北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 53-58. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.01.010
多模态影像融合技术与颅底-颞下区肿瘤的诊断和治疗
- 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,口腔颌面外科 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
Multimodal image fusion technology for diagnosis and treatment of the skull base-infratemporal tumors
Rong YANG,Qing-xiang LI,Chi MAO,Xin PENG,Yang WANG,Yu-xing GUO( ),Chuan-bin GUO(
),Chuan-bin GUO( )
)
- Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
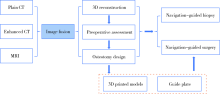
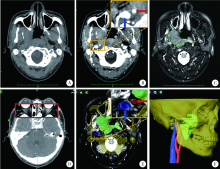
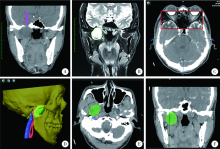
目的:评价多模态影像融合技术联合计算机辅助设计在颅底-颞下区肿瘤诊断和治疗中的应用及效果。方法:选择2011年2月至2018年9月于北京大学口腔医院诊治的颅底-颞下区肿瘤患者资料进行回顾性分析,共入选病例17例,术前所有患者进行平扫CT、增强CT及MRI影像扫描。在导航软件中将平扫CT、增强CT及MRI影像融合后,三维重建肿瘤、血管及颅颌面骨,计算机辅助设计手术方案,并联合导航引导下穿刺活检或手术,术后定期随访,分析患者资料,评价应用效果。结果:17例病例均取得满意的多模态影像融合,在同一帧图像上精确显示通过不同图像描记的病变、颅颌面骨及重要血管。联合计算机辅助三维重建及导航引导穿刺或手术设计,进行术前评估及手术方案设计,取得了良好的应用效果,尤其对肿瘤体积较小、复发及边界不清的病例效果显著。4例利用融合图像进行术前诊断与评估后行手术探查(无术中导航引导,其中3例手术切除,1例仅取活检), 3例行导航引导穿刺活检,12例行导航引导手术切除(其中2例先行导航穿刺活检)。所有患者均成功实施穿刺或手术,1例脑膜瘤复发患者术中出现脑脊液漏,1例腮腺深叶肿瘤患者术后面瘫,穿刺活检病理诊断阳性率为100%(3/3)。手术切除的15例经术中导航检查及术后影像验证显示完全切除14例,次全切除1例,术后随访3~94个月(中位随访时间9个月)。结论:充分利用多模态影像优势,准确分析肿瘤、血管及颅颌面骨的三维空间位置关系,有助于颅底-颞下区肿瘤的术前规划,联合导航技术可进一步提高穿刺活检及手术治疗的精准性和安全性。
中图分类号:
- R78
| [1] |
Choudhri AF, Parmar HA, Morales RE , et al. Lesions of the skull base: imaging for diagnosis and treatment[J]. Otolaryngol Clin North Am, 2012,45(6):1385-1404.
doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-35579-0_20 |
| [2] | 魏宏权 . 咽旁隙和颞下窝肿瘤的外科治疗进展[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉颅底外科杂志, 2018,24(2):91-96, 102. |
| [3] |
郭玉兴, 彭歆, 刘筱菁 , 等. 导航技术在颅底-颞下区肿瘤手术中的应用[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2013,48(11):645-647.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1002-0098.2013.11.002 |
| [4] |
郭传瑸, 郭玉兴 . 外科导航技术引导的颅底肿瘤穿刺活检[J]. 中国实用口腔科杂志, 2014,7(6):321-324.
doi: 10.7504/kq.2014.06.001 |
| [5] |
Guo R, Guo YX, Feng Z , et al. Application of a computer-aided navigation technique in surgery for recurrent malignant infratemporal fossa tumors[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2015,26(2):e126-132.
doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000001350 pmid: 25710743 |
| [6] |
Leong JL, Batra PS, Citardi MJ . CT-MR image fusion for the management of skull base lesions[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2006,134(5):868-876.
doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2005.11.015 pmid: 16647550 |
| [7] |
Guo Y, Guo C . Maxillary-fronto-temporal approach for removal of recurrent malignant infratemporal fossa tumors: Anatomical and clinical study[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2014,42(3):206-212.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2013.05.001 pmid: 23932542 |
| [8] |
Yacoub A, Anschuetz L, Schneider D , et al. Minimally invasive lateral endoscopic multiport approach to the infratemporal fossa: a cadaveric study[J]. World Neurosurg, 2018,112:e489-e496.
doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2018.01.065 pmid: 29391297 |
| [9] | 李成才, 姚国杰, 杜威 , 等. 多模态影像融合在颅底肿瘤的诊断、治疗中的应用价值[J]. 中国临床神经外科杂志, 2018,23(3):145-148. |
| [10] |
O'Neill BE, Hochhalter CB, Carr C , et al.Advances in neuro-oncology imaging techniques[J]. Ochsner J, 2018,18(3):236-241.
