北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (6): 1123-1127. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.06.011
唾液腺超声对干燥综合征的诊断价值
- 上海交通大学医学院附属第九人民医院风湿免疫科, 上海 201999
Diagnostic performances of salivary gland ultrasonography for Sjögren's syndrome
Yang LIU,Fang CHENG,Yan-ling WANG,Xiang-yan AI,Zhen-hang ZHU,Fu-tao ZHAO*( )
)
- Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, the Ninth People's Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 201999, China
摘要:
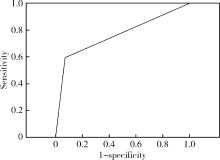
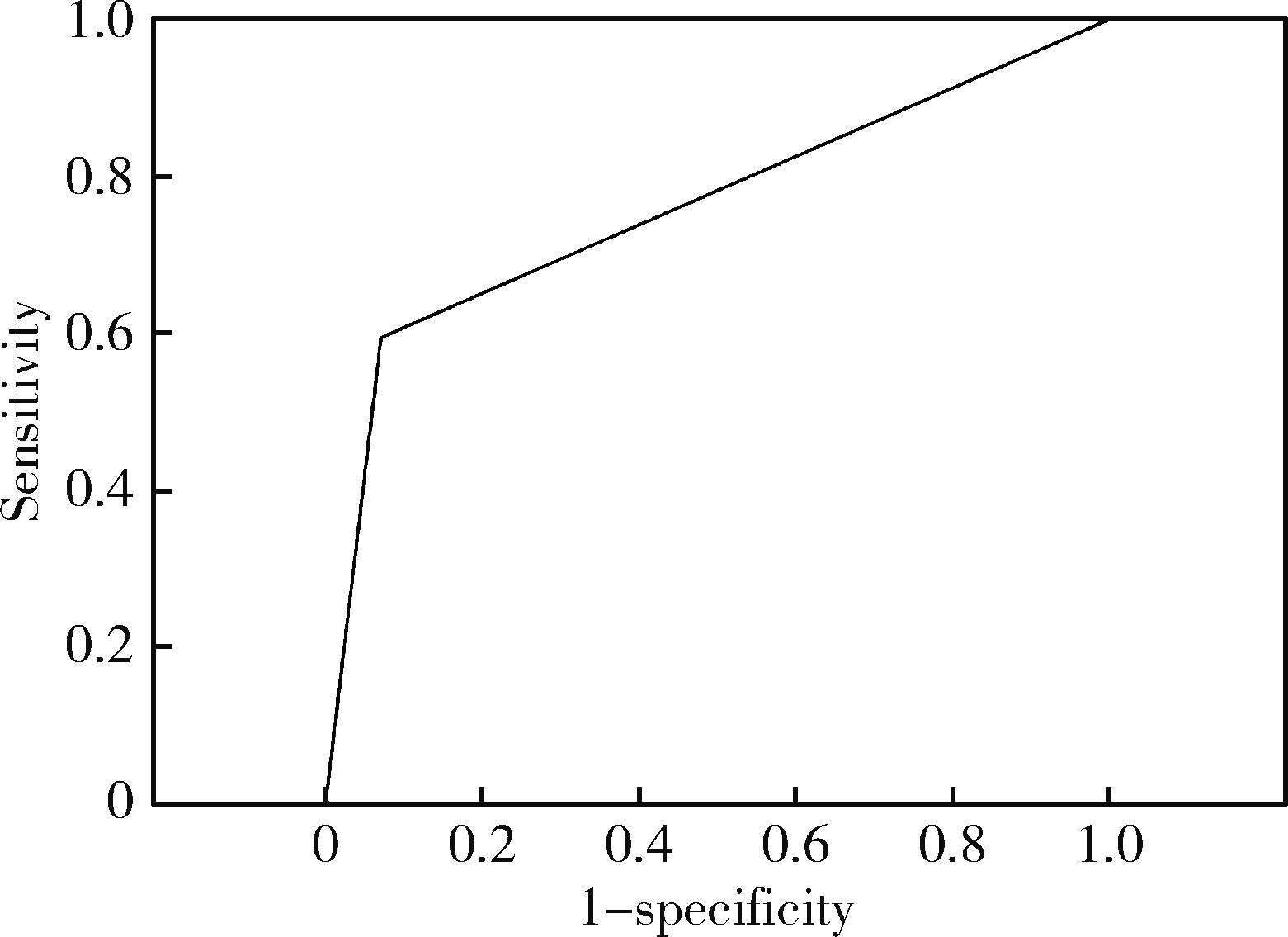
目的: 评估唾液腺超声(salivary gland uhrasonography,SGUS)对干燥综合征(Sj?gren’s syndrome,SS)的诊断价值。方法: 收集2019年12月至2022年1月就诊于上海交通大学医学院附属第九人民医院风湿免疫科门诊及住院部的246例表现为口干和/或眼干燥的患者,均完善SGUS,并采用2019年风湿病临床试验结果指标(outcome measures in rheumatology clinical trial,OMERACT)工作组超声评分系统对患者唾液腺进行评分,记录患者一般资料、未刺激唾液流率(unstimulated saliva flow rate, USFR)、Schirmer试验及血清学检查结果,193例完善唇腺活检检查。采用2016年美国风湿病学会(American College of Rheumatology,ACR)/欧洲抗风湿病联盟(European League Against Rheumatism,EULAR)共识作为SS诊断金标准。采用χ2检验比较两组唾液腺超声评分的差异,用受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic,ROC)曲线评估SGUS诊断SS的准确性,并比较SS患者中SGUS阳性组与阴性组的临床特征。结果: 共175例患者符合2016年ACR/EULAR共识为SS组,余71例不符合ACR/EULAR共识为非SS患者,两组患者年龄[(54.2±11.8)岁 vs.(53.4±14.9)岁,P=0.705]、女性(94.4% vs.93.1%,P=1.000)比较差异均无统计学意义。共109例患者SGUS阳性(≥2分),其中104例符合SS诊断,5例不符合SS诊断,SS组SGUS阳性率明显高于非SS组(59.4% vs.7.0%,P < 0.001)。2019年OMERACT超声评分系统诊断SS的曲线下面积为0.762(95%CI 0.701~0.823),SGUS评分与ACR/EULAR共识的绝对一致性为69.1%(170/246),敏感性为59.4%(104/175),特异性为93.0%(66/71),阳性预测值为95.4%(104/109),阴性预测值为48.2% (66/137)。共81例患者SGUS、抗干燥综合征A (Sj?gren’s syndrome A, SSA)抗体双阳性,均符合ACR/EULAR共识,阳性符合率为100%(81/81);85例患者SGUS阴性且无抗SSA抗体,60例未达到ACR/EULAR共识,阴性符合率为70.6% (60/85)。在SS患者中,SGUS阳性组有更高的抗核抗体(antinuclear antibody, ANA)阳性率(83.1%对98.1%,P < 0.001)。结论: 2019年OMERACT超声评分系统在诊断SS中有重要价值,与抗SSA抗体联合可进一步提高诊断性能。
