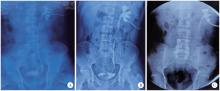
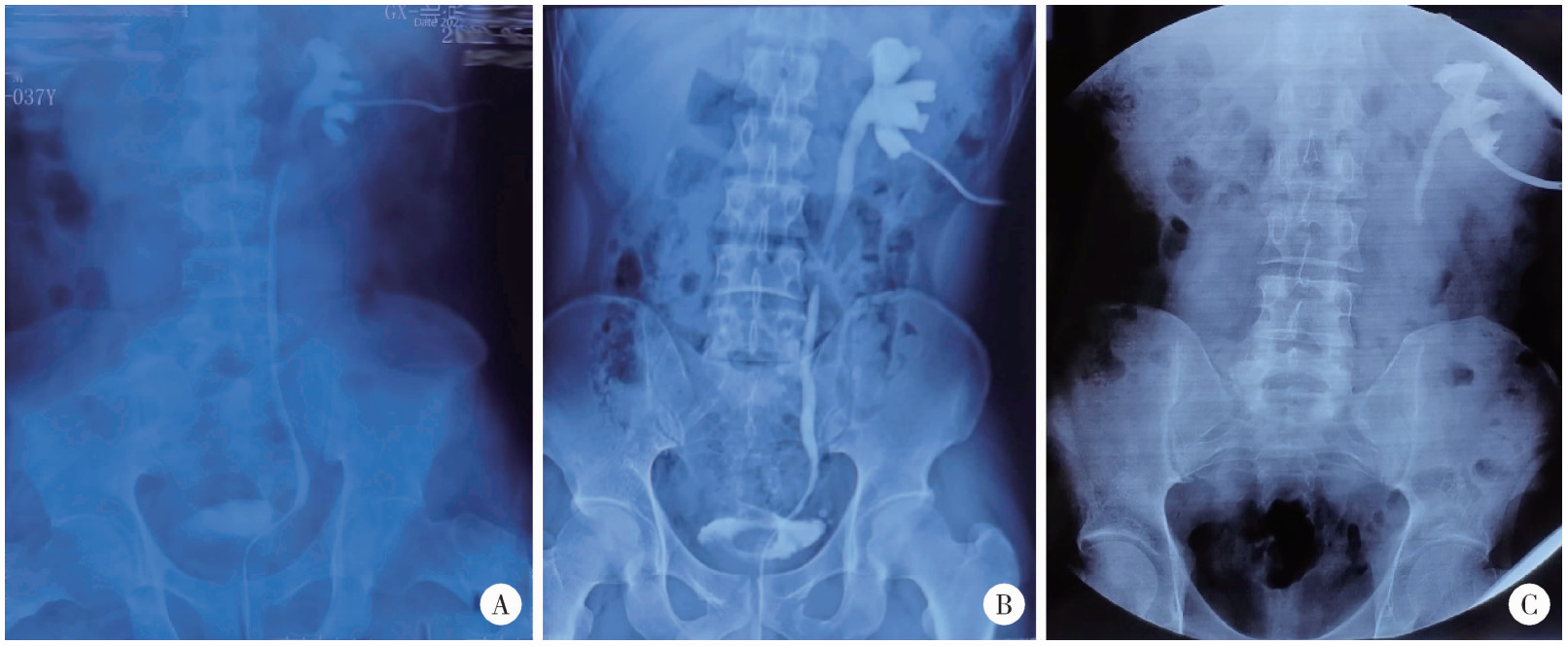
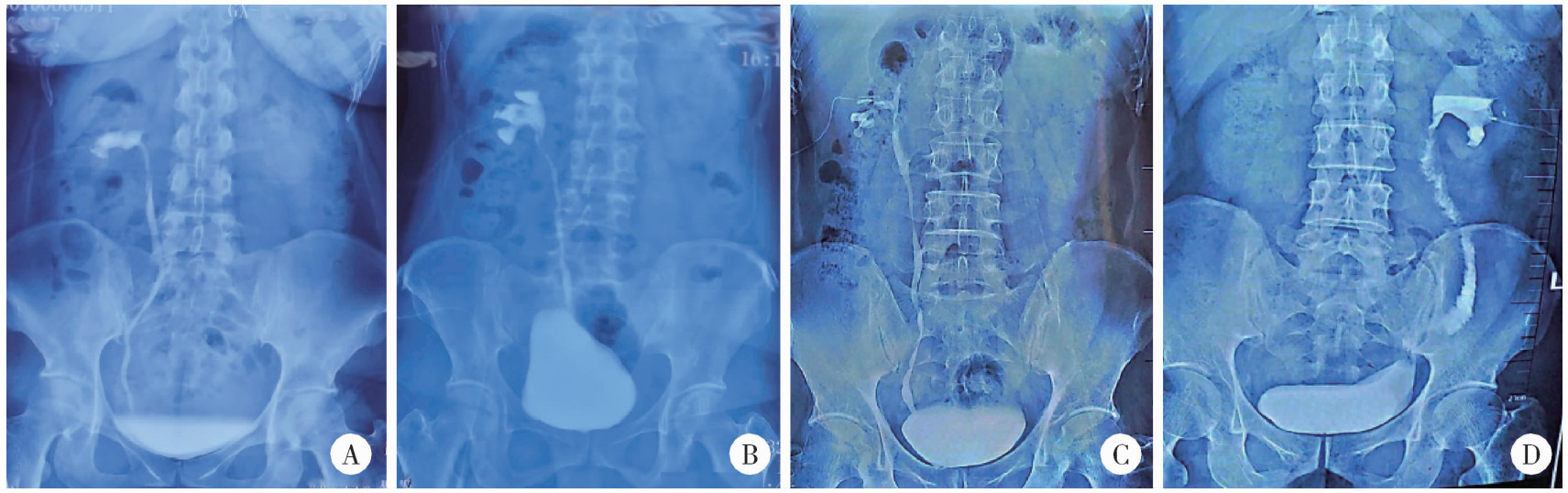
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 670-675. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.04.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
Surgical techniques and clinical outcomes of upper urinary tract reconstruction for stone-related ureteral strictures
Xiaoteng YU, Yixuan HUANG, Xinfei LI, Changfu CHEN, Fangzhou ZHAO, Honggang YING, Zihao TAO, Yiming ZHANG, Liqing XU, Zhihua LI, Kunlin YANG, Liqun ZHOU, Xuesong LI, Zheng ZHAO*( )
)
- Department of Urology, Peking University First Hospital, Institute of Urology, Peking University, National Urological Cancer Center, Beijing 100034, China
CLC Number:
- R699
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
黄健, 张旭. 中国泌尿外科和男科疾病诊断治疗指南2022版[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2022: 803- 806.
