北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (3): 562-568. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.03.021
99mTc-DTPA经脑细胞外间隙给药后的动态分布及消除规律
邹晶1,2,3, 高天姿1,3, 汪洋1,3, 任蒙蒙1,2,3, 刘东阳4, 龙仁1,2,3, 成雨萌1,3,5, 刘萌6, 徐正仁7, 谢肇恒1,3, 吕鹏宇8, 袁兰1,2,3,*( ), 韩鸿宾1,3,5,*(
), 韩鸿宾1,3,5,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学医学部医学技术研究院, 北京 100191
2. 北京大学药学院化学生物学系, 北京 100191
3. 北京市磁共振成像设备与技术重点实验室, 北京 100191
4. 北京大学第三医院药物临床试验机构, 北京 100191
5. 北京大学第三医院放射科, 北京 100191
6. 北京大学第一医院核医学科, 北京 100034
7. 北京大学药学院天然药物学系, 北京 100191
8. 北京大学工学院力学与工程科学系, 北京 100871
Dynamic distribution and clearance of 99mTc-DTPA in brain extracellular space
Jing ZOU1,2,3, Tianzi GAO1,3, Yang WANG1,3, Mengmeng REN1,2,3, Dongyang LIU4, Ren LONG1,2,3, Yumeng CHENG1,3,5, Meng LIU6, Zhengren XU7, Zhaoheng XIE1,3, Pengyu LV8, Lan YUAN1,2,3,*( ), Hongbin HAN1,3,5,*(
), Hongbin HAN1,3,5,*( )
)
- 1. Institute of Medical Technology, Peking University Health Science Center, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Chemical Biology, Peking University School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Beijing 100191, China
3. Beijing Key Lab of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Device and Technique, Beijing 100191, China
4. Peking University Third Hospital Drug Clinical Trial Institute, Beijing 100191, China
