovascular approach in management of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: A single center experience of 27 patients[J]. Surg Neurol Int, 2014, 5:7. |
| [24] | Qi X, Lv L, Han K, et al. Analysis of the embolization spinal dural arteriovenous fistula and surgical treatments on 52 cases of the patients[J]. Int J Clin Exp Med, 2014, 7(9):3062-3071. |
| [25] |
Rashad S, Abdel-Bary M, Aziz W, et al. Management of spinal dural arterio-venous fistulas: Report of 12 cases and review of lite-rature[J]. Clin Neurol Neurosurg, 2014, 125:81-86.
doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2014.07.028 |
| [26] |
Yen PP, Ritchie KC, Shankar JJ. Spinal dural arteriovenous fistula: Correlation between radiological and clinical findings[J]. J Neurosurg Spine, 2014, 21(5):837-842.
doi: 10.3171/2014.7.SPINE13797 |
| [27] |
Chibbaro S, Gory B, Marsella M, et al. Surgical management of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas[J]. J Clin Neurosci, 2015, 22(1):180-183.
doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2014.07.024 |
| [28] |
Özkan N, Kreitschmann-Andermahr I, Goerike SL, et al. Single center experience with treatment of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas[J]. Neurosurg Rev, 2015, 38(4):683-692.
doi: 10.1007/s10143-015-0645-z |
| [29] |
Shin DA, Park KY, Ji GY, et al. The use of magnetic resonance imaging in predicting the clinical outcome of spinal arteriovenous fistula[J]. Yonsei Med J, 2015, 56(2):397-402.
doi: 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.2.397 |
| [30] |
Sri D, Higgins N, Laing R. Combined radiological and surgical management of spinal dural fistulas[J]. Br J Neurosurg, 2015, 29(4):505-507.
doi: 10.3109/02688697.2015.1012049 |
| [31] |
Zogopoulos P, Nakamura H, Ozaki T, et al. Endovascular and surgical treatment of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: Assessment of post-treatment clinical outcome[J]. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo), 2016, 56(1):27-32.
doi: 10.2176/nmc.oa.2015-0100 |
| [32] |
Lee J, Lim YM, Suh DC, et al. Clinical presentation, imaging findings, and prognosis of spinal dural arteriovenous fistula[J]. J Clin Neurosci, 2016, 26:105-109.
doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2015.06.030 |
| [33] |
Sasamori T, Hida K, Yano S, et al. Long-term outcomes after surgical and endovascular treatment of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulae[J]. Eur Spine J, 2016, 25(3):748-754.
doi: 10.1007/s00586-015-3887-0 pmid: 25801745 |
| [34] |
Adrianto Y, Yang KH, Koo HW, et al. Concomitant origin of the anterior or posterior spinal artery with the feeder of a spinal dural arteriovenous fistula (SDAVF)[J]. J Neurointerv Surg, 2017, 9(4):405-410.
doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2016-012267 pmid: 27060157 |
| [35] |
Durnford AJ, Hempenstall J, Sadek AR, et al. Degree and duration of functional improvement on long-term follow-up of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulae occluded by endovascular and surgical treatment[J]. World Neurosurg, 2017, 107:488-494.
doi: S1878-8750(17)31240-8 pmid: 28774761 |
| [36] |
Gross BA, Albuquerque FC, Moon K, et al. Validation of an “endovascular-first” approach to spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: An intention-to-treat analysis[J]. J Neurointerv Surg, 2017, 9(1):102-105.
doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2016-012333 |
| [37] |
Koch MJ, Stapleton CJ, Agarwalla PK, et al. Open and endovascular treatment of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: A 10-year experience[J]. J Neurosurg Spine, 2017, 26(4):519-523.
doi: 10.3171/2016.9.SPINE16394 |
| [38] |
Ma Y, Chen S, Peng C, et al. Clinical outcomes and prognostic factors in patients with spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: A prospective cohort study in two Chinese centres[J]. BMJ Open, 2018, 8(1):e019800.
doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-019800 |
| [39] |
Bretonnier M, Hénaux PL, Gaberel T, et al. Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: Clinical outcome after surgery versus embolization: A retrospective study[J]. World Neurosurg, 2019, 127:e943-e949.
doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.04.005 |
| [40] | 黄承光, 白如林, 陈左权, 等. 15例脊髓硬脊膜动静脉瘘栓塞和手术治疗[J]. 中华神经外科杂志, 2003, 19(5):340. |
| [41] | 李萌, 张鸿祺, 支兴龙, 等. 硬脊膜动静脉瘘的诊断和治疗[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2003, 41(2):99-102. |
| [42] | 潘力, 马廉亭, 余泽, 等. 硬脊膜动静脉瘘的诊治探讨[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2005, 43(5):330-340. |
| [43] | 于加省, 陈劲草, 雷霆, 等. 骶部硬脊膜动静脉瘘的诊断与治疗[J]. 华中科技大学学报(医学版), 2008, 37(3):409-411. |
| [44] | 于加省, 何跃, 陈如东, 等. 硬脊膜动静脉瘘的显微手术与血管内栓塞治疗[J]. 中华神经外科杂志, 2012, 28(7):706-709. |
| [45] | 李治国, 潘力术, 杨铭, 等. 硬脊膜动静脉瘘的治疗策略的选择. 中华中青年神经外科交流协会第二届学术大会论文集[C]. 苏州: 中华中青年神经外科交流协会, 2013: 314-318. |
| [46] | 齐向前, 韩凯伟, 许政, 等. 硬脊膜动静脉瘘的栓塞和手术治疗[J]. 中国微侵袭神经外科杂志, 2014, 19(8):345-348. |
| [47] | 赵丹. 血管内栓塞治疗颅颈交界区硬脊膜动静脉瘘50例临床分析[J]. 大家健康(学术版), 2014, 8(15):291. |
| [48] | 蔡明俊, 马廉亭, 杨铭, 等. 硬脊膜动静脉瘘的治疗分析[J]. 中国临床神经外科杂志, 2018, 23(6):392-394. |
| [49] | 张仁德, 王蒙, 王俊宽, 等. 硬脊膜动静脉瘘的治疗及预后相关因素分析[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2018, 53(4):529-534. |
| [50] | 胡智洪. 41例脊髓硬脊膜动静脉瘘患者手术方式、预后回顾性分析研究[D]. 四川泸州: 西南医科大学, 2019. |
| [51] |
Thron A. Spinale durale arteriovenöse Fisteln [Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas][J]. Radiologe, 2001, 41(11):955-960.
