北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (3): 557-564. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.03.024
不同交联剂处理对脱细胞小肠黏膜下层多孔支架的影响
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院修复科,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心,口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,国家卫生健康委员会口腔医学计算机应用工程技术研究中心,国家药品监督管理局口腔生物材料重点实验室,北京 100081
2. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院综合二科,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心,口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,国家卫生健康委员会口腔医学计算机应用工程技术研究中心,国家药品监督管理局口腔生物材料重点实验室,北京 100081
Effects of different crosslinking treatments on the properties of decellularized small intestinal submucosa porous scaffolds
Yi DENG1,Yi ZHANG2,Bo-wen LI1,Mei WANG1,Lin TANG1,Yu-hua LIU1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NHC Research Center of Engineering and Technology for Computerized Dentistry & NMPA Key Laboratory for Dental Materials, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of General Dentistry Ⅱ, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NHC Research Center of Engineering and Technology for Computerized Dentistry & NMPA Key Laboratory for Dental Materials, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
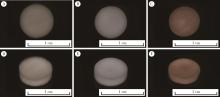
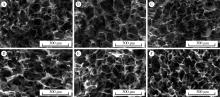
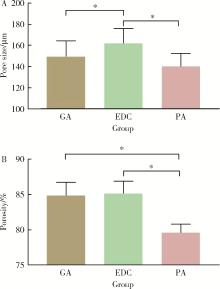
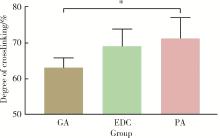
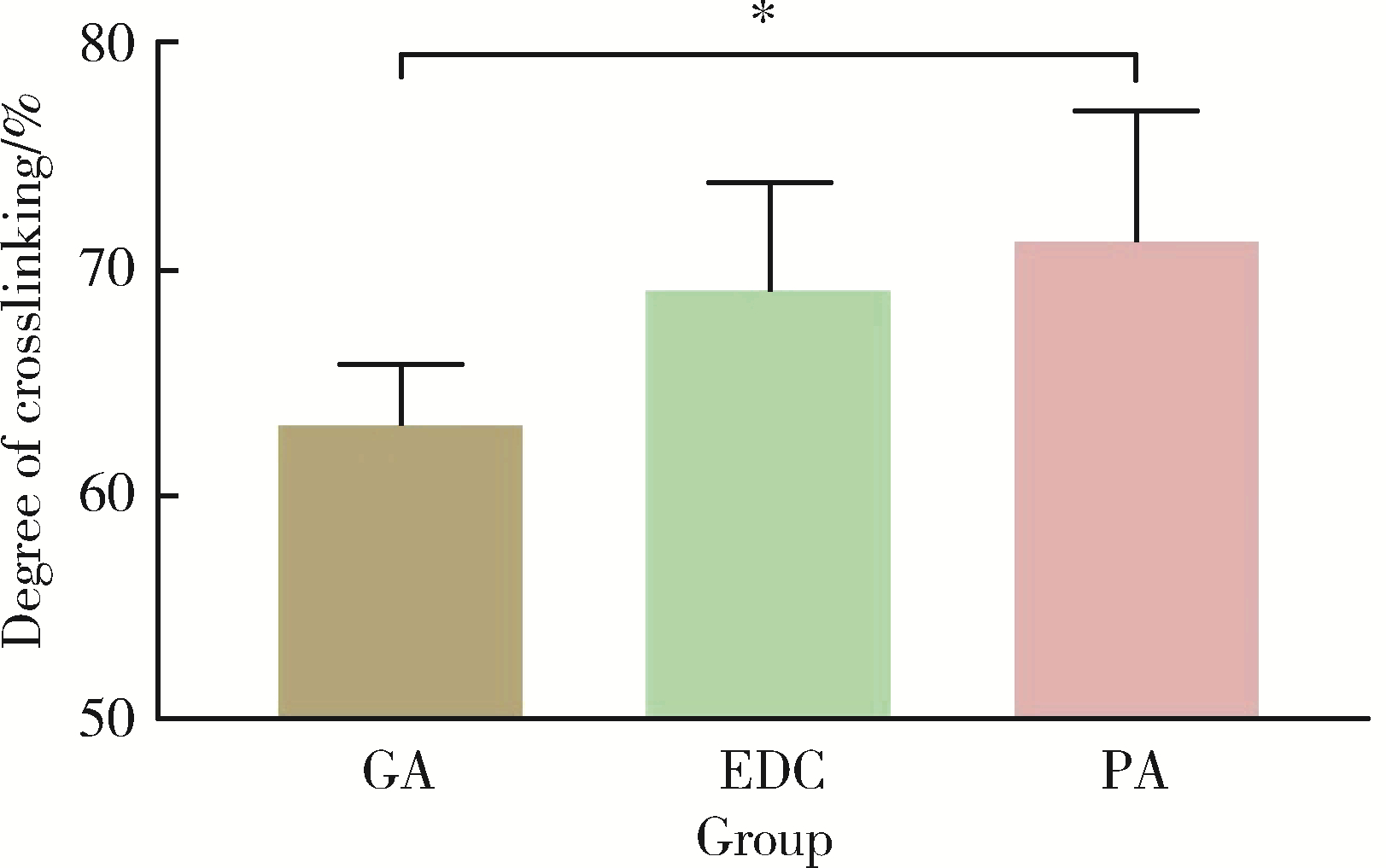
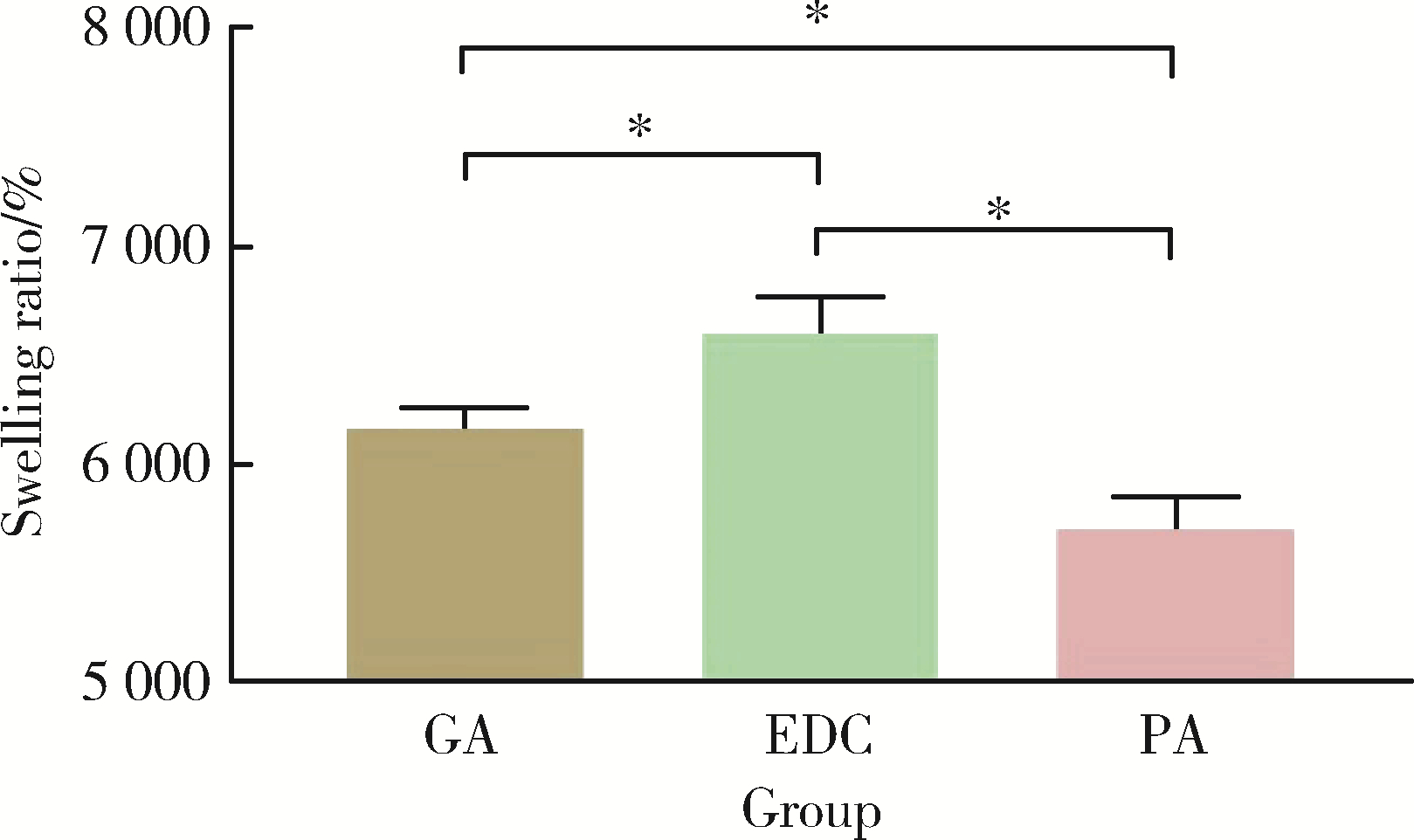
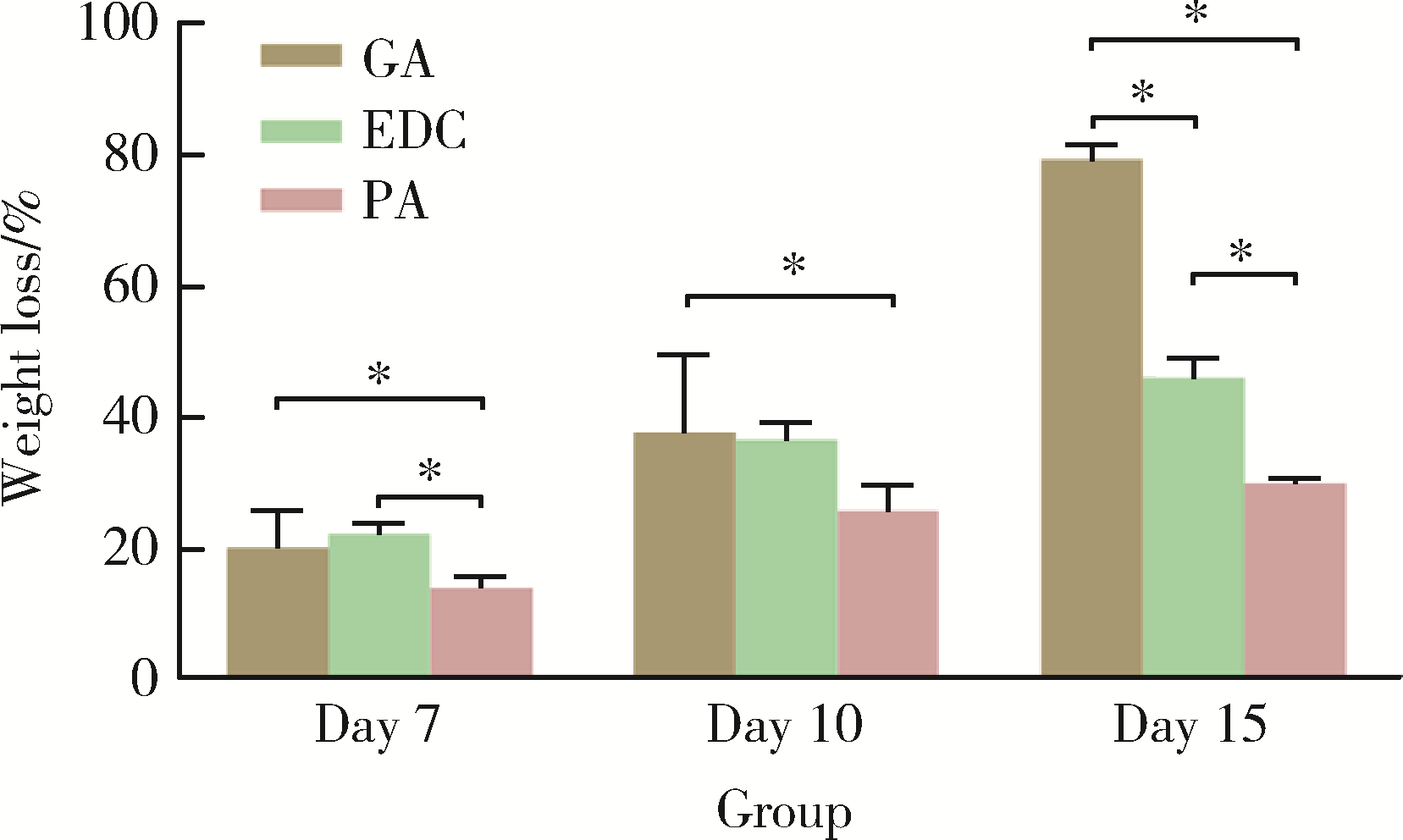
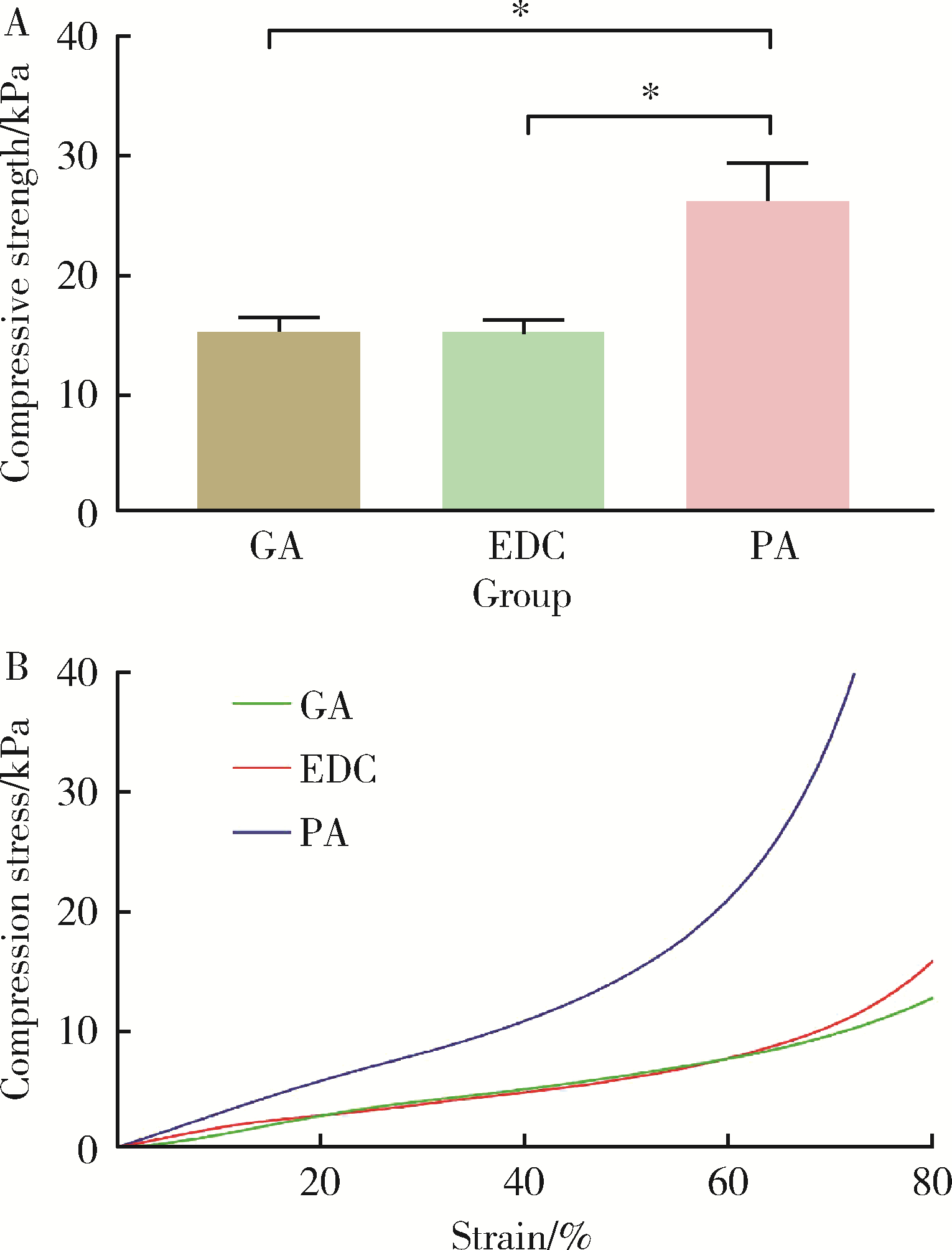
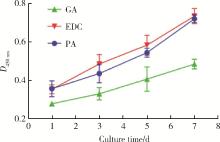
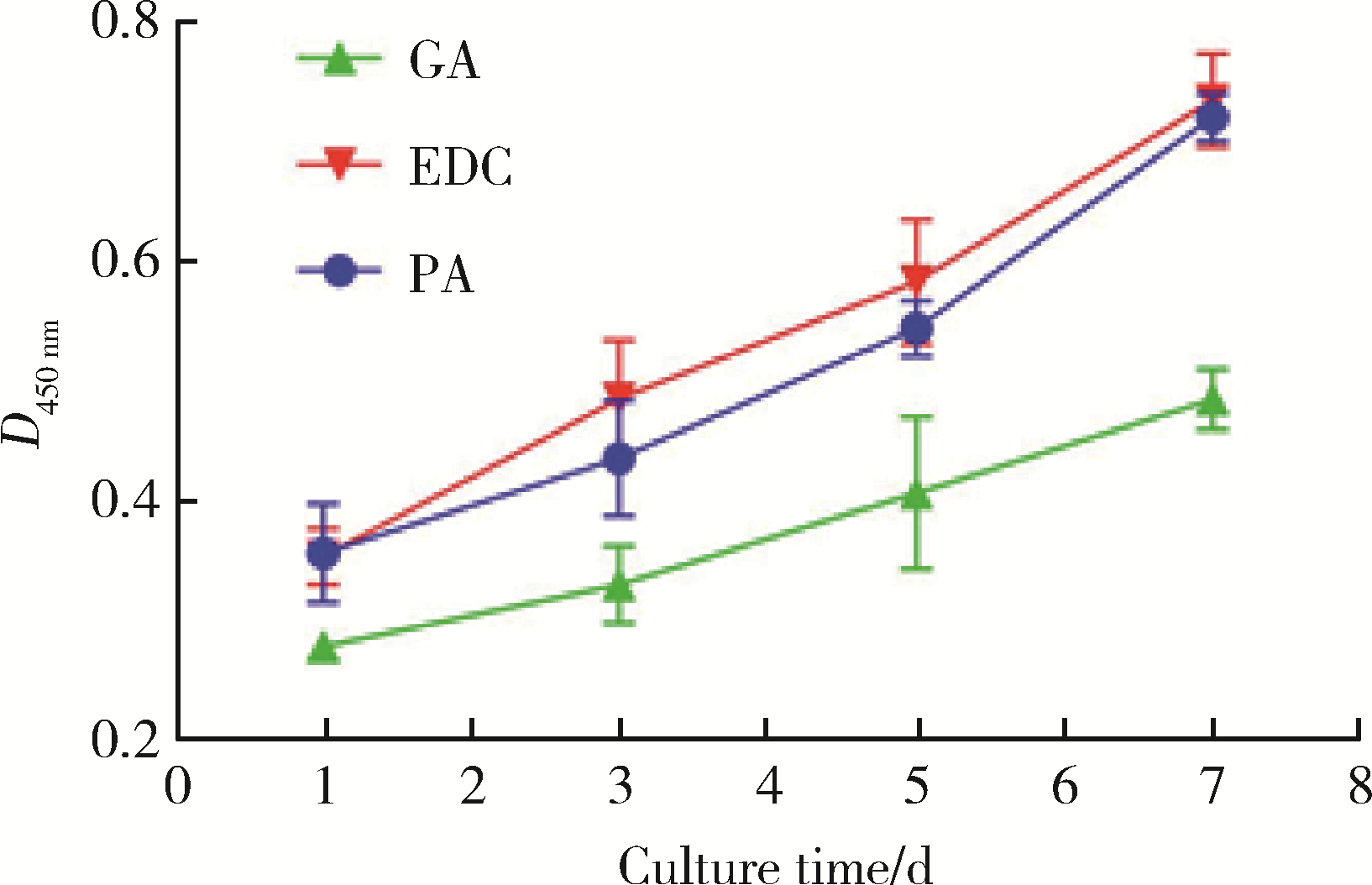
