北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (1): 44-51. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.01.007
不同pH值对脱细胞小肠黏膜下层海绵支架螯合锶离子的影响
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院修复科, 国家口腔医学中心, 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心, 口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心, 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室, 北京 100081
2. 首都医科大学附属北京朝阳医院口腔科, 北京 100020
Effect of pH on the chelation between strontium ions and decellularized small intestinal submucosal sponge scaffolds
Yu-ke LI1,Mei WANG2,Lin TANG1,Yu-hua LIU1,*( ),Xiao-ying CHEN1
),Xiao-ying CHEN1
- 1. Department of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of Stomatology, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100020, China
摘要:
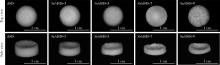
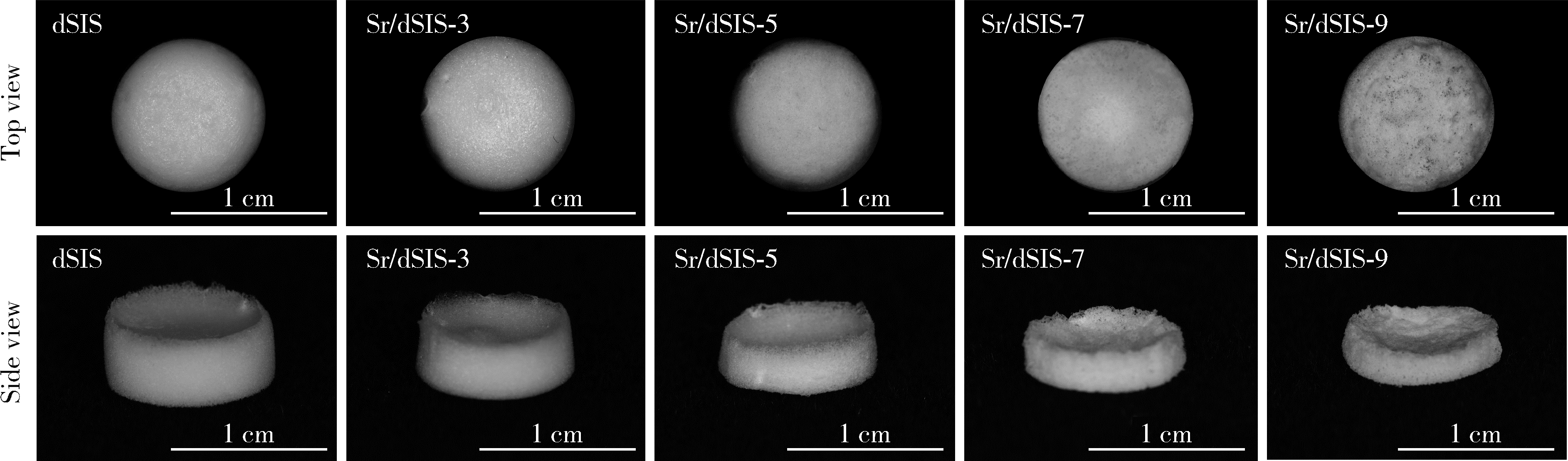
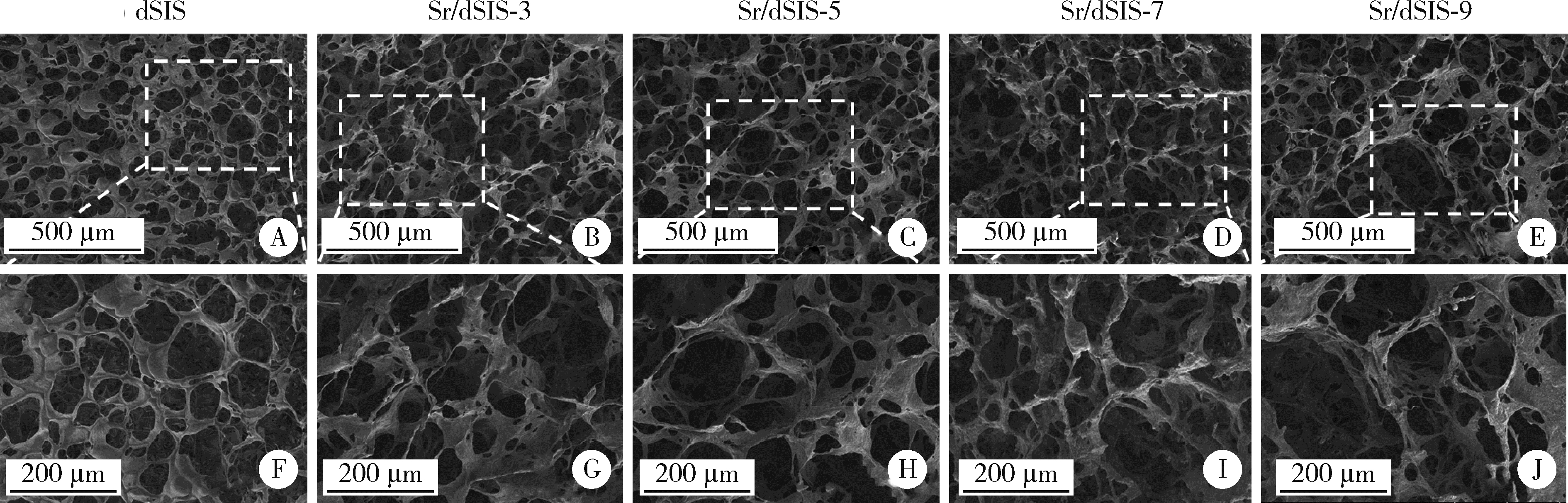
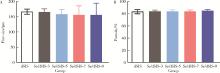
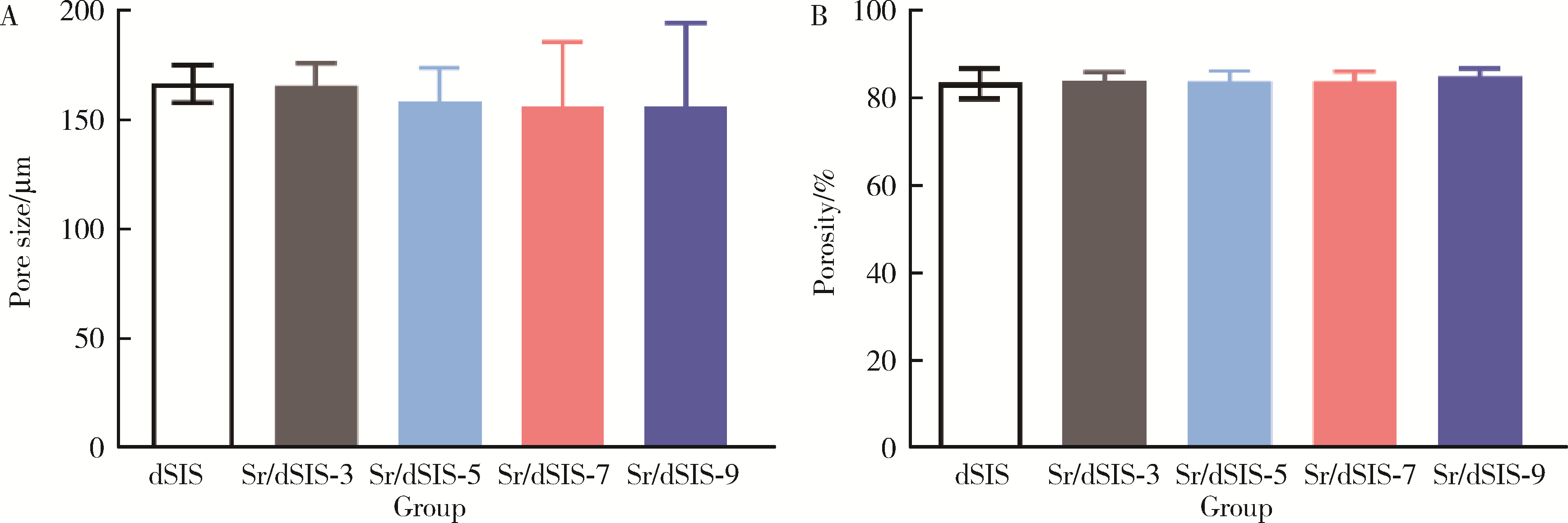
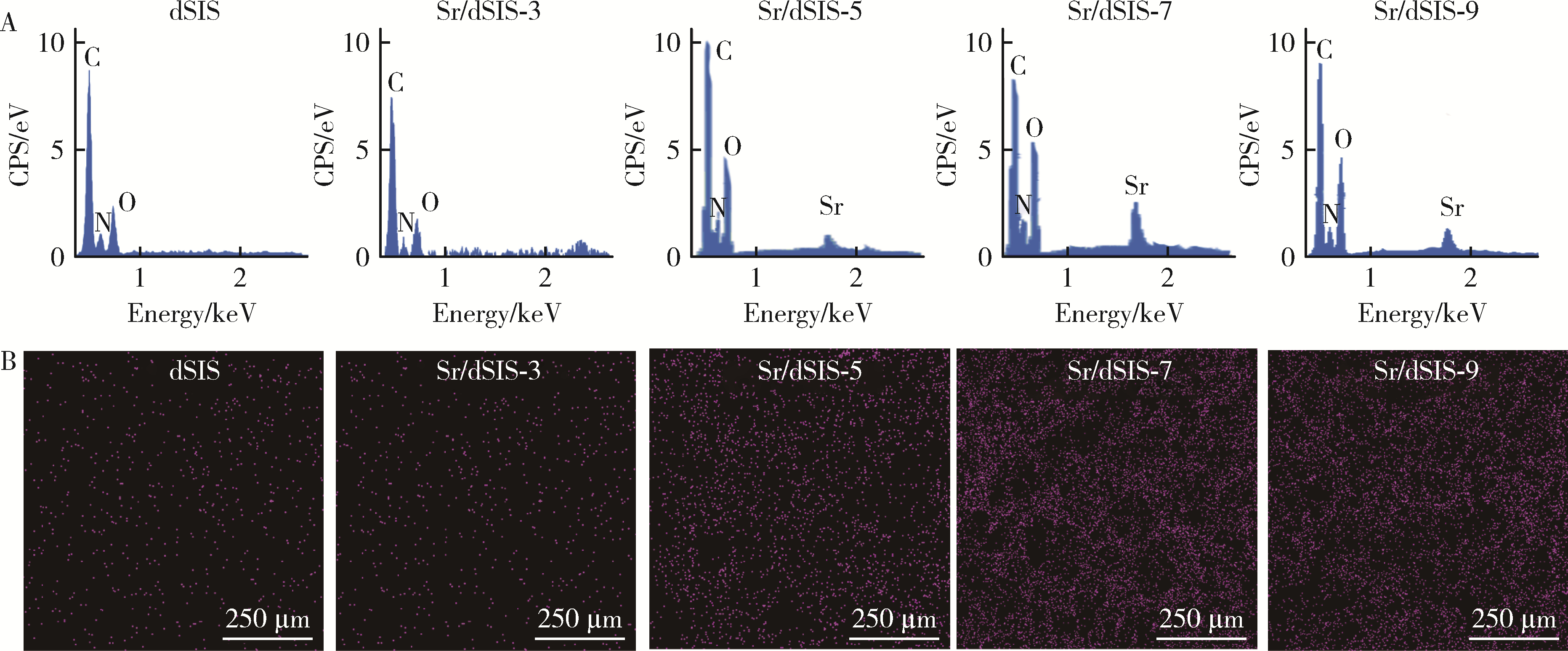
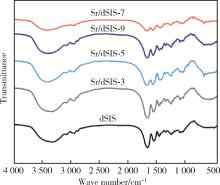
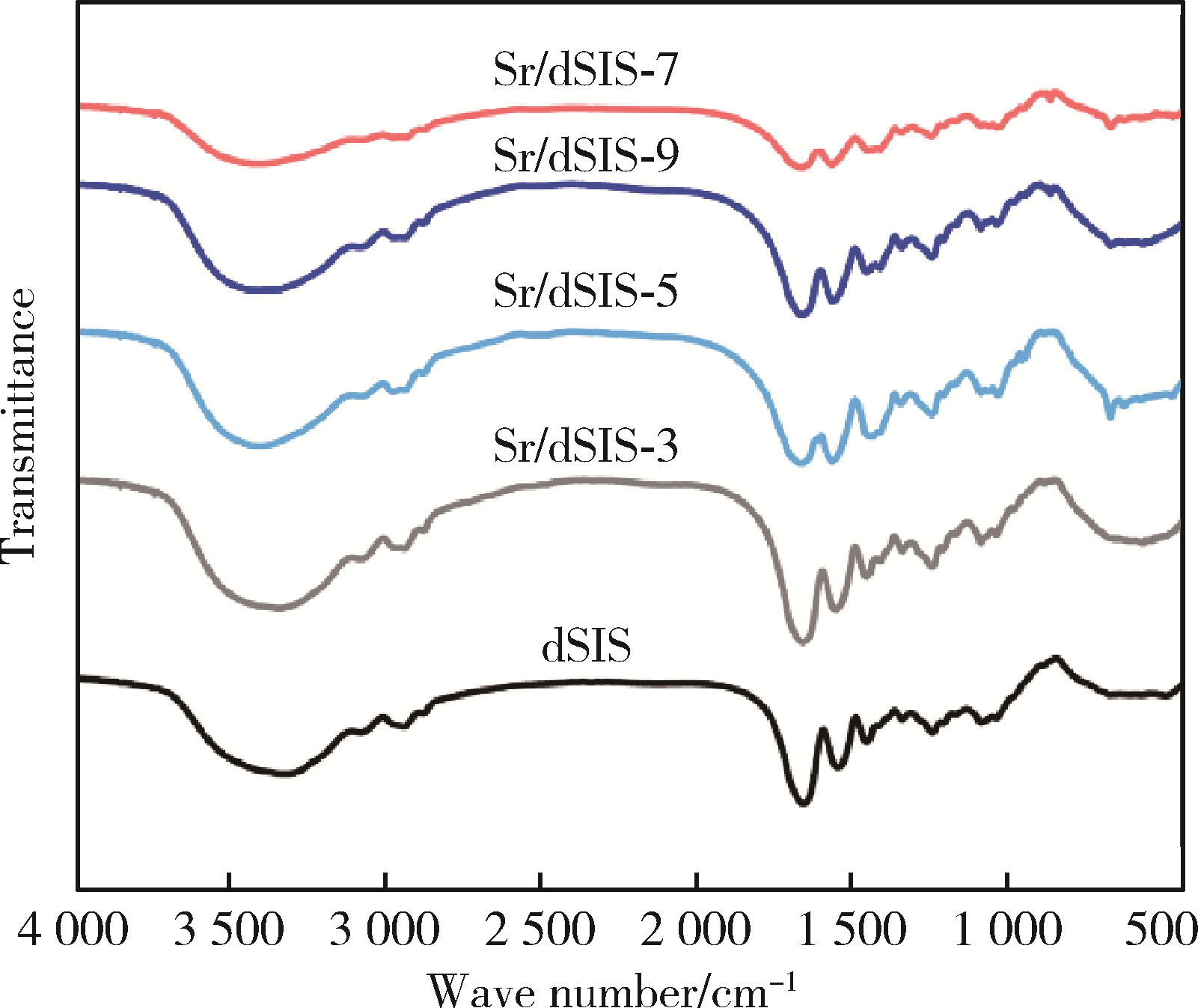
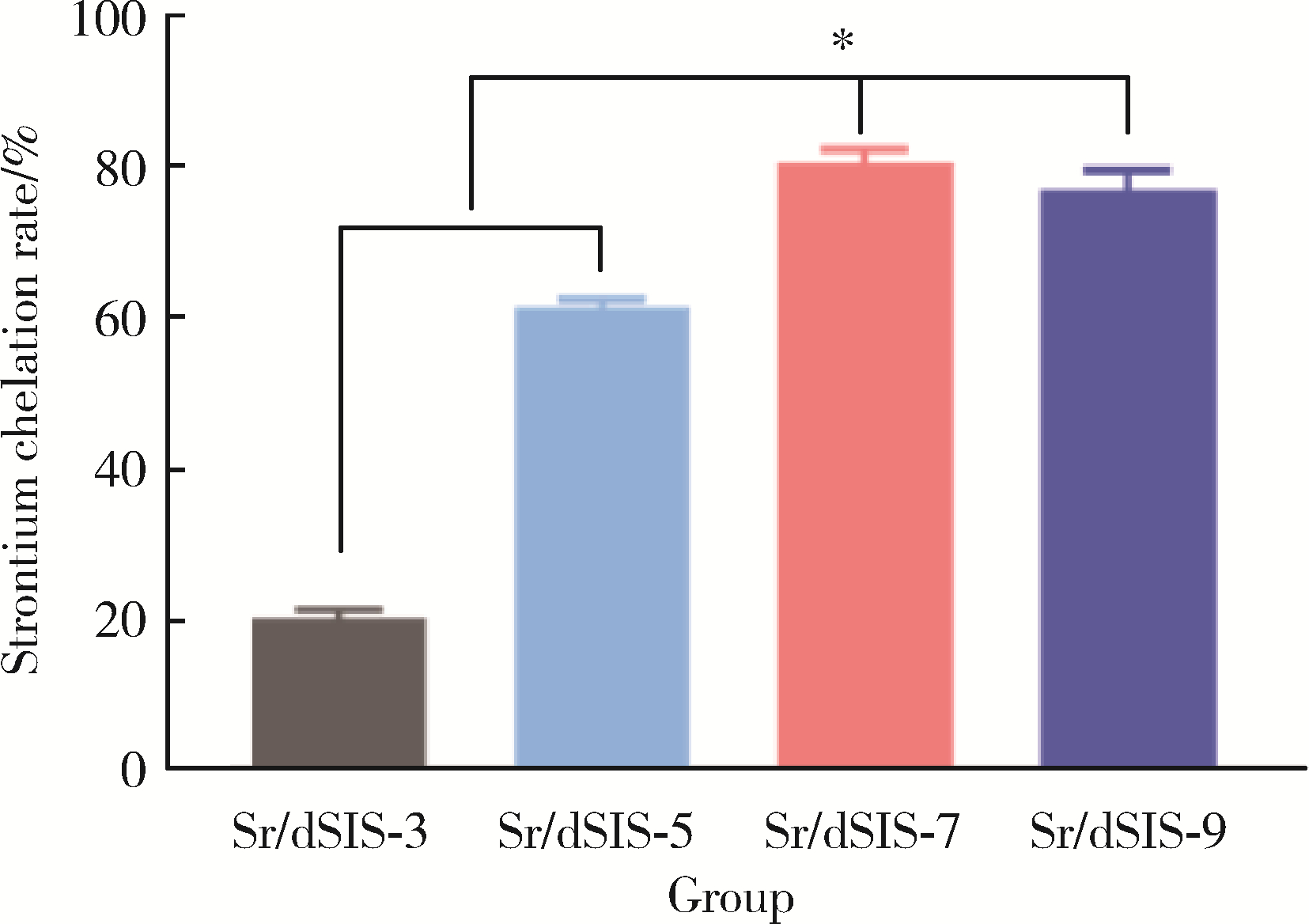
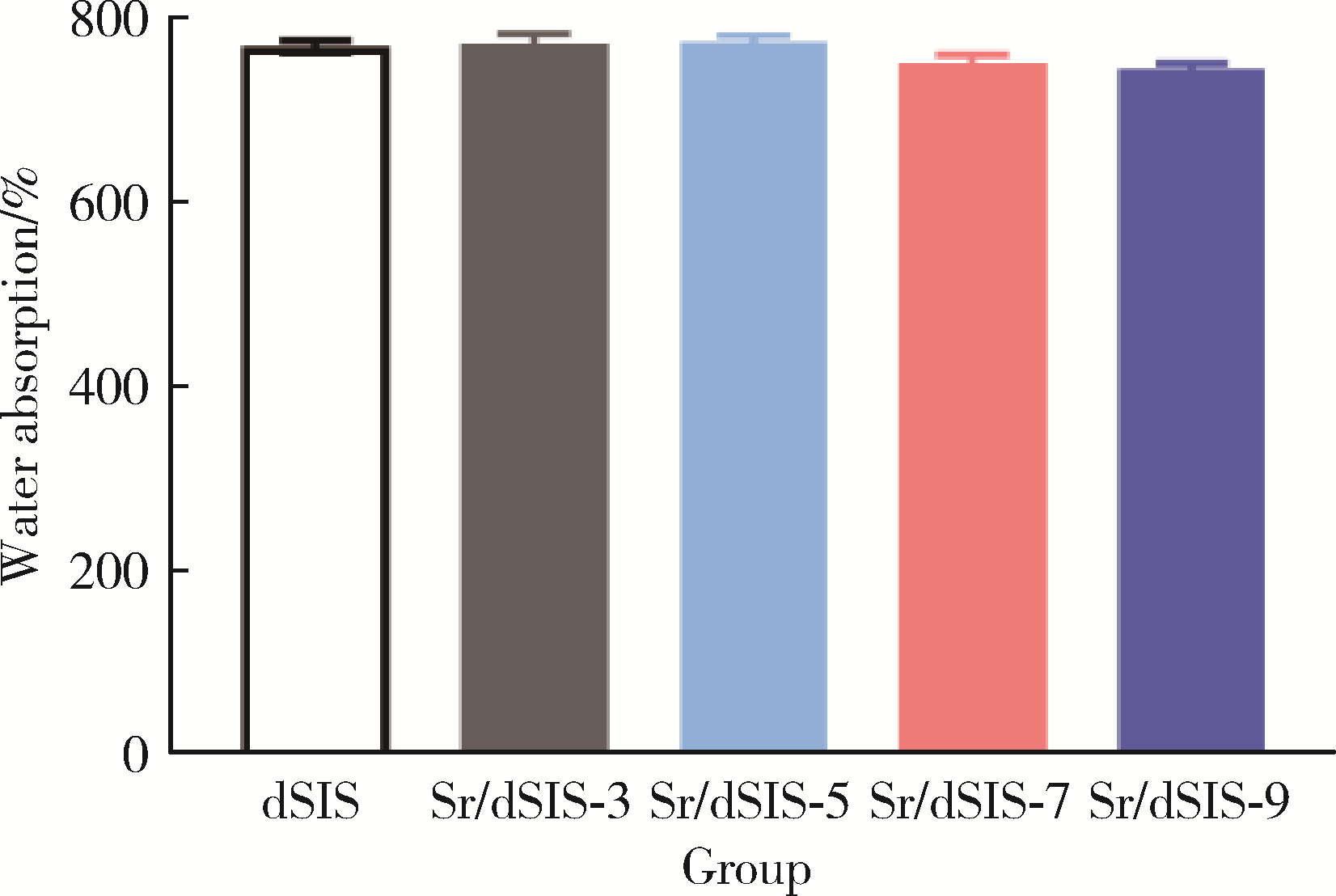
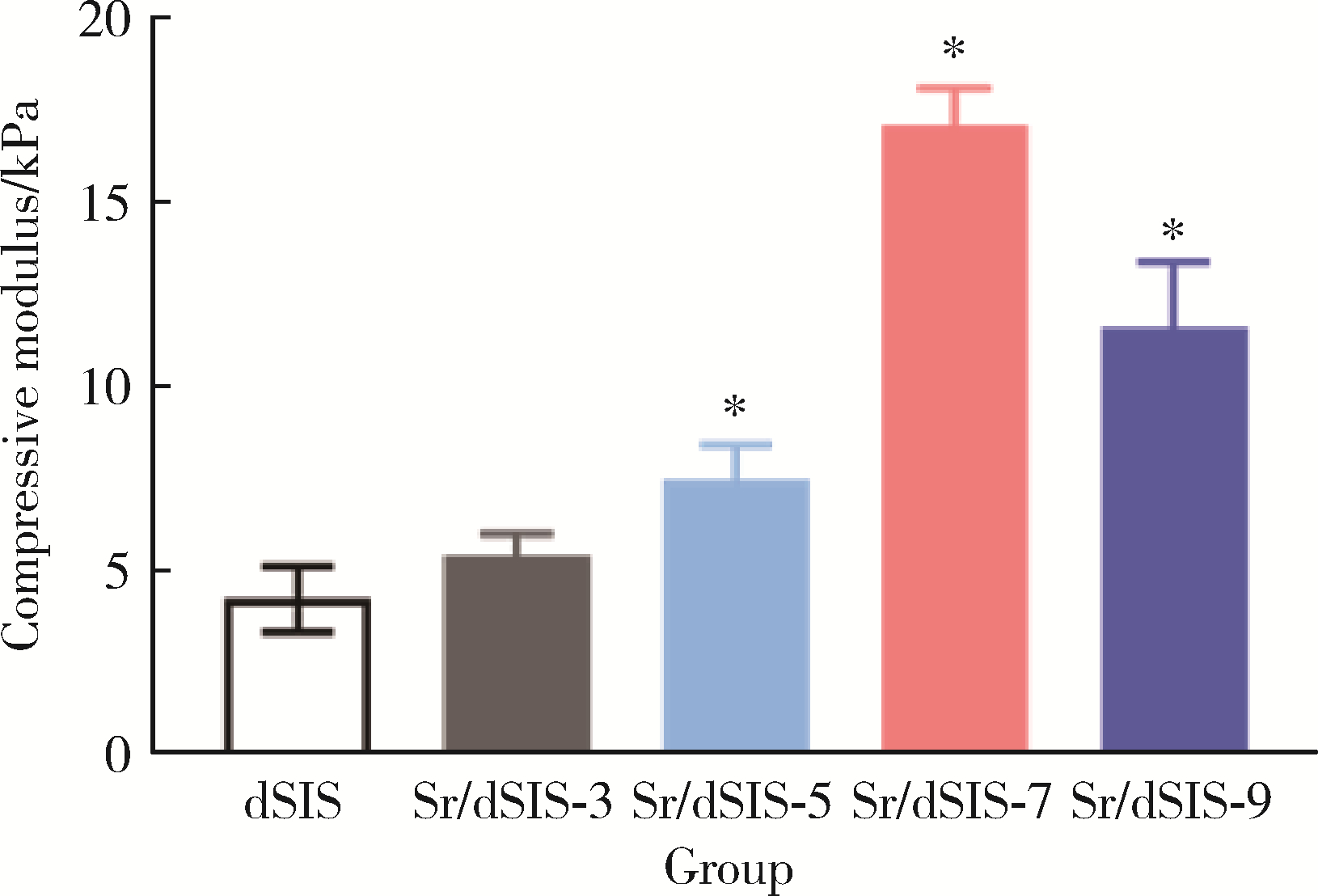