doi: 10.31486/toj.17.0062 |
| [11] |
赵岩, 孙健, 杨学军 . 多模态影像融合技术在神经外科的应用及进展[J]. 中国现代神经疾病杂志, 2012,12(6):645-650.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6731.2012.06.004 |
| [12] |
顾恒乐, 聂生东 . 多模医学图像配准和融合方法及其临床应用进展[J]. 中华放射肿瘤学杂志, 2016,25(8):902-906.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1004-4221.2016.08.024 |
| [13] |
Inoue HK, Nakajima A, Sato H , et al. Image fusion for radiosurgery, neurosurgery and hypofractionated radiotherapy[J]. Cureus, 2015,7(3):e252.
doi: 10.7759/cureus.252 pmid: 26180676 |
| [14] |
Nemec SF, Donat MA, Mehrain S , et al. Ct-mr image data fusion for computer assisted navigated neurosurgery of temporal bone tumors[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2007,62(2):192-198.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2006.11.029 pmid: 17229539 |
| [15] |
Zhang SX, Han PH, Zhang GQ , et al. Comparison of spect/ct, mri and ct in diagnosis of skull base bone invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Biomed Mater Eng, 2014,24(1):1117-1124.
doi: 10.3233/BME-130911 pmid: 24092081 |
| [16] |
Guo YX, Sun ZP, Liu XJ , et al. Surgical safety distances in the infratemporal fossa: three-dimensional measurement study[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2015,44(5):555-561.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2014.06.004 pmid: 25441861 |
| [17] |
吴东东, 卜博, 陈晓雷 , 等. 融合MRI与CT图像的多模态神经导航技术在颅底显微外科手术中的应用[J]. 解放军医学院学报, 2015, ( 5):411-414.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-5227.2015.05.002 |
| [18] |
Hayashi N, Kurimoto M, Hirashima Y , et al. Efficacy of navigation in skull base surgery using composite computer graphics of magnetic resonance and computed tomography images[J]. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo), 2001,41(7):335.
doi: 10.2176/nmc.41.335 pmid: 11487996 |
| [1] | 李君,刘旭红,王工,程程,庄洪卿,杨瑞杰. 手臂位置对射波刀放射治疗脊柱肿瘤患者的剂量学影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 182-186. |
| [2] | 杨朵,周心娜,王硕,王小利,袁艳华,杨化兵,耿会珍,彭兵,李子博,李彬,任军. 树突状细胞疫苗特异肿瘤多肽联合树突状细胞体外刺激淋巴细胞功能评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1094-1098. |
| [3] | 娄雪,廖莉,李兴珺,王楠,刘爽,崔若玫,徐健. 类风湿关节炎患者外周血TWEAK基因启动子区甲基化状态及其表达[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1020-1025. |
| [4] | 牛占岳,薛艳,张静,张贺军,丁士刚. 胃腺瘤性息肉的内镜和病理特点及癌变的危险因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1122-1127. |
| [5] | 叶剑飞,赵磊,王国良,洪锴,马潞林. 睾丸横纹肌肉瘤的诊治分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1178-1182. |
| [6] | 田雨,程晓悦,贺慧颖,王国良,马潞林. 肾细胞癌合并尿路瘤栓的临床病理特征: 6例报道及文献回顾[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 928-932. |
| [7] | 庞泳,张沙,杨华,周柔丽. LAPTM4B-35蛋白作为肝癌血清学诊断新标志物的探讨[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 710-715. |
| [8] | 孙争辉,黄晓娟,董靖晗,刘茁,颜野,刘承,马潞林. 临床T1期肾细胞癌肾窦侵犯的危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 659-664. |
| [9] | 康文玉,王璐,邱敏,张帆,郭巍,强亚勇,拓鹏飞,宗有龙,刘磊磊,王帅帅. 肾上腺海绵状血管瘤1例及文献回顾[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 808-810. |
| [10] | 林国中, 马长城, 王振宇, 谢京城, 刘彬, 陈晓东. 颈1~2硬膜外神经鞘瘤的显微微创治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 586-589. |
| [11] | 杨榕,李庆祥,王逸飞,周闻,王雯,郭传瑸,刘浩,郭玉兴. 碘液浸染在Micro-CT下识别小鼠颅底-颞下区肿瘤组织中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 598-601. |
| [12] | 李新飞, 彭意吉, 余霄腾, 熊盛炜, 程嗣达, 丁光璞, 杨昆霖, 唐琦, 米悦, 吴静云, 张鹏, 谢家馨, 郝瀚, 王鹤, 邱建星, 杨建, 李学松, 周利群. 肾部分切除术前CT三维可视化评估标准的初步探究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 613-622. |
| [13] | 周川, 马雪, 邢云昆, 李璐迪, 陈洁, 姚碧云, 傅娟玲, 赵鹏. 基于肿瘤基因组图谱数据库探索性筛选潜在泛癌生物标志物[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 602-607. |
| [14] | 邱敏,费月阳,邓绍晖,刘承,卢剑,何为,陆敏,田晓军,张树栋,马潞林. 后肾腺瘤的诊治经验及文献回顾[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 417-419. |
| [15] | 陈怀安,刘硕,李秀君,王哲,张潮,李凤岐,苗文隆. 炎症生物标志物对输尿管尿路上皮癌患者预后预测的临床价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 302-307. |
|