北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (6): 1141-1150. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.06.014
高血糖诱导肝星状细胞5-羟色胺降解在2型糖尿病致肝脏炎症和纤维化时的作用
梁秀睿1,闪雪纯1,关晶1,张锐1,杨静1,张怡1,金佳琦1,张誉馨1,徐凡1,傅继华2,*( )
)
- 1. 中国药科大学基础医学与临床药学学院,南京 210009
2. 中国药科大学基础医学与临床药学学院生理系,南京 210009
Role of hyperglycemia-induced 5-hydroxytryptamine degradation of hepatic stellate cells in hepatic inflammation and fibrosis induced by type 2 diabetes mellitus
Xiu-rui LIANG1,Xue-chun SHAN1,Jing GUAN1,Rui ZHANG1,Jing YANG1,Yi ZHANG1,Jia-qi JIN1,Yu-xin ZHANG1,Fan XU1,Ji-hua FU2,*( )
)
- 1. College of Basic Medicine and Clinical Pharmacy, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing 210009, China
2. Department of Physiology, College of Basic Medicine and Clinical Pharmacy, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing 210009, China
摘要:
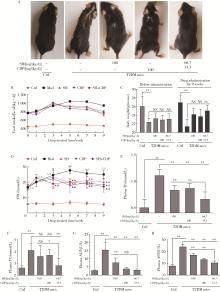
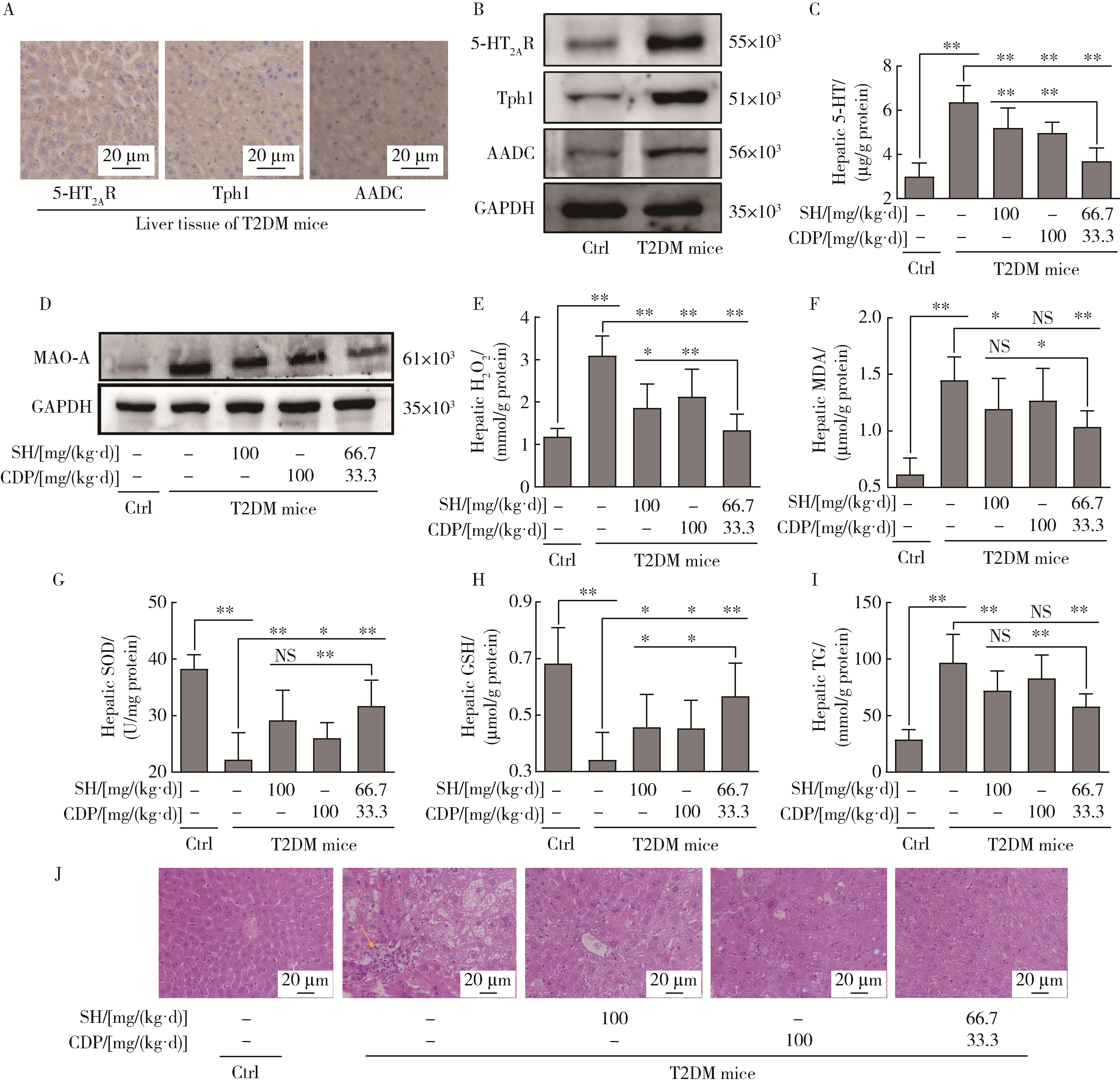
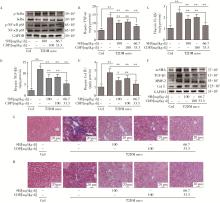
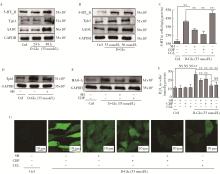
目的: 探讨5-羟色胺(5-hydroxytryptamine,5-HT)在2型糖尿病(type 2 diabetes mellitus,T2DM)引起肝脏炎症及纤维化时的作用。方法: 雄性C57BL/6J小鼠,通过高脂饲料喂养结合腹腔注射链脲佐菌素,建立T2DM模型;将已形成高血糖的小鼠继续用高脂饲料喂养9周或同时用5-HT2A受体(5-HT 2A receptor,5-HT2AR)拮抗剂盐酸沙格雷酯(sarpogrelate hydrochloride,SH)及5-HT合成抑制剂卡比多巴(carbidopa,CDP)分别或联合给药进行治疗。