5. Department of Radiology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
6. Department of Nuclear Medicine, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
7. Department of Natural Medicines, Peking University School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Beijing 100191, China
8. Department of Mechanics and Engineering Science, Peking University School of Engineering, Beijing 100871, China
摘要:
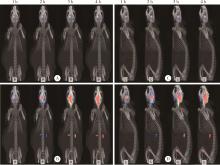
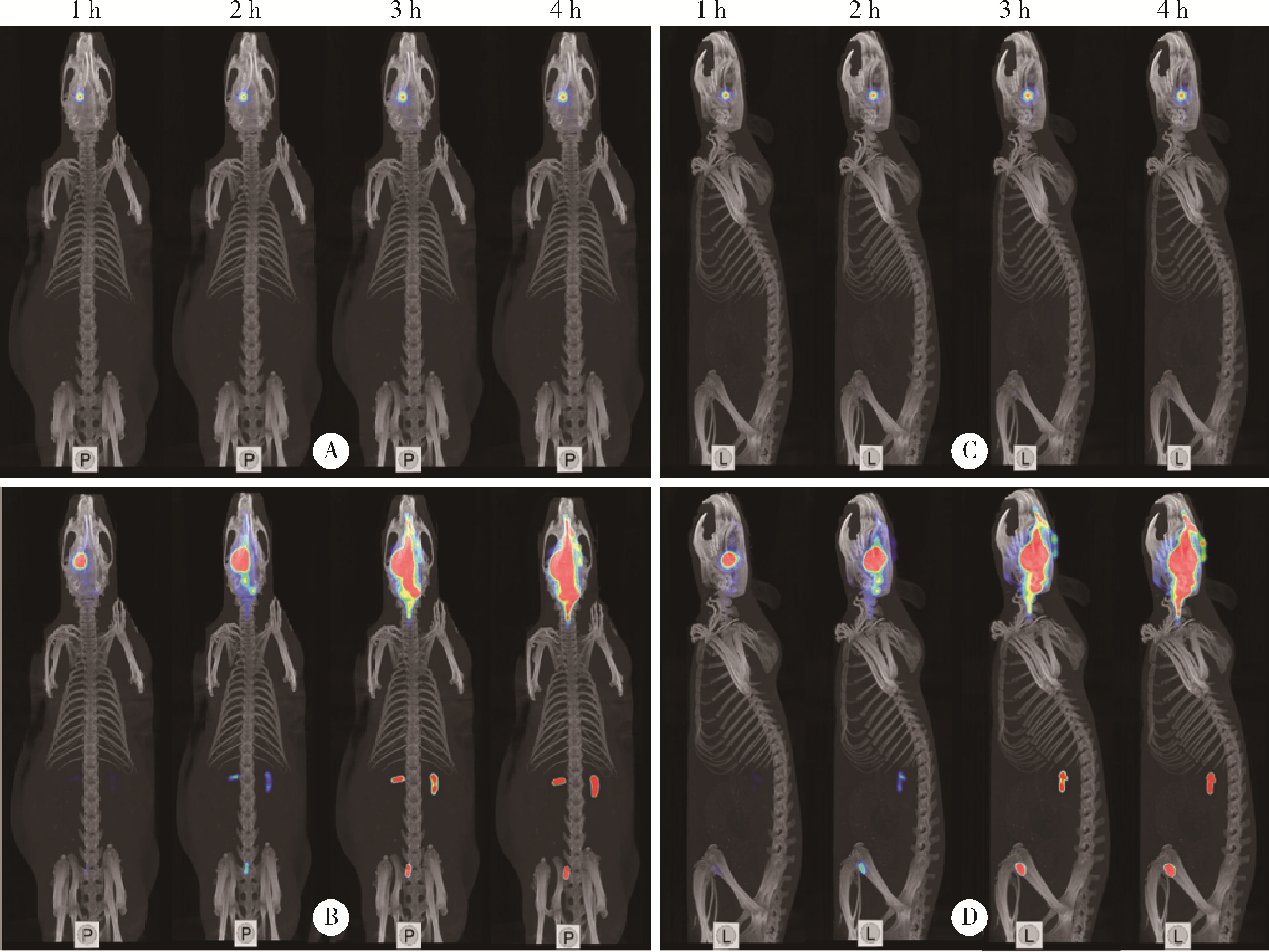
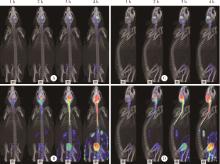
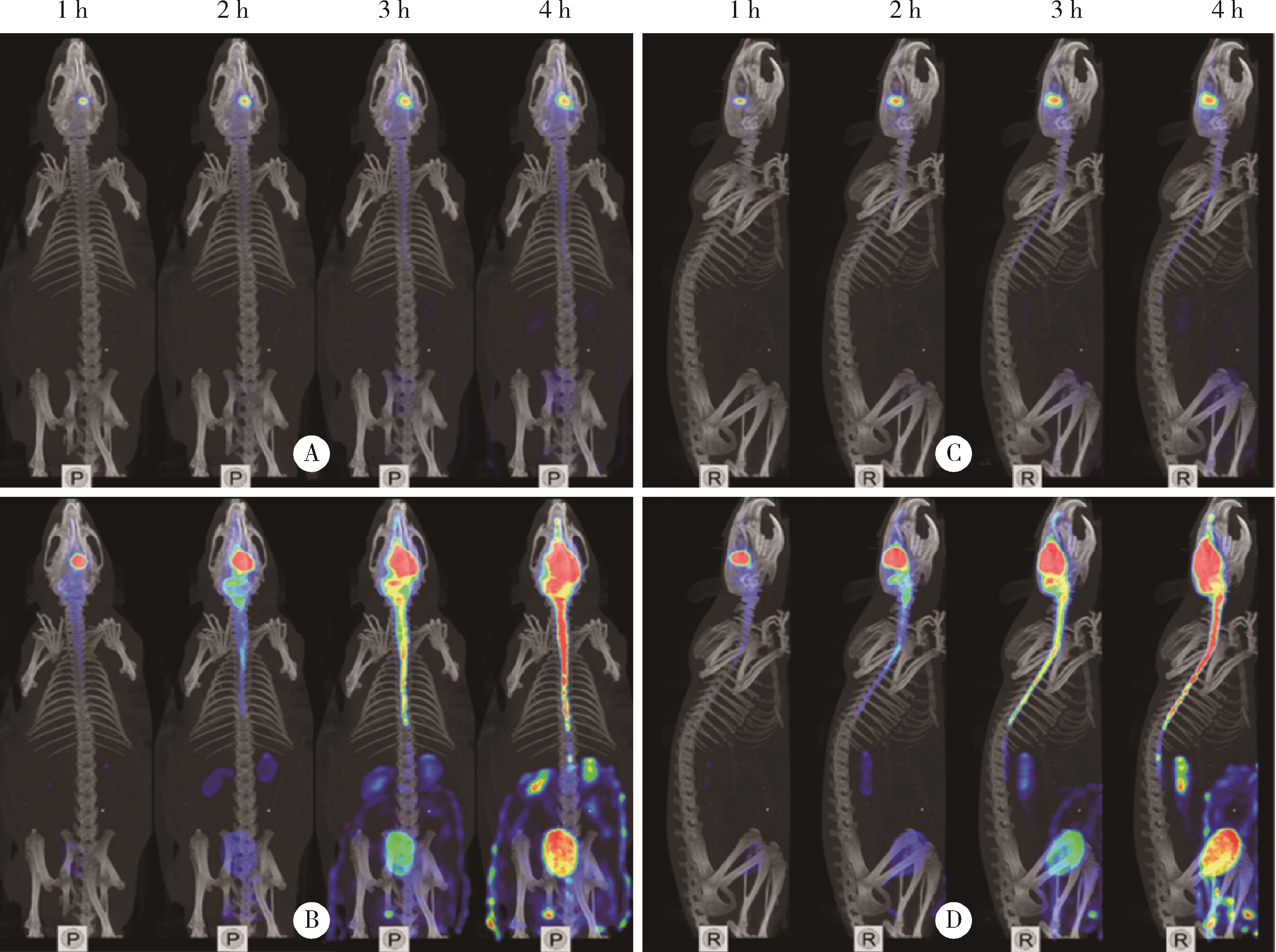
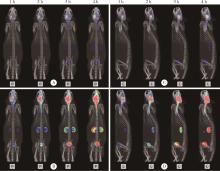