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
程嗣达, 李新飞, 熊盛炜, 等. 机器人辅助腹腔镜上尿路修复手术: 单一术者108例经验总结[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 771- 779.
doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.04.032 |
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
朱照伟, 赵品, 王声政, 等. 腹腔镜或机器人肾盂瓣成形术治疗复杂上段输尿管狭窄[J/OL]. 泌尿外科杂志(电子版), 2023, 15(1): 29-33.
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
包军胜, 范阳, 冯宁翰, 等. 机器人辅助腹腔镜自体组织补片修复输尿管狭窄中国专家共识[J]. 微创泌尿外科杂志, 2024, 13(2): 93- 99.
|
| 18 |
柴帅帅, 李兵, 肖行远. 自体组织补片修复复杂输尿管狭窄的手术要点及围手术期管理中国专家共识(2024版)[J]. 现代泌尿外科杂志, 2024, 29(5): 388- 393.
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
肖行远, 柴帅帅, 董满顺, 等. 阑尾输尿管成形术治疗右侧输尿管狭窄的初步临床经验: 基于8例患者的研究[J]. 泌尿外科杂志(电子版), 2024, 16(4): 8- 12.
|
| 21 |
朱照伟, 赵品, 张雪培. 长段输尿管狭窄外科治疗思考: 不同自体组织成形术的优劣及微创与开放的抉择[J]. 现代泌尿外科杂志, 2025, 30(4): 279- 283.
