北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (2): 275-280. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.02.013
原发性椎管内脓肿的诊断与治疗
- 北京大学第三医院神经外科,北京 100191
Diagnosis and treatment of primary intraspinal abscess
Chang-cheng MA,Zhen-yu WANG( ),Guo-zhong LIN
),Guo-zhong LIN
- Department of Neurosurgery, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing, 100191, China
摘要:
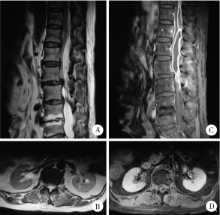
目的 总结原发性椎管内脓肿的特点以及治疗方法,以期提高原发性椎管内脓肿的诊断与治疗水平.方法: 回顾性分析北京大学第三医院近20年来收治的13例原发性椎管内脓肿的病例,分别对其病史,病因,病原学,手术方式以及预后进行分析.结果: 所有病例病程从7 d到6个月不等,所有病例均以疼痛起病,有10例自觉肢体无力,有5例患者有发热史,8例血常规白细胞升高.13例中颈椎管内脓肿1例,颈胸段1例,胸段1例,胸腰段4例,腰骶段6例.病原学中,细菌培养阳性4例,病理学诊断结核3例,1例因发病前感染布氏杆菌(Brucella)按该细菌感染治疗,其余病例病原学结果均阴性.所有病例均行手术治疗,并获得组织病理学诊断.手术目的主要为清除病灶并减压,引流.术后根据病原学结果及临床经验予以抗感染及激素治疗.有2例术后形成切口脓肿再次行手术治疗,手术为清创及转移肌瓣修复.随访0.5~3.0年,平均1.8年.随访期1例术后复发并沿椎管扩散,再次手术治疗.所有病例最后炎症均完全恢复,神经系统体征较术前均有不同程度好转.结论: 原发性椎管内脓肿发病相对较急,主要以疼痛起病,腰骶部最好发,细菌培养多以阴性为主.建议早期手术,使用广谱,足量抗生素.术后如出现切口脓肿形成,宜在清创基础上转移肌瓣修复.术后为缓解脊髓和神经根水肿,可在抗生素保障下使用激素.
中图分类号:
- R632.5
| [1] | Honig A, Or O, Barzilay Y , et al. Spinal epidural abscess with a rapid course in young healthy infantry recruits with multiple skin lacerations[J]. J Clin Neurosci, 2016,31:127-132. |
| [2] | Reihsaus E, Waldbaur H, Seeling W . Spinal epidural abscess: a meta-analysis of 915 patients[J]. Neurosurg Rev, 2000,23(4):175-205. |
| [3] | Ersahin Y . Spinal epidural abscess: a meta-analysis of 915 patients[J]. Neurosurg Rev, 2001,24(2/3):156. |
| [4] | Karikari IO, Powers CJ, Reynolds RM , et al. Management of a spontaneous spinal epidural abscess: a single-center 10-year experience[J]. Neurosurgery, 2009,65(5):919-924. |
| [5] | Bartels RH, de Jong TR, Grotenhuis JA . Spinal subdural abscess[J]. J Neurosurg, 1992,76(2):307-311. |
| [6] | Kirzner H, Oh YK, Lee SH . Intraspinal air: a CT finding of epidural abscess[J]. Am J Roentgenol, 1988,151(6):1217-1218. |
| [7] | Farber SH, Murphy KR, Suryadevara CM , et al. Comparing outcomes of early, late, and non-surgical management of intraspinal abscess[J]. J Clin Neurosci, 2017,36:64-71. |
| [8] | Kulkarni AG, Chu G, Fehlings MG . Pyogenic intradural abscess: a case report[J]. Spine, 2007,32(12):E354-E357. |
| [9] | Thomé C, Krauss JK, Zevgaridis D , et al. Pyogenic abscess of the filum terminale. Case report[J]. J Neurosurg, 2001,95(Suppl 1):100-104. |
| [10] | Darouiche RO . Spinal epidural absces[J]. N Engl J Med, 2006,355(19):2012-2020. |
| [11] | Hanci M, Sarioglu AC, Uzan M , et al. Intramedullary tuberculous abscess: a case report[J]. Spine, 1996,21(6):766-769. |
| [12] | Bingöl A, Yücemen N, Meço O . Medically treated intraspinal "Brucella" granuloma[J]. Surg Neurol, 1999,52(6):570-576. |
| [13] | Kamat AS, Thango NS, Husein MB . Proteus mirabilis abscess involving the entire neural axis[J]. J Clin Neurosci, 2016,30:127-129. |
| [14] | Al Barbarawi M, Khriesat W, Qudsieh S , et al. Management of intramedullary spinal cord abscess: experience with four cases, pathophysiology and outcomes[J]. Eur Spine J, 2009,18(5):710-717. |
| [15] | Hindy J, Shelef I, Slovik Y , et al. Late prevertebral and spinal abscess following chemoradiation for laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Case Rep Otolaryngol, 2014,2014:425724. |
| [16] | Miyazaki M, Yoshiiwa T, Kodera R , et al. Clinical features of cervical pyogenic spondylitis and intraspinal abscess[J]. J Spinal Disord Tech, 2011,24(7):E57-E61. |
| [17] | Ur-rahman N, El-bakry A, Jamjoom AB , et al. Atypical forms of spinal tuberculosis: case report and review of the literature[J]. Surg Neurol, 1999,51(6):602-607. |