目的: 探讨不同交联剂处理对脱细胞小肠黏膜下层(decellularized small intestinal submucosa, SIS)多孔支架理化性能及生物相容性的影响。方法: (1) 将新鲜SIS塑形为三维多孔支架并采用戊二醛(glutaraldehyde, GA)、碳二亚胺[1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide, EDC]和原花青素(procyanidine, PA)3种交联剂进行交联, 获得3组交联后支架, 分别为GA组、EDC组和PA组。(2)理化性能评价: 对3组多孔支架进行宏观形貌观察, 使用场发射环境扫描电镜进行微观形貌观察并测定孔径及孔隙率, 使用茚三酮法测定交联度, 使用酶促降解法评价抗降解性能, 使用万能力学测试机测定应力应变曲线及压缩强度。(3)生物相容性评价: 使用细胞计数试剂盒(cell counting kit-8, CCK-8)法检测交联处理对人骨髓间充质干细胞(human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, hBMSCs)增殖的影响, 使用Calcein-AM/PI活死细胞染色法评价交联处理后支架的细胞毒性。结果: 宏观形貌观察可见交联修饰未破坏支架三维结构; 微观形貌观察可见各组多孔支架具有大小均匀、相互连通的孔隙结构。EDC组孔径最大, 与另两组差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.05);PA组孔隙率最低, 与另两组比较差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。PA组交联度最高而溶胀率最低, EDC组溶胀率最高。EDC组和GA组的体外降解速率均高于PA组, 其中GA组降解速度最快, PA组抗降解能力最佳, 降解至第15天时3组质量丧失率间的差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。