|
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
|
| [1] | Zonghan LI, Yangyue HUANG, Ning LI, Minglei LI, Hongcheng SONG, Weiping ZHANG, Chao LIU. Preliminary application of domestic single-port serpentine arm robotic surgical system in children's pyeloplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(4): 662-665. |
| [2] | Jinghui JI, Xiushi LIN, Dameng PAN, Zhiying WU, Zixuan XUE, Xiaojun TIAN, Shudong ZHANG, Binshuai WANG, Min QIU. Efficacy of rigid ureteroscopic laser lithotripsy combined with N-trap in the treatment of ureteral stones with a maximum diameter equal to or greater than 1.5 cm [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(4): 676-683. |
| [3] | Silu CHEN, Haiju WANG, Yucai WU, Zhihua LI, Yanbo HUANG, Yuhui HE, Yangyang XU, Xuesong LI, Hua GUAN. Etiological analysis of hydronephrosis in adults: A single-center cross-sectional study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 913-918. |
| [4] | Mingrui WANG, Qi WANG, Hao HU, Jinhui LAI, Xinwei TANG, Chunyan WAN, Kexin XU, Tao XU. Efficacy of coated metal ureteral stent in the treatment of pelvic lipomatosis induced hydronephrosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 919-922. |
| [5] | Xin-ling ZHANG,Zhi-yu LIN,Yu-jie CHEN,Wen-fang DONG,Xin YANG. Plastic and reconstruction surgery for non-healing wound after posterior spinal surgery [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 910-914. |
| [6] | Cai-peng QIN,Fei WANG,Yi-qing DU,Xiao-wei ZHANG,Qing LI,Shi-jun LIU,Tao XU. Diagnosis and treatment of four cases of asymptomatic and non-hydrous ureteral calculi [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 939-942. |
| [7] | Lei WANG,Tian-dong HAN,Wei-xing JIANG,Jun LI,Dao-xin ZHANG,Ye TIAN. Comparison of safety and effectiveness of active migration technique and in situ lithotripsy technique in the treatment of 1-2 cm upper ureteral calculi by flexible ure-teroscopy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 553-557. |
| [8] | Deng-gao LIU,Dan-ni ZHENG,Ya-ning ZHAO,Ya-qiong ZHANG,Xin YE,Li-qi ZHANG,Xiao-yan XIE,Lei ZHANG,Zu-yan ZHANG,Guang-yan YU. Recent progress in the treatment of intractable sialolithiasis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 8-12. |
| [9] | Guan-peng HAN,Yang-yang XU,Zhi-hua LI,Chang MENG,Hong-jian ZHU,Kun-lin YANG,Li-qun ZHOU,Xue-song LI. Ureteral stenosis following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(4): 762-765. |
| [10] | Chun-long ZHANG,Ming-rui WANG,Ming-rui WANG,Ke-xin XU,Tao XU,Hao HU. Long-term efficacy evaluation of coated metal stent implantation for ureteroscopic lithotripsy related refractory ureteral stricture [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(4): 674-679. |
| [11] | Shi-bo LIU,Hui GAO,Yuan-chun FENG,Jing LI,Tong ZHANG,Li WAN,Yan-ying LIU,Sheng-guang LI,Cheng-hua LUO,Xue-wu ZHANG. Clinical features of hydronephrosis induced by retroperitoneal fibrosis: 17 cases reports [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(6): 1069-1074. |
| [12] | Run-zhuo MA,Hai-zhui XIA,Min LU,Zhi-ying ZHANG,Qi-ming ZHANG,Jian LU,Guo-liang WANG,Lu-lin MA. Impact of diagnostic ureteroscopy and biopsy on radical nephroureterectomy of upper tract urothelial carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(4): 665-672. |
| [13] | HAO Yi-chang, CHEN Kun, LIU Yu-qing, LU Jian, XIAO Chun-lei, MA Lu-lin. Transurethral flexible ureteroscopic holmium laser resection for tumors of renal pelvis: 6 cases report and literature review [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(5): 816-821. |
| [14] | MA Run-zhuo, QIU Min, HE Wei, YANG Bin, XIA Hai-zhui, ZOU Da, LU Min, MA Lu-lin1, LU Jian. Ureteroscope can assist risk stratification in upper tract urothelial carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(4): 632-637. |
| [15] | YE Hai-yun, XU Qing-quan, MA Kai, HUANG Xiao-bo. Characteristics of ureteral stone position and dilatation of ureter in patients before treated with endourologic lithotripsy [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(4): 622-625. |
|
||