北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (1): 139-143. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.01.021
Neuroform Atlas支架辅助弹簧圈栓塞未破裂性颅内宽颈动脉瘤
韩金涛1,张宇翔1,贾子昌1,*( ),姜除寒2,刘恋2,栾景源1,梁飞1,赵彦清1
),姜除寒2,刘恋2,栾景源1,梁飞1,赵彦清1
- 1. 北京大学第三医院介入血管外科,北京 100191
2. 首都医科大学附属北京天坛医院神经外科,北京 100070
Clinical application of Neuroform Atlas stent-assisted coiling in the treatment of unruptured wide-neck intracranial aneurysms
Jin-tao HAN1,Yu-xiang ZHANG1,Zi-chang JIA1,*( ),Chu-han JIANG2,Lian LIU2,Jing-yuan LUAN1,Fei LIANG1,Yan-qing ZHAO1
),Chu-han JIANG2,Lian LIU2,Jing-yuan LUAN1,Fei LIANG1,Yan-qing ZHAO1
- 1. Department of Interventional Radiology and Vascular Surgery, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Neurosurgery, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100070, China
摘要:
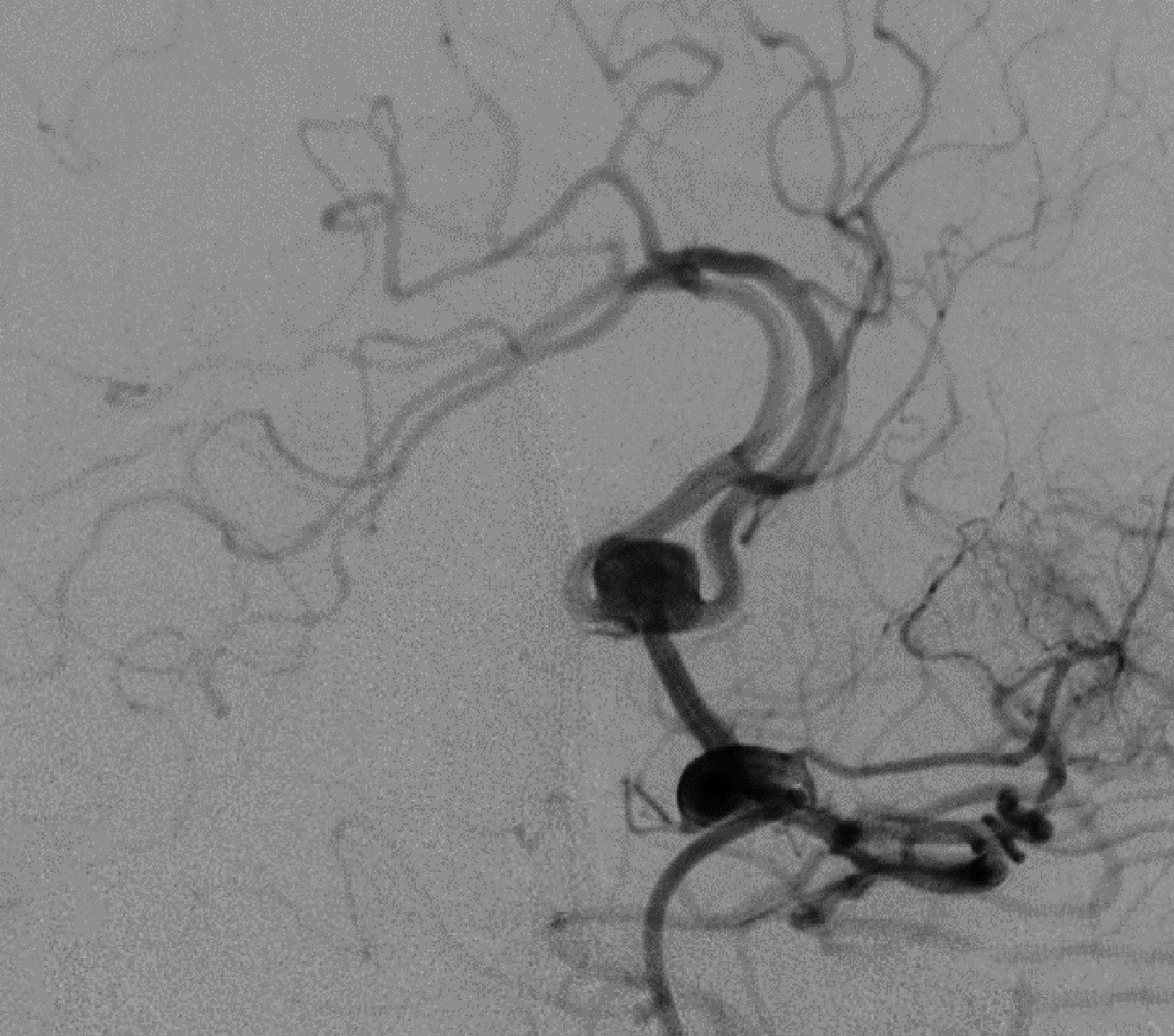
目的: 探讨Neuroform Atlas支架辅助弹簧圈栓塞治疗未破裂性颅内宽颈动脉瘤的安全性和有效性。方法: 回顾性分析2020年8月至2021年9月于北京大学第三医院介入血管外科采用Neuroform Atlas支架辅助弹簧圈栓塞治疗的62例未破裂性颅内宽颈动脉瘤患者的临床资料。62例患者共64个颅内动脉瘤,其中25个位于大脑中动脉M1分叉处,16个位于前交通动脉,10个位于颈内动脉C7段,5个位于颈内动脉C6段,4个位于基底动脉顶端,3个位于大脑前动脉A3段,1个位于大脑中动脉M2段。有49个动脉瘤采取单支架辅助栓塞,其余15个采用双支架技术辅助栓塞(“Y”型14个和“X”型1个)。所有患者术后即刻行数字减影血管造影(digital subtraction angiography,DSA),评估动脉瘤的即刻栓塞效果(Raymond评分)和载瘤动脉血流情况。出院后对患者进行临床随访及影像学随访,临床随访为术后3个月采用改良Rankin评分量表(modified Rankin Scale,mRS)评估患者的临床预后; 影像学随访为术后6个月复查脑血管DSA评估患者动脉瘤闭塞情况(Raymond评分)和载瘤动脉通畅情况。结果: 62例患者手术均获成功,技术成功率为100%。术后即刻DSA显示:57个动脉瘤(89.1%,57/64)完全闭塞(Raymond Ⅰ级),6个动脉瘤(9.3%,6/64)瘤颈残留(Raymond Ⅱ级),1个动脉瘤(1.6%,1/64)瘤体残留(Raymond Ⅲ级)。3例患者(4.8%,3/62)出现围手术期并发症:2例为术中血栓形成,予动脉内替罗非班治疗后血流恢复,1例为术后局限性蛛网膜下腔出血,经保守治疗出院时均无致残性功能障碍。术后3个月时55例患者获临床随访,均预后良好(mRS≤2分),7例患者失访。50例患者(52个动脉瘤)获术后6个月DSA影像随访:Raymond Ⅰ级45个(86.5%,45/52),Raymond Ⅱ级4个(7.7%,4/52),Raymond Ⅲ级3个(5.8%,3/52),12例患者失访。结论: Neuroform Atlas支架辅助弹簧圈栓塞未破裂性颅内宽颈动脉瘤有很高的技术成功率,并具有较低的围手术期并发症发生率和较高的动脉瘤闭塞率,安全性和有效性均较好,但其远期疗效还需进一步随访观察。