细胞实验用人肝星状细胞(hepatic stellate cells,HSCs)株LX-2,高浓度葡萄糖刺激或同时用SH、CDP或单胺氧化酶A(monoamine oxidase A,MAO-A)抑制剂氯吉兰(clorgyline,CGL)处理细胞,观察高糖诱导LX-2细胞肌成纤维细胞化时5-HT的作用。用苏木精-伊红(hematoxylin & eosin,HE)及马松(Masson)染色法检测肝组织切片病理变化,免疫组织化学及Western blot分析蛋白表达,ELISA或酶试剂法检测生化指标,荧光探针法检测细胞内活性氧(reactive oxygen species,ROS)含量。结果: T2DM小鼠肝脏的5-HT2AR、5-HT合成酶和MAO-A表达上调,且5-HT含量升高。SH和CDP治疗在降低肝脏5-HT含量及下调MAO-A表达的同时,可有效地改善肝脏病变:不仅改善肝功能及肝脂肪变性,还明显抑制肝脏ROS(H2O2)含量升高,改善氧化应激,并抑制转化生长因子β1(transforming growth factor β1,TGF-β1)的产生,以及炎症和纤维化的发生,且SH和CDP的作用呈协同效应。LX-2细胞研究表明,高糖可上调5-HT2AR、5-HT合成酶和MAO-A表达,升高细胞内5-HT含量,使细胞的ROS产生增多及肌成纤维细胞化,从而增加TGF-β1合成及炎症和纤维化因子的产生。通过SH拮抗5-HT2AR,高糖作用被明显抑制;通过CGL抑制线粒体5-HT降解,高糖作用被强烈抑制。SH还可抑制高糖诱导的5-HT合成酶及MAO-A表达上调。结论: 高糖诱导HSCs肌成纤维细胞化和TGF-β1产生,从而导致T2DM小鼠肝脏炎症及纤维化损伤,其病理机制可能是诱导了5-HT2AR表达上调,5-HT合成及降解增加,使线粒体的ROS产生增多,其中,5-HT2AR的作用是参与了对5-HT合成酶和MAO-A表达的调控。
中图分类号:
- R363
| 1 |
Younossi ZM , Golabi P , de Avila L , et al. The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Hepatol, 2019, 71 (4): 793- 801.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.06.021 |
| 2 | Ban CR , Twigg SM . Fibrosis in diabetes complications: Pathoge-nic mechanisms and circulating and urinary markers[J]. Vasc Health Risk Manag, 2008, 4 (3): 575- 596. |
| 3 |
Gaspar P , Cases O , Maroteaux L . The developmental role of serotonin: News from mouse molecular genetics[J]. Nat Rev Neuro-sci, 2003, 4 (12): 1002- 1012.
