北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (1): 38-43. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.01.006
低温等离子体对牙本质小管内粪肠球菌的抗菌效果
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院综合科, 国家口腔医学中心, 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心, 口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心, 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室, 北京 100081
2. 首都医科大学附属北京朝阳医院口腔科, 北京 100020
Antibacterial effect of low-temperature plasma on Enterococcus faecalis in dentinal tubules in vitro
Ruo-qing ZHONG1,Meng-qian ZHU1,Ying-long LI2,*( ),Jie PAN1,*(
),Jie PAN1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of General Dentistry, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of Stomatology, Beijing Chaoyang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100020, China
摘要:
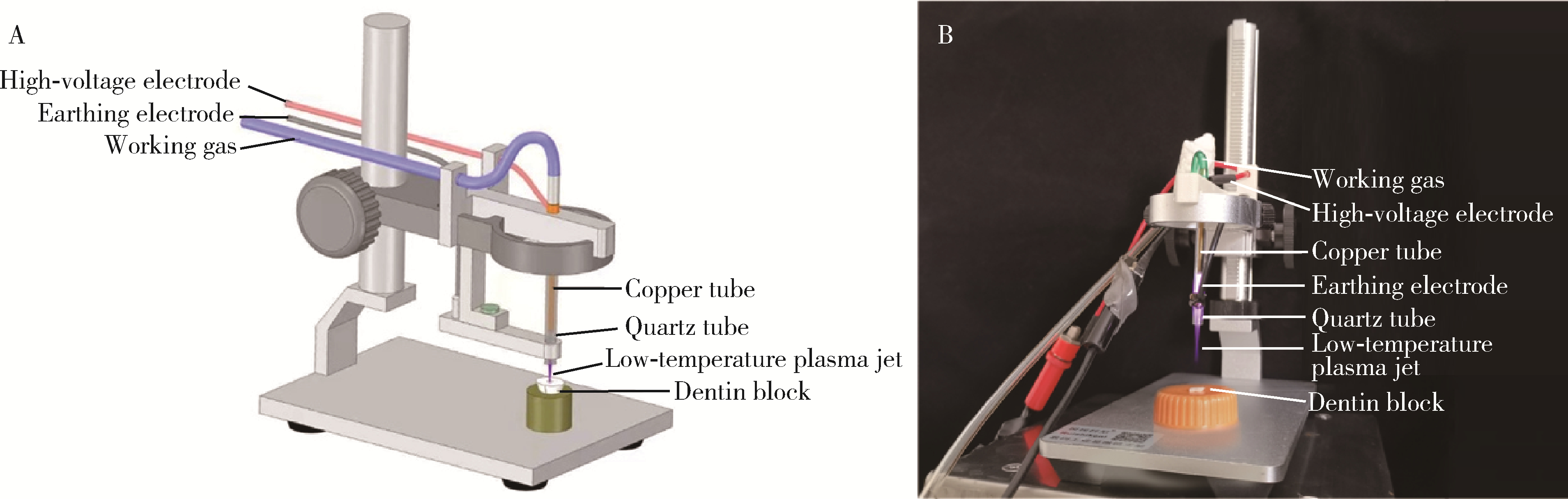
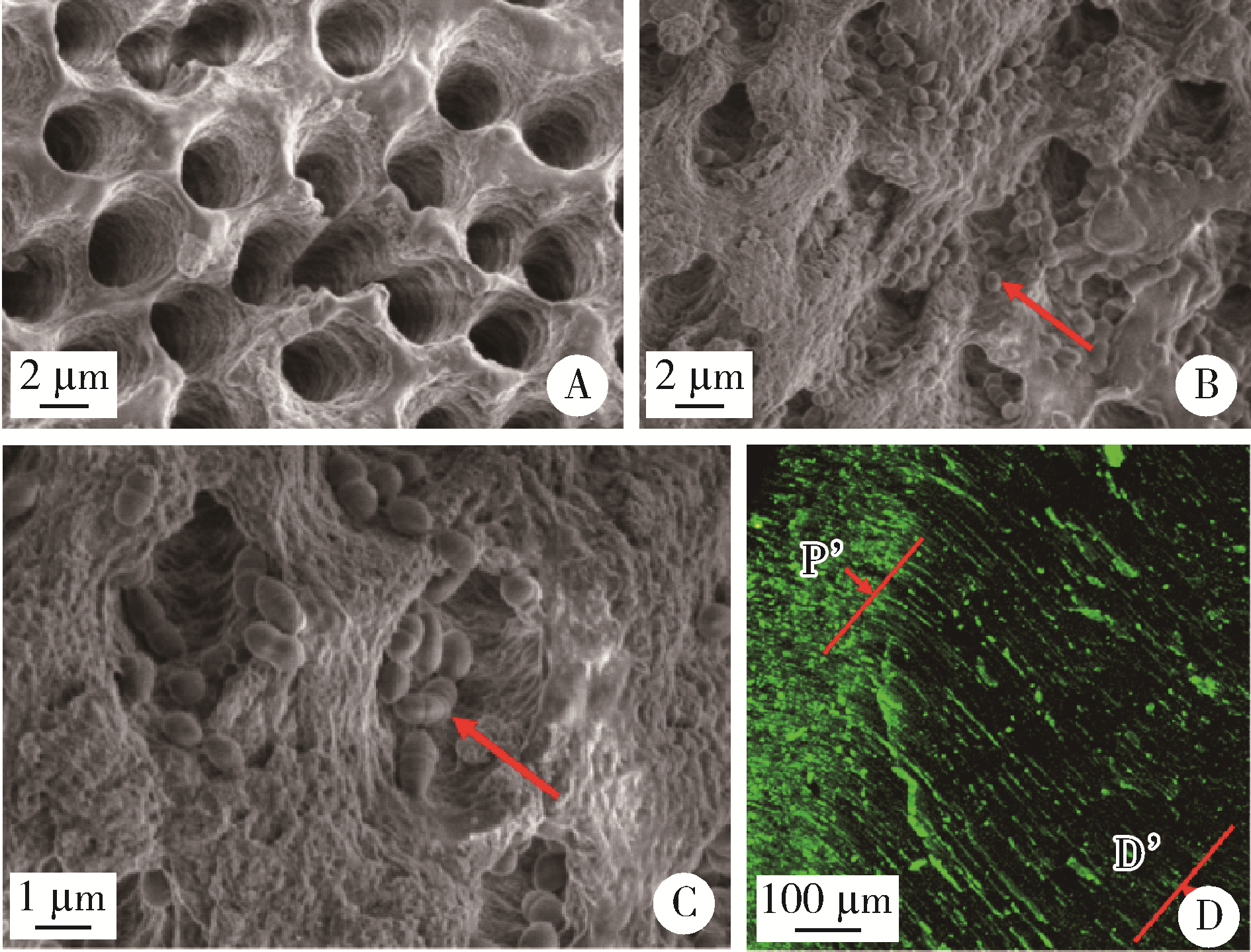
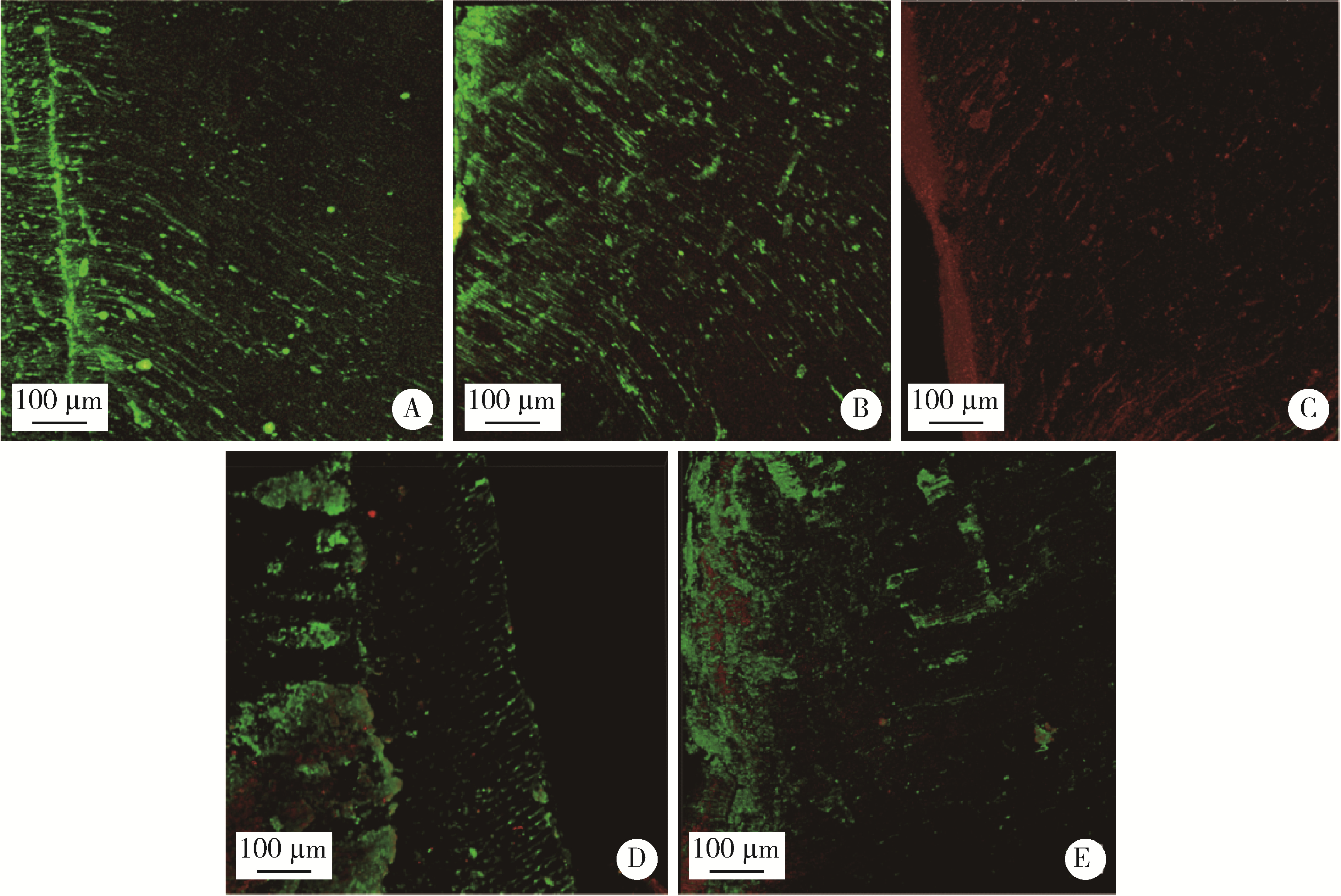
目的: 用梯度离心法构建粪肠球菌牙本质小管感染模型, 评价新型低温等离子体设备对牙本质小管内粪肠球菌的抗菌效果。方法: 选用无龋坏单根管离体牙制备4 mm×4 mm×2 mm标准牙本质块, 置于粪肠球菌菌液中, 梯度离心后培养24 h, 用于构建牙本质小管粪肠球菌感染模型, 将20个粪肠球菌牙本质小管感染样本随机平均分为5组: 低温等离子体射流处理0、5、10 min组, 氢氧化钙糊剂封药7 d组, 2%(质量分数)氯己定凝胶封药7 d组。用扫描电镜和激光共聚焦显微镜评估牙本质小管内感染情况, 并评价低温等离子体的抗菌效果。结果: 扫描电镜和激光共聚焦显微镜结果表明, 利用梯度离心法, 培养24 h后, 粪肠球菌可以充分进入牙本质小管, 深度超过600μm, 能够成功构建粪肠球菌感染牙本质小管模型; 低温等离子体能够进入牙本质小管中发挥作用, 经过10 min的低温等离子体处理, 牙本质小管内绝大多数粪肠球菌被杀灭, 效果超过氢氧化钙糊剂封药7 d以及2%氯己定凝胶封药7 d。结论: 梯度离心法能够有效建立粪肠球菌牙本质小管感染模型, 低温等离子体能够在10 min内有效杀灭牙本质小管中的粪肠球菌, 优于氢氧化钙糊剂封药7 d和2%氯己定凝胶封药7 d。
中图分类号:
- R781.3
| 1 | Friedman S , Mor C . The success of endodontic therapy: Healing and functionality[J]. J Calif Dent Assoc, 2004, 32 (6): 493- 503. |
| 2 |
Baras BH , Melo MAS , Sun J , et al. Novel endodontic sealer with dual strategies of dimethylaminohexadecyl methacrylate and nano-particles of silver to inhibit root canal biofilms[J]. Dent Mater, 2019, 35 (8): 1117- 1129.
doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2019.05.014 |
| 3 |
Stuart CH , Schwartz SA , Beeson TJ , et al. Enterococcus faecalis: Its role in root canal treatment failure and current concepts in retreatment[J]. J Endod, 2006, 32 (2): 93- 98.
doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2005.10.049 |
| 4 |
Sundqvist G , Figdor D , Persson S , et al. Microbiologic analysis of teeth with failed endodontic treatment and the outcome of conservative re-treatment[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod, 1998, 85 (1): 86- 93.
doi: 10.1016/S1079-2104(98)90404-8 |
| 5 |
Chen ZT , Chen GJ , Obenchain R , et al. Cold atmospheric plasma delivery for biomedical applications[J]. Mater Today, 2022, 54, 153- 188.
doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2022.03.001 |
| 6 |
Moreau M , Orange N , Feuilloley MG . Non-thermal plasma technologies: New tools for bio-decontamination[J]. Biotechnol Adv, 2008, 26 (6): 610- 617.
doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.08.001 |
| 7 |
Chen K , Xu DG , Li JN , et al. Application of terahertz time-domain spectroscopy in atmospheric pressure plasma jet diagnosis[J]. Results Phys, 2020, 16, 102928.
doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2020.102928 |
| 8 |
Tornin J , Labay C , Tampieri F , et al. Evaluation of the effects of cold atmospheric plasma and plasma-treated liquids in cancer cell cultures[J]. Nat Protoc, 2021, 16 (6): 2826- 2850.
doi: 10.1038/s41596-021-00521-5 |
| 9 |
Kumar-Dubey S , Dabholkar N , Narayan-Pal U , et al. Emerging innovations in cold plasma therapy against cancer: A paradigm shift[J]. Drug Discov Today, 2022, 27 (9): 2425- 2439.
doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2022.05.014 |
| 10 |
Zhang H , Xu SD , Zhang JS , et al. Plasma-activated thermosensitive biogel as an exogenous ROS carrier for post-surgical treatment of cancer[J]. Biomaterials, 2021, 276, 121057.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.121057 |
| 11 | Kim GC , Kim GJ , Park SR , et al. Air plasma coupled with antibody-conjugated nanoparticles: A new weapon against cancer[J]. J Phys D Appl Phys, 2008, 42 (3): 032005. |
| 12 |
Lu XP , Ye T , Cao YG , et al. The roles of the various plasma agents in the inactivation of bacteria[J]. J Appl Phys, 2008, 104 (5): 053309.
doi: 10.1063/1.2977674 |
| 13 |
Simon HU , Haj-Yehia A , Levi-Schaffer F . Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in apoptosis induction[J]. Apoptosis, 2000, 5 (5): 415- 418.
doi: 10.1023/A:1009616228304 |
| 14 |
Laroussi M . Low temperature plasma-based sterilization: Overview and state-of-the-art[J]. Plasma Process Polym, 2005, 2 (5): 391- 400.
doi: 10.1002/ppap.200400078 |
| 15 |
Pan J , Sun K , Liang YD , et al. Cold plasma therapy of a tooth root canal infected with Enterococcus faecalis biofilms in vitro[J]. J Endod, 2013, 39 (1): 105- 110.
doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2012.08.017 |
| 16 |
Li YL , Sun K , Ye GP , et al. Evaluation of cold plasma treatment and safety in disinfecting 3-week root canal Enterococcus faecalis biofilm in vitro[J]. J Endod, 2015, 41 (8): 1325- 1330.
doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2014.10.020 |
| 17 |
Ma JZ , Wang ZJ , Shen Y , et al. A new noninvasive model to study the effectiveness of dentin disinfection by using confocal laser scanning microscopy[J]. J Endod, 2011, 37 (10): 1380- 1385.
doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2011.06.018 |
| 18 | Du TF , Wang ZJ , Shen Y , et al. Effect of long-term exposure to endodontic disinfecting solutions on young and old Enterococcus faecalis biofilms in dentin canals[J]. J Endod, 2014, 40 (4): 509- 514. |
| 19 | 高岩, 李铁军. 口腔组织学与病理学[M]. 2版 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2013: 74. |
| 20 | 王雅丽, 罗丹, 申婷, 等. 不同冲洗方法对粪肠球菌感染根管的抗菌性研究[J]. 中华口腔医学研究杂志(电子版), 2019, 13 (4): 204- 211. |
| 21 | Li YL , Pan J , Wu D , et al. Regulation of Enterococcus faecalis biofilm formation and quorum sensing related virulence factors with ultra-low dose reactive species produced by plasma activated water[J]. Plasma Chem Plasma P, 2019, 39, 35- 49. |
| 22 | Liang YD , Li YL , Sun K , et al. Plasma thorns: Atmospheric pressure non-thermal plasma source for dentistry applications[J]. Plasma Process Polym, 2015, 12 (10): 1069- 1075. |
| 23 | Asnaashari M , Ashraf H , Rahmati A , et al. A comparison between effect of photodynamic therapy by LED and calcium hydro-xide therapy for root canal disinfection against Enterococcus faecalis: A randomized controlled trial[J]. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther, 2017, 17, 226- 232. |
| 24 | Afkhami F , Rostami G , Batebi S , et al. Residual antibacterial effects of a mixture of silver nanoparticles/calcium hydroxide and other root canal medicaments against Enterococcus faecalis[J]. J Dent Sci, 2022, 17 (3): 1260- 1265. |
| 25 | Gomes BP , Souza SF , Ferraz CC , et al. Effectiveness of 2% chlorhexidine gel and calcium hydroxide against Enterococcus faecalis in bovine root dentine in vitro[J]. Int Endod J, 2003, 36 (4): 267- 275. |
| 26 | Kapralos V , Sunde PT , Camilleri J , et al. Effect of chlorhexidine digluconate on antimicrobial activity, cell viability and physicochemical properties of three endodontic sealers[J]. Dent Mater, 2022, 38 (6): 1044- 1059. |
| [1] | 赵晓一,刘畅,钱锟,潘洁. 成熟恒牙牙髓切断术的疗效及影像学评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 138-143. |
| [2] | 何佩瑶,包旭东. 常温流动牙胶封闭剂GuttaFlow2单尖充填弯曲根管的封闭效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 99-105. |
| [3] | 叶雨阳,岳林,邹晓英,王晓燕. 成牙本质方向分化牙髓干细胞外泌体形态及微小RNA表达谱特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 689-696. |
| [4] | 叶佳学,梁宇红. 牙髓专科医师应用锥形束CT的现况调查[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 114-119. |
| [5] | 钱锟,潘洁,朱文昊,赵晓一,刘畅,雍颹. 两种硅酸钙类材料用于成熟恒牙牙髓切断术的临床效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 113-118. |
| [6] | 王铮,丁茜,高远,马全诠,张磊,葛兮源,孙玉春,谢秋菲. 氧化锆多孔表面显微形貌对成骨细胞增殖及分化的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 31-39. |
| [7] | 孟圆,张丽琪,赵雅宁,柳登高,张祖燕,高岩. 67例上颌根尖周囊肿的三维影像特点分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 396-401. |
| [8] | 李菲,乔静,段晋瑜,张勇,王秀婧. 引导性组织再生术对浓缩生长因子联合植骨术治疗下颌磨牙Ⅱ度根分叉病变临床效果的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(2): 346-352. |
| [9] | 李婧宜,王赛楠,董艳梅. 非甾体类抗炎药对人牙髓细胞的抗炎修复作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 24-29. |
| [10] | 陈颖怡,胡紫琪,惠甜倩,刘鹤. Zeste同源蛋白2增强子通过调节巨噬细胞趋化影响牙髓炎症反应[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 18-23. |
| [11] | 王佳莎,王培育,梁宇红. 利用近场微波系统检测不同方法干燥根管的效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6): 1124-1129. |
| [12] | 张倩莉,袁重阳,刘力,温世鹏,王晓燕. 胶原静电纺纳米纤维膜对人牙髓细胞生物学行为的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(1): 28-34. |
| [13] | 雷玥,杨颖婷,战园. 生物陶瓷材料在乳牙牙髓切断术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(1): 70-74. |
| [14] | 龙赟子,刘思毅,李稳,董艳梅. 生物活性玻璃盖髓剂的理化性质[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(5): 887-891. |
| [15] | 李爽,张清. 玷污层对新型三氧化矿物凝聚体根尖封闭性的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(3): 560-563. |
|
||