北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (3): 552-556. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.03.023
严重创伤患者早期外周血淋巴细胞变化与预后之间的关系
- 北京大学人民医院创伤救治中心, 北京 100044
Early changes within the lymphocyte population are associated with the long term prognosis in severely injured patients
Fu-zheng GUO,Xiu-juan ZHAO,Jiu-xu DENG,Zhe DU,Tian-bing WANG,Feng-xue ZHU*( )
)
- Trauma Medicine Center, Peking University People′s Hospital, Bejing 10044, China
摘要:
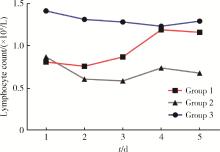
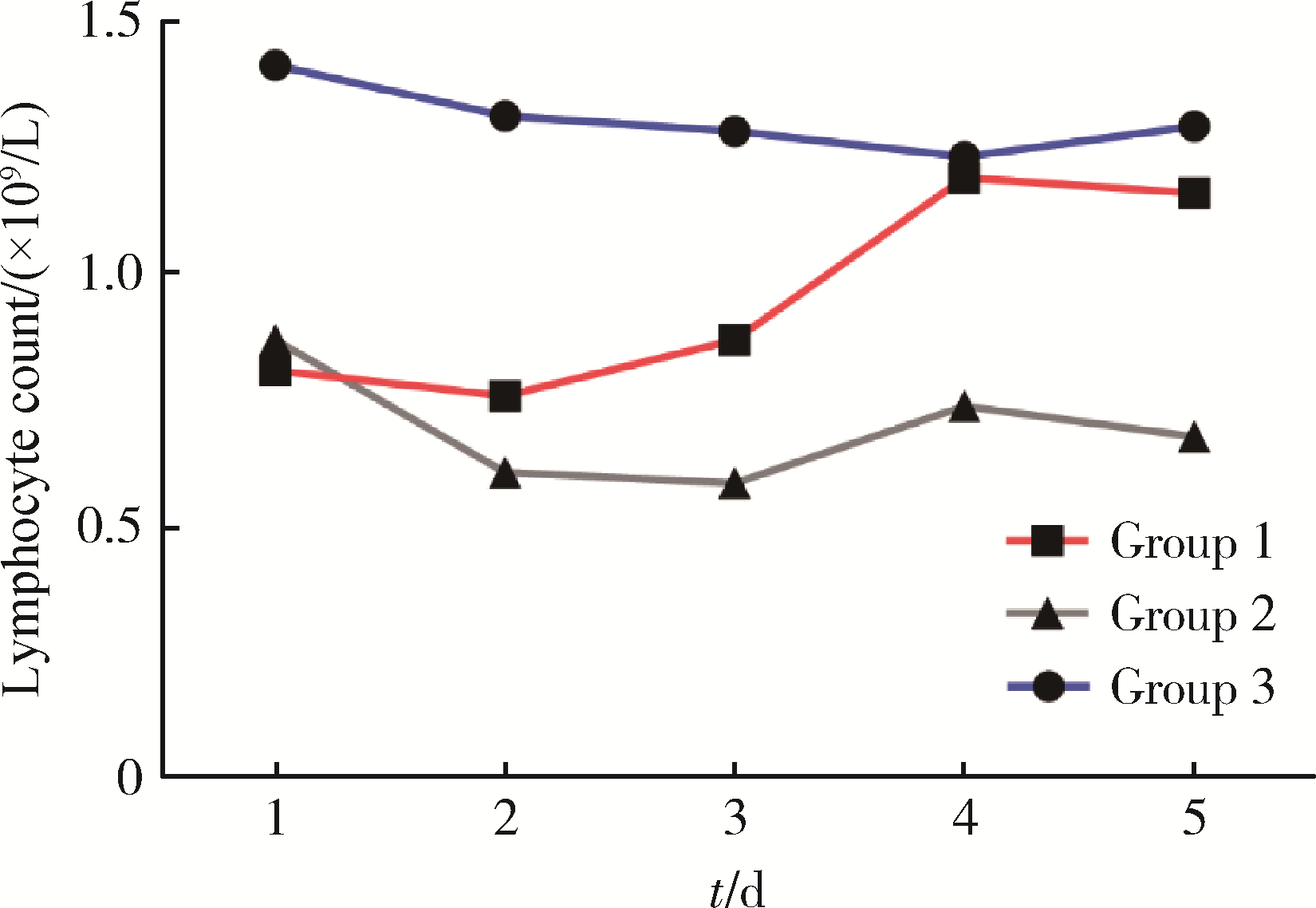
目的: 探讨严重创伤早期外周血淋巴细胞变化趋势与预后间的关系。方法: 选取2017年6月至2020年6月北京大学人民医院创伤救治中心收治的严重多发伤患者作为研究对象进行回顾性研究, 观察入院后连续5 d血常规中淋巴细胞变化趋势并进行分组, 第1组: 淋巴细胞减少后在5 d内恢复正常; 第2组: 淋巴细胞减少后未恢复正常; 第3组: 淋巴细胞一直处于正常水平, 并记录各组患者在住院28 d后的转归情况。对收集的临床资料进行统计学分析, 了解创伤早期淋巴细胞变化趋势与预后间的关系。同时, 为排除年龄的影响, 依据年龄是否≥65岁进行分层, 并根据住院时间是否≥28 d分为住院时间延长组和住院时间非延长组, 在不同年龄组中分别探讨淋巴细胞变化与住院时间的关系。结果: 共纳入患者83例, 其中男性66例, 女性17例, 主要受伤机制为车祸伤和高处坠落伤, 创伤严重程度评分(injury severe score, ISS)为(30±11)分。根据连续5 d淋巴细胞变化趋势分组, 第1组32例, 第2组33例, 第3组18例。第2组33例患者中, 在住院28 d内死亡5例, 死亡率为15.2%(5/33), 未出院9例, 均高于其他两组(P < 0.05)。进一步按年龄进行分层后, 发现在高年龄患者中淋巴细胞处于低水平是住院时间≥28 d的危险因素, 但在低年龄患者中, 发现中性粒细胞持续偏高与预后不良相关。结论: 严重创伤后外周血淋巴细胞一直处于低水平与预后不佳密切相关, 尤其在高年龄患者中明显, 淋巴细胞可作为一项可靠指标用于预后评估。
中图分类号:
- R641
| 1 |
姜保国. 我国严重创伤救治的现状和救治规范的建立[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2012, 50 (7): 577- 578.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-5815.2012.07.001 |
