北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (6): 1151-1157. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.06.015
绵羊外周血间充质干细胞的生物学特性
- 1. 潍坊医学院,山东潍坊 261053
2. 北京大学第三医院运动医学科,北京 100191
Biological characteristics of sheep peripheral blood mesenchymal stem cell
Chao HAN1,Zhu-xing ZHOU2,You-rong CHEN2,Zi-hui DONG1,Jia-kuo YU2,*( )
)
- 1. Weifang Medical University, Weifang 261053, Shandong, China
2. Department of Sports Medicine, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
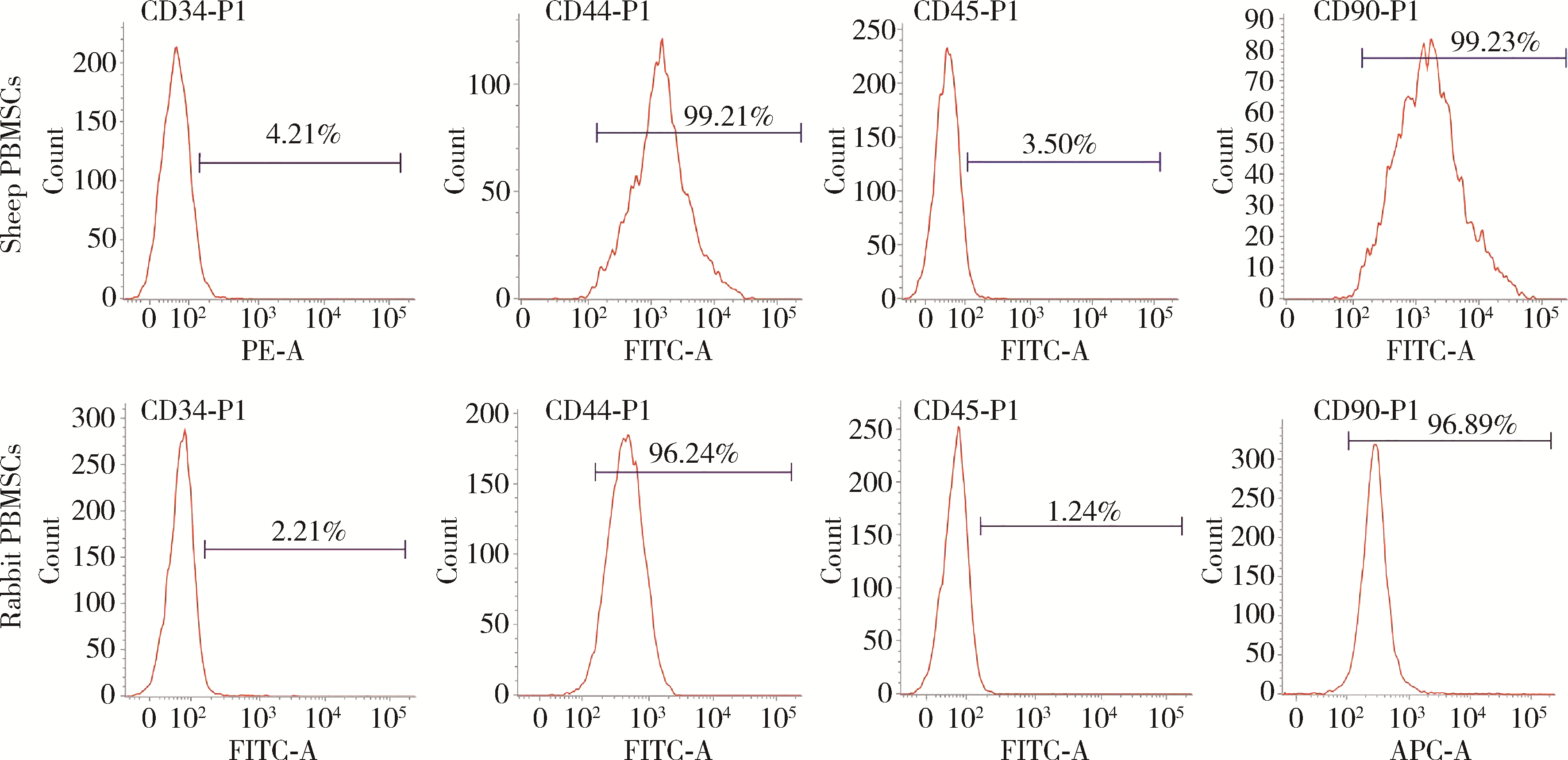
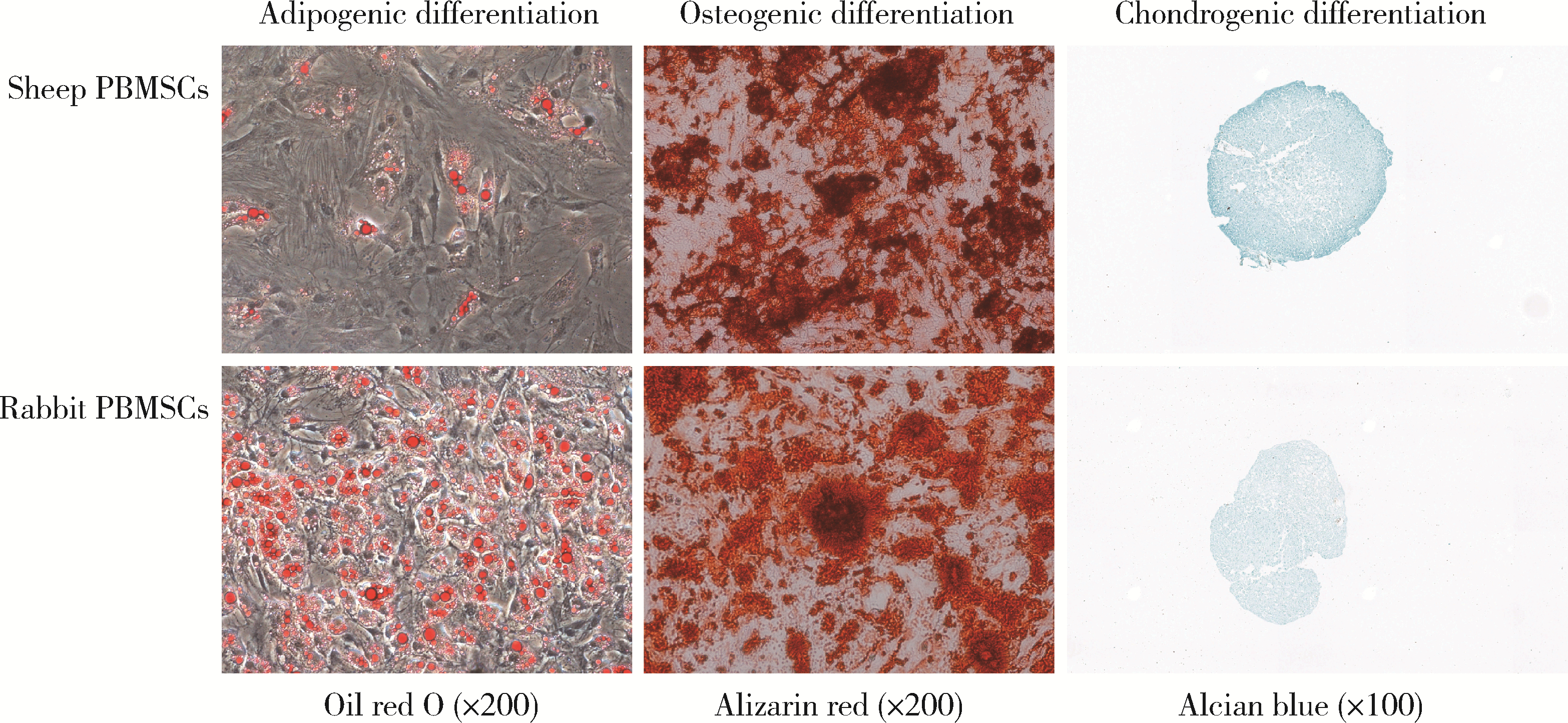
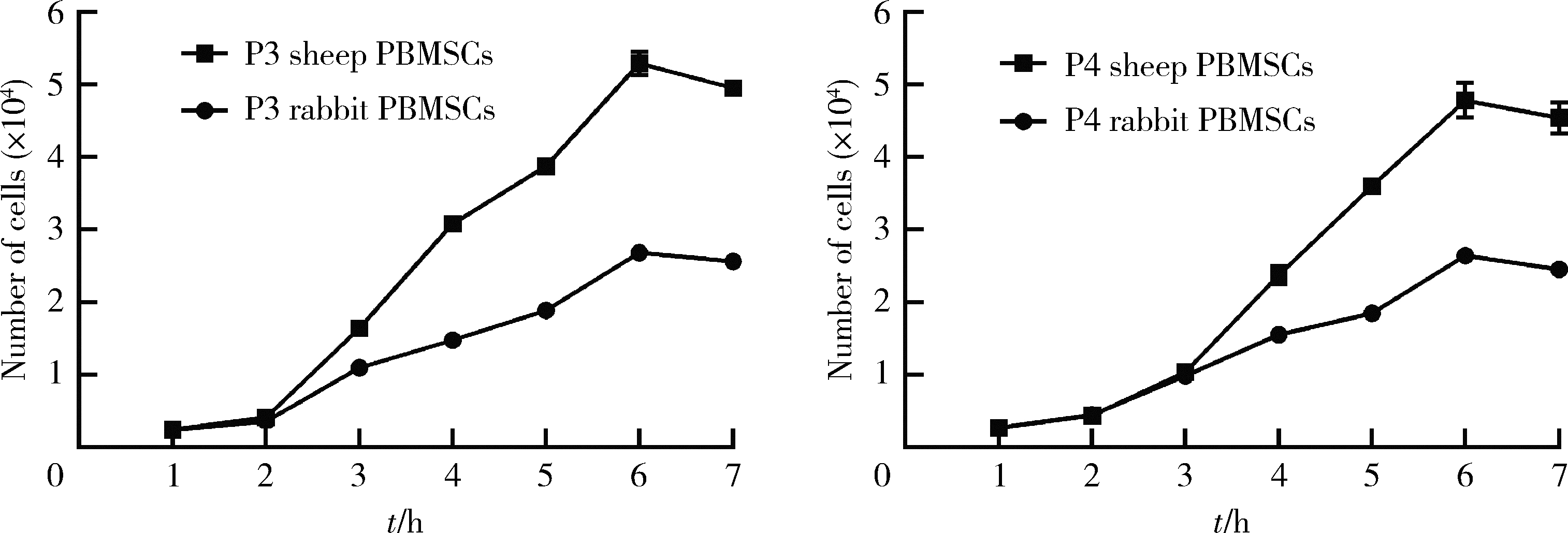
