北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (1): 174-180. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.01.027
基于三维下颌骨平均模型的颌骨标志点自动确定方法
高梓翔1,王勇1,2,温奥楠2,朱玉佳2,秦庆钊2,张昀3,王晶4,*( ),赵一姣1,*(
),赵一姣1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学医学部医学技术研究院,北京 100191
2. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院数字化研究中心,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心,口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,国家卫生健康委员会口腔医学计算机应用工程技术研究中心,北京 100081
3. 兰州市口腔医院,兰州 730031
4. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院口腔颌面外科,北京 100081
Automatic determination of mandibular landmarks based on three-dimensional mandibular average model
Zi-xiang GAO1,Yong WANG1,2,Ao-nan WEN2,Yu-jia ZHU2,Qing-zhao QIN2,Yun ZHANG3,Jing WANG4,*( ),Yi-jiao ZHAO1,*(
),Yi-jiao ZHAO1,*( )
)
- 1. Institute of Medical Technology, Peking University Health Science Center, Beijing 100191, China
2. Center of Digital Dentistry, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NHC Research Center of Engineering and Technology for Computerized Dentistry, Beijing 100081, China
3. Lanzhou Stomatological Hospital, Lanzhou 730031, China
4. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
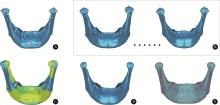
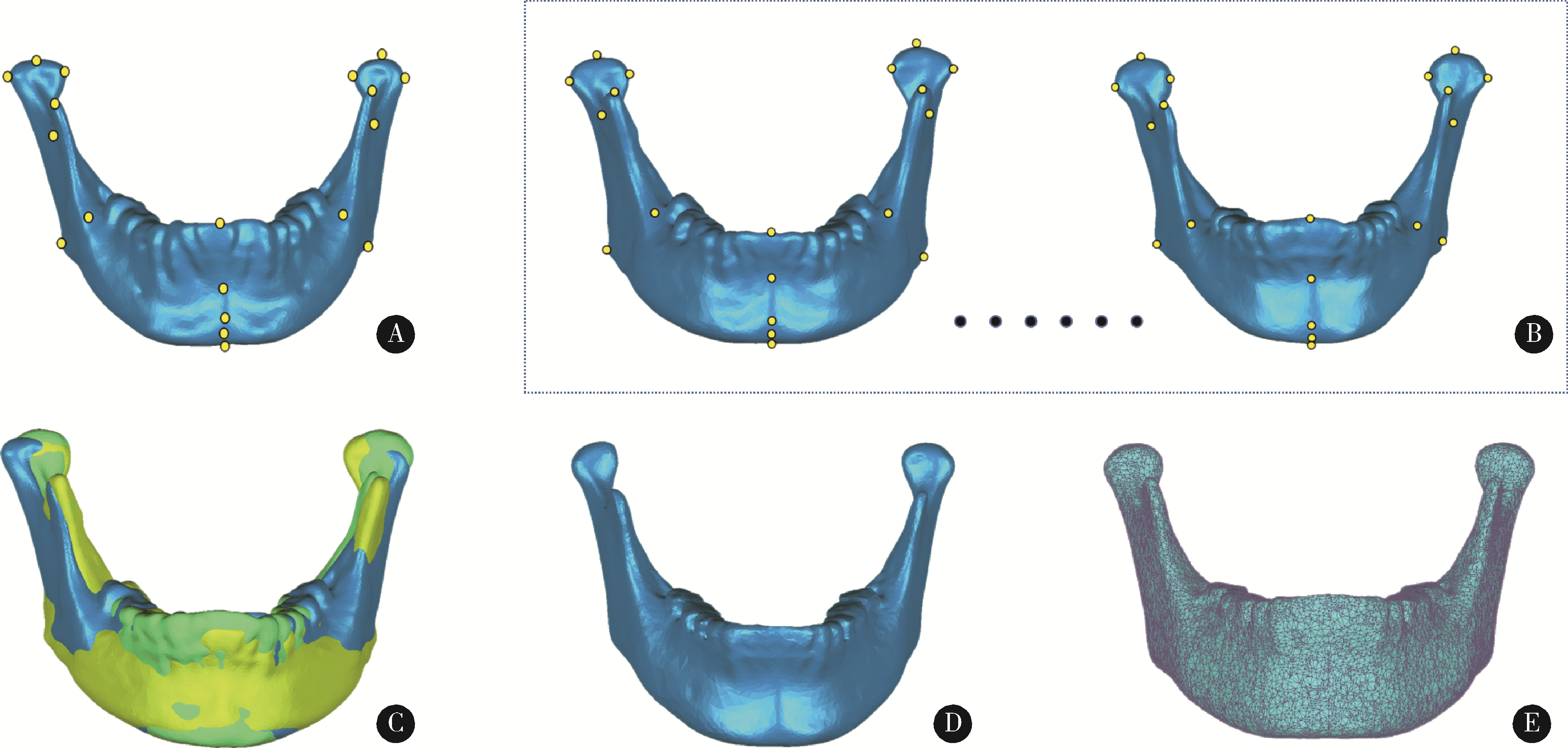
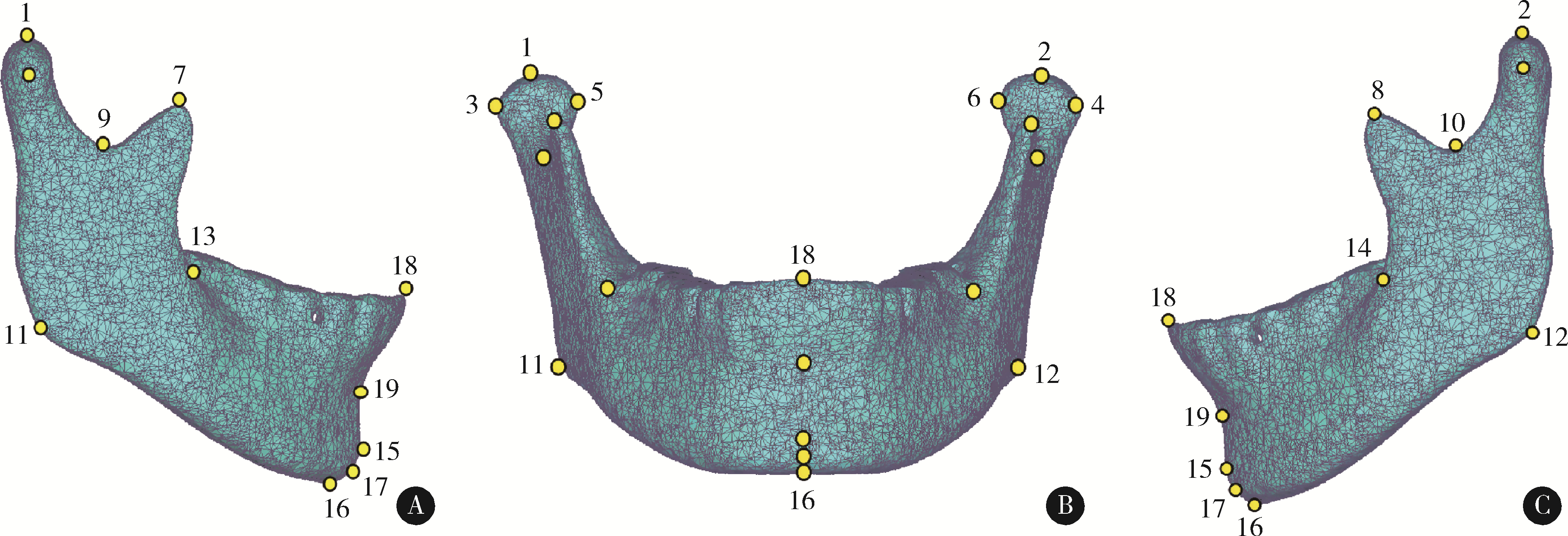
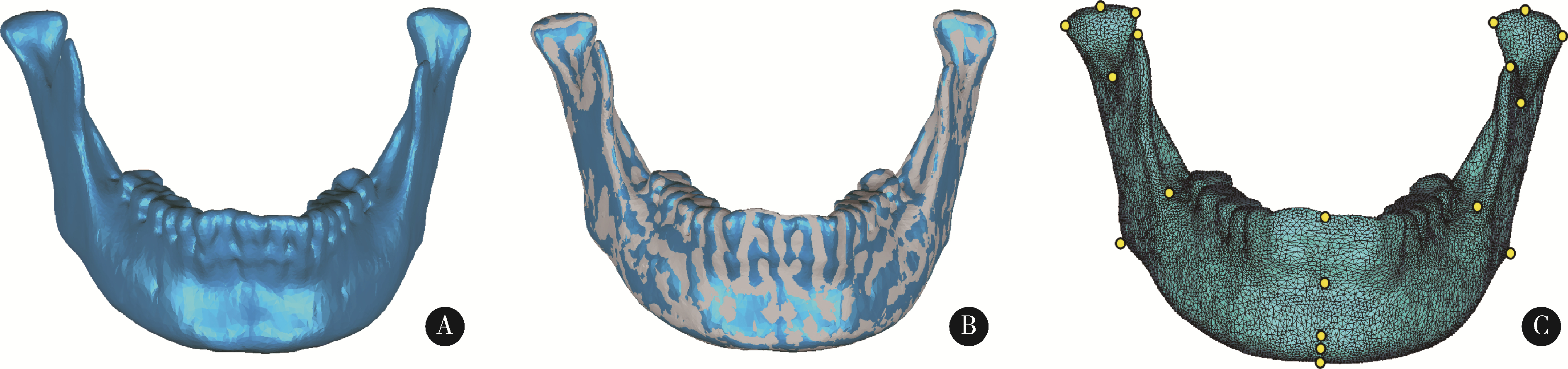
目的: 探索一种高效、自动确定三维下颌骨数据解剖标志点的方法,并对该方法的定点效果进行初步评价。方法: 选取40例颅颌面三维形态正常患者的CT数据(其中30例用来建立三维下颌骨平均模型,10例作为测试本研究方法确定下颌骨标志点效果的测试数据),将数据导入到Mimics软件中进行下颌骨三维重建。