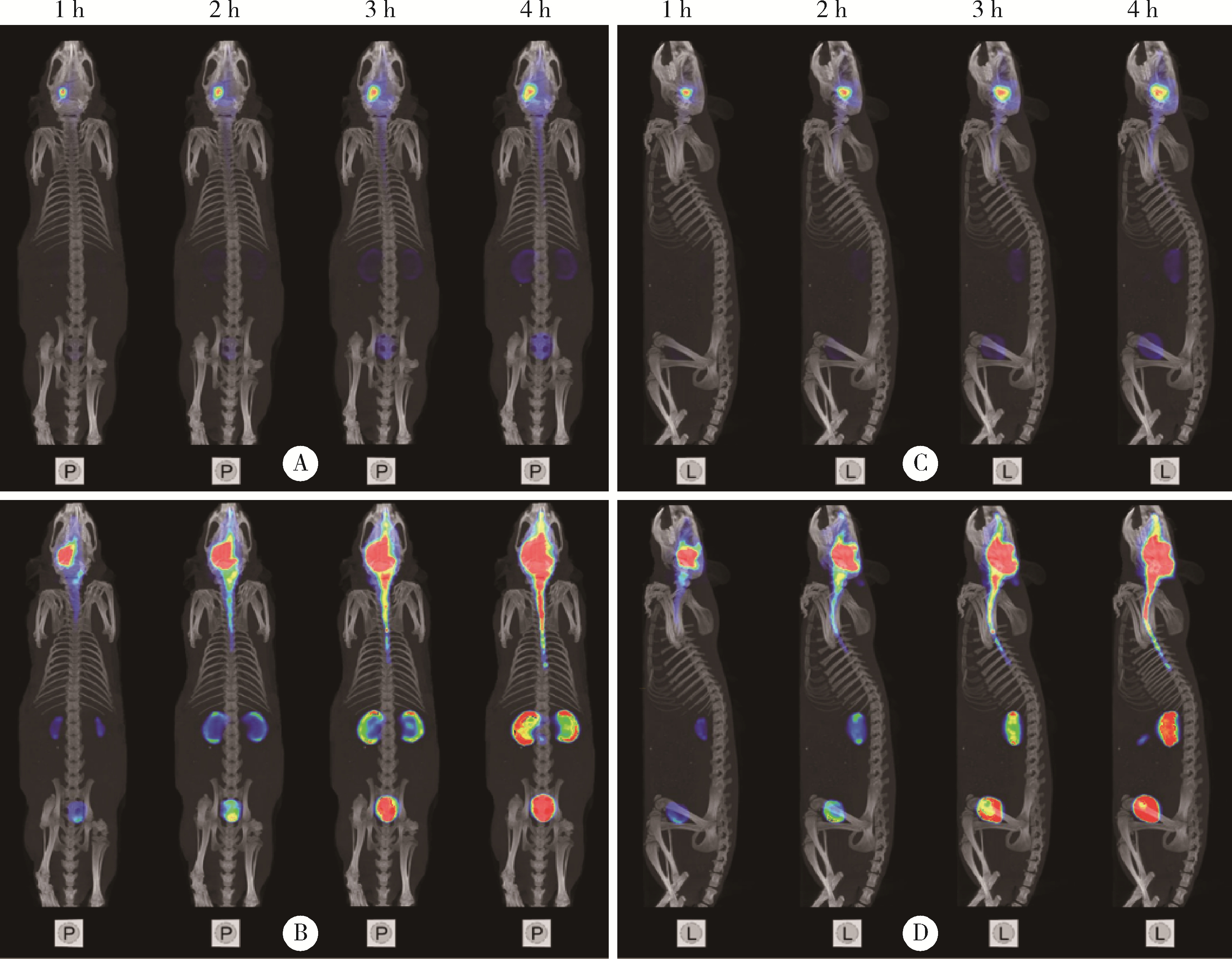
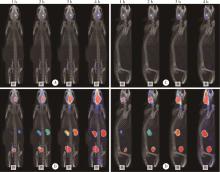
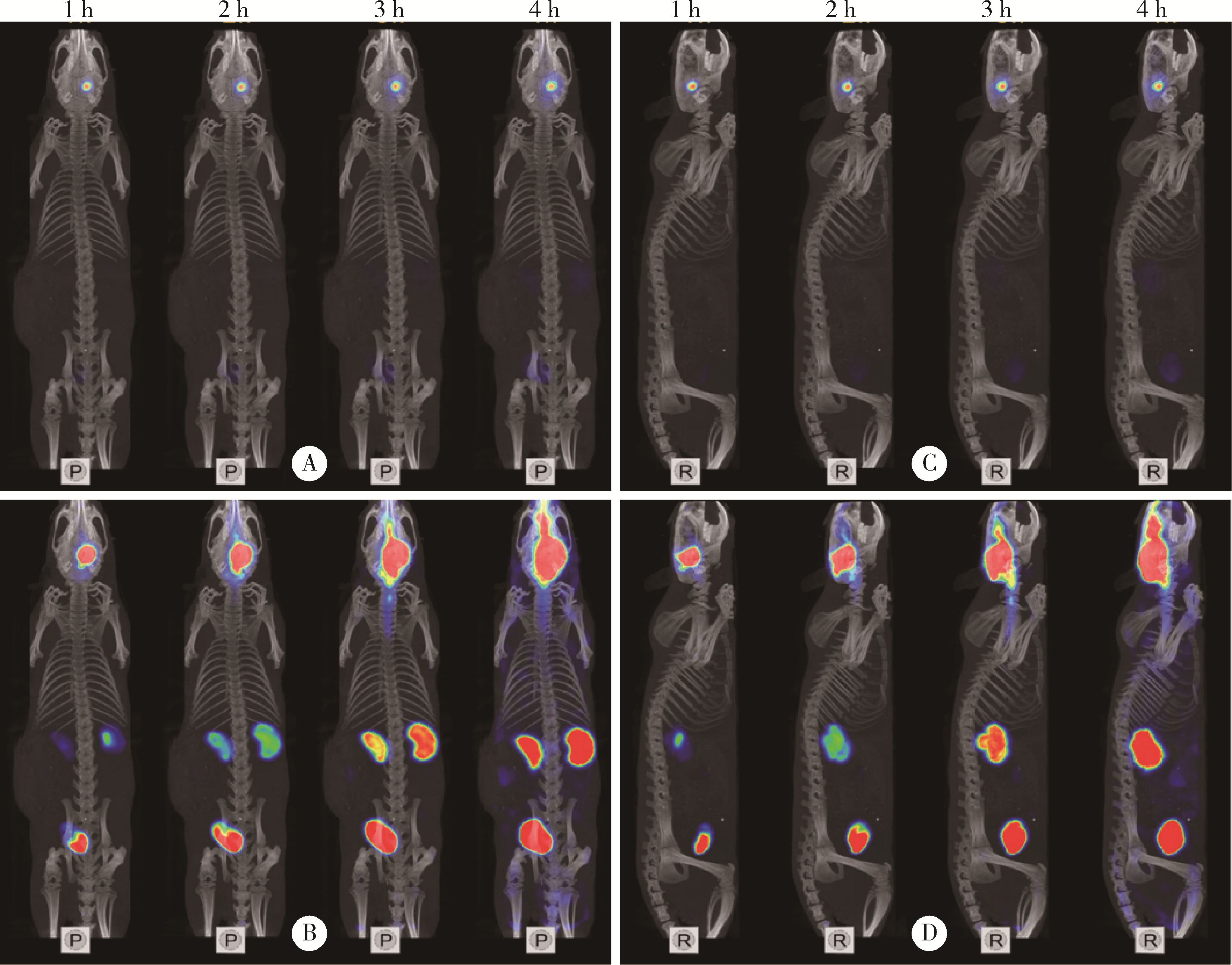
目的: 探索 99mTc-二乙基三胺五乙酸(99mTc-DTPA)经脑细胞外间隙(extracellular space, ECS)途径在不同脑区给药后,正常成年大鼠脑内及全身的药物动态分布及消除规律。方法: 使用鼠脑立体定位仪将SD大鼠固定,将体积为2 μL、放射性活度为3.7 MBq (100 μCi) 的 99mTc-DTPA分别注入大鼠的尾状核区和丘脑区,使用小动物单光子发射型计算机断层扫描/计算机断层扫描(single photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography, SPECT/CT)在不同时间显像,连续观察示踪剂的动态分布和消除规律。生物体内分布实验是在大鼠丘脑区和尾状核区注入 99mTc-DTPA,4 h后处死大鼠,收集血液、尿液,取大脑、小脑、心、肝、脾、肺、肾,称重后用γ计数器测定其放射性强度。结果: 99mTc-DTPA经脑ECS途径给药后,放射性分布浓聚于脑、肾和膀胱,左侧尾状核区给药的示踪剂优先向右侧小脑引流,右侧尾状核区给药的示踪剂优先向左侧小脑引流,尾状核区给药存在“对侧小脑优势引流”现象,而丘脑区给药后会优先向同侧小脑引流。给药4 h后,尿液、小脑和大脑出现高放射性摄取,其次是血液和肾,心、肝、脾、肺的放射性摄取值均较低,主要经泌尿系统排泄。结论: 经脑ECS途径给药是一种极具前景的给药方法,但不同脑区经该途径给药后的动态分布与消除规律存在明显差异,本研究进一步拓展了“脑分区”的内容与意义,也为未来经脑ECS途径给药进行脑病治疗和新药研发提供了理论基础。
中图分类号:
- R817.4
| 1 |
doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2009.07.030 |
| 2 |
doi: 10.1016/j.nec.2017.05.012 |
| 3 |
doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2018.07.013 |
| 4 |
doi: 10.1007/s13311-017-0520-4 |
| 5 |
doi: 10.2176/nmc.ra.2016-0071 |
| 6 |
doi: 10.1097/00001756-200212200-00005 |
| 7 |
doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2015.12.007 |
| 8 |
赵越, 李昀倩, 李怀业, 等. 荧光及磁示踪法观测脑组织液的引流分区特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49 (2): 303- 309.
