北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (4): 589-593. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.04.007
前列腺癌根治术后远期膀胱过度活动症的危险因素
颜野,李小龙,夏海缀,朱学华,张羽婷,张帆,刘可,刘承*( ),马潞林*(
),马潞林*( )
)
- 北京大学第三医院泌尿外科,北京 100191
Analysis of risk factors for long-term overactive bladder after radical prostatectomy
Ye YAN,Xiaolong LI,Haizhui XIA,Xuehua ZHU,Yuting ZHANG,Fan ZHANG,Ke LIU,Cheng LIU*( ),Lulin MA*(
),Lulin MA*( )
)
- Department of Urology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
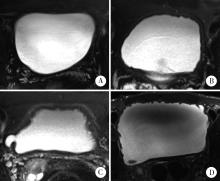
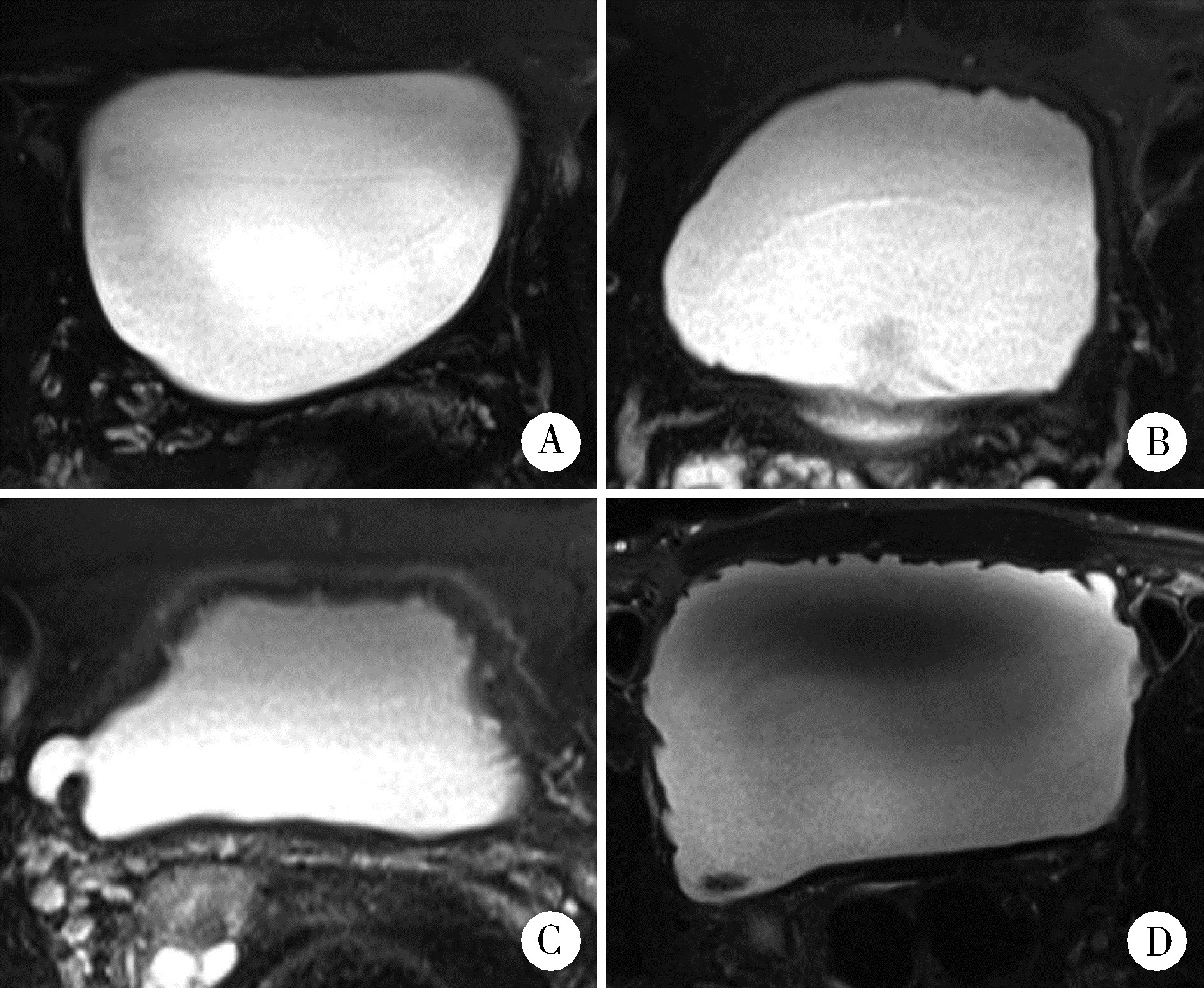
目的: 分析前列腺癌根治术后膀胱过度活动症(overactive bladder, OAB)的发生及转归情况,并探讨其相关危险因素。方法: 选择北京大学第三医院2013年1月至2017年5月住院接受根治性前列腺切除术的263例患者进行回顾性研究,分析并收集患者临床基线信息、计算影像特征、围术期参数、术前患者尿控情况、病理学诊断与术后1年内OAB发生情况的相关性。在影像特征中,定义膀胱壁厚度(bladder wall thickness, BWT)和膀胱黏膜光滑程度(bladder mucosal smoothness, BMS)两个参数,用于预测OAB的发生情况。结果: 263例前列腺癌根治术后患者中,术后1年存在OAB状态者共52例,占所有患者的19.8%。术前既往存在OAB症状者40例,术后缓解者17例(42.5%),症状持续者23例(57.5 %);术后新发OAB者29例,占术后所有OAB患者的55.77%。单因素分析显示膀胱壁厚度、膀胱黏膜光滑程度、膀胱过度活动症状评分和国际前列腺症状评分均与术后OAB的发生相关。进一步多因素分析发现,BMS是远期OAB的独立危险因素(P < 0.001)。结论: 根治性前列腺切除术后远期膀胱过度活动症是临床常见的并发症,通过术前磁共振成像测量充盈状态下膀胱壁厚度或膀胱黏膜光滑程度,可以预测根治术后OAB的发生风险。
中图分类号:
- R737.25
| 1 |