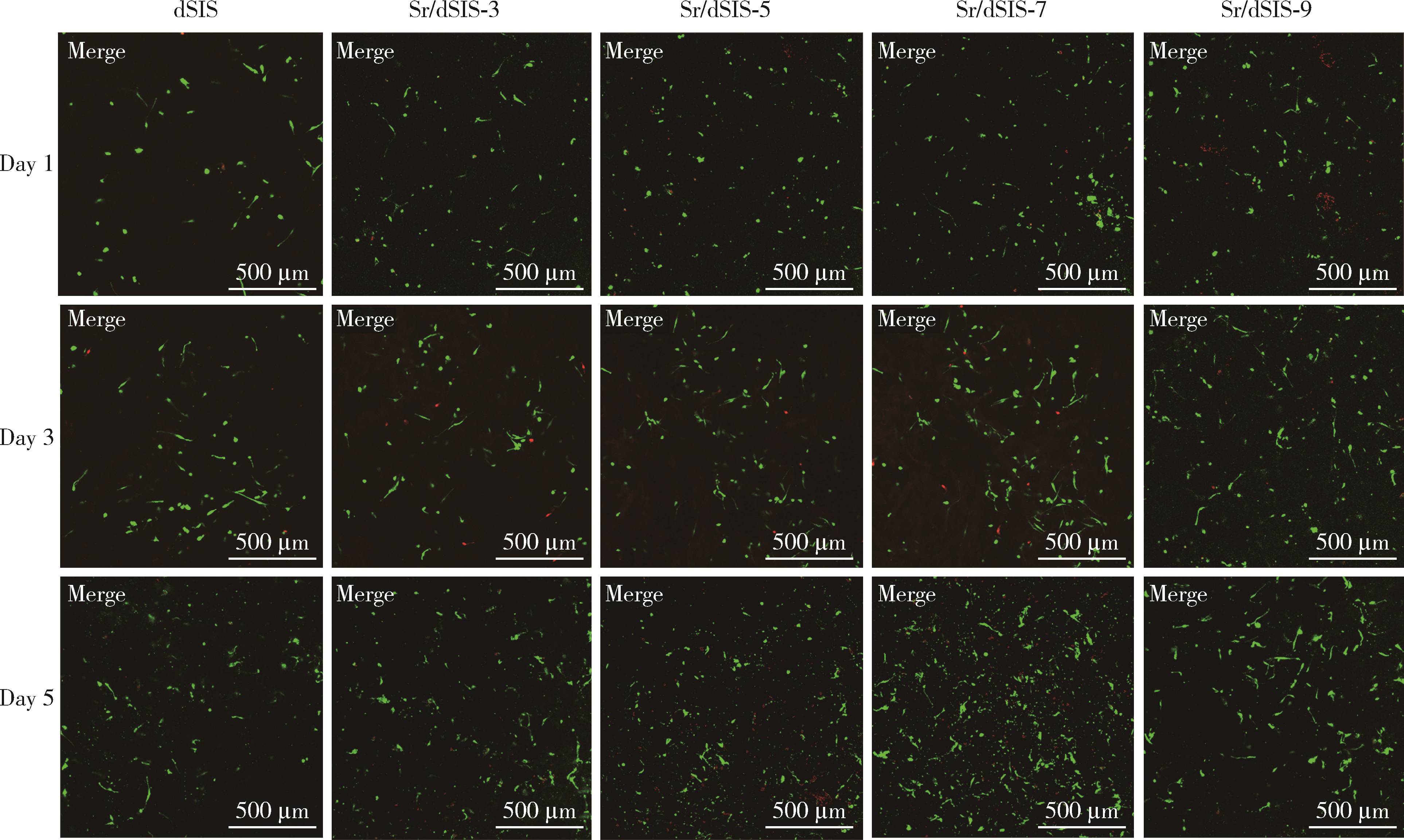
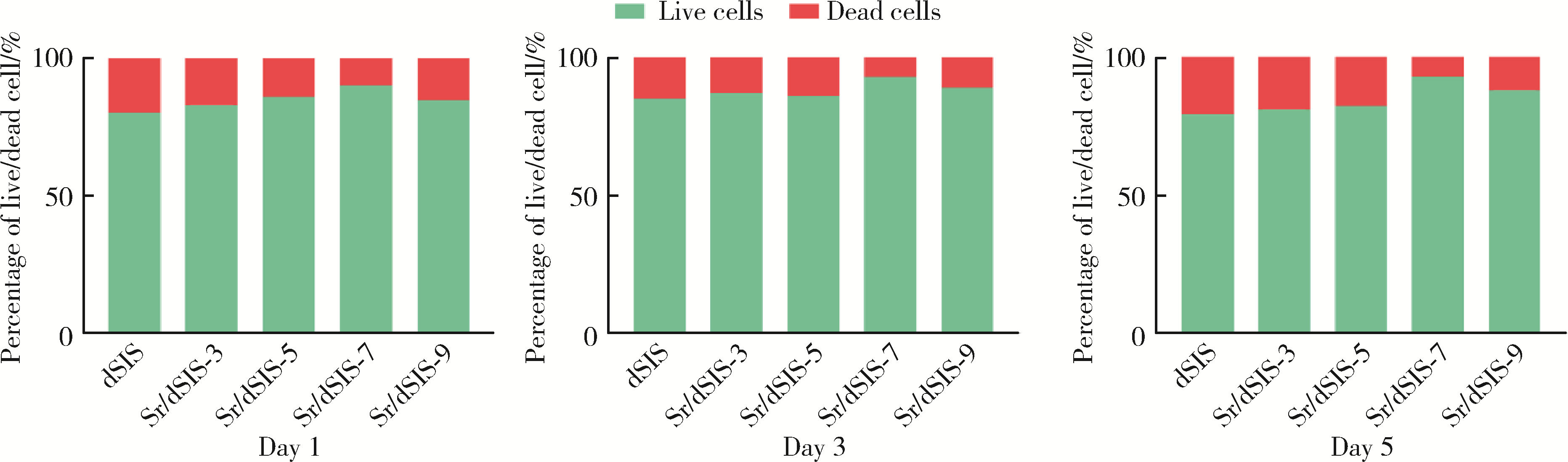
目的: 设计不同pH值下螯合锶(strontium, Sr)的脱细胞小肠黏膜下层(decellularized small intestinal submucosa, dSIS)海绵支架(Sr/dSIS), 以该支架的理化性能和生物相容性为评价指标, 为制备Sr/dSIS选择合适的pH值。方法: (1) Sr/dSIS制备及分组: 将dSIS溶液与氯化锶溶液等体积混合, 调节溶液pH分别为3、5、7、9, 于37℃下充分反应后经冷冻干燥制得多孔支架, 分别命名为Sr/dSIS-3、-5、-7、-9, 以dSIS支架为对照; (2)理化性能评价: 观察支架大体形貌, 采用扫描电镜分析微观形貌并测定孔隙率和孔径, 能谱分析表面元素, 红外光谱分析官能团结构, 原子吸收分光光度法测定螯合率, 比重法检测吸水率, 万能力学测试机评价压缩强度; (3)生物相容性评价: 采用Calcein-AM/PI活细胞/死细胞染色法评价各组支架的毒性和促骨髓间充质干细胞(bone mesenchymal stem cells, BMSCs)增殖效果。