北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (4): 594-599. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.04.008
术前盆底肌电生理参数对前列腺癌根治性切除术后早期尿失禁的预测价值
于书慧1,韩佳凝1,2,钟丽君1,陈聪语1,肖云翔1,黄燕波1,杨洋1,*( ),车新艳1,*(
),车新艳1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学第一医院泌尿外科,北京 100034
2. 北京大学护理学院,北京 100191
Predictive value of preoperative pelvic floor electrophysiological parameters on early urinary incontinence following radical prostatectomy
Shuhui YU1,Jianing HAN1,2,Lijun ZHONG1,Congyu CHEN1,Yunxiang XIAO1,Yanbo HUANG1,Yang YANG1,*( ),Xinyan CHE1,*(
),Xinyan CHE1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Urology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
2. School of Nursing, Peking University, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
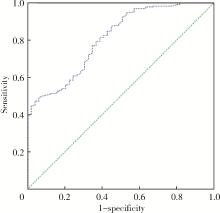
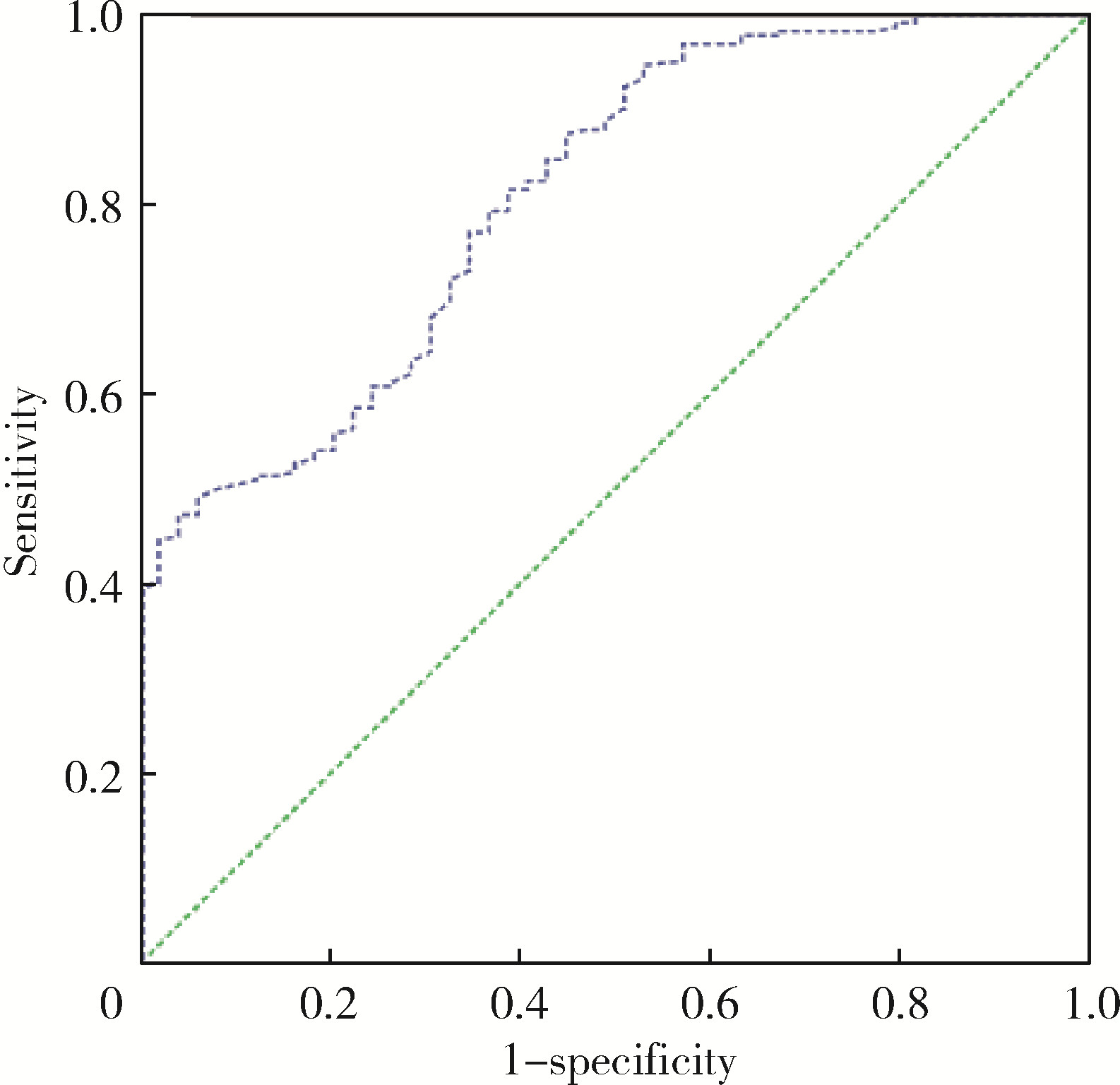
目的: 探索术前盆底肌电生理参数对前列腺癌术后尿失禁风险的预测价值。方法: 选择2020年1月至2022年10月在北京大学第一医院泌尿外科行根治性前列腺切除术患者的病例资料进行回顾性分析,记录患者的年龄、体重指数(body mass index, BMI)、国际前列腺症状评分(international prostate symptom score, IPSS)、前列腺特异性抗原(prostate-specific antigen, PSA)水平、Gleason评分、手术方式、是否尿道功能重建、是否淋巴结清扫、性神经是否保留、留置导尿时间、D’ Amico风险分级、美国麻醉医师协会(American Society of Anesthesiologists, ASA)评分、查尔森(Charlson)合并症指数、术后随访时间、前列腺体积,以及盆底肌电生理参数(前静息均值、快肌均值和慢肌均值)。通过多因素Logistic回归分析,筛选出影响术后早期尿失禁发生的独立危险因素,并通过计算受试者工作特征曲线(receiver operating characteristic, ROC)下面积,评估盆底肌电参数的预测效能,再利用约登指数(Youden index)并结合临床意义,共同确定术后早期尿失禁发生的最佳临界值。结果: 纳入患者271例,术后自主控尿率为81.9%。患者快肌评分为23.5(18.2, 31.6)分,慢肌评分为12.5(9.6, 17.3)分,179例(66.1%)患者未保留性神经,110例(40.6%)患者进行了尿道功能重建。高龄和盆底快肌评分低被确认为尿失禁发生的独立危险因素。≤60岁患者是≥70岁患者自主控尿率的5.482倍(95%CI: 1.532~19.617,P<0.05);患者的盆底快肌评分与尿失禁恢复的关系密切(OR=1.209,95%CI: 1.132~1.291, P<0.05)。当术前盆底快肌评分的最佳临界值设定为18.5分时,ROC的敏感度和特异度分别为80.6%和61.2%。结论: 术前盆底肌电生理参数对于前列腺癌术后尿失禁风险表现出较好的预测准确性和临床应用性,能够用于前列腺癌术后尿失禁风险的早期识别,其中年龄和盆底快肌评分是重要的预测因子。
中图分类号:
- R737.25
| 1 |
赫捷, 陈万青, 李霓, 等. 中国前列腺癌筛查与早诊早治指南(2022, 北京)[J]. 中国肿瘤, 2022, 31 (1): 1- 30.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4136.2022.01.001 |
| 2 |
Zhu Y , Mo M , Wei Y , et al. Epidemiology and genomics of prostate cancer in Asian men[J]. Nat Rev Urol, 2021, 18 (5): 282- 301.
doi: 10.1038/s41585-021-00442-8 |
| 3 |
Mottet N , Bellmunt J , Bolla M , et al. EAU-ESTRO-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer. Part 1: Screening, diagnosis, and local treatment with curative intent[J]. Eur Urol, 2017, 71 (4): 618- 629.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.08.003 |
