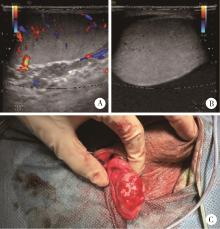
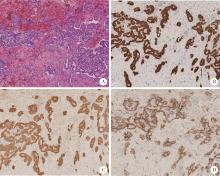
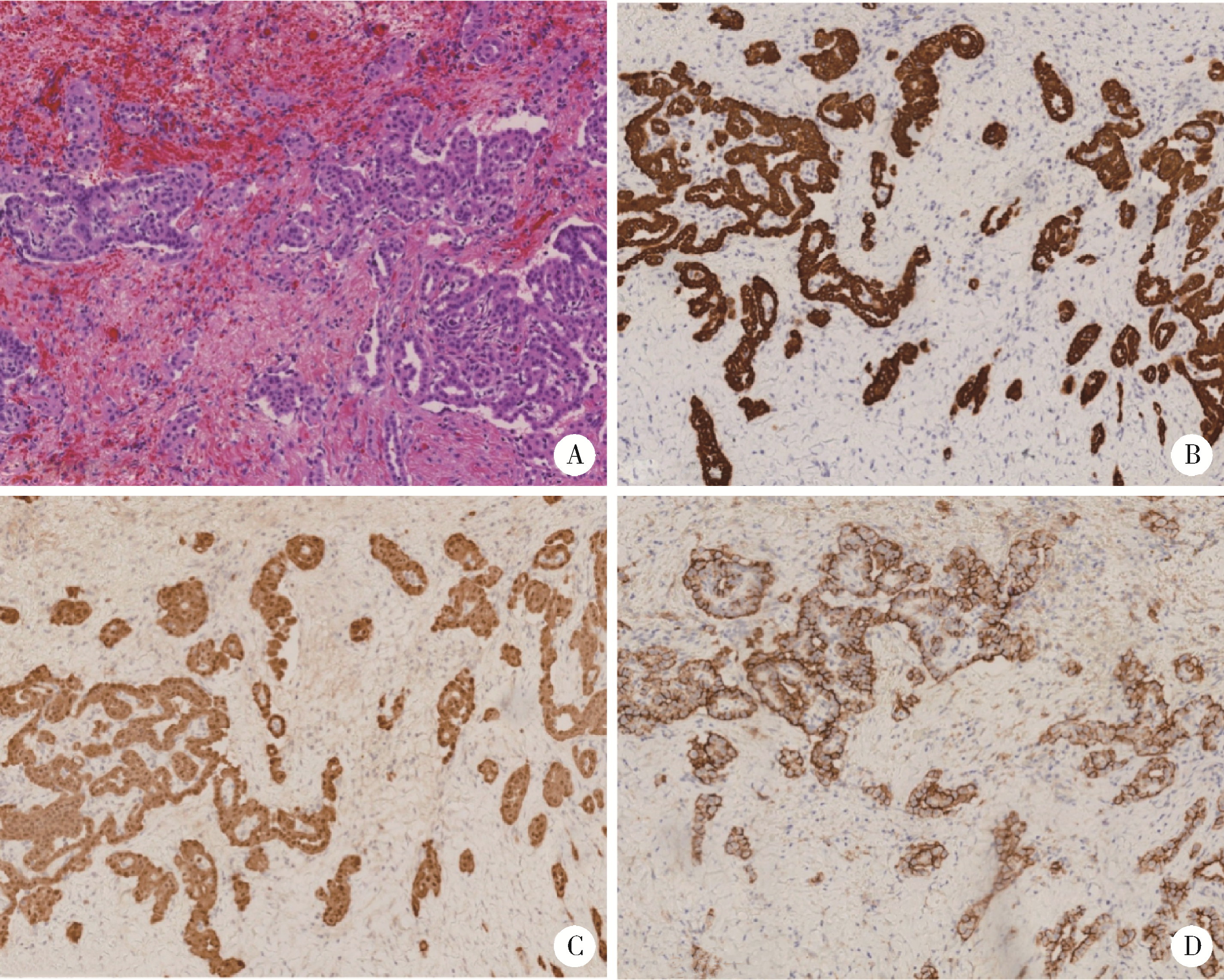
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (4): 741-744. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.04.031
Previous Articles Next Articles
Well-differentiated papillary mesothelial tumour of the tunica vaginalis: A case report
Yangyi FANG1,Qiang LI2,Zhigao HUANG1,Min LU3,Kai HONG1,Shudong ZHANG1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Urology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Urology, Beijing Zhongguancun Hospital, Beijing 100190, China
3. Department of Pathology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R737.2
| 1 |
Brimo F , Illei PB , Epstein JI . Mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis: A series of eight cases with uncertain malignant potential[J]. Mod Pathol, 2010, 23 (8): 1165- 1172.
doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2010.113 |
| 2 | Moch H , Amin MB , Berney DM , et al. The 2022 World Health Organization classification of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs. Part A: Renal, penile, and testicular tumours[J]. Eur Urol, 2022, 85 (5): 458- 468. |
| 3 |
Tan WK , Tan MY , Tan WS , et al. Well-differentiated papillary mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis: Case report and systematic review of literature[J]. Clin Genitourin Cancer, 2016, 14 (4): e435- e439.
doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2016.03.007 |
| 4 |
Drone E , Kwon B , Plamoottil C , et al. Testicular compartment syndrome: An unexpected diagnosis in a case of testicular pain[J]. Urol Case Rep, 2021, 39, 101823.
doi: 10.1016/j.eucr.2021.101823 |
| 5 |
Mutsaers SE . The mesothelial cell[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2004, 36 (1): 9- 16.
doi: 10.1016/S1357-2725(03)00242-5 |
| 6 |
Butnor KJ , Pavlisko EN , Sporn TA , et al. Mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis testis[J]. Hum Pathol, 2019, 92, 48- 58.
doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2019.07.009 |
| 7 |
Barbera V , Rubino M . Papillary mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis[J]. Cancer, 1957, 10 (1): 183- 189.
doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195701/02)10:1<183::AID-CNCR2820100127>3.0.CO;2-1 |
| 8 |
Chetty R . Well differentiated (benign) papillary mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis[J]. J Clin Pathol, 1992, 45 (11): 1029- 1030.
doi: 10.1136/jcp.45.11.1029 |
| 9 | Fujii Y , Masuda M , Hirokawa M , et al. A case of benign mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis testis[J]. Hinyokika Kiyo, 1993, 39 (1): 89- 92. |
| 10 |
Xiao SY , Rizzo P , Carbone M . Benign papillary mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis testis[J]. Arch Pathol Lab Med, 2000, 124 (1): 143- 147.
doi: 10.5858/2000-124-0143-BPMOTT |
| 11 |
Mak CW , Ccheng TC , Chuang SS , et al. Malignant mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis testis[J]. Br J Radiol, 2004, 77 (921): 780- 781.
doi: 10.1259/bjr/25026914 |
| 12 | 朱正龙, 吴佩红, 叶琴, 等. 睾丸鞘膜高分化乳头状间皮瘤一例及文献复习[J]. 江苏医药, 2004, 30 (12): 941- 942. |
| 13 |
Tolhurst SR , Lotan T , Rapp DE , et al. Well-differentiated papillary mesothelioma occurring in the tunica vaginalis of the testis with contralateral atypical mesothelial hyperplasia[J]. Urol Oncol, 2006, 24 (1): 36- 39.
doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2005.06.021 |
| 14 |
Chollet Y , Hauser P , da Silva T , et al. Well-differentiated papillary mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis testis: Imaging on Tc-99m heat-denatured red blood cell scintigraphy[J]. Clin Nucl Med, 2008, 33 (4): 282- 284.
doi: 10.1097/RLU.0b013e3181662b2f |
| 15 | 潘锋, 沈文, 姚华强, 等. 睾丸鞘膜良性乳头状间皮瘤1例报告并文献复习[J]. 医学研究生学报, 2009, 22 (4): 447- 448. |
| 16 |
Fukunaga M . Well-differentiated papillary mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis: A case report with aspirate cytologic, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural studies[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2010, 206 (2): 105- 109.
doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2009.02.006 |
| 17 | 李英, 张冬娅, 王变丽, 等. 睾丸鞘膜高分化乳头状间皮瘤临床病理分析[J]. 长治医学院学报, 2011, 25 (1): 14- 16. |
| 18 | 李文坚, 朱喜山, 张正林, 等. 睾丸鞘膜高分化乳头状间皮瘤一例报告[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2012, 33 (11): 817. |
| 19 | 周张雷, 郭以宝. 睾丸高分化乳头状间皮瘤1例报告并文献复习[J]. 吉林医学, 2013, 34 (25): 5311- 5312. |
| 20 | Manganiello M , Cassalman C , Dugan J , et al. Scrotal mesothelioma[J]. Can J Urol, 2014, 21 (1): 7163- 7165. |
| 21 | 戴桂红, 王建军, 余波, 等. 原发于精索高分化乳头状间皮瘤1例并文献复习[J]. 中华男科学杂志, 2014, 20 (10): 956- 959. |
| 22 | 宋立德, 吕艳婷, 郦秀芳, 等. 睾丸鞘膜高分化乳头状间皮瘤1例临床病理分析[J]. 中华男科学杂志, 2015, 21 (1): 93- 95. |
| 23 | Ko KWS , Tse KS , Shek KW , et al. Well-differentiated papillary mesothelioma of tunica vaginalis testis of unknown malignant potential: Sonographic appearance[J]. J Clin Ultrasound, 2018, 46 (5): 364- 367. |
| 24 | 李浩民, 欧阳鹏, 胡先国, 等. 睾丸鞘膜高分化乳头状间皮瘤1例报告兼文献复习[J]. 国际医药卫生导报, 2020, 26 (4): 466- 468. |
| 25 | Kläger J , Oberndorfer F , Brunel C , et al. Well-differentiated papillary mesothelial tumour of the tunica vaginalis testis: A rare lesion, but one pathologists should know about two patient reports and a review of the literature[J]. Int J Surg Pathol, 2023, 31 (6): 1126- 1131. |