中图分类号:
- R654.3
| 1 |
Li MH , Chen SW , Li YD , et al. Prevalence of unruptured cerebral aneurysms in Chinese adults aged 35 to 75 years: Across-sectional study[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2013, 159 (8): 514- 521.
doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-159-8-201310150-00004 |
| 2 |
Wiebers DO , Whisnant JP , Huston J , et al. International Study of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms Investigators. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: Natural history, clinical outcome, and risks of surgical and endovascular treatment[J]. Lancet, 2003, 362 (9378): 103- 110.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13860-3 |
| 3 |
Mokin M , Primiani CT , Ren Z , et al. Stent-assisted coiling of cerebral aneurysms: Multi-center analysis of radiographic and clinical outcomes in 659 patients[J]. J Neurointerv Surg, 2020, 12 (3): 289- 297.
doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2019-015182 |
| 4 |
曾文贤, 李振均, 张剑波, 等. 支架辅助弹簧圈栓塞治疗急性期颅内破裂宽颈动脉瘤的临床分析[J]. 中华神经医学杂志, 2019, 18 (3): 243- 249.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-8925.2019.03.005 |
| 5 | Sato H , Haraguchi K . Comparison of stent-assisted coiling for unruptured internal carotid artery aneurysms between LVIS or LVIS Jr. and enterprise VRD: A retrospective and single-center analysis[J]. Turk Neurosurg, 2021, 31 (3): 379- 384. |
| 6 |
Ghinda D , Dos-Santos MP , Sabri A , et al. Clinical and angiogra-phic outcomes of stent-assisted coiling of intracranial aneurysms[J]. Interv Neuroradiol, 2015, 21 (2): 146- 154.