中图分类号:
- R593.2
| 1 |
Shiboski CH , Shiboski SC , Seror R , et al. 2016 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria for primary Sjögren's syndrome: A consensus and data-driven methodology involving three international patient cohorts[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2017, 69 (1): 35- 45.
doi: 10.1002/art.39859 |
| 2 |
Theander E , Mandl T . Primary Sjögren's syndrome: Diagnostic and prognostic value of salivary gland ultrasonography using a simplified scoring system[J]. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken), 2014, 66 (7): 1102- 1107.
doi: 10.1002/acr.22264 |
| 3 |
Salaffi F , Carotti M , Iagnocco A , et al. Ultrasonography of salivary glands in primary Sjögren's syndrome: A comparison with contrast sialography and scintigraphy[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2008, 47 (8): 1244- 1249.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ken222 |
| 4 | Lee KA , Lee SH , Kim HR , et al. Diagnostic and predictive eva-luation using salivary glandultrasonography in primary Sjögren's syndrome[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2018, 112 (3): 165- 172. |
| 5 |
Jousse-Joulin S , Gatineau F , Baldini C , et al. Weight of salivary gland ultrasonography compared toother items of the 2016 ACR/EULAR classification criteria for Primary Sjögren's syndrome[J]. J Intern Med, 2020, 287 (2): 180- 188.