Abrams P , Cardozo L , Fall M , et al. The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: Report from the standardisation sub-committee of the international continence society[J]. Neurourol Urodyn, 2002, 21 (2): 167- 178.
doi: 10.1002/nau.10052 |
| 2 |
Porena M , Mearini E , Mearini L , et al. Voiding dysfunction after radical retropubic prostatectomy: More than external urethral sphincter deficiency[J]. Eur Urol, 2007, 52 (1): 38- 45.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2007.03.051 |
| 3 |
Matsukawa Y , Yoshino Y , Ishida S , et al. De novo overactive bladder after robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy[J]. Neurourol Urodyn, 2018, 37 (6): 2008- 2014.
doi: 10.1002/nau.23556 |
| 4 |
Hosier GW , Tennankore KK , Himmelman JG , et al. Overactive bladder and storage lower urinary tract symptoms following radical prostatectomy[J]. Urology, 2016, 94, 193- 197.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2016.05.007 |
| 5 |
Thiruchelvam N , Cruz F , Kirby M , et al. A review of detrusor overactivity and the overactive bladder after radical prostate cancer treatment[J]. BJU Int, 2015, 116 (6): 853- 861.
doi: 10.1111/bju.13078 |
| 6 |
Ventimiglia B , Sigona M , Di Dio A , et al. Urinary incontinence and neuropathy after radical prostatectomy: Diagnosis and treatment[J]. Urologia, 2015, 82 (1): 42- 45.
