北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (4): 582-588. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.04.006
肌层浸润性膀胱癌合并中高危前列腺癌患者的预后因素
欧俊永1,倪坤明2,马潞林1,王国良1,颜野1,杨斌1,李庚午1,宋昊东1,陆敏2,叶剑飞1,*( ),张树栋1,*(
),张树栋1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学第三医院泌尿外科,北京 100191
2. 北京大学第三医院病理科,北京 100191
Prognostic factors of patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer with intermediate-to-high risk prostate cancer
Junyong OU1,Kunming NI2,Lulin MA1,Guoliang WANG1,Ye YAN1,Bin YANG1,Gengwu LI1,Haodong SONG1,Min LU2,Jianfei YE1,*( ),Shudong ZHANG1,*(
),Shudong ZHANG1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Urology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Pathology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
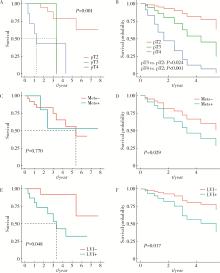
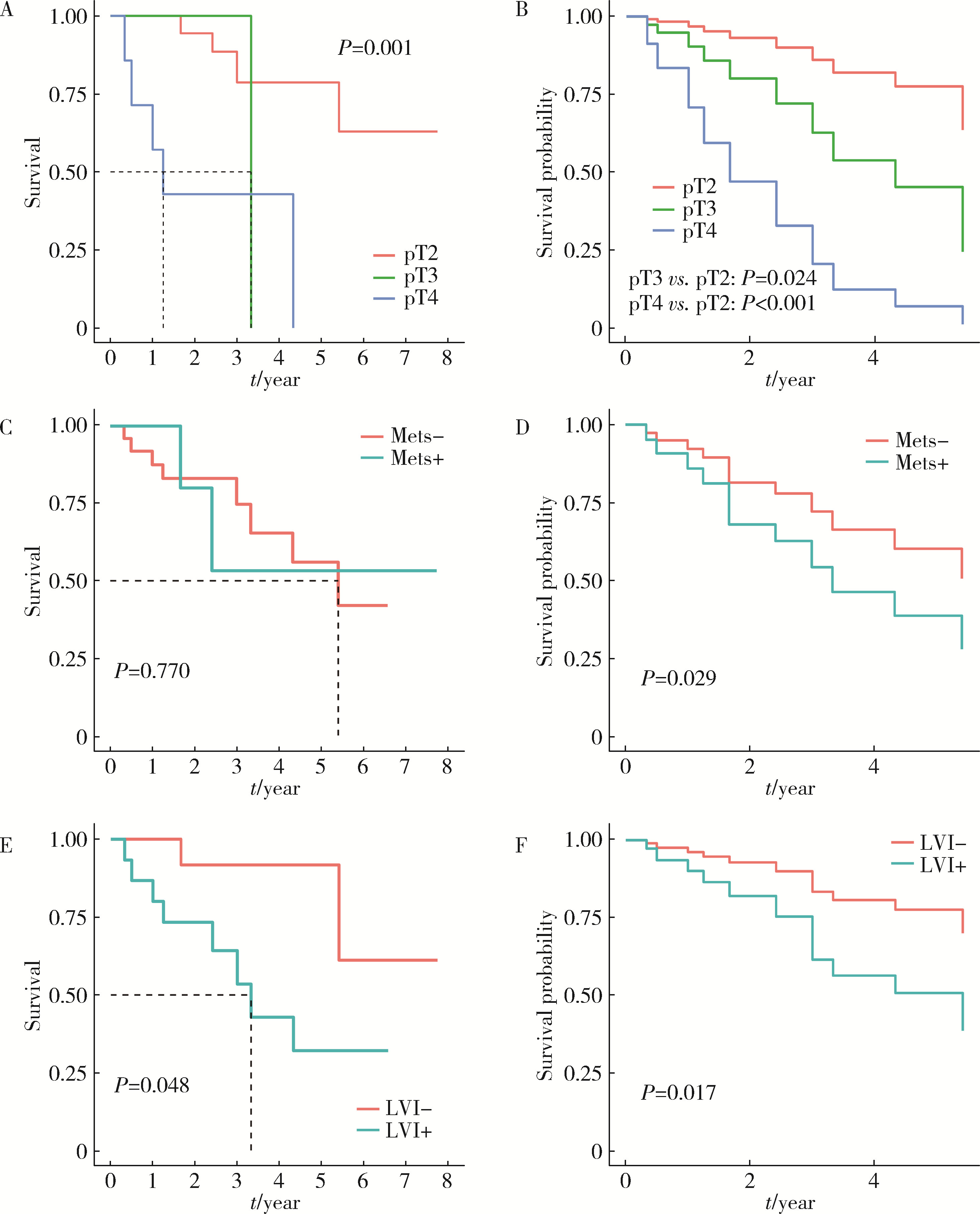
目的: 探究影响肌层浸润性膀胱癌(muscle-invasive bladder cancer, MIBC)合并中高危前列腺癌患者全因死亡结局的预后因素。方法: 回顾性分析2012年1月至2023年10月北京大学第三医院收治的MIBC合并中高危前列腺癌患者临床资料,随访并记录所有患者的全因死亡结局发生时间,并以其作为预后研究的结局事件。采用单因素及多因素Cox比例风险回归分析模型筛选MIBC合并中高危前列腺癌患者预后的独立影响因子,对于重要的影响因素(膀胱癌病理T分期、M分期、神经侵犯),绘制多因素Cox回归调整混杂因素前后的生存曲线。结果: 共纳入32例患者,平均年龄(72.5±6.6)岁,中位术前总前列腺特异性抗原(total prostate specific antigen,tPSA)6.68(2.47,6.84) μg/L,平均术前血肌酐(95±36) μmol/L,中位生存期为65个月。绝大多数(87.5%)患者膀胱癌病理分级为高级别,53.1%患者可见淋巴管侵犯,31.3%患者可见神经侵犯。25.0%的病例可见膀胱癌累及前列腺,手术软组织切缘阳性率为37. 5%。Cox多因素分析结果提示术前血肌酐水平(HR=1.02,95%CI:1.01~1.04)、膀胱癌病理分期T3(HR=11.58,95%CI:1.38~97.36)和T4(HR=19.53,95%CI:4.26~89.52)、膀胱癌转移(HR=9.44,95%CI:1.26~70.49)、膀胱癌神经侵犯(HR=6.26,95%CI:1.39~28.27)是影响患者预后的独立因素(P < 0.05)。调整混杂因素后的生存曲线与Log-rank检验结果提示膀胱癌病理分期T3、T4、M1和神经侵犯为影响患者生存预后的不良因素(P<0.05)。结论: MIBC合并中高危前列腺癌患者整体存在预后较差的趋势; 术前血肌酐高、膀胱癌病理分期T3或T4、膀胱癌转移、膀胱癌神经侵犯是MIBC合并中高危前列腺癌患者的不良预后因素。
中图分类号:
- R737.1
| 1 |
Alfred Witjes J , Max Bruins H , Carrión A , et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer: Summary of the 2023 guidelines[J]. Eur Urol, 2024, 85 (1): 17- 31.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2023.08.016 |
| 2 |
Siegel RL , Giaquinto AN , Jemal A . Cancer statistics, 2024[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2024, 74 (1): 12- 49.
