北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 803-807. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.04.028
低龄、低体重儿童肾移植2例
赵兆1, 张维宇1, 杨文博1, 张勇杰1, 张晓鹏1, 赵慧颖2, 周刚2, 王强1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学人民医院泌尿外科,北京大学应用碎石技术研究所,北京 100044
2. 北京大学人民医院重症医学科,北京 100044
Kidney transplantation in low-age, low-weight children: A report of two cases
Zhao ZHAO1, Weiyu ZHANG1, Wenbo YANG1, Yongjie ZHANG1, Xiaopeng ZHANG1, Huiying ZHAO2, Gang ZHOU2, Qiang WANG1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Urology, Peking University People' s Hospital, Institute of Applied Lithotripsy Technology, Peking University, Beijing 100044, China
2. Department of Critical Care Medicine, Peking University People' s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
摘要:
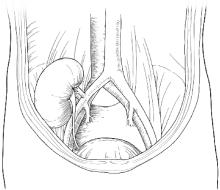
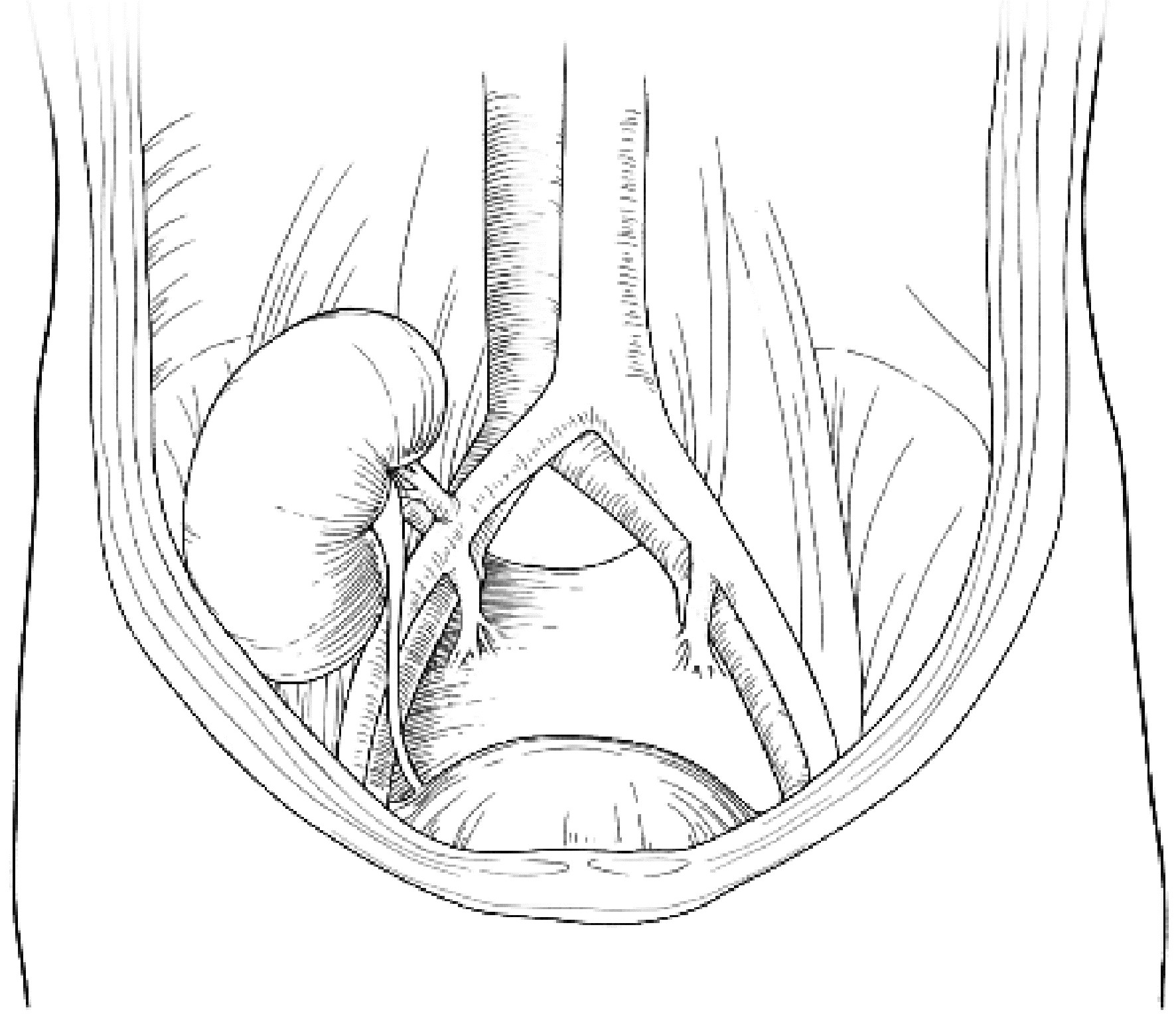
肾移植是儿童终末期肾病的最佳治疗方法,能够改善患儿生长发育,提高患儿生活质量,但是,对于低龄(< 5岁)、低体重(< 15 kg)儿童的肾移植,因患儿血管纤细、手术空间狭小、围术期管理复杂等原因,仍面临很多临床困难。本文报道了北京大学人民医院2例低龄、低体重儿童肾移植:病例1,男,2岁3个月,体重8.8 kg;病例2,女,3岁8个月,体重11.25 kg。均采用经腹膜外途径,供肾动脉和静脉分别与髂总动脉、髂总静脉行端侧吻合,输尿管与膀胱以隧道法吻合,手术过程顺利,术后患儿肾功能恢复良好,均未出现血栓、输尿管狭窄或腹腔间隔室综合征等并发症。结合既往低龄、低体重儿童肾移植的文献报道,以及目前此类肾移植的全球发展现状,讨论低龄、低体重儿童肾移植的临床管理思路,探讨腹腔内途径与腹膜外途径两种手术策略的选择。本中心采用经腹膜外途径完成的2例手术,取得了良好的疗效,希望能为低龄、低体重患儿肾移植提供单中心经验。
中图分类号:
- R726.9
| 1 |
United States Renal Data System. 2023 USRDS Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States[R]. Bethesda: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health, US Department of Health and Human Services, 2023.