doi: 10.5301/uro.5000064 |
| 7 | Chung DE , Dillon B , Kurta J , et al. Detrusor underactivity is prevalent after radical prostatectomy: A urodynamic study including risk factors[J]. Can Urol Assoc J, 2013, 7 (1/2): E33- E37. |
| 8 |
Giannantoni A , Mearini E , Zucchi A , et al. Bladder and urethral sphincter function after radical retropubic prostatectomy: A prospective long-term study[J]. Eur Urol, 2008, 54 (3): 657- 664.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2007.10.054 |
| 9 |
Leach GE , Trockman B , Wong A , et al. Post-prostatectomy incontinence: Urodynamic findings and treatment outcomes[J]. J Urol, 1996, 155 (4): 1256- 1259.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(01)66235-9 |
| 10 |
Haga N , Ogawa S , Yabe M , et al. Association between postoperative pelvic anatomic features on magnetic resonance imaging and lower tract urinary symptoms after radical prostatectomy[J]. Urology, 2014, 84 (3): 642- 649.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2014.04.044 |
| 11 |
Dubbelman Y , Groen J , Wildhagen M , et al. Quantification of changes in detrusor function and pressure-flow parameters after radical prostatectomy: Relation to postoperative continence status and the impact of intensity of pelvic floor muscle exercises[J]. Neurourol Urodyn, 2012, 31 (5): 637- 641.
doi: 10.1002/nau.21199 |
| 12 |
Groutz A , Blaivas JG , Chaikin DC , et al. The pathophysiology of post-radical prostatectomy incontinence: A clinical and video urodynamic study[J]. J Urol, 2000, 163 (6): 1767- 1770.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)67538-6 |
| [1] | 李志存, 吴天俣, 梁磊, 范宇, 孟一森, 张骞. 穿刺活检单针阳性前列腺癌术后病理升级的危险因素分析及列线图模型构建[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 896-901. |
| [2] | 黄教悌,胡菁,韩博. 治疗相关神经内分泌前列腺癌机制研究与靶向治疗新进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 557-561. |
| [3] | 邢念增,王明帅,杨飞亚,尹路,韩苏军. 前列腺免活检创新理念的临床实践及其应用前景[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 565-566. |
| [4] | 于书慧,韩佳凝,钟丽君,陈聪语,肖云翔,黄燕波,杨洋,车新艳. 术前盆底肌电生理参数对前列腺癌根治性切除术后早期尿失禁的预测价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 594-599. |
| [5] | 何海龙,李清,徐涛,张晓威. 构建显微精索手术治疗精索疼痛的术后疼痛缓解预测模型[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 646-655. |
| [6] | 陈延,李况蒙,洪锴,张树栋,程建星,郑仲杰,唐文豪,赵连明,张海涛,姜辉,林浩成. 阴茎海绵体注射试验对阴茎血管功能影响的回顾性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 680-686. |
| [7] | 庞博,郭桐君,陈曦,郭华棋,石嘉章,陈娟,王欣梅,李耀妍,单安琪,余恒意,黄婧,汤乃军,王艳,郭新彪,李国星,吴少伟. 天津与上海35岁以上人群氮氧化物个体暴露水平及其影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 700-707. |
| [8] | 和静,房中则,杨颖,刘静,马文瑶,霍勇,高炜,武阳丰,谢高强. 血浆中脂质代谢分子与颈动脉粥样硬化斑块、传统心血管危险因素及膳食因素的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 722-728. |
| [9] | 蔡珊,张依航,陈子玥,刘云飞,党佳佳,师嫡,李佳欣,黄天彧,马军,宋逸. 北京市中小学生身体活动时间现状及影响因素的路径[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 403-410. |
| [10] | 张祖洪,陈天娇,马军. 中小学生青春发动时相与心血管代谢危险因素的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 418-423. |
| [11] | 林郁婷,王华丽,田宇,巩俐彤,常春. 北京市老年人认知功能的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 456-461. |
| [12] | 朱金荣,赵亚娜,黄巍,赵微微,王悦,王松,苏春燕. 感染新型冠状病毒的血液透析患者的临床特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 267-272. |
| [13] | 赖展鸿,李嘉辰,贠泽霖,张永刚,张昊,邢晓燕,邵苗,金月波,王乃迪,李依敏,李玉慧,栗占国. 特发性炎性肌病完全临床应答相关因素的单中心真实世界研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 284-292. |
| [14] | 司筱芊,赵秀娟,朱凤雪,王天兵. 创伤出血性休克后急性呼吸窘迫综合征的危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 307-312. |
| [15] | 苏俊琪,王晓颖,孙志强. 舌鳞状细胞癌根治性切除术后患者预后预测列线图的构建与验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 120-130. |
|
||