| [18] | Khalil JG, Nassr A, Diehn FE , et al. Thoracolumbosacral spinal subdural abscess: magnetic resonance imaging appearance and limited surgical management[J]. Spine, 2013,38(13):E844-E847. |
| [19] | Narlawar RS, Shah JR, Pimple MK , et al. Isolated tuberculosis of posterior elements of spine: magnetic resonance imaging findings in 33 patients[J]. Spine, 2002,27(3):275-281. |
| [20] | Tanriverdi T, Kizilkiliç O, Hanci M , et al. Atypical intradural spinal tuberculosis: report of three cases[J]. Spinal Cord, 2003,41(7):403-409. |
| [21] | Hung PC, Wang HS, Wu CT , et al. Spinal intramedullary abscess with an epidermoid secondary to a dermal sinus[J]. Pediatr Neurol, 2007,37(2):144-147. |
| [22] | ter Avest E, Uyttenboogaart M, Dorgelo J , et al. A patient with neck pain and fever. Combined prevertebral and intraspinal abscess in a patient with a de novo HIV infection[J]. Neth J Med, 2009,67(10):356-357. |
| [23] | Vajramani GV, Nagmoti MB, Patil CS . Neurobrucellosis presenting as an intramedullary spinal cord abscess[J]. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob, 2005,16(4):14. |
| [24] | Dev R, Husain M, Gupta A , et al. MR of multiple intraspinal abscesses associated with congenital dermal sinus[J]. Am J Neuroradiol, 1997,18(4):742-743. |
| [25] | Nagar VR, Springer JE, Salles S . Increased incidence of spinal abscess and substance abuse after implementation of state mandated prescription drug legislation[J]. Pain Med, 2015,16(10):2031-2035. |
| [26] | Singh I, Rohilla S, Kumar P , et al. Spinal dorsal dermal sinus tract: An experience of 21 cases[J]. Surg Neurol Int, 2015,6(Suppl 17):S429-434. |
| [1] | 原晋芳, 王新利, 崔蕴璞, 王雪梅. 尿促黄体生成素在女童中枢性性早熟预测中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 788-793. |
| [2] | 张树栋,谢睿扬. 机器人手术时代的肾癌合并腔静脉瘤栓治疗策略[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 562-564. |
| [3] | 颜野,李小龙,夏海缀,朱学华,张羽婷,张帆,刘可,刘承,马潞林. 前列腺癌根治术后远期膀胱过度活动症的危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 589-593. |
| [4] | 王明瑞,刘军,熊六林,于路平,胡浩,许克新,徐涛. 经皮微通道-微电子肾镜-微超声探针碎石术治疗1.5~2.5 cm肾结石的疗效和安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 605-609. |
| [5] | 应沂岑,杜毅聪,李志华,张一鸣,李新飞,王冰,张鹏,朱宏建,周利群,杨昆霖,李学松. 机器人辅助腹腔镜下颊黏膜补片输尿管成形术治疗复杂输尿管狭窄[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 640-645. |
| [6] | 虞乐,邓绍晖,张帆,颜野,叶剑飞,张树栋. 具有低度恶性潜能的多房囊性肾肿瘤的临床病理特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [7] | 乔佳佳,田聪,黄晓波,刘军. 肾结石合并系统性红斑狼疮行经皮肾镜碎石取石术的安全性和有效性评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 745-749. |
| [8] | 陈克伟,邓绍晖,刘茁,张洪宪,马潞林,张树栋. 肾血管平滑肌脂肪瘤破裂出血的手术时机[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 326-331. |
| [9] | 任晓萌,李凯一,李春蕾. 基于转录组测序探索口腔扁平苔藓局部激素治疗敏感性相关分子特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 32-38. |
| [10] | 徐心雨,吴灵,宋凤岐,李自力,张益,刘筱菁. 基于下颌运动轨迹的正颌外科术中下颌骨髁突定位方法及初步精度验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 57-65. |
| [11] | 蔡安东,王晓霞,周文娟,柳忠豪. 下颌前突畸形患者上颌骨及髁突虚拟位置与术后现实位置的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 74-80. |
| [12] | 王薇,王佳宁,虞巍,朱赛楠,高莹,张俊清. 肾上腺性库欣综合征与无功能腺瘤患者的凝血功能比较及其影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1062-1067. |
| [13] | 王丽芳,石连杰,宁武,高乃姝,王宽婷. 干燥综合征合并冷凝集素病1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1130-1134. |
| [14] | 毛海,张帆,张展奕,颜野,郝一昌,黄毅,马潞林,褚红玲,张树栋. 基于MRI前列腺腺体相关参数构建腹腔镜前列腺癌术后尿失禁的预测模型[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 818-824. |
| [15] | 刘慧丽,吕彦函,王晓晓,李民. 老年患者腹腔镜泌尿系肿瘤根治术后慢性疼痛的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 851-856. |
|
||