北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (5): 781-792. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.05.003
肾透明细胞癌中核蛋白1对阿昔替尼耐药的作用及机制
刘耘充,吴宗龙,葛力源,杜坦,吴雅倩,宋一萌,刘承*( ),马潞林*(
),马潞林*( )
)
- 北京大学第三医院泌尿外科, 北京 100191
Mechanism of nuclear protein 1 in the resistance to axitinib in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Yun-chong LIU,Zong-long WU,Li-yuan GE,Tan DU,Ya-qian WU,Yi-meng SONG,Cheng LIU*( ),Lu-lin MA*(
),Lu-lin MA*( )
)
- Department of Urology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
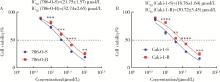
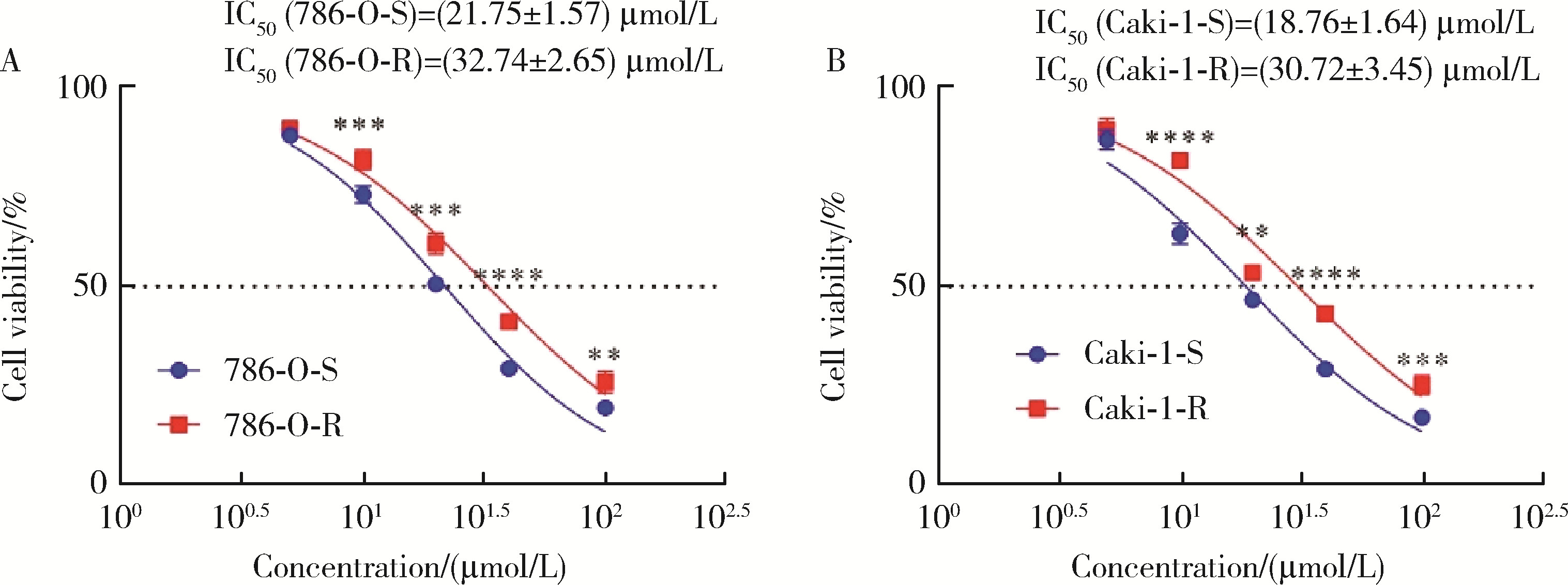
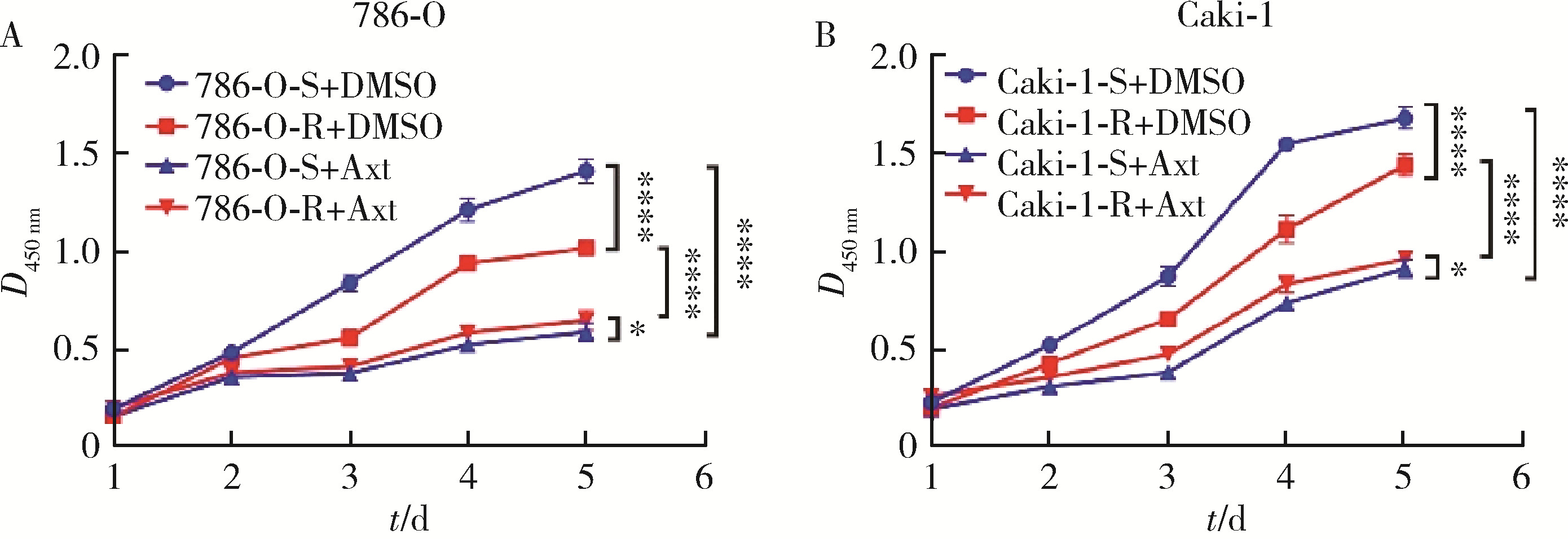
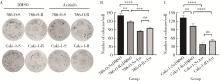
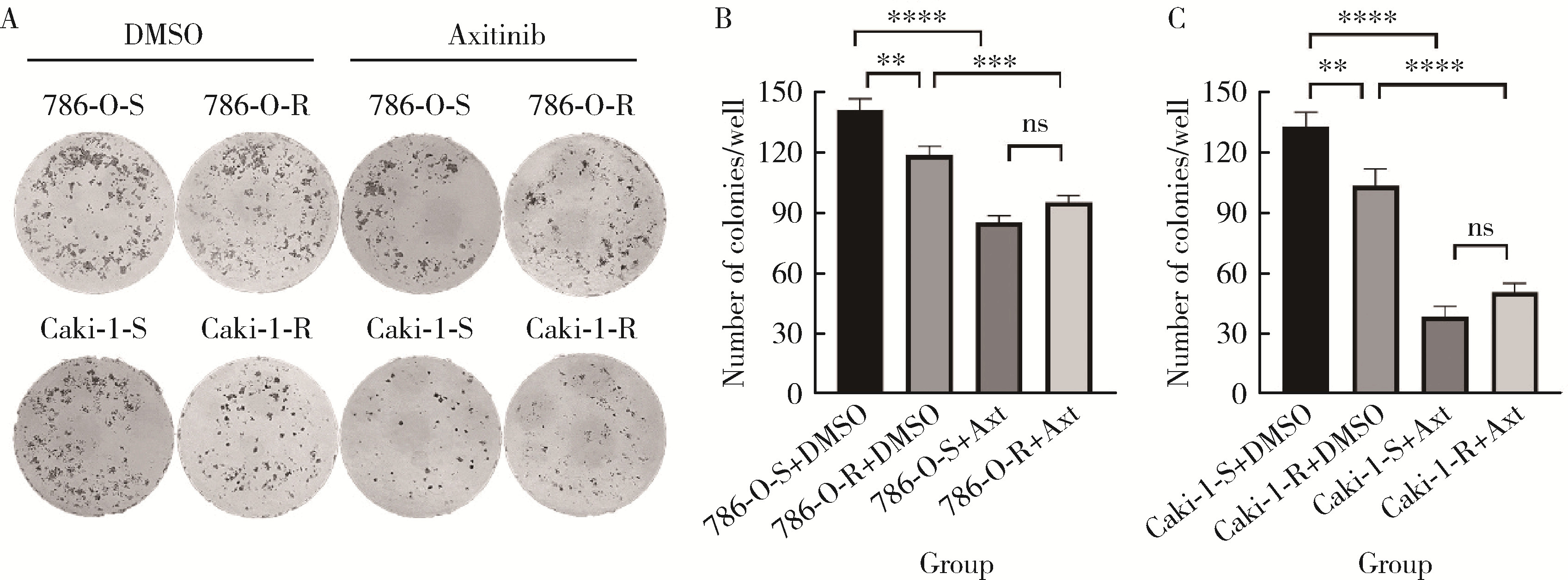
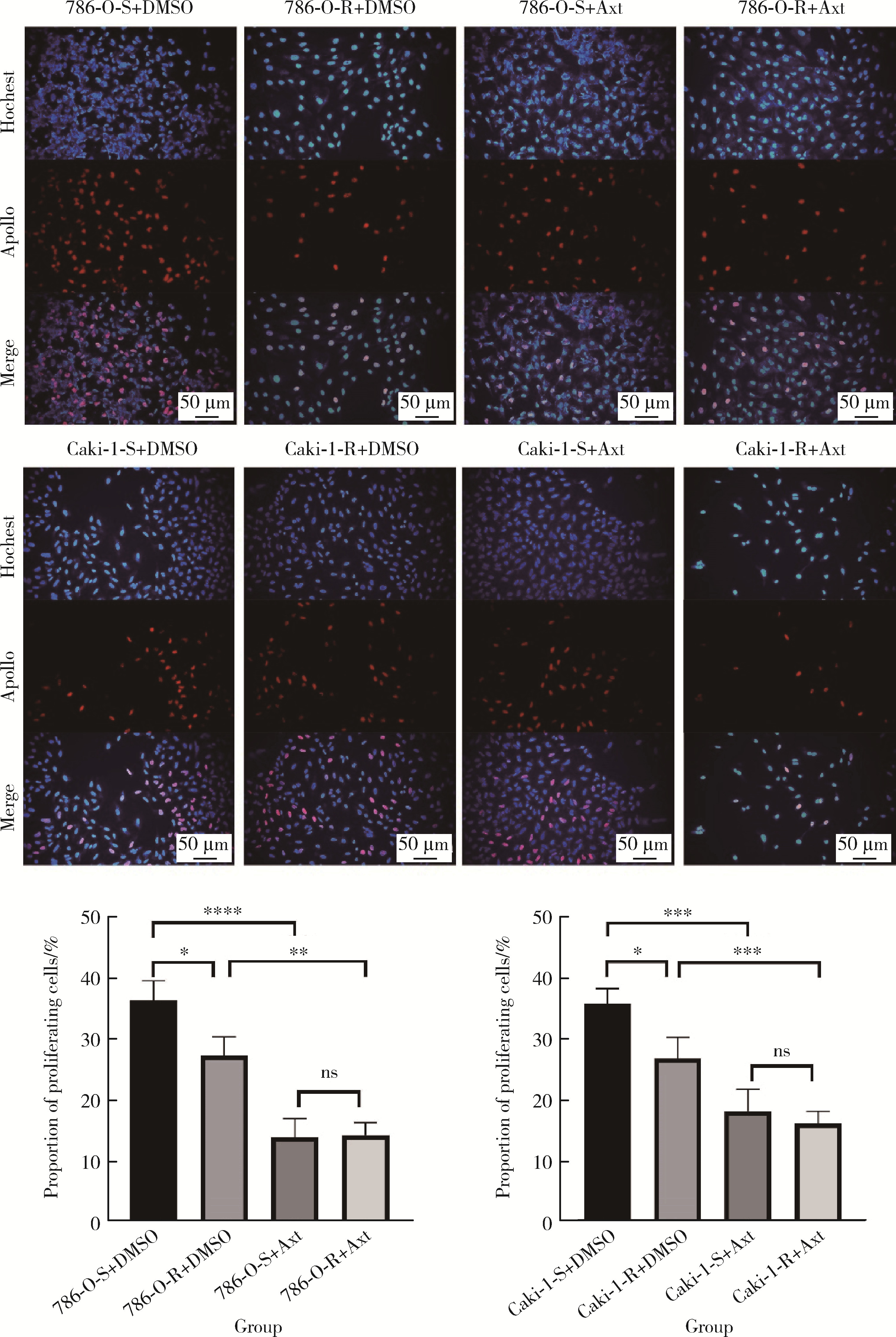
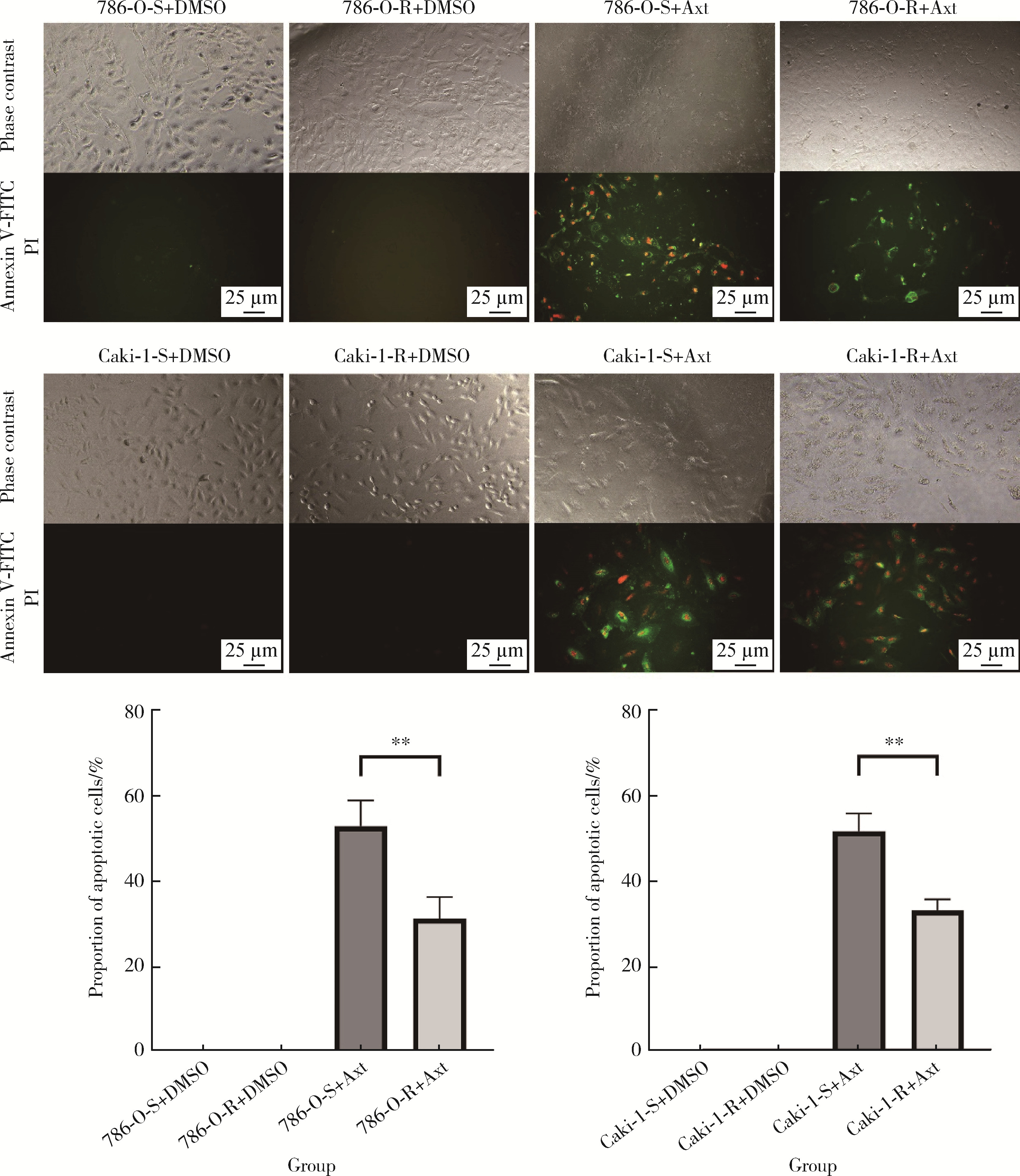
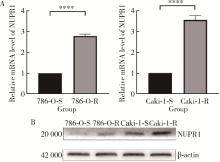
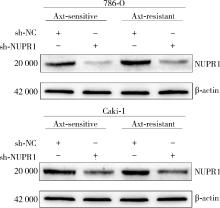
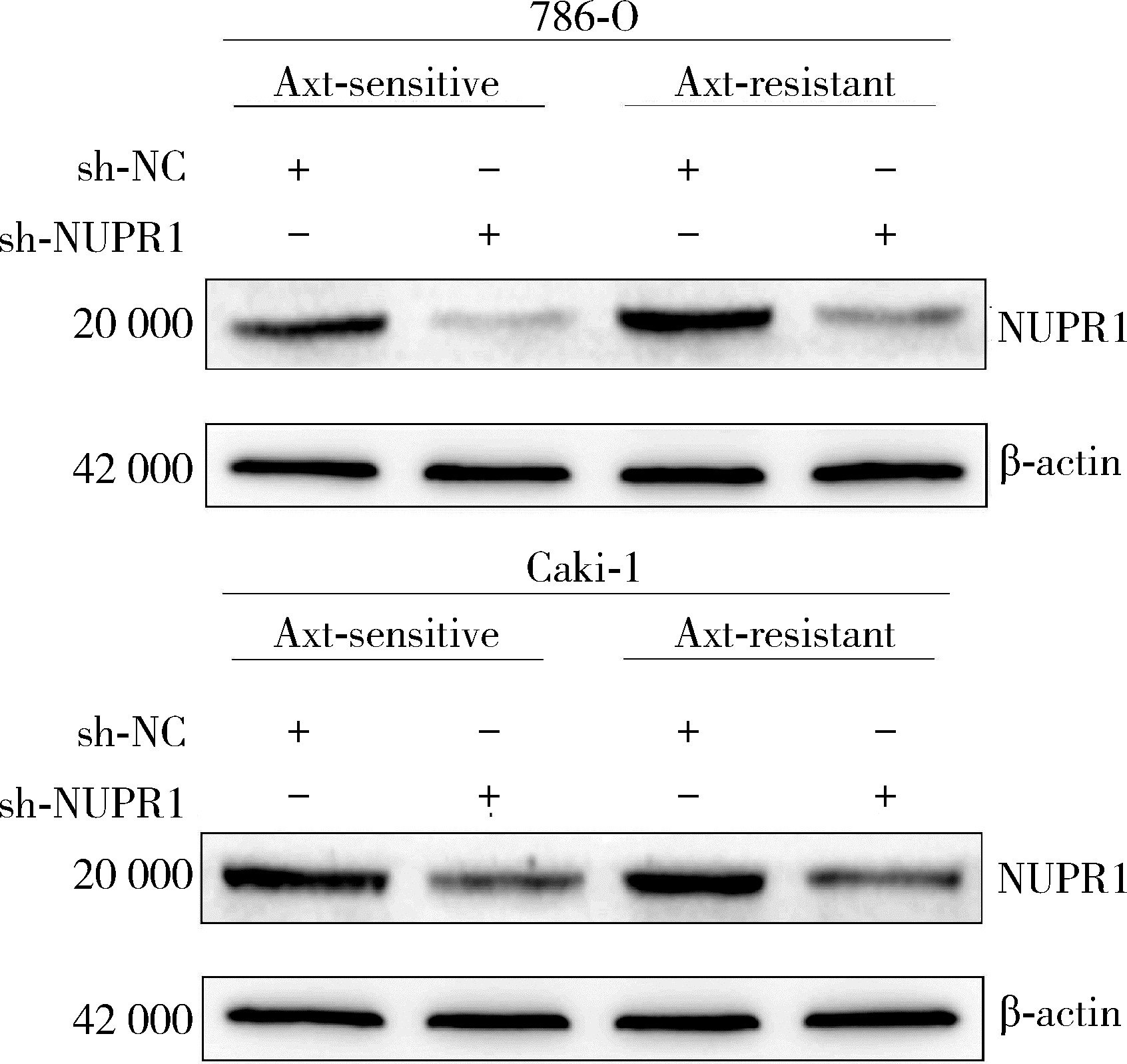
