北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (6): 1158-1162. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.06.016
肌萎缩侧索硬化患者认知功能改变与脑皮层厚度分析
叶珊1,2,金萍萍1,2,张楠1,2,邬海博3,石林4,5,赵强3,杨坤3,袁慧书3,樊东升1,2,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学第三医院神经内科,北京 100191
2. 神经退行性疾病生物标志物研究及转化北京市重点实验室,北京 100191
3. 北京大学第三医院放射科,北京 100191
4. 香港中文大学威尔斯亲王医院影像及介入放射学系,中国香港特别行政区 000852
5. 深圳博脑研究院,广东深圳 518000
Cortical thickness and cognitive impairment in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Shan YE1,2,Ping-ping JIN1,2,Nan ZHANG1,2,Hai-bo WU3,Lin SHI4,5,Qiang ZHAO3,Kun YANG3,Hui-shu YUAN3,Dong-sheng FAN1,2,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Neurology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Beijing Municipal Key Laboratory of Biomarker and Translational Research in Neurodegenerative Diseases, Beijing 100191, China
3. Department of Radiology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
4. Department of Imaging and Interventional Radiology, Prince of Wales Hospital, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region 000852, China
5. BrainNow Research Institute, Shenzhen 518000, Guangdong, China
摘要:
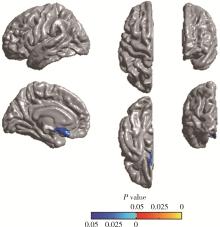
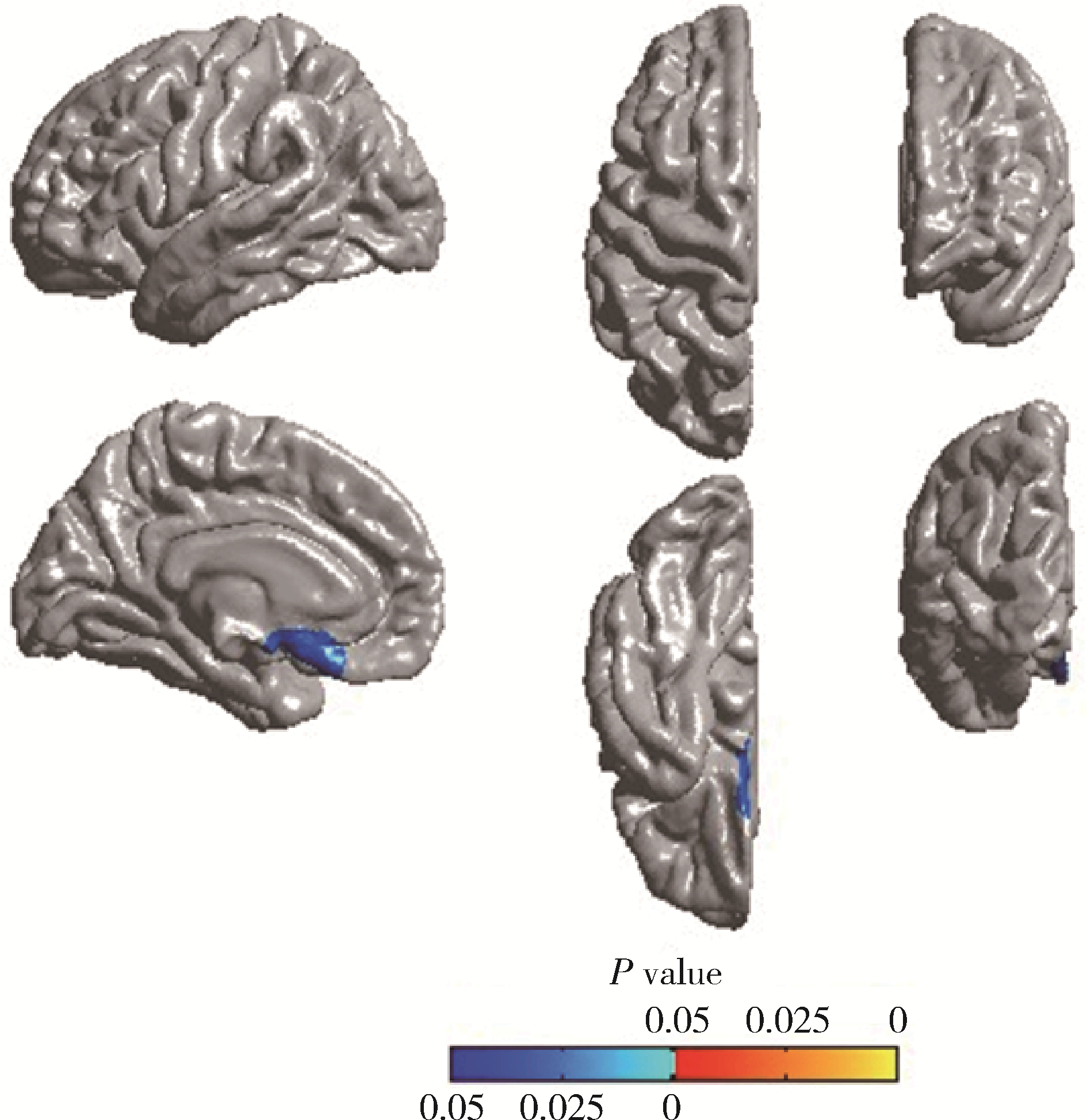
目的: 通过MRI皮层厚度分析法,探讨肌萎缩侧索硬化(amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, ALS)患者脑结构变化,并分析其与认知功能改变的相关性。方法: 纳入ALS患者18例,以及性别、年龄、教育程度匹配的正常对照者18例,对所有研究对象进行3D磁化准备快速递度回波(magnetization prepared rapid gradient echo imaging, MPRAGE)序列MRI扫描,进行皮层厚度分析,同时对所有ALS患者进行神经心理学测评,包括简易精神状态检查(mini-mental state examination,MMSE)、言语流畅性试验、Stroop色词试验、前瞻性记忆、情绪图片感知及再认、失言识别测验。结果: 经过认知评估,2例ALS患者存在认知功能障碍。比较18例ALS患者和18例正常对照的顶点水平全脑皮层厚度,ALS组左侧大脑半球内侧眶额叶后部、颞叶内侧皮层厚度明显减低(P < 0.05);区域水平比较,ALS组左内嗅区、左颞下回、左内侧眶额叶、左岛叶皮层厚度明显减低(P < 0.05)。认知功能正常的16例ALS患者与正常对照相比较,两组间顶点水平和区域水平的皮层厚度差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。前瞻性记忆、情绪图片感知及再认、失言识别测验评分与对应脑区皮层厚度值存在相关性(P < 0.05)。结论: ALS患者皮层厚度与神经心理学检查具有相关性,可能反映认知测评所对应的脑区皮层结构改变,可能为ALS患者认知改变的早期诊断提供帮助。
