北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (6): 1117-1122. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.06.010
氧化型低密度脂蛋白抗体在抗磷脂综合征中的临床意义
- 北京大学人民医院风湿免疫科, 北京 100044
Clinical significance of oxidized low-density lipoprotein antibody in antiphospholipid syndrome
Yu-ke HOU,Qing-meng CAI,Xiang-jun LIU,Ze-lin YUN,Chun LI*( ),Xue-wu ZHANG*(
),Xue-wu ZHANG*( )
)
- Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University People's Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
摘要:
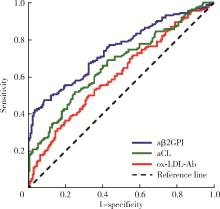
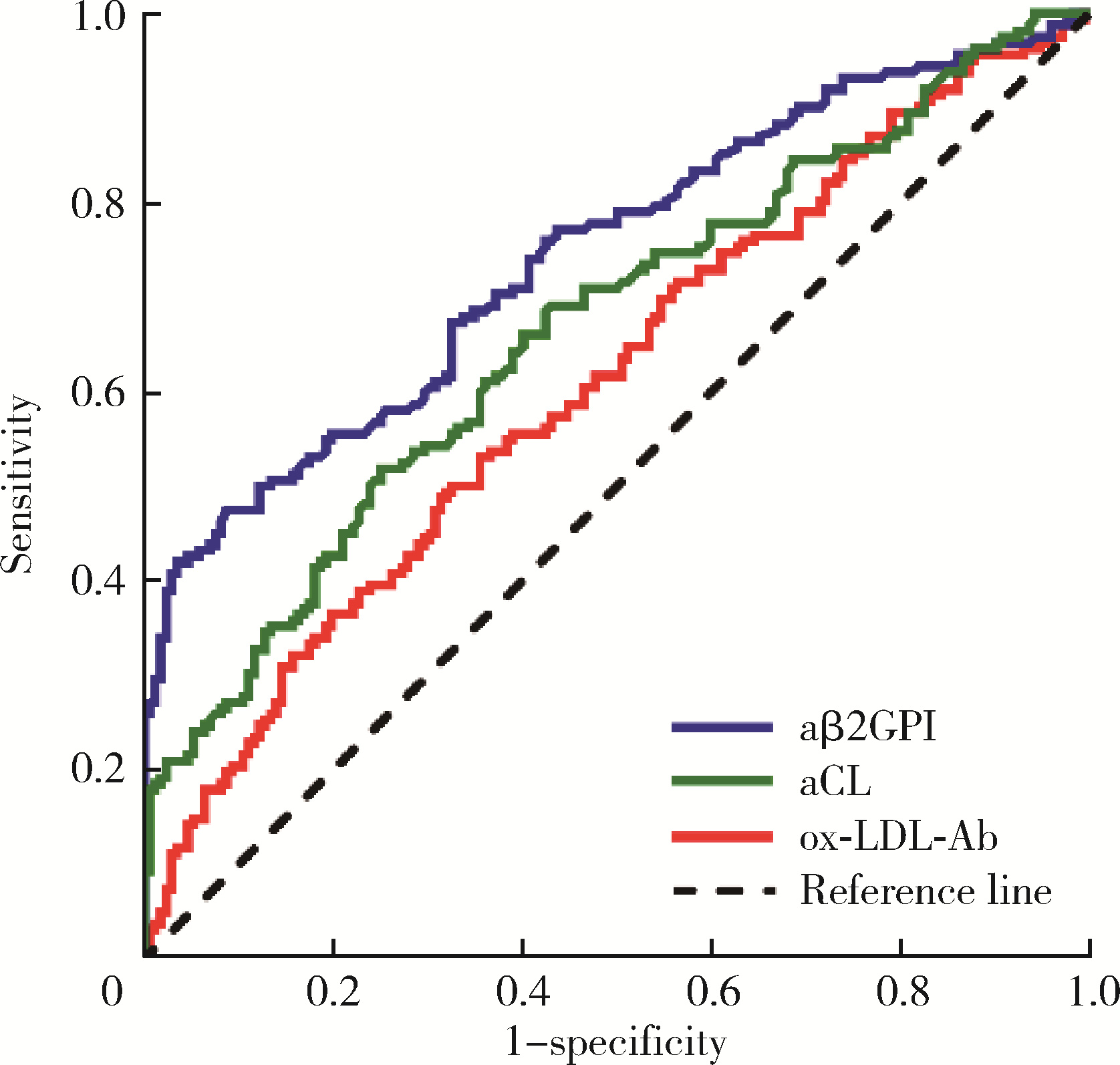
目的: 探讨氧化型低密度脂蛋白抗体(oxidized low-density lipoprotein antibodies, ox-LDL-Ab)在抗磷脂综合征(antiphospholipid syndrome, APS)中的分布及其临床意义。方法: 共纳入334例患者,包括162例APS患者,122例无血栓或病态妊娠的其他自身免疫性疾病患者作为疾病对照,以及50例健康对照。收集APS患者的临床资料及实验室检查指标,采用酶联免疫吸附试验检测患者的ox-LDL-Ab、IgG/IgA/IgM型抗心磷脂抗体(anticardioli-pin, aCL)、IgG/IgA/IgM型抗β2糖蛋白Ⅰ抗体(anti-β2-glycoprotein Ⅰ, aβ2GPI)。采用统计软件SPSS 27.0分析ox-LDL-Ab与临床及实验室检查指标之间的相关性。结果: APS组60.5%的患者合并血栓,48.1%的患者出现病态妊娠,34.0%的患者合并血小板减少,aCL、aβ2GPI和狼疮抗凝物(lupus anticoagulant, LAC)的阳性率分别为17.9%、34.6%和46.9%。