北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (5): 809-814. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.05.009
青少年抑郁症患者心理弹性影响因素的路径分析
- 焦作市第四人民医院心理科, 河南焦作 454000
Path analysis of influencing factors of mental resilience in adolescents with depression
- Department of Psychology, Jiaozuo Fourth People ' s Hospital, Jiaozuo 454000, Henan, China
摘要:
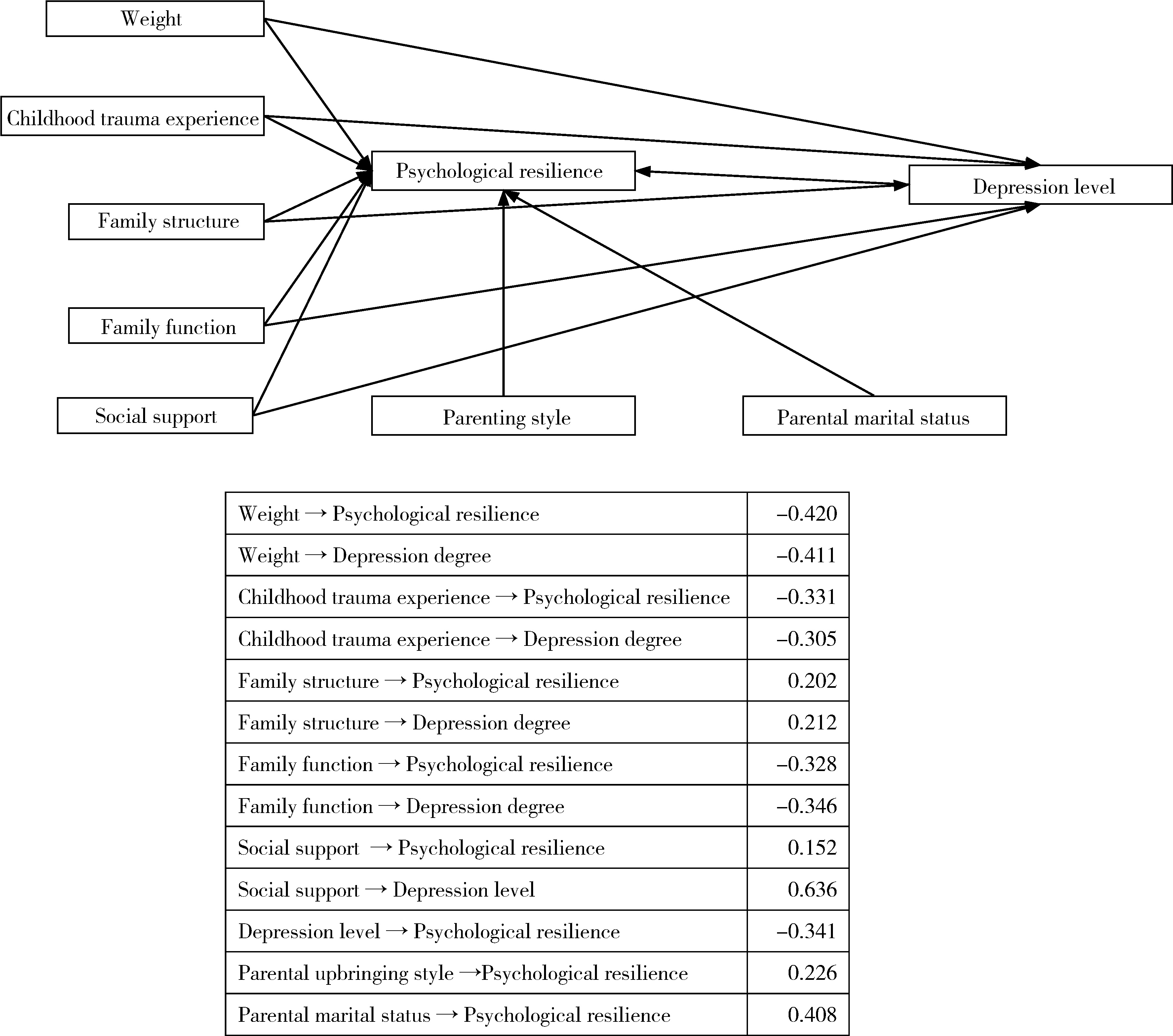
目的: 探讨青少年抑郁症患者心理弹性的影响因素及其路径,旨在确定合理的防治措施,提高患者的心理弹性水平。方法: 本次调查为横断面研究,采取便利抽样方法,采用一般资料问卷、Connor-Davidson心理弹性量表(Connor-Davidson resilience scale,CD-RISC)、家庭功能评定量表(family assessment device,FAD)、社会支持评定量表(social support rating scale,SSRS)对焦作市第四人民医院门诊就诊的162例青少年抑郁症患者展开调查,采用单因素和多因素分析青少年抑郁症患者心理弹性的影响因素,采用Amos 22.0软件建立结构方程模型,分析影响因素的作用路径。结果: (1) 青少年抑郁症患者CD-RISC总分及坚韧性、力量性、乐观性评分均低于国内常模(P < 0.05);(2)多元线性回归结果显示,体质量、童年创伤体验、家庭结构、家庭功能、父母教养方式、父母婚姻状况、社会支持、抑郁程度是青少年抑郁症患者心理弹性的影响因素;(3)模型显示,体质量、童年创伤体验、家庭结构、家庭功能、社会支持对青少年抑郁症患者的心理弹性有直接影响,亦可通过抑郁程度对青少年抑郁症患者的心理弹性产生间接影响(P < 0.05)。结论: 体质量、童年创伤体验、社会支持、抑郁程度等因素对青少年抑郁症患者的心理弹性有影响效应,建议学校管理者增加体育课程的课时和课程内容,做好心理援助,有助于提高青少年抑郁症患者的心理弹性水平。
中图分类号:
- R749.4
| 1 |
Shorey S , Ng ED , Wong CHJ , et al. Global prevalence of depression and elevated depressive symptoms among adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Br J Clin Psychol, 2022, 61 (2): 287- 305.
doi: 10.1111/bjc.12333 |
| 2 |
Dwyer JB , Landeros-Weisenberger A , Johnson JA , et al. Efficacy of intravenous ketamine in adolescent treatment-resistant depression: A randomized midazolam-controlled trial[J]. Am J Psychiatry, 2021, 178 (4): 352- 362.
doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2020.20010018 |
| 3 | 徐莉, 赵锦涵, 金于雄, 等. 青少年抑郁症患者非自杀性自伤的相关因素[J]. 昆明医科大学学报, 2022, 43 (5): 58- 64. |
| 4 |
Wang MF , Lu X , Liu MH , et al. The mediating effect of psychological resilience on the level of mindfulness and general well-being in patients with inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Ann Palliat Med, 2021, 10 (8): 9215- 9222.
doi: 10.21037/apm-21-2053 |
| 5 | 周晓璇, 叶海森. 青少年抑郁症患者心理弹性与父母养育方式, 自我接纳程度相关性分析[J]. 精神医学杂志, 2021, 34 (4): 304- 307. |
| 6 | 抑郁障碍中西医整合诊治专家共识组, 中国民族医药学会神志病分会. 抑郁障碍中西医整合专家共识[J]. 中国医药导报, 2021, 18 (6): 4- 12. |
| 7 |