doi: 10.3322/caac.21820 |
| 3 |
Dyrskjøt L , Hansel DE , Efstathiou JA , et al. Bladder cancer[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2023, 9 (1): 58.
doi: 10.1038/s41572-023-00468-9 |
| 4 |
Compérat E , Amin MB , Cathomas R , et al. Current best practice for bladder cancer: A narrative review of diagnostics and treatments[J]. Lancet, 2022, 400 (10364): 1712- 1721.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01188-6 |
| 5 |
Lopez-Beltran A , Cheng L , Montorsi F , et al. Concomitant bladder cancer and prostate cancer: Challenges and controversies[J]. Nat Rev Urol, 2017, 14 (10): 620- 629.
doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2017.124 |
| 6 |
Jing Y , Zhang R , Ma P , et al. Prevalence and clonality of synchronous primary carcinomas in the bladder and prostate[J]. J Pathol, 2018, 244 (1): 5- 10.
doi: 10.1002/path.4997 |
| 7 |
Aljabery F , Liedberg F , Häggström C , et al. Treatment and prognosis of patients with urinary bladder cancer with other primary cancers: A nationwide population-based study in the bladder can-cer data base Sweden (BladderBaSe)[J]. BJU Int, 2020, 126 (5): 625- 632.
doi: 10.1111/bju.15198 |
| 8 | Claps F , Pavan N , Umari P , et al. Incidence, predictive factors and survival outcomes of incidental prostate cancer in patients who underwent radical cystectomy for bladder cancer[J]. Minerva Urol Nephrol, 2021, 73 (3): 349- 356. |
| 9 |
Malte R , Kluth LA , Kaushik D , et al. Frequency and prognostic significance of incidental prostate cancer at radical cystectomy: Results from an international retrospective study[J]. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2017, 43 (11): 2193- 2199.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2017.08.013 |
| 10 |
Fahmy O , Khairul-Asri MG , Schubert T , et al. Clinicopathological features and prognostic value of incidental prostatic adenocarcinoma in radical cystoprostatectomy specimens: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 13 140 patients[J]. J Urol, 2017, 197 (2): 385- 390.
doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2016.08.088 |
| 11 |
Kaelberer JB , O'donnell MA , Mitchell DL , et al. Incidental prostate cancer diagnosed at radical cystoprostatectomy for bladder cancer: Disease-specific outcomes and survival[J]. Prostate Int, 2016, 4 (3): 107- 112.
doi: 10.1016/j.prnil.2016.06.002 |
| 12 |
Wu S , Lin SX , Lu M , et al. Assessment of 5-year overall survival in bladder cancer patients with incidental prostate cancer identified at radical cystoprostatectomy[J]. Int Urol Nephrol, 2019, 51 (9): 1527- 1535.
doi: 10.1007/s11255-019-02181-7 |
| 13 |
Mazzucchelli R , Barbisan F , Scarpelli M , et al. Is incidentally detected prostate cancer in patients undergoing radical cystoprostatectomy clinically significant?[J]. Am J Clin Pathol, 2009, 131 (2): 279- 283.
doi: 10.1309/AJCP4OCYZBAN9TJU |
| 14 |
Moschini M , Shariat SF , Freschi M , et al. Impact of prostate involvement on outcomes in patients treated with radical cystoprostatectomy for bladder cancer[J]. Urol Int, 2017, 98 (3): 290- 297.
doi: 10.1159/000454736 |
| [1] | 李志存, 吴天俣, 梁磊, 范宇, 孟一森, 张骞. 穿刺活检单针阳性前列腺癌术后病理升级的危险因素分析及列线图模型构建[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 896-901. |
| [2] | 田宇轩,阮明健,刘毅,李德润,吴静云,沈棋,范宇,金杰. 双参数MRI改良PI-RADS评分4分和5分病灶的最大径对临床有意义前列腺癌的预测效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 567-574. |
| [3] | 姚凯烽,阮明健,李德润,田宇轩,陈宇珂,范宇,刘毅. 靶向穿刺联合区域系统穿刺对PI-RADS 4~5分患者的前列腺癌诊断效能[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 575-581. |
| [4] | 刘帅,刘磊,刘茁,张帆,马潞林,田晓军,侯小飞,王国良,赵磊,张树栋. 伴静脉癌栓的肾上腺皮质癌的临床治疗及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [5] | 虞乐,邓绍晖,张帆,颜野,叶剑飞,张树栋. 具有低度恶性潜能的多房囊性肾肿瘤的临床病理特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [6] | 周泽臻,邓绍晖,颜野,张帆,郝一昌,葛力源,张洪宪,王国良,张树栋. 非转移性T3a肾细胞癌患者3年肿瘤特异性生存期预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 673-679. |
| [7] | 方杨毅,李强,黄志高,陆敏,洪锴,张树栋. 睾丸鞘膜高分化乳头状间皮肿瘤1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 741-744. |
| [8] | 曾媛媛,谢云,陈道南,王瑞兰. 脓毒症患者发生正常甲状腺性病态综合征的相关因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 526-532. |
| [9] | 苏俊琪,王晓颖,孙志强. 舌鳞状细胞癌根治性切除术后患者预后预测列线图的构建与验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 120-130. |
| [10] | 李建斌,吕梦娜,池强,彭一琳,刘鹏程,吴锐. 干燥综合征患者发生重症新型冠状病毒肺炎的早期预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1007-1012. |
| [11] | 薛蔚,董樑,钱宏阳,费笑晨. 前列腺癌新辅助治疗与辅助治疗的现状及进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 775-780. |
| [12] | 刘欢锐,彭祥,李森林,苟欣. 基于HER-2相关基因构建风险模型用于膀胱癌生存预后评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 793-801. |
| [13] | 薛子璇,唐世英,邱敏,刘承,田晓军,陆敏,董靖晗,马潞林,张树栋. 青年肾肿瘤伴瘤栓的临床病理特征及预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 802-811. |
| [14] | 刘毅,袁昌巍,吴静云,沈棋,肖江喜,赵峥,王霄英,李学松,何志嵩,周利群. 靶向穿刺+6针系统穿刺对PI-RADS 5分患者的前列腺癌诊断效能[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 812-817. |
| [15] | 毛海,张帆,张展奕,颜野,郝一昌,黄毅,马潞林,褚红玲,张树栋. 基于MRI前列腺腺体相关参数构建腹腔镜前列腺癌术后尿失禁的预测模型[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 818-824. |
|
||