结果: 扫描电镜下各组支架具有三维多孔网络结构, 孔径和孔隙率差异无统计学意义; 能谱分析中Sr/dSIS-5、-7、-9组检测出锶元素的特征峰, 且锶元素均匀分布于支架; 官能团分析验证了Sr/dSIS-5、-7、-9组有螯合物形成; 螯合率分析显示Sr/dSIS-7组锶离子螯合率最高, 与其他组的差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);各组支架吸水性良好; Sr/dSIS-5、-7、-9组的压缩强度显著高于对照组(P < 0.05);各组支架的生物相容性良好, Sr/dSIS-7组展现出最佳的促细胞增殖能力。结论: pH为7时, Sr/dSIS支架具有高锶离子螯合率以及更好的促BMSCs增殖效果, 是制备Sr/dSIS支架的理想pH值。
中图分类号:
- R318.08
| 1 |
Andrée B , Bär A , Haverich A , et al. Small intestinal submucosa segments as matrix for tissue engineering: review[J]. Tissue Eng Part B Rev, 2013, 19 (4): 279- 291.
doi: 10.1089/ten.teb.2012.0583 |
| 2 | Tian Q , Fan Y , Hao L , et al. A comprehensive review of calcium and ferrous ions chelating peptides: Preparation, structure and transport pathways[J]. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 2021, 61 (11): 1- 13. |
| 3 |
O'Neill E , Awale G , Daneshmandi L , et al. The roles of ions on bone regeneration[J]. Drug Discov Today, 2018, 23 (4): 879- 890.
doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2018.01.049 |
| 4 | Wu W , He L , Liang Y , et al. Preparation process optimization of pig bone collagen peptide-calcium chelate using response surface methodology and its structural characterization and stability analysis[J]. Food Chem, 2019, 284 (30): 80- 89. |
| 5 |
蔡冰娜, 陈忻, 潘剑宇, 等. 响应面法优化鳕鱼皮胶原蛋白肽螯合铁工艺[J]. 食品科学, 2012, 33 (2): 48- 52.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1513.2012.02.010 |
| 6 |
Bi J , Wang X , Zhou Y , et al. Preparation and characterization for peptide-chelated calcium of deer bone[J]. Food Sci Technol Res, 2018, 24 (4): 717- 728.
doi: 10.3136/fstr.24.717 |
| 7 |
韩克光, 甄守艳, 范华, 等. 钙螯合羊骨胶原多肽的制备及表征分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31 (21): 301- 307.
doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2015.21.040 |
| 8 | Zhang H , Zhao L , Shen Q , et al. Preparation of cattle bone collagen peptides-calcium chelate and its structural characterization and stability[J]. LWT-Food Sci Technol, 2021, 144 (12): 111264. |
| 9 | 陆剑锋, 孟昌伟, 李进, 等. 斑点叉尾鱼骨胶原多肽螯合钙的制备及其特征[J]. 水产学报, 2012, 36 (2): 314- 320. |
| 10 |
Crapo PM , Gilbert TW , Badylak SF . An overview of tissue and whole organ decellularization processes[J]. Biomaterials, 2011, 32 (12): 3233- 3243.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.01.057 |
| 11 |
Li B , Wang M , Liu Y , et al. Independent effects of structural optimization and resveratrol functionalization on extracellular matrix scaffolds for bone regeneration[J]. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces, 2022, 212, 112370.