| 4 |
Ficarra V , Novara G , Rosen RC , et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of studies reporting urinary continence recovery after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy[J]. Eur Urol, 2012, 62 (3): 405- 417.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2012.05.045 |
| 5 |
Abdollah F , Sun M , Suardi N , et al. Prediction of functional outcomes after nerve-sparing radical prostatectomy: Results of conditional survival analyses[J]. Eur Urol, 2012, 62 (1): 42- 52.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2012.02.057 |
| 6 |
Eastham JA , Kattan MW , Rogers E , et al. Risk factors for urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy[J]. J Urol, 1996, 156 (5): 1707- 1713.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(01)65488-0 |
| 7 |
Sandhu J S , Breyer B , Comiter C , et al. Incontinence after prostate treatment: AUA/SUFU guideline[J]. J Urol, 2019, 202 (2): 369- 378.
doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000000314 |
| 8 |
Levy A , Fleishman A , Jackson M , et al. Using preoperative pelvic floor assessment to predict early return of continence after robotic radical prostatectomy[J]. Urology, 2021, 155, 160- 164.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2021.04.029 |
| 9 |
Kubo Y , Tanaka K , Yamasaki M , et al. Influences of the charlson comorbidity index and nutrition status on prognosis after esophageal cancer surgery[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2021, 28 (12): 7173- 7182.
doi: 10.1245/s10434-021-09779-1 |
| 10 |
Jeong S J , Yeon J S , Lee J K , et al. Development and validation of nomograms to predict the recovery of urinary continence after radical prostatectomy: Comparisons between immediate, early, and late continence[J]. World J Urol, 2014, 32 (2): 437- 444.
doi: 10.1007/s00345-013-1127-y |
| 11 |
Collette ERP , Klaver SO , Lissenberg-Witte BI , et al. Patient reported outcome measures concerning urinary incontinence after robot assisted radical prostatectomy: Development and validation of an online prediction model using clinical parameters, lower urinary tract symptoms and surgical experience[J]. J Robot Surg, 2021, 15 (4): 593- 602.
doi: 10.1007/s11701-020-01145-9 |
| 12 |
Ali M , Hutchison DD , Ortiz NM , et al. A narrative review of pelvic floor muscle training in the management of incontinence following prostate treatment[J]. Transl Androl Urol, 2022, 11 (8): 1200- 1209.
