北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (5): 908-912. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.05.024
优化环磷酰胺剂量在间质性膀胱炎/膀胱疼痛综合征啮齿动物模型中的应用
- 北京大学人民医院泌尿外科,北京大学应用碎石研究所,北京 100044
Optimization study of an animal model for interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome based on the dose effect of cyclophosphamide
Hanwei KE, Qi WANG, Kexin XU*( )
)
- Department of Urology, Peking University Applied Liyhotripsy Institute, Peking University People's Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
摘要:
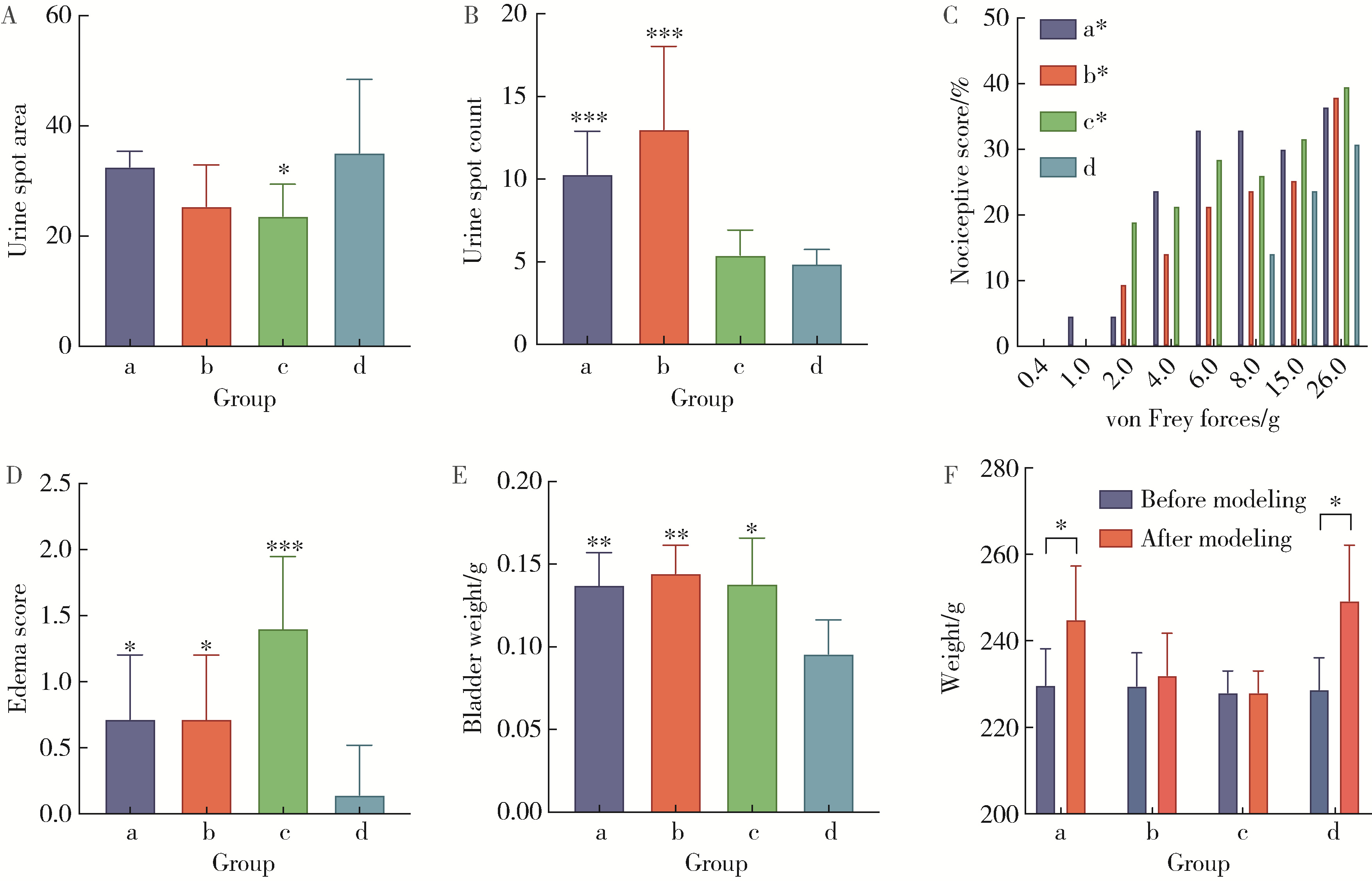
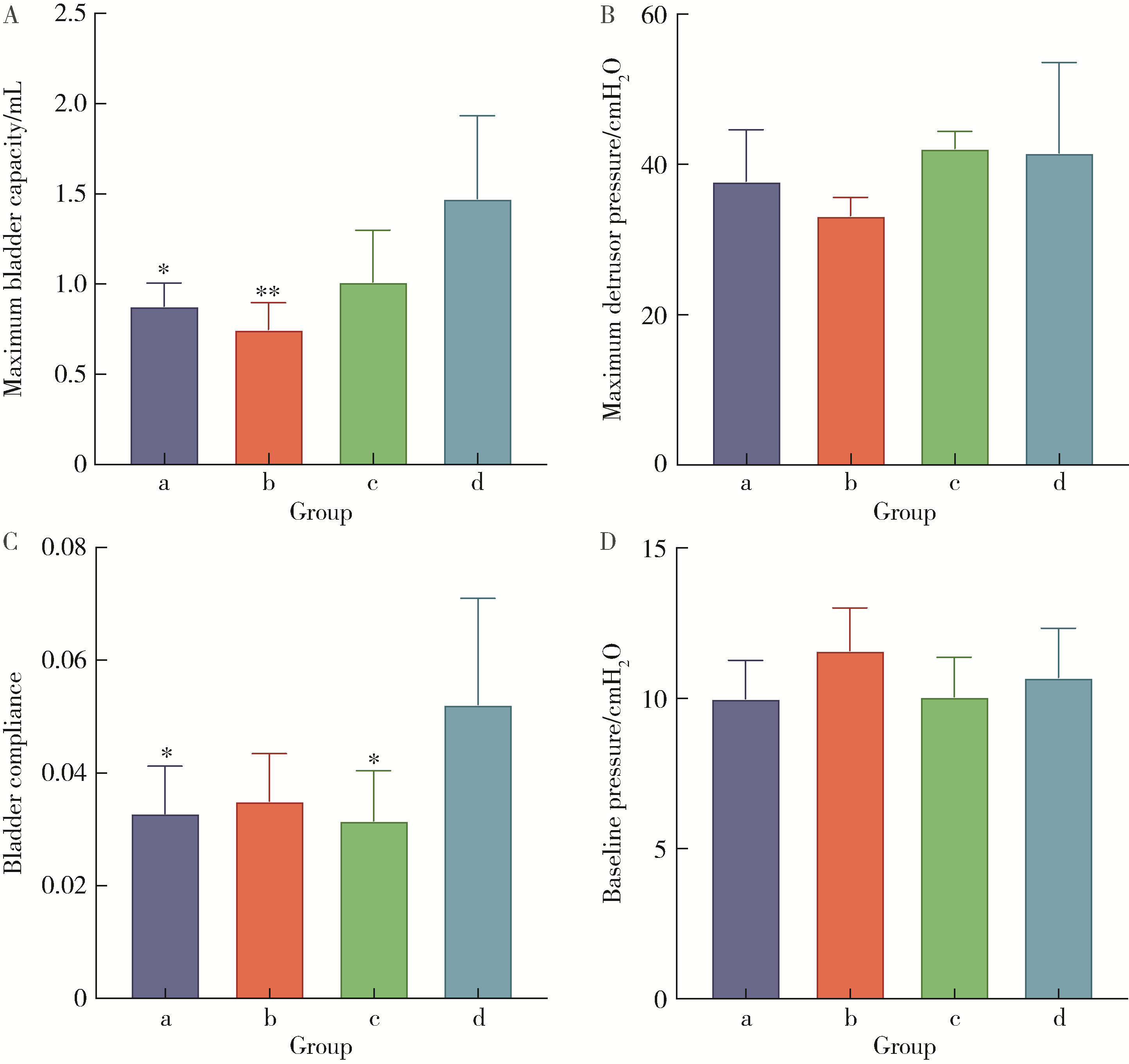
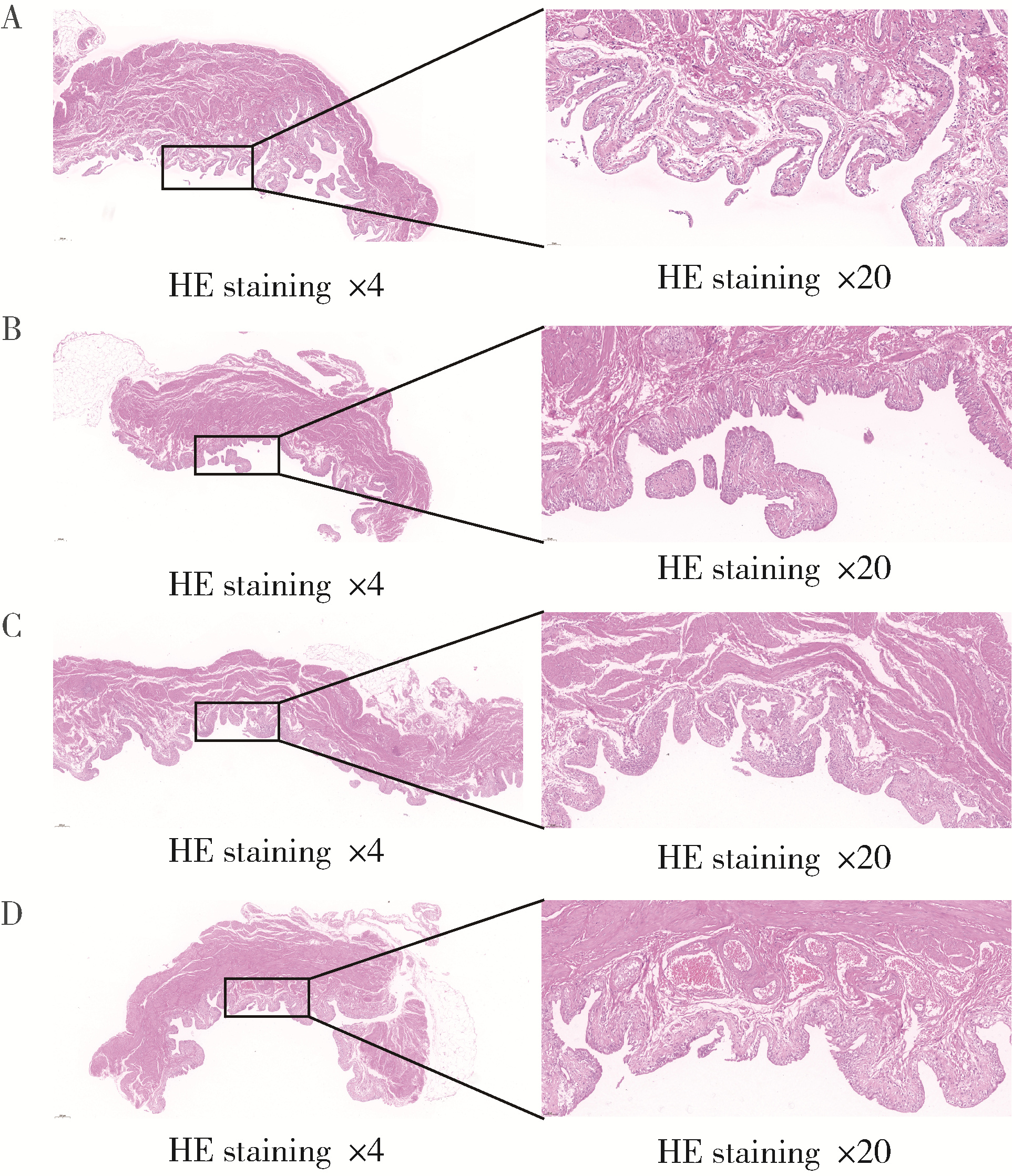
目的: 评估不同剂量的环磷酰胺(cyclophosphamide,CYP)诱导的间质性膀胱炎/膀胱痛综合征(interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome, IC/BPS)动物模型模拟疾病症状的准确性与可重复性,以期为IC/BPS的病理生理学研究和治疗策略评估提供实验模型依据。