ox-LDL-Ab在APS患者中的滴度和阳性率显著高于健康对照组[滴度:40.8 (25.4~66.0) U/mL vs. 24.1 (12.3~36.5) U/mL, P=0.001;阳性率:67.3% vs. 36.0%, P=0.001],与疾病对照组的差异无统计学意义[滴度:40.8 (25.4~66.0) U/mL vs. 35.9 (24.2~53.1) U/mL, P=0.118;阳性率:67.3% vs. 61.5%, P=0.318]。aβ2GPI、aCL、ox-LDL-Ab的曲线下面积分别是0.745 (95%CI: 0.692~0.797)、0.666 (95%CI: 0.608~0.724)、0.609 (95%CI: 0.549~0.669),约登指数(Youden’s index)分别为0.388、0.269、0.132。ox-LDL-Ab在血清阴性APS中的曲线下面积是0.562 (95%CI: 0.480~0.645),敏感性和特异性分别为63.9%和47.0%,约登指数为0.109。ox-LDL-Ab阳性组aβ2GPI (42.2% vs. 18.9%, P=0.003)和aCL (22.9% vs. 7.5%, P=0.017)的阳性率高于ox-LDL-Ab阴性组。ox-LDL-Ab与血栓形成、冠心病、病态妊娠、高脂血症、低补体血症及LAC阳性率无相关性。结论: ox-LDL-Ab与aCL、aβ2GPI有一定相关性,但与血栓、病态妊娠及冠心病不相关。
中图分类号:
- R593.2
| 1 |
Devreese KMJ , Ortel TL , Pengo V , et al. Laboratory criteria for antiphospholipid syndrome: Communication from the SSC of the ISTH[J]. J Thromb Haemost, 2018, 16 (4): 809- 813.
doi: 10.1111/jth.13976 |
| 2 |
Conti F , Andreoli L , Crisafulli F , et al. Does seronegative obstetric APS exist? "pro" and "cons"[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2019, 18 (12): 102407.
doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2019.102407 |
| 3 |
Abreu MM , Danowski A , Wahl DG , et al. The relevance of "non-criteria" clinical manifestations of antiphospholipid syndrome: 14th International Congress on Antiphospholipid Anti-bodies Technical Task Force Report on Antiphospholipid Syndrome Clinical Features[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2015, 14 (5): 401- 414.
doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2015.01.002 |
| 4 | Hulthe J . Antibodies to oxidized LDL in atherosclerosis development: Clinical and animal studies[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2004, 348 (1/2): 1- 8. |
| 5 |
Steinberg D . Low density lipoprotein oxidation and its pathobio-logical significance[J]. J Biol Chem, 1997, 272 (34): 20963- 20966.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.34.20963 |
| 6 |
Salonen JT , Ylä-Herttuala S , Yamamoto R , et al. Autoantibody against oxidised LDL and progression of carotid atherosclerosis[J]. Lancet, 1992, 339 (8798): 883- 887.
doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90926-T |
| 7 |
Vaarala O . Antiphospholipid antibodies and atherosclerosis[J]. Lupus, 1996, 5 (5): 442- 447.
doi: 10.1177/096120339600500522 |
| 8 |
Ryan M , Owens D , Kilbride B , et al. Antibodies to oxidized lipoproteins and their relationship to myocardial infarction[J]. QJM, 1998, 91 (6): 411- 415.
doi: 10.1093/qjmed/91.6.411 |
| 9 |
Bellomo G , Maggi E , Poli M , et al. Autoantibodies against oxidatively modified low-density lipoproteins in NIDDM[J]. Diabetes, 1995, 44 (1): 60- 66.
doi: 10.2337/diab.44.1.60 |
| 10 | Lopez D , Kobayashi K , Merrill JT , et al. IgG autoantibodies against beta2-glycoprotein Ⅰ complexed with a lipid ligand derived from oxidized low-density lipoprotein are associated with arterial thrombosis in antiphospholipid syndrome[J]. Clin Dev Immunol, 2003, 10 (2/3/4): 203- 211. |
| 11 |
Romero FI , Amengual O , Atsumi T , et al. Arterial disease in lupus and secondary antiphospholipid syndrome: association with anti-beta2-glycoprotein Ⅰ antibodies but not with antibodies against oxidized low-density lipoprotein[J]. Br J Rheumatol, 1998, 37 (8): 883- 888.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/37.8.883 |
| 12 | Bec'arevic' M , Andrejevic' S , Miljic' P , et al. Serum lipids and anti-oxidized LDL antibodies in primary antiphospholipid syndrome[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2007, 25 (3): 361- 366. |
| 13 |
Miyakis S , Lockshin MD , Atsumi T , et al. International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS)[J]. J Thromb Haemost, 2006, 4 (2): 295- 306.
doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2006.01753.x |
| 14 |
Rezende L , Couto NFD , Fernandes-Braga W , et al. OxLDL induces membrane structure rearrangement leading to biomechanics alteration and migration deficiency in macrophage[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr, 2022, 1864 (9): 183951.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2022.183951 |
| 15 |
Hartley A , Haskard D , Khamis R . Oxidized LDL and anti-oxidized LDL antibodies in atherosclerosis: Novel insights and future directions in diagnosis and therapy[J]. Trends Cardiovasc Med, 2019, 29 (1): 22- 26.
doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2018.05.010 |
| 16 |
Itakura H , Yokoyama M , Matsuzaki M , et al. Relationships between plasma fatty acid composition and coronary artery disease[J]. J Atheroscler Thromb, 2011, 18 (2): 99- 107.
doi: 10.5551/jat.5876 |
| 17 |
Yang SH , Li YT , Du DY . Oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced CD147 expression and its inhibition by high-density lipoprotein on platelets in vitro[J]. Thromb Res, 2013, 132 (6): 702- 711.
doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2013.10.003 |
| 18 |
Strobel NA , Fassett RG , Marsh SA , et al. Oxidative stress biomarkers as predictors of cardiovascular disease[J]. Int J Cardiol, 2011, 147 (2): 191- 201.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2010.08.008 |
| 19 |
Jiang D , Lim W , Crowther M , et al. A systematic review of the association between anti-beta-2 glycoprotein Ⅰ antibodies and APS manifestations[J]. Blood Adv, 2021, 5 (20): 3931- 3936.
doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021005205 |
| 20 |
Hayem G , Nicaise-Roland P , Palazzo E , et al. Anti-oxidized low-density-lipoprotein (OxLDL) antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus with and without antiphospholipid syndrome[J]. Lupus, 2001, 10 (5): 346- 351.
doi: 10.1191/096120301667475689 |
| 21 | Li J , Chi Y , Liu S , et al. Recombinant domain V of β2-glycoprotein Ⅰ inhibits the formation of atherogenic oxLDL/β2-glycoprotein Ⅰ complexes[J]. J Clin Immunol, 2014, 34 (6): 669- 676. |
| 22 | Matsuura E , Lopez LR . Autoimmune-mediated atherothrombosis[J]. Lupus, 2008, 17 (10): 878- 887. |
| 23 | 白玲, 谭雪峰, 刘平. 冠心病患者抗心磷脂抗体与PON、ox-LDL、MDA和SOD的相关性[J]. 心脏杂志, 2014, 26 (4): 453- 455. |
| [1] | 汤晓菲,李永红,丁秋玲,孙卓,张阳,王育梅,田美伊,刘坚. 类风湿关节炎患者下肢深静脉血栓发病率及危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 279-283. |
| [2] | 卢情怡,艾尼扎提·哈斯木,李宇菲,李春. 抗神经酰胺抗体在抗磷脂综合征中的分布及临床意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1139-1143. |
| [3] | 洪丽荣,陈雨佳,江庆来,贾汝琳,李春,冯亮华. 新型血栓四项联合常规凝血指标预测抗磷脂综合征患者血栓形成的价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1033-1038. |
| [4] | 庄金满,李天润,李选,栾景源,王昌明,冯琦琛,韩金涛. Rotarex旋切导管在股腘动脉狭窄合并血栓形成中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 328-332. |
| [5] | 王玉华,张国华,张令令,罗俊丽,高兰. 系统性红斑狼疮合并自发性肾上腺出血1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6): 1178-1181. |
| [6] | 顾婕昱,陆翠,石慧,杨程德. 14例恶性抗磷脂综合征病例报道及临床分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(6): 1033-1038. |
| [7] | 李记,郑莉,石连杰,徐婧,舒建龙,张学武. 可溶性内皮糖蛋白在抗磷脂综合征患者的血清水平及临床意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(6): 1027-1032. |
| [8] | 郑晓娟, 邓晓莉, 刘湘源. 54例抗磷脂综合征患者的妊娠结局[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(2): 323-328. |
| [9] | 褚亚明, 窦勇, 李玉军, 周一新△. 人工膝关节置换术后小腿深静脉血栓的转归[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(5): 708-710. |
| [10] | 唐琦,宋毅,李学松,张崔建,蔡林,宋刚,张骞,王进,何志嵩,周利群. 肾癌伴静脉瘤栓患者的外科治疗策略及长期疗效观察[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(4): 549-. |
| [11] | 李茹*, 周云杉*, 贾园, 栗占国. 抗磷脂综合征患者血栓事件的危险因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(5): 788-791. |
| [12] | 于峥嵘, 李淳德, 邑晓东, 林景荣, 刘宪义, 刘洪, 卢海霖. 脊柱手术后静脉血栓栓塞的预防[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2011, 43(5): 661-665. |
| [13] | 高鹏骥, 朱继业, 栗光明, 冷希圣. 合并门静脉血栓的肝病患者的肝移植方法及疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2009, 41(5): 558-560. |
| [14] | 宋琳琳, 吴新民, 袁训芝, 袁家颖, 赵国立. 易栓症相关分子与髋膝关节大手术后下肢深静脉血栓[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2009, 41(2): 237-238. |
|
||