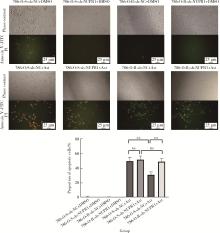
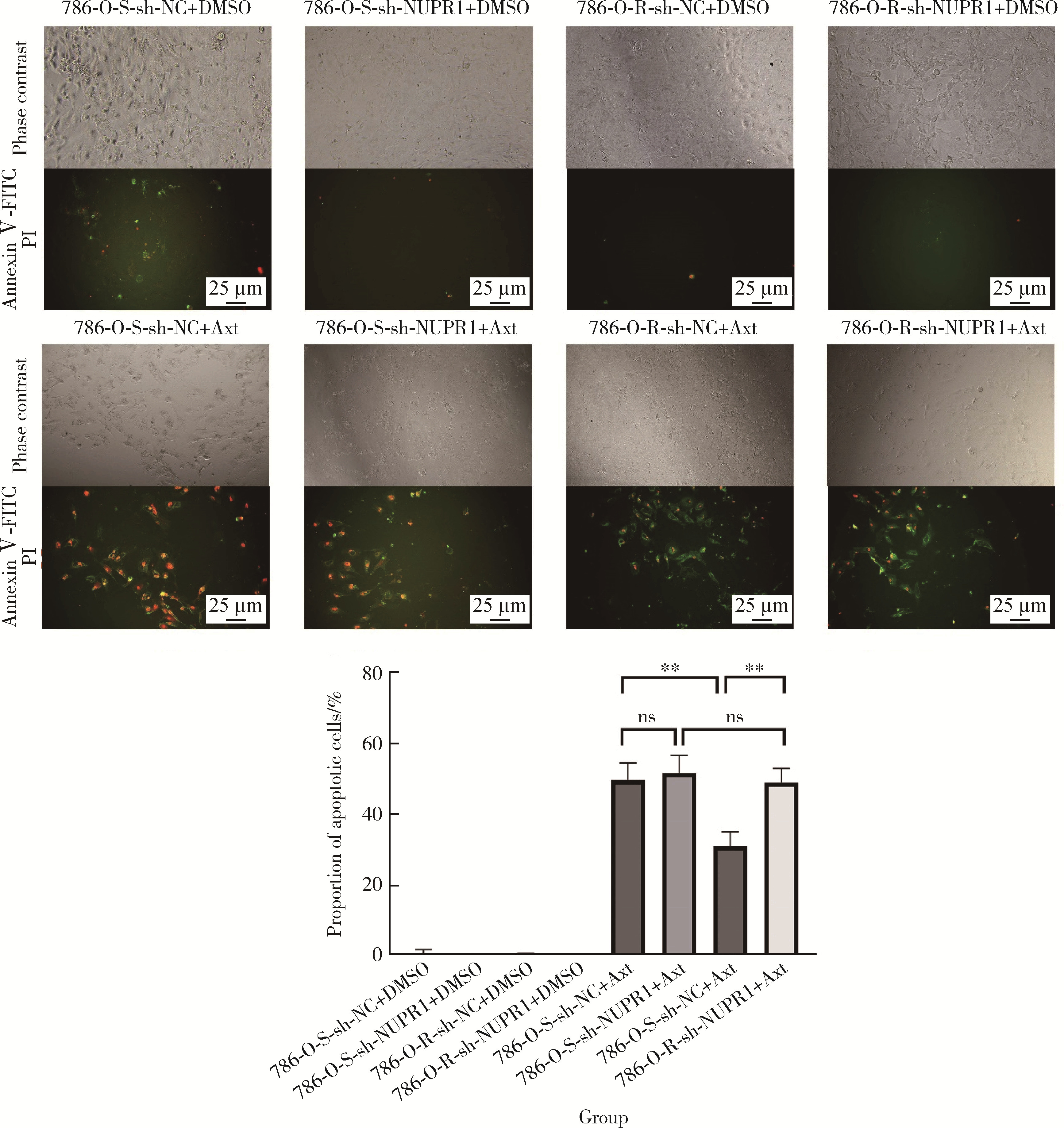
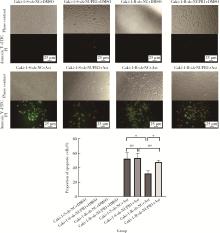
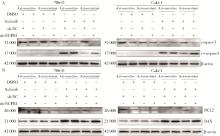
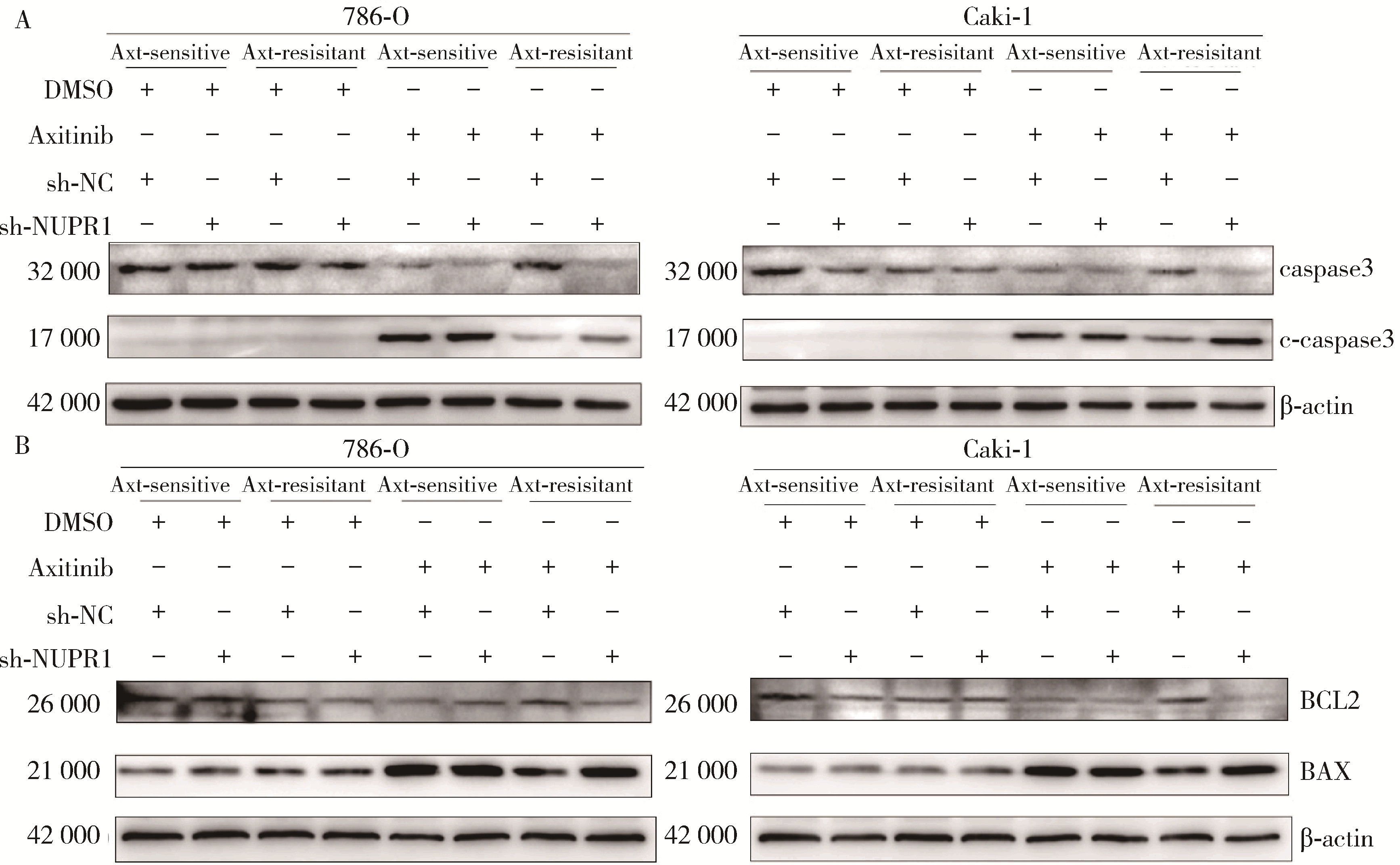
目的: 寻找肾透明细胞癌(clear cell renal cell carcinoma, ccRCC)对阿昔替尼耐药的潜在机制,以期拓展对阿昔替尼耐药的理解,便于设计更有针对性的治疗方案,提高患者的治疗效果及生存预后。方法: 通过摸索阿昔替尼对ccRCC细胞系786-O与Caki-1的半抑制浓度(half maximal inhibitory concentration, IC50),使用此浓度下的阿昔替尼体外反复刺激细胞30个周期, 构建对阿昔替尼耐药的细胞系,未被阿昔替尼处理过的细胞系为敏感细胞系,检测耐药细胞系及敏感细胞系在细胞增殖、细胞凋亡水平上的表型差异。