刘莉莉, 孔凡贞, 季彩芳, 等. 反刍思维对首发抑郁症患者1年结局的影响: 家庭功能的中介作用[J]. 中华行为医学与脑科学杂志, 2022, 31 (10): 887- 892.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn371468-20220402-00157 |
| 8 | 吴秋彦, 邱丹, 肖水源. 新冠肺炎防控常态化期间医务人员睡眠质量与社会支持的关系[J]. 中国心理卫生杂志, 2023, 37 (5): 442- 448. |
| 9 | 郑春叶, 蔡巧娣, 陈信捷, 等. 柴甘解忧汤联合重复经颅磁刺激对帕金森病合并轻中度抑郁的随机对照研究[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2022, 42 (11): 1312- 1317. |
| 10 | 李健, 祁娜. 慢性前列腺炎/慢性盆腔疼痛综合征患者的心理弹性及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国性科学, 2022, 31 (12): 60- 63. |
| 11 | 李文俊, 布龙华, 郑竻云, 等. 抑郁症患者心理弹性与自尊水平及自我病耻感相关性分析[J]. 临床心身疾病杂志, 2023, 28 (3): 95- 97. |
| 12 | Chen N , Xi JZ , Fan XW , et al. Correlations among psychological resilience, cognitive fusion, and depressed emotions in patients with depression[J]. Behav Sci (Basel), 2023, 13 (2): 100. |
| 13 | 黄欣欣, 李雨婷, 陈剑华, 等. 家庭结构对青少年抑郁和焦虑症状的影响: 情感忽视的中介作用[J]. 中国当代儿科杂志, 2023, 25 (1): 80- 85. |
| 14 | Martinez AB , Co M , Lau J , et al. Filipino help-seeking for mental health problems and associated barriers and facilitators: A syste-matic review[J]. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol, 2020, 55 (11): 1397- 1413. |
| 15 | Huang JG , Xu LL , Xu Z , et al. The relationship among pregnancy-related anxiety, perceived social support, family function and resilience in Chinese pregnant women: A structural equation modeling analysis[J]. BMC Womens Health, 2022, 22 (1): 546. |
| 16 | Peleg O , Tzischinsky O , Spivak-Lavi Z , et al. Depression and social anxiety mediate the relationship between parenting styles and risk of eating disorders: A study among Arab adolescents[J]. Int J Psychol, 2021, 56 (6): 853- 864. |
| 17 | Forbes EE , Eckstrand KL , Rofey DL , et al. A social affective neuroscience model of risk and resilience in adolescent depression: Preliminary evidence and application to sexual and gender minority adolescents[J]. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging, 2021, 6 (2): 188- 199. |
| 18 | Dong CQ , Xu R , Xu LQ , et al. Relationship of childhood trauma, psychological resilience, and family resilience among undergraduate nursing students: A cross-sectional study[J]. Perspect Psychiatr Care, 2021, 57 (2): 852- 859. |
| 19 | 马冰, 黄求进, 王晓春. 黑龙江省男护士心理弹性在社会支持和简单应对方式间的中介作用[J]. 中国实用护理杂志, 2021, 37 (32): 2500- 2505. |