EDC组和GA组压缩强度近似, PA组压缩强度最高, 与另两组比较差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。GA组支架的细胞毒性最大, hBMSCs在EDC组和PA组支架上具有更好的增殖能力, 在GA组增殖较慢。结论: 3种交联剂处理均可达到较高的交联度, 经EDC和PA交联处理的SIS多孔支架在拥有较好理化性能的同时具有良好的生物相容性, 相比于GA是更有应用前景的交联处理方法。
中图分类号:
- R783.1
| 1 |
Sengupta D , Waldman S , Li S . From in vitro to in situ tissue engineering[J]. Ann of Biomed Eng, 2014, 42 (7): 1537- 1545.
doi: 10.1007/s10439-014-1022-8 |
| 2 |
Li Y , Qiao Z , Yu F , et al. Transforming growth factor-β3/chitosan sponge (TGF-β3/CS) facilitates osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20 (20): 4982.
doi: 10.3390/ijms20204982 |
| 3 | Veres SP , Harrison JM , Lee JM . Cross-link stabilization does not affect the response of collagen molecules, fibrils, or tendons to tensile overload[J]. J OrthopRes, 2013, 31 (12): 1907- 1913. |
| 4 | Theocharis AD, Skandalis SS, Gialeli C, et al. Extracellular matrix structure[J/OL]. Adv Drug Deliv Rev, 2016, 97: 4-27[2020-03-01]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169409X15002574. |
| 5 | Li M, Zhang C, Cheng M, et al. Small intestinal submucosa: A potential osteoconductive and osteoinductive biomaterial for bone tissue engineering[J/OL]. Mater Sci Eng C, 2017, 75: 149-156[2020-10-01]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0928493116322937. |
| 6 | 李博文, 吴唯伊, 唐琳, 等. 改良猪小肠黏膜下层可吸收膜在兔下颌骨缺损早期愈合中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51 (5): 887- 892. |
| 7 | Sun L, Li B, Jiang D, et al. Nile tilapia skin collagen sponge modified with chemical cross-linkers as a biomedical hemostatic material[J/OL]. Colloids Surf. B, 2017, 159: 89-96[2020-03-01]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0927776517304836. |
| 8 |
Tottey S , Johnson SA , Crapo PM , et al. The effect of source animal age upon extracellular matrix scaffold properties[J]. Biomaterials, 2011, 32 (1): 128- 136.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.09.006 |
| 9 | Castilla B, Buttigieg J, Juan C, et al. Development and charac-terization of a novel porous small intestine submucosa-hydroxyapatite scaffold for bone regeneration[J/OL]. Mater Sci Eng C, 2017, 72: 519-525[2020-10-01]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0928493116309675. |
| 10 | Liu X, Zheng C, Luo X, et al. Recent advances of collagen-based biomaterials: Multi-hierarchical structure, modification and biomedical applications[J/OL]. Mater Sci Eng C, 2019, 99: 1509-1522[2020-10-01]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092849311831765X. |
| 11 |
Olde D , Van L , Dijkstra P , et al. Glutaraldehyde as a cross-linking agent for collagen-based biomaterials[J]. J Mater Sci Mater Med, 1995, 6 (8): 460- 472.