|
| 9 |
doi: 10.1007/s00723-015-0670-7 |
| 10 |
doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(95)00039-9 |
| 11 |
doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2009.10.012 |
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
doi: 10.14336/AD.2018.1206 |
| 14 |
doi: 10.12659/MSM.903010 |
| 15 |
doi: 10.14336/AD.2017.1115 |
| 16 |
doi: 10.14336/AD.2017.0415 |
| 17 |
李艳玲, 彭本君. 99mTc-DTPA肾动态显像对多囊肾病患者诊断价值分析[J]. 泰山医学院学报, 2019, 40 (10): 752- 753.
|
| [1] | 钟鹏, 胡晓丹, 王振洲. 大鼠脑创伤半暗带光学相干断层血管造影及微血管密度定量[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(2): 262-266. |
| [2] | 李晋娜,许丽娜,李敏,宋怡,张静,贾龙斌. 急性脑梗死患者血清BDNF、IL-18、hs-CRP水平与血管性认知障碍的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 708-714. |
| [3] | 龙仁, 毛鑫, 高天姿, 解倩, 谈瀚博, 李子寅, 韩鸿宾, 袁兰. 熊果酸改善精神分裂症小鼠脱髓鞘和脑组织间液引流紊乱[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 487-494. |
| [4] | 刘颖,霍然,徐慧敏,王筝,王涛,袁慧书. 磁共振血管壁成像评估颈动脉中重度狭窄患者斑块特征与脑血流灌注的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 646-651. |
| [5] | 范常锋,黄亚平,李霞,陈芸,李真,乔淑冬. 以发作性体位性视物双影为前期症状的后循环卒中1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 762-765. |
| [6] | 于欢,杨若彤,王斯悦,吴俊慧,王梦莹,秦雪英,吴涛,陈大方,武轶群,胡永华. 2型糖尿病患者使用二甲双胍与缺血性脑卒中发病风险的队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 456-464. |
| [7] | 叶珊,金萍萍,张楠,邬海博,石林,赵强,杨坤,袁慧书,樊东升. 肌萎缩侧索硬化患者认知功能改变与脑皮层厚度分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1158-1162. |
| [8] | 陈素华,杨军,陈新,杨辰龙,孙建军,林国中,于涛,杨欣,韩芸峰,吴超,司雨,马凯明. 大型、巨大型上矢状窦中后1/3侵犯颅外复发脑膜瘤的手术治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 1006-1012. |
| [9] | 陆林,刘晓星,袁凯. 中国脑科学计划进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 791-795. |
| [10] | 杜燕燕,王健,贺兰,季丽娜,徐樨巍. 儿童川崎病合并轻微脑炎/脑病伴可逆性胼胝体压部病变综合征1例并文献复习[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 756-761. |
| [11] | 杨若彤,王梦莹,李春男,于欢,王小文,吴俊慧,王斯悦,王伽婷,陈大方,吴涛,胡永华. 缺血性脑卒中全基因组关联研究提示阳性基因位点与睡眠行为的交互作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 412-420. |
| [12] | 孟广艳,张筠肖,张渝昕,刘燕鹰. IgG4相关性疾病中枢神经系统受累的临床特点分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1043-1048. |
| [13] | 任国勇,吴雪梅,李颖,李婕妤,孙伟平,黄一宁. 大血管闭塞性脑卒中亚急性期磁敏感血管征的表现[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1133-1138. |
| [14] | 白鹏,王涛,周阳,陶立元,李刚,李正迁,郭向阳. 不同转流标准对颈动脉内膜切除术后脑梗死的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1144-1151. |
| [15] | 苗欣,黄红拾,胡晓青,时会娟,任爽,敖英芳. 膝关节前交叉韧带断裂后单腿位置觉测试时脑电功率谱的变化特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 871-876. |
|
||