doi: 10.1038/nrn1256 |
| 4 | Murphy DL , Lesch KP . Targeting the murine serotonin transporter: Insights into human neurobiology[J]. Nat Rev Neurosci, 2008, 9 (2): 85- 96. |
| 5 |
Keszthelyi D , Troost FJ , Masclee AAM . Understanding the role of tryptophan and serotonin metabolism in gastrointestinal function[J]. Neurogastroenterol Motil, 2009, 21 (12): 1239- 1249.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2009.01370.x |
| 6 |
Nickel AG , von Hardenberg A , Hohl M , et al. Reversal of mitochondrial transhydrogenase causes oxidative stress in heart failure[J]. Cell Metab, 2015, 22 (3): 472- 484.
doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.07.008 |
| 7 | Boess FG , Martin IL . Molecular biology of 5-HT receptors[J]. Neuropharmacology, 1994, 33 (3/4): 275- 317. |
| 8 |
Tsuchida T , Lee YA , Fujiwara N , et al. A simple diet- and chemical-induced murine NASH model with rapid progression of steatohepatitis, fibrosis and liver cancer[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 69 (2): 385- 395.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.03.011 |
| 9 |
Nocito A , Dahm F , Jochum W , et al. Serotonin mediates oxidative stress and mitochondrial toxicity in a murine model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2007, 133 (2): 608- 618.
doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.05.019 |
| 10 |
Knockaert L , Berson A , Ribault C , et al. Carbon tetrachloride-mediated lipid peroxidation induces early mitochondrial alterations in mouse liver[J]. Lab Invest, 2012, 92 (3): 396- 410.
doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2011.193 |
| 11 |
Kim DC , Jun DW , Kwon YI , et al. 5-HT2A receptor antagonists inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation and facilitate apoptosis[J]. Liver Int, 2013, 33 (4): 535- 543.
doi: 10.1111/liv.12110 |
| 12 |
Fu JH , Li C , Zhang GL , et al. Crucial roles of 5-HT and 5-HT2 receptor in diabetes-related lipid accumulation and pro-inflammatory cytokine generation in hepatocytes[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 48 (6): 2409- 2428.
doi: 10.1159/000492656 |
| 13 |
Fu JH , Ma SX , Li X , et al. Long-term stress with hyperglucocorticoidemia-induced hepatic steatosis with VLDL overproduction is dependent on both 5-HT2 receptor and 5-HT synthesis in liver[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2016, 12 (2): 219- 234.
doi: 10.7150/ijbs.13062 |
| 14 |
Ma SX , Li T , Guo KK , et al. Effective treatment with combination of peripheral 5-hydroxytryptamine synthetic inhibitor and 5-hydroxytryptamine 2 receptor antagonist on glucocorticoid-induced whole-body insulin resistance with hyperglycemia[J]. J Diabetes Investig, 2016, 7 (6): 833- 844.
doi: 10.1111/jdi.12526 |
| 15 | Li X , Guo KK , Li T , et al. 5-HT 2 receptor mediates high-fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis and very low density lipoprotein overproduction in rats[J]. Obes Res Clin Pract, 2018, 12 (Suppl 2): 16- 28. |
| 16 |
Zhang YX , Li C , Liang XR , et al. Role of 5-HT degradation in acute liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2021, 908, 174355.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174355 |
| 17 |
Zhang YX , Liang XR , Guan J , et al. Carbon tetrachloride induced mitochondrial division, respiratory chain damage, abnormal intracellular [H+] and apoptosis are due to the activation of 5-HT degradation system in hepatocytes[J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2022, 439, 115929.
doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2022.115929 |
| 18 | Schuppan D , Pinzani M . Anti-fibrotic therapy: Lost in translation?[J]. J Hepatol, 2012, 56 (Suppl 1): S66- S74. |
| 19 |
Park SY , Shin HW , Lee KB , et al. Differential expression of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in thioacetamide-induced chronic liver injury[J]. J Korean Med Sci, 2010, 25 (4): 570- 576.
doi: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.4.570 |
| 20 |
Zhang CY , Yuan WG , He P , et al. Liver fibrosis and hepatic stellate cells: Etiology, pathological hallmarks and therapeutic targets[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2016, 22 (48): 10512- 10522.
doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i48.10512 |
| 21 |
Weiskirchen R , Tacke F . Liver Fibrosis: From pathogenesis to novel therapies[J]. Dig Dis, 2016, 34 (4): 410- 422.
doi: 10.1159/000444556 |
| 22 |
Mitchell C , Couton D , Couty JP , et al. Dual role of CCR2 in the constitution and the resolution of liver fibrosis in mice[J]. Am J Pathol, 2009, 174 (5): 1766- 1775.
doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.080632 |
| 23 |
Sugimoto R , Enjoji M , Kohjima M , et al. High glucose stimulates hepatic stellate cells to proliferate and to produce collagen through free radical production and activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase[J]. Liver Int, 2005, 25 (5): 1018- 1026.
doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2005.01130.x |
| 24 |
Shih JC , Chen K , Ridd MJ . Monoamine oxidase: from genes to behavior[J]. Annu Rev Neurosci, 1999, 22, 197- 217.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.22.1.197 |
| 25 |
Farzanegi P , Dana A , Ebrahimpoor Z , et al. Mechanisms of beneficial effects of exercise training on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Roles of oxidative stress and inflammation[J]. Eur J Sport Sci, 2019, 19 (7): 994- 1003.
doi: 10.1080/17461391.2019.1571114 |
| 26 |
Ruddell RG , Mann DA , Ramm GA . The function of serotonin within the liver[J]. J Hepatol, 2008, 48 (4): 666- 675.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2008.01.006 |
| 27 | Papadimas GK , Tzirogiannis KN , Mykoniatis MG , et al. The emerging role of serotonin in liver regeneration[J]. Swiss Med Wkly, 2012, 142, w13548. |
| 28 |
Choi W , Namkung J , Hwang I , et al. Serotonin signals through a gut-liver axis to regulate hepatic steatosis[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9 (1): 4824.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07287-7 |
| [1] | 马会超,李军,王永清. 妊娠合并炎症性肠病的临床特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 260-266. |
| [2] | 俞光岩. 儿童唾液腺疾病[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 1-3. |
| [3] | 殳畅,韩烨,孙雨哲,杨再目,侯建霞. Ⅲ期牙周炎患者牙周基础治疗前后炎症性贫血相关指标的变化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 45-50. |
| [4] | 赵祥格,刘佳庆,黄会娜,陆智敏,白自然,李霞,祁荆荆. 干扰素-α介导系统性红斑狼疮外周血CD56dimCD57+自然杀伤细胞功能的损伤[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 975-981. |
| [5] | 王磊,金香淑,董慧君,欧国敏,赖鑫源,庄辉,李彤,向宽辉. 基于COL1A1启动子和增强型绿色荧光蛋白基因建立人肝星状细胞活化的细胞模型[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 876-885. |
| [6] | 贺冰洁,刘志科,沈鹏,孙烨祥,陈彬,詹思延,林鸿波. 2011—2020年宁波市鄞州区炎症性肠病发病的流行病学研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 511-519. |
| [7] | 郭辅政,赵秀娟,邓玖旭,杜哲,王天兵,朱凤雪. 严重创伤患者早期外周血淋巴细胞变化与预后之间的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 552-556. |
| [8] | 王向熙,李臻臻,赖彦云,杨莉,史霖丽,仲少敏,吴艳. 585 nm Q开关激光治疗痤疮炎症性皮损和炎症后红斑的疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 283-288. |
| [9] | 伊文霞,魏翠洁,吴晔,包新华,熊晖,常杏芝. 长疗程利妥昔单抗治疗难治性幼年型特发性炎症性肌病3例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1191-1195. |
| [10] | 陈怀安,刘硕,李秀君,王哲,张潮,李凤岐,苗文隆. 炎症生物标志物对输尿管尿路上皮癌患者预后预测的临床价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 302-307. |
| [11] | 杨林承,张瑞涛,郭丽君,肖晗,祖凌云,张幼怡,程秦,赵志伶,葛庆岗,高炜. 低氧状态及炎症反应是新型冠状病毒肺炎患者发生急性心肌损伤的危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 159-166. |
| [12] | 胡永玮,刘蕊,罗莉. 慢性多灶性骨髓炎1例及文献回顾[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 1140-1145. |
| [13] | 轩艳,蔡宇,王啸轩,石巧,邱立新,栾庆先. 牙龈卟啉单胞菌感染对载脂蛋白e基因敲除小鼠动脉粥样硬化的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 743-749. |
| [14] | 李军,牛占岳,薛艳,石雪迎,张波,王媛. 重度溃疡性结肠炎合并卡波西肉瘤1例并文献综述[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(2): 373-377. |
| [15] | 王平,宋婧,方翔宇,李鑫,刘栩,贾园,栗占国,胡凡磊. 成红细胞样Ter细胞在胶原诱导性关节炎发病中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(3): 445-450. |
|
||