通过转录组测序,在两耐药细胞系共同上调表达的差异基因内筛选出可能参与耐药过程的基因,通过实时荧光定量聚合酶链式反应(real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction, RT-qPCR)及蛋白质免疫印迹(Western blot, WB)验证耐药细胞系中靶基因的表达量。在基因表达谱交互分析(Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis,GEPIA)数据库中分析靶基因在ccRCC肿瘤及瘤旁组织的表达差异,在卡普兰-梅尔绘图(Kaplan-Meier Plotter,K-M Plotter)数据库中分析靶基因对ccRCC患者的预后影响。对耐药细胞系的靶基因使用慢病毒载体的核糖核酸干扰进行敲低后, 再次检测细胞表型差异。使用WB检测不同处理细胞系的细胞凋亡相关蛋白的水平,寻找可能导致耐药的分子通路。结果: 体外成功构建出对阿昔替尼耐药的ccRCC细胞系786-O-R与Caki-1-R,其较敏感细胞系的IC50显著升高(分别高出10.99 μmol/L,P < 0.01;11.96 μmol/L,P < 0.01)。细胞计数试剂盒-8(cell counting kit-8,CCK-8)、集落形成、5-乙炔基-2’-脱氧尿苷(5-ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine,EdU)实验结果显示耐药细胞系的增殖能力较敏感细胞系下降,但凋亡染色结果显示耐药细胞系的细胞凋亡水平显著降低(P < 0.01)。尽管对阿昔替尼耐药,但耐药细胞系在20 μmol/L阿昔替尼环境中无明显的新生肿瘤细胞产生。转录组测序筛选出核蛋白1(nuclear protein 1, NUPR1)基因,其核糖核酸(P < 0.000 1)及蛋白表达水平在耐药细胞系中显著上升。GEPIA数据库分析结果显示NUPR1在ccRCC肿瘤组织中显著高表达(P < 0.05);NUPR1高表达的ccRCC患者生存预后更差(P < 0.001)。细胞凋亡染色结果显示,敲低NUPR1后抑制了各耐药细胞系对阿昔替尼的抗凋亡能力(786-O,P < 0.01;Caki-1, P < 0.05)。WB结果显示,敲低NUPR1,被阿昔替尼处理后耐药细胞系的B细胞淋巴瘤(B-cell lymphoma-2,BCL2)蛋白水平下降,BCL2相关X蛋白(BCL2-associated X protein,BAX)水平增加,前体caspase3蛋白表达水平下降,剪切体c-caspase3水平上升。结论: ccRCC细胞系通过NUPR1 -BAX/ BCL2 -caspase3通路减少细胞凋亡,参与了对阿昔替尼的耐药过程。
中图分类号:
- R737.1
| 1 |
SiegelRL , MillerKD , WagleNS ,et al.Cancer statistics, 2023[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2023,73(1):17-48.