doi: 10.1007/BF00123371 |
| 12 | Usha R, Sreeram KJ, Rajaram A. Stabilization of collagen with EDC/NHS in the presence of l-lysine: A comprehensive study[J/OL]. Colloids Surf. B, 2012, 90: 83-90[2020-10-01]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092777651100573X. |
| 13 |
Mitra T , Sailakshmi G , Gnanamani A , et al. Preparation and characterization of a thermostable and biodegradable biopolymers using natural cross-linker[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2011, 48 (2): 276- 285.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2010.11.011 |
| 14 | Sun L, Li B, Song W, et al. Comprehensive assessment of nile tilapia skin collagen sponges as hemostatic dressings[J/OL]. Mater Sci Eng C, 2020, 109: 1105-1132[2020-10-01]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0928493118327012. |
| 15 |
Ward J , Kelly J , Wang W , et al. Amine functionalization of collagen matrices with multifunctional polyethylene glycol systems[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2010, 11 (11): 3093- 3101.
doi: 10.1021/bm100898p |
| 16 |
Charulatha V , Rajaram A . Influence of different crosslinking treatments on the physical properties of collagen membranes[J]. Biomaterials, 2003, 24 (5): 759- 767.
doi: 10.1016/S0142-9612(02)00412-X |
| 17 | Delgado LM , Fuller K , Zeugolis D . Collagen cross-linking: Biophysical, biochemical, and biological besponse analysis[J]. Tissue Eng Pt A, 2017, 23 (19/20): 1064- 1077. |
| 18 |
Ma L , Gao C , Mao Z , et al. Collagen/chitosan porous scaffolds with improved biostability for skin tissue engineering[J]. Biomaterials, 2003, 24 (26): 4833- 4841.
doi: 10.1016/S0142-9612(03)00374-0 |
| 19 | Chandika P, Ko S, Oh G, et al. Fish collagen/alginate/chitooligosaccharides integrated scaffold for skin tissue regeneration application[J/OL]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2015, 81: 504-513[2020-10-01]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0141813015005826. |
| 20 |
Shi Y , Zhang H , Zhang X , et al. A comparative study of two porous sponge scaffolds prepared by collagen derived from porcine skin and fish scales as burn wound dressings in a rabbit model[J]. Regen Biomater, 2020, 7 (1): 63- 70.
doi: 10.1093/rb/rbz036 |
| 21 | Vidal C, Zhu W, Manohar S, et al. Collagen-collagen interactions mediated by plant-derived proanthocyanidins: A spectroscopic and atomic force microscopy study[J/OL]. Acta Biomater, 2016, 41: 110-118[2020-03-01]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1742706116302446. |
| 22 |
He L , Mu C , Shi J , et al. Modification of collagen with a natural cross-linker, procyanidin[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2011, 48 (2): 354- 359.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2010.12.012 |
| 23 |
Trifković K , Milašinović N , Djordjević V , et al. Chitosan crosslinked microparticles with encapsulated polyphenols: Water sorption and release properties[J]. J Biomater Appl, 2015, 30 (5): 618- 631.
doi: 10.1177/0885328215598940 |
| 24 | Li Q, Mu L, Zhang F, et al. A novel fish collagen scaffold as dural substitute[J/OL]. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl, 2017, 80: 346-351[2020-10-01]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0928493117310627. |
| [1] | 李雨柯,王梅,唐琳,刘玉华,陈晓颖. 不同pH值对脱细胞小肠黏膜下层海绵支架螯合锶离子的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 44-51. |
|
||