在这40例三维重建后的下颌骨数据中,选取与中国人下颌骨特征均值更为接近的30例,在MATLAB软件中基于普氏分析(Procrustes analysis)算法对此30例下颌骨数据进行尺寸归一化处理,并在Geomagic Wrap软件中,构建上述30例下颌骨数据的三维平均形状模型,通过对称化处理、曲率采样、索引标记等过程,构建出具有18 996个类标志点和19个下颌骨解剖标志点索引的三维下颌骨结构化模板。应用开源非刚性配准算法程序Meshmonk,将上述构建的三维下颌骨模板通过非刚性变形与患者三维下颌骨数据进行匹配,获得患者三维下颌骨数据的19个解剖标志点位置。与口腔专家手动标注的标志点位置误差(定点误差)进行比较,评价本方法的准确性。结果: 将本研究方法应用于10例无显著下颌骨形态畸形患者数据,19个标志点的平均定点误差为1.42 mm,其中最小和最大误差分别为喙突顶点[右:(1.01±0.44) mm;左:(0.56±0.14) mm]和下颌升支前缘点[右:(2.52±0.95) mm;左:(2.57±1.10) mm],中线点平均定点误差为(1.15±0.60) mm,双侧点平均定点误差为(1.51±0.67) mm。结论: 基于三维下颌骨平均模型和非刚性配准算法的三维下颌骨解剖标志点自动确定方法,可有效提高三维下颌骨数据特征自动标注的效率,其对无显著畸形下颌骨数据解剖标志点的自动确定效果可基本满足口腔临床应用的需求,对畸形下颌骨数据的标注效果有待进一步测试。
中图分类号:
- R782.2
| 1 |
Kakarala K , Shnayder Y , Tsue TT , et al. Mandibular reconstruction[J]. Oral Oncol, 2018, 77, 111- 117.
doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2017.12.020 |
| 2 | 中华口腔医学会口腔颌面修复专业委员会. 下颌骨缺损修复重建治疗专家共识[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2019, 54 (7): 433- 439. |
| 3 |
Bak M , Jacobson AS , Buchbinder D , et al. Contemporary reconstruction of the mandible[J]. Oral Oncol, 2010, 46 (2): 71- 76.
doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2009.11.006 |
| 4 |
张鑫, 刘洋, 周建萍, 等. 点构法构建下颌骨正中矢状平面的初步探究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2019, 39 (1): 52- 59.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2019.01.010 |
| 5 |
周子疌, 朱向阳, 韩婧, 等. 基于机器学习的颌骨特征点还原法辅助跨中线颌骨缺损重建[J]. 中国口腔颌面外科杂志, 2020, 18 (4): 323- 327.
doi: 10.19438/j.cjoms.2020.04.007 |
| 6 | Wang E , Tran KL , D'Heygere E , et al. Predicting the premorbid shape of a diseased mandible[J]. Laryngoscope, 2021, 131 (3): E781- E786. |
| 7 | 史雨林. 骨性Ⅲ类患者正颌手术前后面部软硬组织变化的3D研究[D]. 西安: 中国人民解放军空军军医大学, 2018. |
| 8 |
潘思思, 王昕, 戴微微, 等. 替牙期儿童下颌骨发育的三维特征[J]. 温州医科大学学报, 2014, 44 (10): 712- 717.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-9400.2014.10.004 |
| 9 |
Neelapu BC , Kharbanda OP , Sardana V , et al. Automatic localization of three-dimensional cephalometric landmarks on CBCT images by extracting symmetry features of the skull[J]. Dentomaxillofac Radiol, 2018, 47 (2): 20170054.
doi: 10.1259/dmfr.20170054 |
| 10 | Zhang J , Liu M , Wang L , et al. Joint craniomaxillofacial bone segmentation and landmark digitization by context-guided fully convolutional networks[J]. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv, 2017, 10434, 720- 728. |
| 11 |
Zhang J , Liu M , Wang L , et al. Context-guided fully convolu-tional networks for joint craniomaxillofacial bone segmentation and landmark digitization[J]. Med Image Anal, 2020, 60, 101621.
doi: 10.1016/j.media.2019.101621 |
| 12 | Zheng YF, Liu D, Georgescu B, et al. 3D deep learning for efficient and robust landmark detection in volumetric data: 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI)[C]. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2015: 565-572. |
| 13 |
White JD , Ortega-Castrillón A , Matthews H , et al. MeshMonk: Open-source large-scale intensive 3D phenotyping[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9 (1): 6085.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42533-y |
| 14 | 任敏. 基于MSCT汉族成年人群活体下颌骨三维测量数据库的建立及三维测量研究[D]. 北京: 北京协和医学院, 2008. |
| 15 | Goodall C . Procrustes methods in the statistical analysis of shape[J]. J R Stat Soc B, 1991, 53 (2): 285- 321. |
| 16 |
温奥楠, 朱玉佳, 郑盛文, 等. 基于三维人脸模板的颜面解剖标志点自动定点方法初探[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2022, 57 (4): 358- 365.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112144-20210913-00409 |
| 17 |
Ghoddousi H , Edler R , Haers P , et al. Comparison of three methods of facial measurement[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2007, 36 (3): 250- 258.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2006.10.001 |
| 18 |
Douglas TS . Image processing for craniofacial landmark identification and measurement: A review of photogrammetry and cephalo-metry[J]. Comput Med Imaging Graph, 2004, 28 (7): 401- 409.
doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2004.06.002 |
| 19 | Abu A , Ngo CG , Abu-Hassan NIA , et al. Automated craniofacial landmarks detection on 3D image using geometry characteristics information[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2019, 19 (Suppl 13): 548. |
| 20 | Liang S, Wu J, Weinberg SM, et al. Improved detection of landmarks on 3D human face data: 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE-Engineering-in-Medicine-and-Biology-Society (EMBC)[C] Osaka, Japan: Institule of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, 2013: 6482-6485. |
| 21 |
Wang K , Zhao X , Gao W , et al. A coarse-to-fine approach for 3D facial landmarking by using deep feature fusion[J]. Symmetry, 2018, 10 (8): 308.