| 2 | Hillman PE , Scott NR , van Tienhoven A . Effect of 5-hydroxytryptamine and acetylcholine on the energy budget of chickens[J]. Am J Physiol, 1980, 239 (1): R57- R61. |
| 3 |
Cotton BA , Reddy N , Hatch QM , et al. Damage control resuscitation is associated with a reduction in resuscitation volumes and improvement in survival in 390 damage control laparotomy patients[J]. Ann Surg, 2011, 254 (4): 598- 605.
doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e318230089e |
| 4 |
Minei JP , Cuschieri J , Sperry J , et al. The changing pattern and implications of multiple organ failure after blunt injury with hemorrhagic shock[J]. Crit Care Med, 2012, 40 (4): 1129- 1135.
doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182376e9f |
| 5 |
Lord JM , Midwinter MJ , Chen YF , et al. The systemic immune response to trauma: an overview of pathophysiology and treatment[J]. Lancet, 2014, 384 (9952): 1455- 1465.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60687-5 |
| 6 |
Manson J , Hoffman R , Chen S , et al. Innate-like lymphocytes are immediate participants in the hyper-acute immune response to trauma and hemorrhagic shock[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10, 1501.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01501 |
| 7 |
Deitch EA , Landry KN , McDonald JC . Postburn impaired cell-mediated immunity may not be due to lazy lymphocytes but to overwork[J]. Ann Surg, 1985, 201 (6): 793- 802.