方法: 选用7周龄的Sprague-Dawley雌性大鼠28只分为a组(25 mg/kg CYP)、b组(75 mg/kg CYP)、c组(125 mg/kg CYP)和d组(对照组)4组,每组7只,通过腹腔注射CYP或生理盐水建立动物模型,评估指标包括尿斑实验、von Frey纤维触痛实验、尿动力学检查,以及组织学分析。结果: 25 mg/kg CYP剂量的大鼠在模拟IC/BPS膀胱功能障碍和炎症反应方面显著优于其他CYP剂量组,且对生理功能影响较小。所有剂量CYP处理的大鼠都表现出膀胱炎症,但25 mg/kg剂量的症状与IC/BPS临床特征更为一致。此外,25 mg/kg CYP剂量组大鼠膀胱顺应性降低,内脏疼痛增加,但未显著增加排尿频率,与IC/BPS患者表现相似。结论: 25 mg/kg的CYP剂量在模拟非溃疡性IC/BPS的关键特征方面表现出明显的优势,对未来IC/BPS的研究和治疗策略提供了重要参考。但尽管如此,由于IC/BPS的多因素性质,未来研究需要探索更多诱导手段,以复现疾病的复杂病理过程。
中图分类号:
- R694.3
| 1 |
Driscoll A , Teichman JMH . How do patients with interstitial cystitis present[J]. J Urol, 2001, 166 (6): 2118- 2120.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)65517-6 |
| 2 |
Hanno PM , Erickson D , Moldwin R , et al. Diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: AUA guideline amendment[J]. J Urol, 2015, 193 (5): 1545- 1553.
doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2015.01.086 |
| 3 |