目的: 用粒细胞集落刺激因子(granulocyte colony-stimulating factor,G-CSF)连续动员法获取绵羊与兔外周血间充质干细胞(peripheral blood mesenchymal stem cells,PBMSCs),通过比较两种来源PBMSCs的获取成功率、细胞产量及生物学特性的差异,为PBMSCs移植修复关节软骨损伤及软骨组织工程的临床前研究提供实验依据。方法: 经G-CSF连续动员获取绵羊与兔外周血单核细胞,通过形态学特征、流式法分析其表面标记、体外定向诱导两种细胞三系分化(即:成脂分化、成骨分化、成软骨分化),确证获取的细胞为PBMSCs。统计并比较两种PBMSCs的集落形成单位(colony-forming units, CFUs)、获取成功率,用血细胞计数板统计并比较两种第2代PBMSCs的产量,用细胞增殖-毒性检测试剂盒检测两种PBMSCs倍增时间,用图像处理法定量分析三系分化结果。结果: 镜下见梭形绵羊和兔PBMSCs呈鱼群状排列,第2代绵羊与兔PBMSCs表达CD44、CD90,不表达CD34、CD45,三系分化结果良好。原代绵羊与兔PBMSCs的CFUs(个)分别为7.27±1.56、5.73±1.62,绵羊与兔PBMSCs的获取成功率分别为78.57%、36.67%,每毫升外周血可获取的第2代绵羊与兔PBMSCs数(个)分别为29 582±2 138、26 732±2 286,第3代绵羊与兔PBMSCs的细胞倍增时间(h)分别为22.32±0.28、33.21±0.64,第4代绵羊与兔PBMSCs的细胞倍增时间(h)分别为23.62±0.56、35.30±0.38,绵羊与兔PBMSCs量化成脂比分别为7.77%±3.81%、17.05%±1.52%,绵羊与兔PBMSCs软骨球酸性粘多糖阳性比分别为11.67%±0.53%、8.14%±0.57%,以上各组间比较差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。结论: 经G-CSF连续动员获取绵羊PBMSCs更高效,绵羊PBMSCs产量更丰富、增殖能力更强,在适当环境下能产生更多酸性粘多糖,且成脂能力更低,在自体干细胞移植修复关节软骨损伤及软骨组织工程的临床前动物在体实验中具有良好的研究前景,并为该类研究进一步提供实验依据。
中图分类号:
- R34
| 1 |
Luz-Crawford P , Hernandez J , Djouad F , et al. Mesenchymal stem cell repression of Th17 cells is triggered by mitochondrial transfer[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2019, 10 (1): 232.
doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1307-9 |
| 2 |
Shahror RA , Ali AAA , Wu CC , et al. Enhanced homing of mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing fibroblast growth factor 21 to injury site in a mouse model of traumatic brain injury[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20 (11): e2624.
doi: 10.3390/ijms20112624 |
| 3 |
de Windt TS , Vonk LA , Slaper-Cortenbach I , et al. Allogeneic MSCs and recycled autologous chondrons mixed in a one-stage cartilage cell transplantion: a first-in-man trial in 35 patients[J]. Stem Cells, 2017, 35 (8): 1984- 1993.
doi: 10.1002/stem.2657 |
| 4 |
Al-Najar M , Khalil H , Al-Ajlouni J , et al. Intra-articular injection of expanded autologous bone marrow mesenchymal cells in moderate and severe knee osteoarthritis is safe: a phase Ⅰ/Ⅱ study[J]. J Orthop Surg Res, 2017, 12 (1): 190.
doi: 10.1186/s13018-017-0689-6 |
| 5 |
Park YB , Ha CW , Lee CH , et al. Restoration of a large osteochondral defect of the knee using a composite of umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells and hyaluronic acid hydrogel: A case report with a 5-year follow-up[J]. BMC Musculoske-let Disord, 2017, 18 (1): 59.
doi: 10.1186/s12891-017-1422-7 |
| 6 |
Gobbi A , Whyte GP . One-stage cartilage repair using a hyaluronic acid-based scaffold with activated bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells compared with microfracture: Five-year follow-up[J]. Am J Sports Med, 2016, 44 (11): 2846- 2854.
doi: 10.1177/0363546516656179 |
| 7 | Chen XB , Wang L , Hou JY , et al. Study on the dynamic biological characteristics of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell senescence[J]. Stem Cells Int, 2019, 2019, 9271595. |
| 8 |
Hu PF , Pu YB , Li XY , et al. Isolation, in vitro culture and identification of a new type of mesenchymal stem cell derived from fetal bovine lung tissues[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2015, 12 (3): 3331- 3338.
doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3854 |
| 9 | Zheng PF , Hu XY , Lou Y , et al. A rabbit model of osteochondral regeneration using three-dimensional printed polycaprolactone-hydroxyapatite scaffolds coated with umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells and chondrocytes[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2019, 25, 7361- 7369. |
| 10 |
Zhan XS , El-Ashram S , Luo DZ , et al. A comparative study of biological characteristics and transcriptome profiles of mesenchymal stem cells from different canine tissues[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20 (6): e1485.
doi: 10.3390/ijms20061485 |
| 11 |
Lee Y , Chan Y , Hsieh S , et al. Comparing the osteogenic potentials and bone regeneration capacities of bone marrow and dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells in a rabbit calvarial bone defect mo-del[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20 (20): e5015.
doi: 10.3390/ijms20205015 |
| 12 |
Bharti D , Shivakumar SB , Park JK , et al. Comparative analysis of human Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells derived from different parts of the same umbilical cord[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 2018, 372 (1): 51- 65.
doi: 10.1007/s00441-017-2699-4 |
| 13 |
Heo JS , Choi Y , Kim HS , et al. Comparison of molecular profiles of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, placenta and adipose tissue[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2016, 37 (1): 115- 125.
doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2413 |
| 14 |
Li ZL , Liu CX , Xie ZH , et al. Epigenetic dysregulation in mesenchymal stem cell aging and spontaneous differentiation[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6 (6): e20526.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020526 |
| 15 |
Zhu XS , He BX , Zhou XN , et al. Comparison of the effects of human adipose and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on T lymphocytes[J]. Cell Biol Int, 2013, 37 (1): 11- 18.
doi: 10.1002/cbin.10002 |
| 16 |
Fu WL , Zhou CY , Yu JK . A new source of mesenchymal stem cells for articular cartilage repair: MSCs derived from mobilized peripheral blood share similar biological characteristics in vitro and chondrogenesis in vivo as MSCs from bone marrow in a rabbit model[J]. Am J Sports Med, 2014, 42 (3): 592- 601.
doi: 10.1177/0363546513512778 |
| 17 |
Wang SJ , Yin MH , Jiang DH , et al. The chondrogenic potential of progenitor cells derived from peripheral blood: A systematic review[J]. Stem Cells Dev, 2016, 25 (16): 1195- 1207.