doi: 10.3390/sym10080308 |
| 22 | Paulsen RR, Juhl KA, Haspang TM, et al. Multi-view consensus CNN for 3D facial landmark placement: 14th Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV)[C]. Australia: Springer, 2019: 706-719. |
| 23 | 李婧宇. 北方汉族女性三维平均脸的构建并用于面部形态随年龄变化研究[D]. 北京: 北京协和医学院, 2017. |
| 24 |
Kuijpers M , Maal T , Meulstee JW , et al. Nasolabial shape and aesthetics in unilateral cleft lip and palate: An analysis of nasolabial shape using a mean 3D facial template[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2021, 50 (2): 267- 272.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2020.06.003 |
| 25 |
Damstra J , Fourie Z , De Wit M , et al. A three-dimensional comparison of a morphometric and conventional cephalometric midsagittal planes for craniofacial asymmetry[J]. Clin Oral Investig, 2012, 16 (1): 285- 294.
doi: 10.1007/s00784-011-0512-4 |
| 26 |
Fagertun J , Harder S , Rosengren A , et al. 3D facial landmarks: Inter-operator variability of manual annotation[J]. BMC Med Imaging, 2014, 14, 35.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2342-14-35 |
| [1] | 徐心雨,吴灵,宋凤岐,李自力,张益,刘筱菁. 基于下颌运动轨迹的正颌外科术中下颌骨髁突定位方法及初步精度验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 57-65. |
| [2] | 王聪伟,高敏,于尧,章文博,彭歆. 游离腓骨瓣修复下颌骨缺损术后义齿修复的临床分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 66-73. |
| [3] | 卢汉,张建运,杨榕,徐乐,李庆祥,郭玉兴,郭传瑸. 下颌牙龈鳞状细胞癌患者预后的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 702-707. |
| [4] | 张雯,刘筱菁,李自力,张益. 基于解剖标志的鼻翼基底缩窄缝合术对正颌患者术后鼻唇部形态的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 736-742. |
| [5] | 周伟,安金刚,荣起国,张益. 下颌骨颏部骨折联合双侧髁突囊内骨折致伤机制的三维有限元分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 983-989. |
| [6] | 李博文,吴唯伊,唐琳,张一,刘玉华. 改良猪小肠黏膜下层可吸收膜在兔下颌骨缺损早期愈合中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(5): 887-892. |
| [7] | 李明哲,王晓霞,李自力,伊彪,梁成,何伟. 计算机导航辅助下口内入路髁突切除术精确性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(1): 182-186. |
| [8] | 戴帆帆,刘怡,许天民,陈贵. 探索成人正畸前后下颌三维数字化模型的重叠方法[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(2): 271-278. |
| [9] | 李世赢,李刚,冯海兰,潘韶霞. 锥形束CT分析下颌无牙颌患者前部颌弓形态对“All-on-4”种植设计的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(4): 699-703. |
| [10] | 何伟, 谢晓艳, 王兴, 王晓霞, 傅开元, 李自力. 上颌Le FortⅠ型分块截骨术及双侧下颌升支矢状劈开术对骨性Ⅲ类错牙合畸形患者髁突位置的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(5): 829-833. |
| [11] | 陈全, 郭传瑸, 高涛. 54例大致正常成年汉族人下颌骨三维CT形态学测量[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(1): 113-119. |
| [12] | 蒋析, 林野, 胡秀莲, 邸萍, 罗佳, 李健慧. 下颌后牙游离缺失伴重度垂直骨量不足的计算机 辅助种植修复[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(2): 294-298. |
| [13] | 赵莹,董颖韬,王晓燕,王祖华,李刚,刘木青,傅开元. 4 674颗下颌前牙根管构型的锥形束CT分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(1): 95-99. |
| [14] | 张磊,李云霞,康艳凤,杨广聚,谢秋菲. 自主后退法和双手引导法确定下颌后退接触位切点位移的比较研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(1): 67-70. |
| [15] | 王霄, 张益, 李江明. 髁突矢状骨折继发颞下颌关节强直动物模型的建立[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2011, 43(6): 903-907. |
|
||