doi: 10.1111/joim.12992 |
| 6 |
van Nimwegen JF , Mossel E , Delli K , et al. Incorporation of salivary gland ultrasonography into the ACR EULAR criteria for primary Sjögren's syndrome[J]. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken), 2020, 72 (4): 583- 590.
doi: 10.1002/acr.24017 |
| 7 |
Takagi Y , Nakamura H , Sumi M , et al. Combined classification system based on ACR/EULAR and ultrasonographic scores for improving the diagnosis of Sjögren's syndrome[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13 (4): e0195113.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195113 |
| 8 |
Jousse-Joulin S , D'Agostino MA , Nicolas C , et al. Video clip assessment of a salivary gland ultrasound scoring system in Sjögren's syndrome using consensual definitions: An OMERACT uhrasound working group reliability exercise[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2019, 78 (7): 967- 973.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215024 |
| 9 |
Zhou M , Song S , Wu S , et al. Diagnostic accuracy of salivary gland ultrasonography with different scoring systems in Sjögren's syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8 (1): 17128.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35288-5 |
| 10 | Ramsubeik K , Motilal S , Sanchez-Ramos L , et al. Diagnostic accuracy of salivary gland ultrasound in Sjögren's syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis, 2020, 12, 1- 21. |
| 11 |
Jousse-Joulin S , Milic V , Jonsson MV , et al. Is salivary gland ultrasonography a useful tool in Sjögren's syndrome? A systematic review[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2016, 55 (5): 789- 800.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kev385 |
| 12 | Carotti M , Sala F , Di Carlo M , et al. Diagnostic value of major salivary gland ultrasonography in primary Sjögren's syndrome: The role of grey-scale and colour/power Doppler sonography[J]. Gland Surg, 2019, 8 (Suppl 3): S159- S167. |
| 13 |
Mossel E , Arends S , van Nimwegen JF , et al. Scoring hypoechogenic areas in one parotid and one submandibular gland increases feasibility of ultrasound in primary Sjögren's syndrome[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2018, 77 (4): 556- 562.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211992 |
| 14 |
Izzetti R , Fulvio G , Nisi M , et al. Reliability of OMERACT scoring system in ultra-high frequency ultrasonography of minor salivary glands: Inter-rater agreement study[J]. J Imaging, 2022, 8 (4): 111.
doi: 10.3390/jimaging8040111 |
| 15 |
Al Tabaa O , Gouze H , Hamroun S , et al. Normal salivary gland ultrasonography could rule out the diagnosis of Sjögren's syndrome in anti-SSA-negative patients with sicca syndrome[J]. RMD Open, 2021, 7 (1): e001503.
doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001503 |
| 16 |
Fana V , Dohn UM , Krabbe S , et al. Application of the OMERACT grey-scale ultrasound scoring system for salivary glands in a single-centre cohort of patients with suspected Sjögren's syndrome[J]. RMD Open, 2021, 7 (2): e001516.
doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001516 |
| 17 | Robin F, Albert JD, Lescoat A, et al. Diagnostic performances of ultrasound evaluation of major salivary glands according to the 2019 OMERACT US scoring system[J/OL]. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken), 2021, 5 (2021-05-10)[2022-04-15]. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/acr.24631. |
| 18 |
Gazeau P , Cornec D , Jousse-Joulin S , et al. Time-course of ultrasound abnormalities of major salivary glands in suspected Sjögren's syndrome[J]. Joint Bone Spine, 2018, 85 (2): 227- 232.
doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2017.02.007 |
| 19 | Zandonella-Callegher S , Zabotti A , Giovannini I , et al. Normal-appearing salivary gland ultrasonography identifies a milder phenotype of primary Sjögren's syndrome[J]. Front Med (Lausanne), 2020, 7, 602354. |
| 20 |
Mossel E , Delli K , Nimwegen GF , et al. Ultrasonography of major salivary glands compared with parotid and labial gland biopsy and classification criteria in patients with clinically suspected primary Sjögren's syndrome[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2017, 76 (11): 1883- 1889.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211250 |
| 21 |
Kim JW , Lee H , Park SH , et al. Salivary gland ultrasonography findings are associated with clinical, histological, and serologic features of Sjögren's syndrome[J]. Scand J Rheumatol, 2018, 47 (4): 303- 310.
doi: 10.1080/03009742.2017.1374451 |
| 22 |
Jousse-Joulin S , Devauchelle-Pensec V , Cornec D , et al. Brief report: Ultrasonographic assessment of salivary gland response to rituximab in primary Sjögren's syndrome[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2015, 67 (6): 1623- 1628.
doi: 10.1002/art.39088 |
| 23 |
Lorenzon M , Spina E , Di Franco FT , et al. Salivary gland ultrasound in primary Sjögren's syndrome: Current and future perspectives[J]. Open Access Rheumatol, 2022, 14, 147- 160.
doi: 10.2147/OARRR.S284763 |
| [1] | 原晋芳, 王新利, 崔蕴璞, 王雪梅. 尿促黄体生成素在女童中枢性性早熟预测中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 788-793. |
| [2] | 杨玉淑, 齐晅, 丁萌, 王炜, 郭惠芳, 高丽霞. 抗唾液腺蛋白1抗体联合抗腮腺分泌蛋白抗体对干燥综合征的诊断价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 845-852. |
| [3] | 王明瑞,刘军,熊六林,于路平,胡浩,许克新,徐涛. 经皮微通道-微电子肾镜-微超声探针碎石术治疗1.5~2.5 cm肾结石的疗效和安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 605-609. |
| [4] | 杨捷,冯杰莉,张树栋,马潞林,郑清. 经食管超声心动图在肾切除术联合Mayo Ⅲ~Ⅳ级静脉瘤栓取栓术不同手术方式中的临床作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 631-635. |
| [5] | 陈延,李况蒙,洪锴,张树栋,程建星,郑仲杰,唐文豪,赵连明,张海涛,姜辉,林浩成. 阴茎海绵体注射试验对阴茎血管功能影响的回顾性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 680-686. |
| [6] | 俞光岩. 儿童唾液腺疾病[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 1-3. |
| [7] | 韩艺钧,李常虹,陈秀英,赵金霞. 抗SSB抗体阳性和阴性的原发性干燥综合征患者临床及免疫学特征的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1000-1006. |
| [8] | 李建斌,吕梦娜,池强,彭一琳,刘鹏程,吴锐. 干燥综合征患者发生重症新型冠状病毒肺炎的早期预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1007-1012. |
| [9] | 魏越,姚兰,陆希,王军,蔺莉,刘鲲鹏. 胃超声检查评估剖宫产产妇术前饮用碳水化合物后胃排空的效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1082-1087. |
| [10] | 孟彦宏,陈怡帆,周培茹. CENP-B抗体阳性的原发性干燥综合征患者的临床和免疫学特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1088-1096. |
| [11] | 吴洁,张雯,梁舒,秦艺璐,范文强. 妊娠期原发性干燥综合征合并视神经脊髓炎谱系疾病危重症1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1118-1124. |
| [12] | 王丽芳,石连杰,宁武,高乃姝,王宽婷. 干燥综合征合并冷凝集素病1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1130-1134. |
| [13] | 魏越,陆希,张静,刘鲲鹏,王永军,姚兰. 术前2 h口服碳水化合物对妇科腹腔镜特殊体位手术患者胃容量及反流误吸风险的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 893-898. |
| [14] | 邢海霞,王琳,乔迪,刘畅,潘洁. 干燥综合征口腔疾病的治疗特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 929-933. |
| [15] | 傅强,高冠英,徐雁,林卓华,孙由静,崔立刚. 无症状髋关节前上盂唇撕裂超声与磁共振检查的对比研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 665-669. |
|
||