doi: 10.1097/00000658-198506000-00018 |
| 8 |
Hotchkiss RS , Tinsley KW , Swanson PE , et al. Prevention of lymphocyte cell death in sepsis improves survival in mice[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1999, 96 (25): 14541- 14546.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.25.14541 |
| 9 |
Heffernan DS , Monaghan SF , Thakkar RK , et al. Failure to normalize lymphopenia following trauma is associated with increased mortality, independent of the leukocytosis pattern[J]. Crit Care, 2012, 16 (1): R12.
doi: 10.1186/cc11157 |
| 10 |
Nacionales DC , Szpila B , Ungaro R , et al. A detailed charac-terization of the dysfunctional immunity and abnormal myelopoiesis induced by severe shock and trauma in the aged[J]. J Immunol, 2015, 195 (5): 2396- 2407.
doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500984 |
| 11 |
Manson J , Cole E , de Ath HD , et al. Early changes within the lymphocyte population are associated with the development of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in trauma patients[J]. Crit Care, 2016, 20 (1): 176.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1341-2 |
| 12 |
Brakenridge SC , Efron PA , Stortz JA , et al. The impact of age on the innate immune response and outcomes after severe sepsis/septic shock in trauma and surgical intensive care unit patients[J]. J Trauma Acute Care Surg, 2018, 85 (2): 247- 255.
doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000001921 |
| 13 |
Vanzant EL , Hilton RE , Lopez CM , et al. Advanced age is associated with worsened outcomes and a unique genomic response in severely injured patients with hemorrhagic shock[J]. Crit Care, 2015, 19, 77.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-0788-x |
| 14 |
Girardot T , Rimmele T , Venet F , et al. Apoptosis-induced lymphopenia in sepsis and other severe injuries[J]. Apoptosis, 2017, 22 (2): 295- 305.
doi: 10.1007/s10495-016-1325-3 |
| 15 |
Kasten KR , Goetzman HS , Reid MR , et al. Divergent adaptive and innate immunological responses are observed in humans following blunt trauma[J]. BMC Immunol, 2010, 11, 4.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-11-4 |
| 16 |
Servia L , Jove M , Sol J , et al. A prospective pilot study using metabolomics discloses specific fatty acid, catecholamine and tryptophan metabolic pathways as possible predictors for a negative outcome after severe trauma[J]. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med, 2019, 27 (1): 56.
doi: 10.1186/s13049-019-0631-5 |
| 17 |
Ploder M , Spittler A , Schroecksnadel K , et al. Tryptophan degradation in multiple trauma patients: survivors compared with non-survivors[J]. Clin Sci (Lond), 2009, 116 (7): 593- 598.
doi: 10.1042/CS20080319 |
| 18 |
Kahloul M , Bouida W , Boubaker H , et al. Value of anatomic and physiologic scoring systems in outcome prediction of trauma patients[J]. Eur J Emerg Med, 2014, 21 (2): 125- 129.
doi: 10.1097/MEJ.0b013e32836188ce |
| [1] | 陈逸凡,刘中砥,张鹏,黄伟. 严重创伤患者损伤严重度评分的一致性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 157-160. |
| [2] | 杜哲,黄伟,王志伟,周靖,熊建,李明,张鹏,刘中砥,朱凤雪,王传林,姜保国,王天兵. 多学科协作诊疗模式在严重创伤患者救治中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(2): 298-301. |
| [3] | 朱振杰,许清泉,黄晓波,洪扬,杨庆亚,王澍,安立哲,徐涛. 糖尿病患者经皮肾镜取石术后发生全身炎症反应综合征的危险因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(4): 643-649. |
| [4] | 陈亮, 李建兴, 黄晓波, 王晓峰. 一期经皮肾镜手术治疗无发热结石性脓肾术后发生全身炎症反应综合征的危险因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(4): 566-569. |
| [5] | 刘慧琳, 田勍, 洪天配, 刘桂花, 潘欢, 王海宁, 高洪伟. 脓毒症患者中血清程序化细胞死亡因子5水平的变化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(2): 238-. |
|
||