Parsons CL . The role of the urinary epithelium in the pathogenesis of interstitial cystitis/prostatitis/urethritis[J]. Urology, 2007, 69, S9- S16.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2006.03.084 |
| 4 |
van de Merwe JP . Interstitial cystitis and systemic autoimmune diseases[J]. Nat Clin Pract Urol, 2007, 4 (9): 484- 491.
doi: 10.1038/ncpuro0874 |
| 5 |
Cox PJ . Cyclophosphamide cystitis: Identification of acrolein as the causative agent[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 1979, 28 (13): 2045- 2049.
doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90222-3 |
| 6 |
Liu XY , Zhu MZ , Xie JP . Mutagenicity of acrolein and acrolein-induced DNA adducts[J]. Toxicol Mech Methods, 2010, 20 (1): 36- 44.
doi: 10.3109/15376510903530845 |
| 7 |
Vera PL , Iczkowski KA , Wang X , et al. Cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis increases bladder CXCR4 expression and CXCR4-macrophage migration inhibitory factor association[J]. PLoS One, 2008, 3 (12): e3898.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003898 |
| 8 |
Boucher M , Meen M , Codron JP , et al. Cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis in freely-moving conscious rats: Behavioral approach to a new model of visceral pain[J]. J Urol, 2000, 164 (1): 203- 208.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)67495-2 |
| 9 | Augé C , Chene G , Dubourdeau M , et al. Relevance of the cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis model for pharmacological studies targeting inflammation and pain of the bladder[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2013, 707 (1/2/3): 32- 40. |
| 10 |
Augé C , Gamé X , Vergnolle N , et al. Characterization and validation of a chronic model of cyclophosphamide-induced interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome in rats[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11, 1305.