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
杨文博, 余磊, 张维宇, 等. 带线输尿管支架自排技术在肾移植受者中的效果及安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56 (4): 656- 660.
doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.04.018 |
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
中华医学会器官移植学分会. 儿童肾移植技术操作规范(2019版)[J]. 器官移植, 2019, 10 (5): 499- 504.
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
杨文博, 赖世聪, 张晓鹏, 等. 儿童肾移植受者髂内动脉袖片技术完成儿童供肾移植动脉成形术12例[J]. 中华移植杂志(电子版), 2022, 16 (6): 365- 368.
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
|
| 28 |
朱兰, 郭志良, 赵大强, 等. 婴幼儿肾移植疗效及预后分析[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2023, 103 (38): 3010- 3016.
|
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
|
| 31 |
|
| 32 |
|
| [1] | 李宗瀚, 黄洋阅, 李宁, 李明磊, 宋宏程, 张潍平, 刘超. 国产单孔蛇形臂机器人手术系统在儿童肾盂成形术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(4): 662-665. |
| [2] | 张启鸣, 陈泽波, 田雨, 潘大猛, 刘磊, 张洪宪, 赵磊, 张树栋, 马潞林, 侯小飞. 机器人辅助腹腔镜移植肾切除术经验总结[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(4): 666-669. |
| [3] | 左超, 王国立, 杨昆霖, 车新艳, 孟一森, 张凯. 前列腺体积不同的患者经尿道光纤铥激光前列腺剜除术的有效性及安全性比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(4): 711-716. |
| [4] | 张依航, 蔡珊, 陈子玥, 刘云飞, 党佳佳, 师嫡, 李佳欣, 黄天彧, 宋逸. 基于RE-AIM框架儿童青少年近视与肥胖共病综合干预实施性研究结局指标的构建[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(3): 436-441. |
| [5] | 唐孟利, 刘扬, 秦冉, 郭欣, 李宏田. 我国10省幼儿园5~6岁儿童近视和近视前期流行特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(3): 442-447. |
| [6] | 刘光旭, 张良, 赵厚宇, 邓思危, 杨君婷, 李宁, 马瑞, 何艳, 许国章, 刘志科, 詹思延. 2015—2021年宁波市6岁以下儿童热性惊厥的流行病学特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(3): 584-591. |
| [7] | 李琳, 廖津津. 应用ROC曲线评估久坐行为对儿童青少年视力不良的预测价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(3): 614-619. |
| [8] | 王紫薇, 李闵, 高慧, 邓芳. 链球菌感染与过敏性紫癜肾炎患儿肾损害的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(2): 284-290. |
| [9] | 余磊, 杨文博, 杨宇帆, 王强. 自体肾移植术治疗患儿复杂肾动脉瘤1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(2): 396-399. |
| [10] | 邓敏婷, 王楠, 夏斌, 赵玉鸣, 朱俊霞. 儿童及青少年挫入恒前牙自行再萌出的相关影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(1): 148-153. |
| [11] | 杨颖婷, 李若竹, 窦桂丽, 雷玥, 夏斌. iRoot BP Plus用于年轻恒牙外伤部分牙髓切断治疗的临床随机对照研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 1083-1088. |
| [12] | 赵双云, 邹思雨, 李雪莹, 沈丽娟, 周虹. 中文版口腔健康素养量表简版(HeLD-14)在学龄前儿童家长中应用的信度和效度评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 828-832. |
| [13] | 陈心心, 唐哲, 乔艳春, 荣文笙. 北京市密云区4岁儿童患龋状况及其与龋活跃性检测的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [14] | 丁汉东, 王琴, 廖贵益, 郝宗耀. 肾移植术后并发消化道出血的诊治[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 902-907. |
| [15] | 杨文博,余磊,张维宇,徐涛,王强. 带线输尿管支架自排技术在肾移植受者中的效果及安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 656-660. |
|
||