doi: 10.1089/scd.2016.0055 |
| 18 |
Sasaki T , Akagi R , Akatsu Y , et al. The effect of systemic administration of G-CSF on a full-thickness cartilage defect in a rabbit model MSC proliferation as presumed mechanism: G-CSF for cartilage repair[J]. Bone Joint Res, 2017, 6 (3): 123- 131.
doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.63.BJR-2016-0083 |
| 19 |
Delgaudine M , Lambermont B , Lancellotti P , et al. Effects of granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor on progenitor cell mobilization and heart perfusion and function in normal mice[J]. Cytotherapy, 2011, 13 (2): 237- 247.
doi: 10.3109/14653249.2010.491820 |
| 20 |
Fu QH , Tang NN , Zhang QN , et al. Preclinical study of cell therapy for osteonecrosis of the femoral head with allogenic peri-pheral blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Yonsei Med J, 2016, 57 (4): 1006- 1015.
doi: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.4.1006 |
| 21 |
Music E , Futrega K , Doran MR . Sheep as a model for evaluating mesenchymal stem/stromal cell (MSC)-based chondral defect repair[J]. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 2018, 26 (6): 730- 740.
doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2018.03.006 |
| 22 |
Landa-Solis C , Granados-Montiel J , Olivos-Meza A , et al. Cryopreserved CD90+cells obtained from mobilized peripheral blood in sheep: A new source of mesenchymal stem cells for preclinical applications[J]. Cell Tissue Bank, 2016, 17 (1): 137- 145.
doi: 10.1007/s10561-015-9526-5 |
| 23 |
Martínez-Lorenzo MJ , Royo-Cañas M , Alegre-Aguarón E , et al. Phenotype and chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal cells from adipose tissue of different species[J]. J Orthop Res, 2009, 27 (11): 1499- 1507.
doi: 10.1002/jor.20898 |
| 24 |
Dhar M , Neilsen N , Beatty K , et al. Equine peripheral blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Isolation, identification, trilineage differentiation and effect of hyperbaric oxygen treatment[J]. Equine Vet J, 2012, 44 (5): 600- 605.
doi: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.2011.00536.x |
| 25 | 孙良, 栾保华, 李中华, 等. 兔外周血间充质干细胞的体外分离培养及诱导成骨[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009, 13 (27): 5291- 5295. |
| 26 |
Liu LZ , Yu Q , Lin J , et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha is essential for hypoxia-induced mesenchymal stem cell mobilization into the peripheral blood[J]. Stem Cells Dev, 2011, 20 (11): 1961- 1971.
doi: 10.1089/scd.2010.0453 |
| 27 |
Salazar TE , Richardson MR , Beli E , et al. Electroacupuncture promotes central nervous system-dependent release of mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Stem cells (Dayton, Ohio), 2017, 35 (5): 1303- 1315.
doi: 10.1002/stem.2613 |
| 28 |
张继英, 刘刚, 马栋, 等. Sprague-Dawley大鼠外周血来源间充质干细胞的动员、分离培养及鉴定[J]. 中国运动医学杂志, 2012, 31 (9): 811- 816.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6710.2012.09.010 |
| 29 |
Ri M , Matsue K , Sunami K , et al. Effcacy and safety of plerixafor for the mobilization collection of peripheral hematopoietic stem cells for autologous transplantation in Japanese patients with multiple myeloma[J]. Int J Hematol, 2017, 106 (4): 562- 572.
doi: 10.1007/s12185-017-2255-8 |
| 30 | 刘岐焕, 陈龙, 程范军, 等. 鼠尾胶在小鼠外周血间充质干细胞分离培养中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008, 12 (21): 4017- 4020. |
| 31 | 王东来, 冯建刚. 干细胞因子和粒细胞集落刺激因子联合动员小鼠外周血培养间充质干细胞的生物学特性[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008, 12 (16): 3105- 3109. |
| 32 | Daems R , van Hecke L , Schwarzkopf I , et al. A feasibility study on the use of equine chondrogenic induced mesenchymal stem cells as a treatment for natural occurring osteoarthritis in dogs[J]. Stem Cells Int, 2019, 2019, 4587594. |
| [1] | 杨渝平,孔思敏,邓佳良,蒋艳芳,敖英芳. 休闲滑雪者和滑雪运动员急性运动损伤的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 838-842. |
| [2] | 王新宇,崔哲,和清源,邓湘宁,郭歌,冯新恒,冯杰莉. 斑点追踪技术评价中国优秀男子举重运动员心脏的改变[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 832-837. |
|
||