pmid: 11765536 |
| [52] | Guillevin R, Vallee JN, Cormier E, et al. N-butyl 2-cyanoacrylate embolization of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulae: CT evaluation, technical features, and outcome prognosis in 26 cases[J]. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 2005, 26(4):929-935. |
| [53] |
Nogueira RG, Dabus G, Rabinov JD, et al. Onyx embolization for the treatment of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulae: Initial expe-rience with long-term follow-up. Technical case report[J]. Neurosurgery, 2009, 64(1):E197-E198.
doi: 10.1227/01.NEU.0000335157.90249.97 |
| [54] |
Steinmetz MP, Chow MM, Krishnaney AA, et al. Outcome after the treatment of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulae: A contemporary single-institution series and meta-analysis[J]. Neurosurgery, 2004, 55(1):77-88.
pmid: 15214976 |
| [55] |
Bakker NA, Uyttenboogaart M, Luijckx GJ, et al. Recurrence rates after surgical or endovascular treatment of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: A meta-analysis[J]. Neurosurgery, 2015, 77(1):137-144.
doi: 10.1227/NEU.0000000000000727 |
| [56] | 丁璇, 王志刚, 沈寻, 等. NBCA和ONYX栓塞治疗不同类型脑动静脉畸形的对比研究[J]. 中华神经外科杂志, 2006, 22(8):464-466. |
| [57] |
Blackburn SL, Kadkhodayan Y, Ray WZ, et al. Onyx is asso-ciated with poor venous penetration in the treatment of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas[J]. J Neurointerv Surg, 2014, 6(7):536-540.
doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2013-010779 pmid: 23943815 |
| [58] |
Marquardt G, Berkefeld J, Seifert V, et al. Preoperative coil marking to facilitate intraoperative localization of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas[J]. Eur Spine J, 2009, 18(8):1117-1120.
doi: 10.1007/s00586-009-0946-4 pmid: 19330362 |
| [1] | 万利, 张周沧, 丁嘉祥, 王梅. 中心静脉导管拔除后静脉空气栓塞1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 938-941. |
| [2] | 汤晓菲,李永红,丁秋玲,孙卓,张阳,王育梅,田美伊,刘坚. 类风湿关节炎患者下肢深静脉血栓发病率及危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 279-283. |
| [3] | 彭清,刘佳君,刘焱,尚华,唐果,韩雅欣,龙丽. Padua预测评分和血清白蛋白水平在评估风湿病住院患者静脉血栓栓塞中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 625-630. |
| [4] | 林国中,谢京城,陈晓东,杨军. 成人原发性脊髓拴系综合征的分型及显微外科手术治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 641-645. |
| [5] | 韩金涛,张宇翔,贾子昌,姜除寒,刘恋,栾景源,梁飞,赵彦清. Neuroform Atlas支架辅助弹簧圈栓塞未破裂性颅内宽颈动脉瘤[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 139-143. |
| [6] | 谢京城,陈晓东,杨军. 成人先天性皮窦道脊髓拴系综合征的诊断和治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1163-1166. |
| [7] | 穆东亮,薛铖,安彬,王东信. 硬膜外阻滞与结直肠癌患者术后远期生存状态的关系:一项倾向性评分匹配的回顾性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1152-1158. |
| [8] | 林国中, 马长城, 王振宇, 谢京城, 刘彬, 陈晓东. 颈1~2硬膜外神经鞘瘤的显微微创治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 586-589. |
| [9] | 冯菁楠,高乐,孙一鑫,杨继春,邓思危,孙凤,詹思延. Xpert®MTB/RIF对我国人群活动性肺结核和利福平耐药肺结核诊断准确性的meta分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 320-326. |
| [10] | 朱冯赟智,邢晓燕,汤晓菲,李依敏,邵苗,张学武,李玉慧,孙晓麟,何菁. 肌炎合并血栓栓塞患者的临床及免疫学特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 995-1000. |
| [11] | 高健,胡立宝,陈尘,郅新,徐涛. 经皮肾镜去石术后出血的介入治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 667-671. |
| [12] | 曾保起,于树青,陈瑶,翟伟,刘斌,詹思延,孙凤. 主动脉瓣生物瓣膜安全性的系统评价与meta分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(3): 547-556. |
| [13] | 林国中,王振宇,谢京城,刘彬,马长城,陈晓东. 内含终丝的骶管囊肿21例临床研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(3): 582-585. |
| [14] | 赵海燕,樊东升,韩金涛. 重度颈内动脉狭窄伴未破裂动脉瘤的治疗策略[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(5): 829-834. |
| [15] | 张志刚,刘新民. 急性肾梗死的临床特征:单中心52例临床分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(5): 863-869. |
|
||