| 20 | Moradi M , Mozaffari H , Askari M , et al. Association between overweight/obesity with depression, anxiety, low self-esteem, and body dissatisfaction in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies[J]. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 2022, 62 (2): 555- 570. |
| [1] | 陈敬,单蕊,肖伍才,张晓蕊,刘峥. 青春期和成年早期自制力与抑郁症状和超重肥胖共病风险的关联:基于全国调查的十年前瞻性队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 397-402. |
| [2] | 曾媛媛,谢云,陈道南,王瑞兰. 脓毒症患者发生正常甲状腺性病态综合征的相关因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 526-532. |
| [3] | 刘笑晗,杨帆,王昕迪,黄宁,程陶朱,郭静. 中国流动人口自评健康状况影响因素及公平性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 223-229. |
| [4] | 汤华萌,袁典琪,王明星,杨晗冰,郭超. 数字融入和健康生活方式对社会经济状况与老年人抑郁关系的序列中介作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 230-238. |
| [5] | 沈鹤军,侍崇艳,郑清,黄玉,景涛. 我国高中生静坐时长与健康素养现状及其影响因素调查[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 239-246. |
| [6] | 安思兰,郑群怡,王锴,高姗. 全膝关节置换术后患者早期疼痛的特点及其影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 167-173. |
| [7] | 赖金惠,王起,姬家祥,王明瑞,唐鑫伟,许克新,徐涛,胡浩. 新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情期间延迟拔除输尿管支架对泌尿系结石术后患者生活质量和心理状态的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 857-864. |
| [8] | 祝春素,连至炜,崔一民. 中国中老年人抑郁和慢性病的关联[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 606-611. |
| [9] | 王婷,李乔晟,刘皓冉,简伟研. 人格特征、城乡差异与抑郁症状变化的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 385-391. |
| [10] | 崔孟杰,马奇,陈曼曼,马涛,王鑫鑫,刘婕妤,张奕,陈力,蒋家诺,袁雯,郭桐君,董彦会,马军,星一. 不同生长模式与7~17岁儿童青少年代谢综合征的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 415-420. |
| [11] | 党佳佳,蔡珊,钟盼亮,王雅琪,刘云飞,师嫡,陈子玥,张依航,胡佩瑾,李晶,马军,宋逸. 室外夜间人工光暴露与中国9~18岁儿童青少年超重肥胖的关联[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 421-428. |
| [12] | 袁雯,张奕,陈力,蒋家诺,陈曼曼,刘婕妤,马涛,马奇,崔孟杰,郭桐君,王鑫鑫,董彦会,马军. 儿童青少年身体脂肪分布与抑郁和社交焦虑的关联:基于双能X线检测的横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 429-435. |
| [13] | 张紫薇,花语蒙,刘爱萍. 中国中老年人群抑郁症状、缺血性心血管疾病10年风险对心血管疾病的联合影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 465-470. |
| [14] | 郑丹枫,李君禹,李佳曦,张英爽,钟延丰,于淼. 青少年特发性脊柱侧凸椎旁肌的病理特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 283-291. |
| [15] | 陆林,刘晓星,袁凯. 中国脑科学计划进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 791-795. |
|
||