doi: 10.1177/1591019915582152 |
| 7 |
Hanel RA , Yoon N , Sauvageau E , et al. Neuroform Atlas stent for treatment of middle cerebral artery aneurysms: 1-year outcomes from Neuroform Atlas stent pivotal trial[J]. Neurosurgery, 2021, 89 (1): 102- 108.
doi: 10.1093/neuros/nyab090 |
| 8 |
Jankowitz BT , Jadhav AP , Gross B , et al. Pivotal trial of the Neuroform Atlas stent for treatment of posterior circulation aneurysms: One-year outcomes[J]. J Neurointerv Surg, 2022, 14 (2): 143- 148.
doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2020-017115 |
| 9 | 邵秋季, 李立, 李天晓, 等. Neuroform Atlas支架辅助弹簧圈治疗颅内宽颈动脉瘤的初步应用[J]. 中华神经外科杂志, 2022, 38 (1): 59- 64. |
| 10 |
Cognard C , Pierot L , Anxionnat R , et al. Results of embolization used as the first treatment choice in a consecutive non-selected population of ruptured aneurysms: Clinical results of the Clarity GDC study[J]. Neurosurgery, 2011, 69 (4): 837- 841.
doi: 10.1227/NEU.0b013e3182257b30 |
| 11 | Roh H , Kim J , Bae H , et al. Comparison of stent-assisted and no-stent coil embolization for safety and effectiveness in the treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms[J]. J Neurosurg, 2019, 30, 1- 7. |
| 12 | 中华医学会神经外科学分会神经介入学组. 颅内动脉瘤血管内介入治疗中国专家共识(2013)[J]. 中国脑血管病杂志, 2013, 10 (11): 606- 616. |
| 13 | Khattak YJ , Sibaie AA , Anwar M , et al. Stents and stent mimickers in endovascular management of wide-neck intracranial aneurysms[J]. Cureus, 2018, 10 (10): e3420. |
| 14 | 李淦诚, 张炘, 范海燕, 等. 支架辅助弹簧圈栓塞治疗颅内动脉瘤围手术期并发症的危险因素分析[J]. 中华神经医学杂志, 2019, 18 (2): 136- 143. |
| 15 |
Jankowitz BT , Hanel R , Jadhav AP , et al. Neuroform Atlas stent system for the treatment of intracranial aneurysm: Primary results of the Atlas humanitarian device exemption cohort[J]. J Neurointerv Surg, 2019, 11 (8): 801- 806.
doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2018-014455 |
| 16 |
Lynch J , Sciacca S , Siddiqui J , et al. Safety and efficacy of the Neuroform Atlas stent for treatment of intracranial aneurysms: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Clin Neuroradiol, 2021, 31 (4): 1167- 1180.
doi: 10.1007/s00062-020-00979-y |
| 17 | Kim J , Han HJ , Lee W , et al. Safety and efficacy of stent-assisted coiling of unruptured intracranial aneurysms using low-profile stents in small parent arteries[J]. Am J Neuroradiol, 2021, 42 (9): 1621- 1626. |
| 18 | Lefevre PH , Schramm P , Kemmling A , et al. Multi-centric European post-market follow-up study of the Neuroform Atlas stent system: Primary results[J]. J Neurointerv Surg, 2022, 14 (7): 694- 698. |
| [1] | 庄金满,李天润,李选,栾景源,王昌明,冯琦琛,韩金涛. Rotarex旋切导管在股腘动脉狭窄合并血栓形成中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 328-332. |
| [2] | 李伟浩,李伟,张学民,李清乐,焦洋,张韬,蒋京军,张小明. 去分支杂交手术和传统手术治疗胸腹主动脉瘤的结果比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 177-181. |
| [3] | 庄金满, 李选, 李天润, 傅军, 栾景源, 王昌明. 股腘动脉病变球囊扩张与支架植入的疗效对比研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(1): 160-165. |
| [4] | 卿洪琨, 张学民, 蒋京军, 张小明, 何长顺, 孙占国. 自制髂动脉分支装置治疗腹主动脉瘤腔内修复术后髂动脉瘤1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(5): 888-890. |
|
||