中图分类号:
- R744.8
| 1 | Strong M , Abrahams S , Goldstein L , et al. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-frontotemporal spectrum disorder (ALS-FTSD): Revised diagnostic criteria[J]. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener, 2017, 18 (3/4): 153- 174. |
| 2 | Hanstock C , Sun K , Choi C , et al. Spectroscopic markers of neurodegeneration in the mesial prefrontal cortex predict survival in ALS[J]. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener, 2020, 21 (3/4): 246- 251. |
| 3 |
Trojsi F , Nardo F , Siciliano M , et al. Frontotemporal degeneration in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS): A longitudinal MRI one-year study[J]. CNS Spectr, 2021, 26 (3): 258- 267.
doi: 10.1017/S109285292000005X |
| 4 |
Hu T , Hou Y , Wei Q , et al. Patterns of brain regional functional coherence in cognitive impaired ALS[J]. Int J Neurosci, 2020, 130 (8): 751- 758.
doi: 10.1080/00207454.2019.1705806 |
| 5 |
Brooks BR , Miller RG , Swash M , et al. El Escorial revisited: Revised criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis[J]. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord, 2000, 1 (5): 293- 299.
doi: 10.1080/146608200300079536 |
| 6 |
Desikan RS , Segonne F , Fischl B , et al. An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest[J]. Neuroimage, 2006, 31 (3): 968- 980.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.01.021 |
| 7 |
Chiara C , Alessandra D , Stefano FC , et al. Multimodal MRI quantification of the common neurostructural bases within the FTD-ALS continuum[J]. Neurobiol Aging, 2018, 62, 95- 104.
doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.09.019 |
| 8 | Verstraete E , Veldink JH , Hendrikse J , et al. Structural MRI reveals cortical thinning in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis[J]. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 2011, 83 (4): 383- 388. |
| 9 |
Bergmann M . Motor neuron disease/amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Lessons from ubiquitin[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 1993, 189 (8): 902- 912.
doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(11)81102-7 |
| 10 | Shen D , Hou B , Cui B , et al. Comparing brain structural and perfusion MRI changes across ALS-FTD continuum[J]. Clin Neurophysiol, 2018, 129, e162. |
| 11 |
Labar KS , Cabeza R . Cognitive neuroscience of emotional memory[J]. Nat Rev Neurosci, 2006, 7 (1): 54- 64.
doi: 10.1038/nrn1825 |
| 12 | Dolcos F , Labar KS , Cabeza R . Dissociable effects of arousal and valence on prefrontal activity indexing emotional evaluation and subsequent memory: An event-related fMRI study[J]. Neuro-image, 2004, 23 (1): 64- 74. |
| 13 |
Lule D , Diekmann V , Anders S , et al. Brain responses to emotional stimuli in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)[J]. J Neurol, 2007, 254 (4): 519- 527.
doi: 10.1007/s00415-006-0409-3 |
| [1] | 邢念增,王明帅,杨飞亚,尹路,韩苏军. 前列腺免活检创新理念的临床实践及其应用前景[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 565-566. |
| [2] | 田宇轩,阮明健,刘毅,李德润,吴静云,沈棋,范宇,金杰. 双参数MRI改良PI-RADS评分4分和5分病灶的最大径对临床有意义前列腺癌的预测效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 567-574. |
| [3] | 李晋娜,许丽娜,李敏,宋怡,张静,贾龙斌. 急性脑梗死患者血清BDNF、IL-18、hs-CRP水平与血管性认知障碍的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 708-714. |
| [4] | 林郁婷,王华丽,田宇,巩俐彤,常春. 北京市老年人认知功能的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 456-461. |
| [5] | 刘毅,袁昌巍,吴静云,沈棋,肖江喜,赵峥,王霄英,李学松,何志嵩,周利群. 靶向穿刺+6针系统穿刺对PI-RADS 5分患者的前列腺癌诊断效能[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 812-817. |
| [6] | 袁昌巍,李德润,李志华,刘毅,山刚志,李学松,周利群. 多参数磁共振成像中动态对比增强状态在诊断PI-RADS 4分前列腺癌中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 838-842. |
| [7] | 鲍雷,蔡夏夏,张明远,任磊磊. 维生素D3对2型糖尿病小鼠轻度认知障碍的改善作用及机制研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 587-592. |
| [8] | 刘颖,霍然,徐慧敏,王筝,王涛,袁慧书. 磁共振血管壁成像评估颈动脉中重度狭窄患者斑块特征与脑血流灌注的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 646-651. |
| [9] | 傅强,高冠英,徐雁,林卓华,孙由静,崔立刚. 无症状髋关节前上盂唇撕裂超声与磁共振检查的对比研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 665-669. |
| [10] | 林浩,李菁华,杨潇,陈晓婷,史宇晖,常春,郝元涛,曹望楠. 中国成都男男性行为人群HIV暴露前预防用药行为-认知偏差现状及其影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 511-520. |
| [11] | 蔡颖,万巧琴,蔡宪杰,高亚娟,韩鸿宾. 光生物调节加速脑组织间液引流及其机制[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 1000-1005. |
| [12] | 金旭,董一丹,陈云赛,赵晟娅,黄文初,何丽华. 潜航员深海潜航任务前后警觉度及工作记忆容量的变化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 581-586. |
| [13] | 王书磊,高阳旭,张宏武,杨海波,李辉,李宇,沈笠雪,姚红新. 儿童基底节区生殖细胞瘤30例临床分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 222-226. |
| [14] | 张帆,陈曲,郝一昌,颜野,刘承,黄毅,马潞林. 术前及术后膜性尿道长度与腹腔镜根治性前列腺切除术后控尿功能恢复的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 299-303. |
| [15] | 吴一凡,张晓圆,任爽,玉应香,常翠青. 基于磁共振的青年男性股四头肌的测量和评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 843-849. |
|
||