| 26 | Grogg JB , Fronzaroli JN , Oliveira P , et al. Clinicopathological characteristics and outcomes in men with mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis testis: Analysis of published case-series data[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2021, 147, 2671- 2679. |
| 27 | Plas E , Riedl CR , Pflüger H . Malignant mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis testis: Review of the literature and assessment of prognostic parameters[J]. Cancer, 1998, 83 (12): 2437- 2446. |
| 28 | Farah M , Song M , Mahmalji W . Epididymal adenomatoid tumour: A case report[J]. Cureus, 2023, 15 (10): e47505. |
| 29 | Huddart R , Norman A , Moynihan C , et al. Fertility, gonadal and sexual function in survivors of testicular cancer[J]. Br J Cancer, 2005, 93 (2): 200- 207. |
| [1] | Junyong OU,Kunming NI,Lulin MA,Guoliang WANG,Ye YAN,Bin YANG,Gengwu LI,Haodong SONG,Min LU,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Prognostic factors of patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer with intermediate-to-high risk prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [2] | Shuai LIU,Lei LIU,Zhuo LIU,Fan ZHANG,Lulin MA,Xiaojun TIAN,Xiaofei HOU,Guoliang WANG,Lei ZHAO,Shudong ZHANG. Clinical treatment and prognosis of adrenocortical carcinoma with venous tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [3] | Le YU,Shaohui DENG,Fan ZHANG,Ye YAN,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of multilocular cystic renal neoplasm of low malignant potential [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [4] | Zezhen ZHOU,Shaohui DENG,Ye YAN,Fan ZHANG,Yichang HAO,Liyuan GE,Hongxian ZHANG,Guoliang WANG,Shudong ZHANG. Predicting the 3-year tumor-specific survival in patients with T3a non-metastatic renal cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 673-679. |
| [5] | Yuanyuan ZENG,Yun XIE,Daonan CHEN,Ruilan WANG. Related factors of euthyroid sick syndrome in patients with sepsis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 526-532. |
| [6] | Jian-bin LI,Meng-na LYU,Qiang CHI,Yi-lin PENG,Peng-cheng LIU,Rui WU. Early prediction of severe COVID-19 in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1007-1012. |
| [7] | Huan-rui LIU,Xiang PENG,Sen-lin LI,Xin GOU. Risk modeling based on HER-2 related genes for bladder cancer survival prognosis assessment [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 793-801. |
| [8] | Zi-xuan XUE,Shi-ying TANG,Min QIU,Cheng LIU,Xiao-jun TIAN,Min LU,Jing-han DONG,Lu-lin MA,Shu-dong ZHANG. Clinicopathologic features and prognosis of young renal tumors with tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 802-811. |
| [9] | Han LU,Jian-yun ZHANG,Rong YANG,Le XU,Qing-xiang LI,Yu-xing GUO,Chuan-bin GUO. Clinical factors affecting the prognosis of lower gingival squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 702-707. |
| [10] | Yun-fei SHI,Hao-jie WANG,Wei-ping LIU,Lan MI,Meng-ping LONG,Yan-fei LIU,Yu-mei LAI,Li-xin ZHOU,Xin-ting DIAO,Xiang-hong LI. Analysis of clinicopathological and molecular abnormalities of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 521-529. |
| [11] | Xiao-juan ZHU,Hong ZHANG,Shuang ZHANG,Dong LI,Xin LI,Ling XU,Ting LI. Clinicopathological features and prognosis of breast cancer with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 low expression [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 243-253. |
| [12] | Yu-mei LAI,Zhong-wu LI,Huan LI,Yan WU,Yun-fei SHI,Li-xin ZHOU,Yu-tong LOU,Chuan-liang CUI. Clinicopathological features and prognosis of anorectal melanoma: A report of 68 cases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 262-269. |
| [13] | Qi SHEN,Yi-xiao LIU,Qun HE. Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of kidney: Clinicopathology and prognosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 276-282. |
| [14] | Qian SU,Xin PENG,Chuan-xiang ZHOU,Guang-yan YU. Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in oral and maxillofacial regions: An analysis of 369 cases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 13-21. |
| [15] | Quan ZHANG,Hai-feng SONG,Bing-lei MA,Zhe-nan ZHANG,Chao-hui ZHOU,Ao-lin LI,Jun LIU,Lei LIANG,Shi-yu ZHU,Qian ZHANG. Pre-operative prognostic nutritional index as a predictive factor for prognosis in non-metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with surgery [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 149-155. |
|
||