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2022.112370 |
| 12 |
Reing JE , Brown BN , Daly KA , et al. The effects of processing methods upon mechanical and biologic properties of porcine dermal extracellular matrix scaffolds[J]. Biomaterials, 2010, 31 (33): 8626- 8633.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.07.083 |
| 13 | Ji Y , Zhou J , Sun T , et al. Diverse preparation methods for small intestinal submucosa (SIS): Decellularization, components, and structure[J]. J Biomed Mater Res A, 2019, 107 (3): 689- 697. |
| 14 |
Cowles EA , Brailey LL , Gronowicz GA . Integrin-mediated signaling regulates AP-1 transcription factors and proliferation in osteoblasts[J]. J Biomed Mater Res, 2000, 52 (4): 725- 737.
doi: 10.1002/1097-4636(20001215)52:4<725::AID-JBM18>3.0.CO;2-O |
| 15 |
Yi S , Ding F , Gong L , et al. Extracellular matrix scaffolds for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine[J]. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther, 2017, 12 (3): 233- 246.
doi: 10.2174/1574888X11666160905092513 |
| 16 | Liao J , Xu B , Zhang R , et al. Applications of decellularized materials in tissue engineering: Advantages, drawbacks and current improvements, and future perspectives[J]. J Mater Chem B, 2020, 8 (44): 10023- 10049. |
| 17 | Gorschewsky O , Puetz A , Riechert K , et al. Quantitative analysis of biochemical characteristics of bone-patellar tendon-bone allografts[J]. Biomed Mater Eng, 2005, 15 (6): 403- 411. |
| 18 | Bharadwaz A , Jayasuriya AC . Recent trends in the application of widely used natural and synthetic polymer nanocomposites in bone tissue regeneration[J]. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl, 2020, 110, 110698. |
| 19 | Chandika P , Ko SC , Oh GW , et al. Fish collagen/alginate/chitooligosaccharides integrated scaffold for skin tissue regeneration application[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2015, 81 (8): 504- 513. |
| 20 | Castilla Bolaños MA , Buttigieg J , Briceño Triana JC . Development and characterization of a novel porous small intestine submucosa-hydroxyapatite scaffold for bone regeneration[J]. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl, 2017, 72, 519- 525. |
| 21 | Liu J , Zeng H , Xiao P , et al. Sustained release of magnesium ions mediated by a dynamic mechanical hydrogel to enhance BMSC proliferation and differentiation[J]. ACS Omega, 2020, 5 (38): 24477- 24486. |
| [1] | 刘园梅, 傅义程, 郝靖欣, 张福春, 刘慧琳. 老年髋部骨折患者住院期间发生术后心力衰竭的列线图预测模型的构建及验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 874-883. |
| [2] | 汪琪伟, 包鹏宇, 洪士皓, 杨昕, 王宇, 曹永平. 改良股骨颈截骨术在伴严重屈曲畸形强直性脊柱炎患者手术治疗过程中的疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 884-889. |
| [3] | 王明瑞, 王起, 胡浩, 赖金惠, 唐鑫伟, 万春艳, 许克新, 徐涛. 覆膜金属输尿管支架治疗盆腔脂肪增多症所致肾积水的疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 919-922. |
| [4] | 杨文博,余磊,张维宇,徐涛,王强. 带线输尿管支架自排技术在肾移植受者中的效果及安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 656-660. |
| [5] | 李红光,韩玮华,吴训,冯继玲,李刚,孟娟红. 关节腔冲洗联合液态浓缩生长因子注射治疗单侧颞下颌关节骨关节炎的初步研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 338-344. |
| [6] | 周颖,赵宁,黄竑远,李庆祥,郭传瑸,郭玉兴. 左侧三叉神经第三支带状疱疹并发左侧下颌骨骨坏死1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 366-370. |
| [7] | 白心竹,何金徽,陆松松,李春,王依林,熊建. 椎体骨折合并活化部分凝血活酶时间延长1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 371-374. |
| [8] | 毛渤淳,田雅婧,王雪东,李晶,周彦恒. 骨性Ⅱ类高角患者拔牙矫治前后的面部软硬组织变化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 111-119. |
| [9] | 陈晓颖,张一,李雨柯,唐琳,刘玉华. 不同种类聚合物对猪小肠黏膜下层支架仿生矿化的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 17-24. |
| [10] | 董佳芸,李雪芬,路瑞芳,胡文杰,孟焕新. 血管化骨瓣重建颌骨种植体周软组织病理学特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 25-31. |
| [11] | 赵菡,卫彦,张学慧,杨小平,蔡晴,宁成云,徐明明,刘雯雯,黄颖,何颖,郭亚茹,江圣杰,白云洋,吴宇佳,郭雨思,郑晓娜,李文静,邓旭亮. 口腔硬组织修复材料仿生设计制备和临床转化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 4-8. |
| [12] | 周颖,赵宁,黄竑远,李庆祥,郭传瑸,郭玉兴. 双层软组织缝合封闭技术在下颌骨中早期药物相关性颌骨骨坏死患者手术治疗中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 51-56. |
| [13] | 徐心雨,吴灵,宋凤岐,李自力,张益,刘筱菁. 基于下颌运动轨迹的正颌外科术中下颌骨髁突定位方法及初步精度验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 57-65. |
| [14] | 王聪伟,高敏,于尧,章文博,彭歆. 游离腓骨瓣修复下颌骨缺损术后义齿修复的临床分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 66-73. |
| [15] | 潘媛,顾航,肖涵,赵笠君,汤祎熳,葛雯姝. 泛素特异性蛋白酶42调节人脂肪干细胞成骨向分化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 9-16. |
|
||