doi: 10.3322/caac.21763 |
| 2 |
MotzerRJ , BukowskiRM , FiglinRA ,et al.Prognostic nomogram for sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma[J].Cancer,2008,113(7):1552-1558.
doi: 10.1002/cncr.23776 |
| 3 | NerichV , HuguesM , PaillardMJ ,et al.Clinical impact of targeted therapies in patients with metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma[J].Onco Targets Ther,2014,7,365-374. |
| 4 |
PowlesT , PlimackER , SoulièresD ,et al.Pembrolizumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib monotherapy as first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (KEYNOTE-426): Extended follow-up from a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial[J].Lancet Oncol,2020,21(12):1563-1573.
doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30436-8 |
| 5 |
IncorvaiaL , MadoniaG , CorsiniLR ,et al.Challenges and advances for the treatment of renal cancer patients with brain metastases: From immunological background to upcoming clinical evidence on immune-checkpoint inhibitors[J].Crit Rev Oncol Hematol,2021,163,103390.
doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2021.103390 |
| 6 |
ShepardDR , GarciaJA .Toxicity associated with the long-term use of targeted therapies in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma[J].Expert Rev Anticancer Ther,2009,9(6):795-805.
doi: 10.1586/era.09.29 |
| 7 |
RiniBI , EscudierB , TomczakP ,et al.Comparative effectiveness of axitinib versus sorafenib in advanced renal cell carcinoma (AXIS): A randomised phase 3 trial[J].Lancet,2011,378(9807):1931-1939.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61613-9 |
| 8 | CaiW , CaiB , ZhouJ ,et al.Comparison of efficacy and safety among axitinib, sunitinib, and sorafenib as neoadjuvant therapy for renal cell carcinoma: A retrospective study[J].Cancer Commun (Lond),2019,39(1):56. |
| 9 |
ZhouX , HouW , GaoL ,et al.Synergies of antiangiogenic therapy and immune checkpoint blockade in renal cell carcinoma: From theoretical background to clinical reality[J].Front Oncol,2020,10,1321.
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01321 |
| 10 |
GulatiS , LabakiC , KarachaliouGS ,et al.First-line treatments for metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma: An ever-enlarging landscape[J].Oncologist,2022,27(2):125-134.
doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyab056 |
| 11 |
ChoueiriTK , MotzerRJ , RiniBI ,et al.Updated efficacy results from the JAVELIN Renal 101 trial: First-line avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma[J].Ann Oncol,2020,31(8):1030-1039.
doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.04.010 |
| 12 |
BuchlerT , BortlicekZ , PoprachA ,et al.Outcomes for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma achieving a complete response on targeted therapy: A registry-based analysis[J].Eur Urol,2016,70(3):469-475.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.12.031 |
| 13 |
BuchlerT , PoprachA , BortlicekZ ,et al.Outcomes of patients with long-term treatment response to vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy for metastatic renal cell cancer[J].Clin Genitourin Cancer,2017,15(6):e1047-e1053.
doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2017.06.006 |
| 14 |
LuS , SteinJE , RimmDL ,et al.Comparison of biomarker moda-lities for predicting response to PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint blockade: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J].JAMA Oncol,2019,5(8):1195-1204.
doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.1549 |
| 15 |
BallesterosP , ChamorroJ , Román-GilMS ,et al.Molecular mechanisms of resistance to immunotherapy and antiangiogenic treatments in clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J].Cancers (Basel),2021,13(23):5981.
doi: 10.3390/cancers13235981 |
| 16 |
XiangY , ZhengG , ZhongJ ,et al.Advances in renal cell carcinoma drug resistance models[J].Front Oncol,2022,12,870396.
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.870396 |
| 17 | HeW , ChengF , ZhengB ,et al.NUPR1 is a novel potential biomarker and confers resistance to sorafenib in clear cell renal cell carcinoma by increasing stemness and targeting the PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway[J].Aging (Albany NY),2021,13(10):14015-14038. |
| 18 |
GotinkKJ , VerheulHM .Anti-angiogenic tyrosine kinase inhibitors: What is their mechanism of action?[J].Angiogenesis,2010,13(1):1-14.
doi: 10.1007/s10456-009-9160-6 |
| 19 |
EllisLM , HicklinDJ .VEGF-targeted therapy: Mechanisms of anti-tumour activity[J].Nat Rev Cancer,2008,8(8):579-591.
doi: 10.1038/nrc2403 |
| 20 |
ChenY , LuZ , QiC ,et al.N(6)-methyladenosine-modified TRAF1 promotes sunitinib resistance by regulating apoptosis and angiogenesis in a METTL14-dependent manner in renal cell carcinoma[J].Mol Cancer,2022,21(1):111.
doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01549-1 |
| 21 | SakaiI , MiyakeH , FujisawaM .Acquired resistance to sunitini-bin human renal cell carcinoma cells is mediated by constitutive activation of signal transduction pathways associated with tumour cell proliferation[J].BJU Int,2013,112(2):211-220. |
| 22 |
AzamF , MehtaS , HarrisAL .Mechanisms of resistance to antiangiogenesis therapy[J].Eur J Cancer,2010,46(8):1323-1332.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2010.02.020 |
| 23 |
HuangH , ZhangJ , JiangP ,et al.FXR1 facilitates axitinib resistance in clear cell renal cell carcinoma via regulating KEAP1/Nrf2 signaling pathway[J].Anticancer Drugs,2023,34(2):248-256.
doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000001416 |
| 24 |
MalloGV , FiedlerF , CalvoEL ,et al.Cloning and expression of the rat p8 cDNA, a new gene activated in pancreas during the acute phase of pancreatitis, pancreatic development, and regeneration, and which promotes cellular growth[J].J Biol Chem,1997,272(51):32360-32369.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.51.32360 |
| 25 |
EmmaMR , IovannaJL , BachvarovD ,et al.NUPR1, a new target in liver cancer: implication in controlling cell growth, migration, invasion and sorafenib resistance[J].Cell Death Dis,2016,7(6):e2269.
doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.175 |
| 26 |
MartinTA , LiAX , SandersAJ ,et al.NUPR1 and its potential role in cancer and pathological conditions[J].Int J Oncol,2021,58(5):21.
doi: 10.3892/ijo.2021.5201 |
| 27 |
Santofimia-CastañoP , LanW , BintzJ ,et al.Inactivation of NUPR1 promotes cell death by coupling ER-stress responses with necrosis[J].Sci Rep,2018,8(1):16999.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35020-3 |
| 28 |
MaddenE , LogueSE , HealySJ ,et al.The role of the unfolded protein response in cancer progression: From oncogenesis to chemoresistance[J].Biol Cell,2019,111(1):1-17.
doi: 10.1111/boc.201800050 |
| 29 |
HetzC .The unfolded protein response: Controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond[J].Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,2012,13(2):89-102.
doi: 10.1038/nrm3270 |
| 30 |
KowalczykT , SitarekP , SkałaE ,et al.Induction of apoptosis by in vitro and in vivo plant extracts derived from Menyanthes trifoliata L. in human cancer cells[J].Cytotechnology,2019,71(1):165-180.
doi: 10.1007/s10616-018-0274-9 |
| 31 |
KluckRM , Bossy-WetzelE , GreenDR ,et al.The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria: A primary site for Bcl-2 regulation of apoptosis[J].Science,1997,275(5303):1132-1136.
doi: 10.1126/science.275.5303.1132 |
| [1] | 蔡天玉,朱振鹏,徐纯如,吉星,吕同德,郭振可,林健. 成纤维细胞生长因子受体2在肾透明细胞癌中的表达及意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 628-635. |
| [2] | 左美妮,杜依青,于路平,戴翔,徐涛. 代谢综合征与肾透明细胞癌患者预后的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 636-643. |
| [3] | 耿良,吕静,范敬. 肺瘤平膏联合环磷酰胺化疗对肺癌的抑瘤作用和酸性微环境的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(2): 247-253. |
| [4] | 王昊,陈亮,叶小云. 雷公藤甲素对TM4细胞氧化应激及PI3K/AKT通路的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(4): 607-612. |
| [5] | 王玉洁,郭向阳,王军. 重复异丙酚麻醉对新生大鼠海马细胞凋亡及远期学习记忆能力的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(2): 310-314. |
| [6] | 杨光,程庆砾,李春霖,贾雅丽,岳文,裴雪涛,刘洋,赵佳慧,杜婧,敖强国. 高糖减弱肾组织干细胞条件培养液对缺氧损伤肾小管上皮细胞的修复作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(1): 125-130. |
| [7] | 曹珮,姜学军,席志军. 舒尼替尼通过抑制Akt/mTOR信号通路诱导肾癌细胞自噬[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(4): 584-589. |
| [8] | 李刚,张洪宪,王云鹏,张径,洪锴,田晓军,马潞林. 间苯三酚对大鼠肾缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(5): 743-748. |
| [9] | 郑少强, 陈雪, 王雅杰, 安立新. 七氟烷对幼鼠脑细胞凋亡和远期学习记忆功能的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(4): 674-678. |
| [10] | 温静,程庆砾,马强,齐云,赵佳慧,杜婧,王小丹,刘胜,李美花,张晓英. 肾组织干细胞对人肾小管上皮细胞损伤修复的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(4): 619-. |
| [11] | 杨轩, 袁栋栋, 姜学军, 席志军. 顺铂通过诱导膀胱癌细胞自噬促进细胞凋亡[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(2): 221-. |
| [12] | 刘慧琳, 田勍, 洪天配, 刘桂花, 潘欢, 王海宁, 高洪伟. 脓毒症患者中血清程序化细胞死亡因子5水平的变化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(2): 238-. |
| [13] | 罗道升, 米其武, 孟祥军, 高勇, 戴宇平, 邓春华. 外磁场协同卟啉-葡聚糖磁性纳米微粒的光动力学对人膀胱癌细胞的杀伤作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(4): 524-537. |
| [14] | 潘云, 李向培, 孙甲峰, 王俐, 陈竹, 厉小梅, 陶金辉, 钱龙, 张宏. 糖皮质激素对系统性红斑狼疮患者CD4+CD25+CD127 dim/-T淋巴细胞GITR表达及凋亡的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(2): 215-220. |
| [15] | 郭健, 聂海瑜, 王海芳, 贾光. 不同修饰多壁碳纳米管诱导的细胞毒性及内质网相关基因表达[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2011, 43(3): 342-347. |
|
||