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01305 |
| 11 |
Gray KJ , Engelmann UH , Johnson EH , et al. Evaluation of misoprostol cytoprotection of the bladder with cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan) therapy[J]. J Urol, 1986, 136 (2): 497- 500.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)44929-9 |
| 12 |
Hakimi Z , Houbiers J , Pedersini R , et al. The burden of bladder pain in five european countries: A cross-sectional study[J]. Urology, 2017, 99, 84- 91.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2016.08.038 |
| 13 |
Smaldone MC , Vodovotz Y , Tyagi V , et al. Multiplex analysis of urinary cytokine levels in rat model of cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis[J]. Urology, 2009, 73 (2): 421- 426.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2008.07.031 |
| 14 |
Arms L , Girard BM , Vizzard MA . Expression and function of CXCL12/CXCR4 in rat urinary bladder with cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis[J]. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2010, 298 (3): F589- F600.
doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00628.2009 |
| 15 |
May V , Vizzard MA . Bladder dysfunction and altered somatic sensitivity in PACAP-/-mice[J]. J Urol, 2010, 183 (2): 772- 779.
doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2009.09.077 |
| 16 |
Augé C , Basso L , Blanpied C , et al. Pain management in a model of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome by a vaccinal strategy[J]. Front Pain Res (Lausanne), 2021, 2, 642706.
doi: 10.3389/fpain.2021.642706 |
| 17 |
Koziol JA , Adams HP , Frutos A . Discrimination between the ulcerous and the nonulcerous forms of interstitial cystitis by noninvasive findings[J]. J Urol, 1996, 155 (1): 87- 90.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(01)66551-0 |
| [1] | 辛鹏,张昊,姜振明. 膀胱内灌注电灼联合水扩张法治疗女性间质性膀胱炎[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 865-870. |
| [2] | 孟令玮,李雪,高胜寒,李悦,曹瑞涛,张毅,潘韶霞. 三种方法建立大鼠种植体周炎模型的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 22-29. |
| [3] | 邵苗,郭惠芳,雷玲彦,赵清,丁艳杰,林进,吴锐,于峰,李玉翠,苗华丽,张莉芸,杜燕,焦瑞英,庞丽霞,龙丽,栗占国,李茹. 短间期小剂量环磷酰胺治疗系统性红斑狼疮耐受性的多中心对照研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1112-1116. |
| [4] | 朱琳,张维宇,许克新. 环磷酰胺诱导SD大鼠膀胱疼痛综合征模型的有效性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 735-740. |
| [5] | 王贵红,左婷,李然,左正才. 瑞巴派特在大鼠痛风性关节炎急性发作中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 716-720. |
| [6] | 王佳文,刘敬超,孟令峰,张威,刘晓东,张耀光. 间质性膀胱炎/膀胱疼痛综合征患者生活质量及相关因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 653-658. |
| [7] | 王涛,许克新,张维宇,胡浩,张晓威,王焕瑞,刘献辉,陈京文,张晓鹏. 男性膀胱过度活动症的尿动力学分型及临床疗效随访[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6): 1048-1051. |
| [8] | 张维宇,夏秋翔,胡浩,陈京文,孙屹然,许克新,张晓鹏. 门诊女性下尿路症状患者尿动力学检查结果分析及逼尿肌无力患者的随访[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(5): 856-862. |
| [9] | 张维宇,张晓鹏,陈京文,孙屹然,王佳,胡浩,许克新. 年龄因素对女性尿失禁患者尿动力学参数的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(5): 825-829. |
| [10] | 张维宇,胡浩,王起,陈京文,许克新. 女性压力性尿失禁患者术前尿动力学检查的意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(4): 655-658. |
| [11] | 许丹, 林峰, 朱小语, 刘文颖, 陈晓文, 冯金秋, 范爱琴, 蔡木易, 许雅君. 牡蛎肽对免疫抑制小鼠免疫功能的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(3): 392-397. |
| [12] | 刘宁, 何峰, 满立波, 黄广林, 王海东, 王海, 李贵忠, 王建伟. 尿动力学检查中伪像的曲线特征及影响因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(5): 817-820. |
| [13] | 邓小林, 张虎, 史本涛, 关志忱. 家庭尿流率测定在下尿路症状患者评估中的研究进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(4): 655-658. |
| [14] | 关志忱, 邓小林, 张黔. 新型移动式家庭电子尿流率仪和Laborie 尿流率仪临床检测结果比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2011, 43(4): 616-619. |
| [15] | 胡卫国, 王晓峰, 徐涛, 李建兴, 陈亮, 于澄钒, 黄晓波. 纳米细菌大鼠肾结石模型初步建立及成石因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2010, 42(4): 433-435. |
|
||