doi: 10.21037/tau-22-143 |
| 13 | Hoyland K , Vasdev N , Abrof A , et al. Post-radical prostatectomy incontinence: Etiology and prevention[J]. Rev Urol, 2014, 16 (4): 181- 188. |
| 14 |
Mungovan SF , Carlsson SV , Gass GC , et al. Preoperative exercise interventions to optimize continence outcomes following radical prostatectomy[J]. Nat Rev Urol, 2021, 18 (5): 259- 281.
doi: 10.1038/s41585-021-00445-5 |
| 15 |
Laycock J , Jerwood D . Pelvic floor muscle assessment: The PERFECT scheme[J]. Physiotherapy, 2001, 87 (12): 631- 642.
doi: 10.1016/S0031-9406(05)61108-X |
| 16 |
Manassero F , Traversi C , Ales V , et al. Contribution of early intensive prolonged pelvic floor exercises on urinary continence recovery after bladder neck-sparing radical prostatectomy: Results of a prospective controlled randomized trial[J]. Neurourol Urodyn, 2007, 26 (7): 985- 989.
doi: 10.1002/nau.20442 |
| 17 |
Stanford JL , Feng Z , Hamilton AS , et al. Urinary and sexual function after radical prostatectomy for clinically localized prostate cancer: The prostate cancer outcomes study[J]. JAMA, 2000, 283 (3): 354- 360.
doi: 10.1001/jama.283.3.354 |
| 18 |
Strasser H , Tiefenthaler M , Steinlechner M , et al. Urinary incontinence in the elderly and age-dependent apoptosis of rhabdosphincter cells[J]. Lancet, 1999, 354 (9182): 918- 919.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(99)02588-X |
| 19 |
Heesakkers J , Farag F , Bauer RM , et al. Pathophysiology and contributing factors in postprostatectomy incontinence: A review[J]. Eur Urol, 2017, 71 (6): 936- 944.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.09.031 |
| [1] | 李雨清,王飚,乔鹏,王玮,关星. 经耻骨后尿道中段悬吊带术治疗女性复发性压力性尿失禁的中长期疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 600-604. |
| [2] | 张帆,陈曲,郝一昌,颜野,刘承,黄毅,马潞林. 术前及术后膜性尿道长度与腹腔镜根治性前列腺切除术后控尿功能恢复的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 299-303. |
| [3] | 郝瀚,刘越,陈宇珂,司龙妹,张萌,范宇,张中元,唐琦,张雷,吴士良,宋毅,林健,赵峥,谌诚,虞巍,韩文科. 机器人辅助前列腺癌根治术后患者的控尿恢复时间[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 697-703. |
| [4] | 张帆,黄晓娟,杨斌,颜野,刘承,张树栋,黄毅,马潞林. 前列腺尖部深度与腹腔镜前列腺癌根治术后早期控尿功能恢复的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 692-696. |
| [5] | 车新艳,吴士良,陈宇珂,黄燕波,杨洋. 女性医务人员尿失禁及其对生活质量影响的现况调查[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(4): 706-710. |
| [6] | 刘献辉,张维宇,胡浩,王起,王涛,贺永新,许克新. 耻骨后和经闭孔尿道中段悬吊术对不同分型压力性尿失禁疗效的长期随访[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(4): 694-697. |
| [7] | 张帆,肖春雷,张树栋,黄毅,马潞林. 前列腺体积及前列腺突入膀胱长度与腹腔镜前列腺癌根治术后控尿功能恢复的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(4): 621-625. |
| [8] | 张维宇,张晓鹏,胡浩,陈京文,刘献辉,许克新. 无张力尿道中段悬吊术治疗女性混合性尿失禁的疗效分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(4): 638-642. |
| [9] | 张维宇,张晓鹏,陈京文,孙屹然,王佳,胡浩,许克新. 年龄因素对女性尿失禁患者尿动力学参数的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(5): 825-829. |
| [10] | 张维宇,胡浩,王起,陈京文,许克新. 女性压力性尿失禁患者术前尿动力学检查的意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(4): 655-658. |
| [11] | 廖晓星, 邢念增, 乔鹏, 康宁, 张军晖, 牛亦农. “三明治”法尿道重建技术改善腹腔镜下根治性前列腺切除术后早期尿控的效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(4): 601-604. |
| [12] | 贾晓君, 方志伟, 胡浩, 许克新, 黄晓波, 王晓峰. 中段尿道无张力吊带术对女性压力性尿失禁患者性功能的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(4): 570-573. |
| [13] | 许克新, 霍飞, 夏秋翔, 王晓峰. 人工尿道括约肌植入术治疗男性前列腺术后压力性尿失禁[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(4): 507-510. |
| [14] | 黄建林, 邱敏, 马潞林. 腹腔镜根治性前列腺切除术后控尿功能的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(03): 499-503. |
| [15] | 黄建林, 马潞林, 黄毅, 侯小飞, 王国良, 洪锴, 卢剑, 肖春雷. 腹腔镜根治性前列腺切除术后控尿功能及学习曲线[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(4): 563-567. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 112
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 197
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||