北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (6): 1112-1116. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.06.009
短间期小剂量环磷酰胺治疗系统性红斑狼疮耐受性的多中心对照研究
邵苗1,郭惠芳2,雷玲彦2,赵清3,丁艳杰3,林进4,吴锐5,于峰6,李玉翠7,苗华丽7,张莉芸7,杜燕8,焦瑞英9,庞丽霞9,龙丽10,栗占国1,*( ),李茹1,*(
),李茹1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学人民医院风湿免疫科,北京 100044
2. 河北医科大学第二医院风湿免疫科,石家庄 050000
3. 河南大学淮河医院风湿免疫科,河南开封 475000
4. 浙江大学医学院附属第一医院风湿免疫科,杭州 310003
5. 南昌大学第一附属医院风湿免疫科,南昌 330006
6. 北京大学第一医院肾内科,北京 100034
7. 山西白求恩医院风湿免疫科,太原 030032
8. 浙江大学医学院附属第二医院风湿免疫科,杭州 310009
9. 呼伦贝尔市人民医院风湿免疫科,内蒙古呼伦贝尔 021008
10. 四川省人民医院风湿免疫科,成都 610071
A multicenter study on the tolerance of intravenous low-dose cyclophosphamide in systemic lupus erythematosus
Miao SHAO1,Hui-fang GUO2,Ling-yan LEI2,Qing ZHAO3,Yan-jie DING3,Jin LIN4,Rui WU5,Feng YU6,Yu-cui LI7,Hua-li MIAO7,Li-yun ZHANG7,Yan DU8,Rui-ying JIAO9,Li-xia PANG9,Li LONG10,Zhan-guo LI1,*( ),Ru LI1,*(
),Ru LI1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University People's Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
2. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, The Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050000, China
3. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Huaihe Hospital of Henan University, Kaifeng 475000, Henan, China
4. Department of Rheumatology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310003, China
5. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, China
6. Renal Division, Department of Medicine, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
7. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Shanxi Bethune Hospital, Taiyuan 030032, China
8. Department of Rheumatology, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310009, China
9. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Hulunbuir People's Hospital, Hulunbuir 021008, Inner Mongolia, China
10. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Sichuan Provincial People's Hospital, Chengdu 610071, China
摘要:
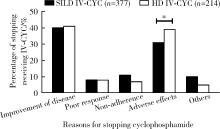
目的: 比较大剂量环磷酰胺及短间期小剂量环磷酰胺两种方案治疗系统性红斑狼疮(systemic lupus erythematosus,SLE)患者的耐受性。方法: 收集2017年3月至2018年7月期间在全国17个省份24家医院就诊的1 022例SLE患者的基本信息、临床表现、实验室检查结果、不良反应及伴随疾病等。根据静脉输注环磷酰胺的治疗方案分为短间期小剂量环磷酰胺组(short-interval low-dose intravenous cyclophosphamide therapy,SILD IV-CYC,每次400 mg,每2周1次)和大剂量环磷酰胺组(high-dose intravenous cyclophosphamide therapy,HD IV-CYC,每次500 mg/m2体表面积,每月1次),有256例接受大剂量环磷酰胺治疗,506例接受短间期小剂量环磷酰胺治疗,比较两组患者停药原因及治疗过程中的不良反应发生率,另有260例患者因没有规律应用环磷酰胺未纳入两组治疗方案不良反应的比较。此外,377例接受短间期小剂量环磷酰胺治疗和214例接受大剂量环磷酰胺治疗的SLE患者随访到停用环磷酰胺,对其停药原因进行分析。结果: 在所有591例停环磷酰胺的患者中,有199例(33.67%)SLE患者因发生药物相关不良反应停药,238例(40.27%)SLE患者因为病情改善而停用环磷酰胺。大剂量环磷酰胺治疗组的SLE患者中因不良反应停用环磷酰胺的比例为38.79%(83/214),明显高于短间期小剂量环磷酰胺治疗组的30.77%(116/377,P=0.048)。进一步比较506例接受短间期小剂量环磷酰胺治疗和256例接受大剂量环磷酰胺治疗患者的不良反应提示,短间期小剂量环磷酰胺治疗组感染(13.04% vs. 22.27%,P=0.001)、胃肠道反应(17.39% vs. 31.25%,P < 0.001)、骨髓抑制(9.68% vs. 19.92%,P < 0.001)、月经异常(25.18% vs. 39.72%,P=0.001)、脱发(13.44% vs. 19.14%,P=0.039)等不良反应发生率明显低于大剂量环磷酰胺治疗组。结论: 短间期小剂量环磷酰胺方案(SILD方案)治疗SLE的耐受性明显优于大剂量环磷酰胺治疗,患者不良反应的发生率较低。
中图分类号:
- R593.2
| 1 |
Fanouriakis A , Kostopoulou M , Alunno A , et al. 2019 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2019, 78 (6): 736- 745.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215089 |
| 2 |
Donadio JV , Holley KE , Ferguson RH , et al. Treatment of diffuse proliferative lupus nephritis with prednisone and combined prednisone and cyclophosphamide[J]. N Engl J Med, 1978, 299 (21): 1151- 1155.
doi: 10.1056/NEJM197811232992102 |
| 3 |
Boumpas DT , Austin HA , Vaughn EM , et al. Controlled trial of pulse methylprednisolone versus two regimens of pulse cyclophosphamide in sever lupus nephritis[J]. Lancet, 1992, 340 (8822): 741- 745.
doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92292-N |
| 4 |
Austin HA , Klippel JH , Balow JE , et al. Therapy of lupus nephritis. Controlled trial of prednisone and cytotoxic drugs[J]. N Engl J Med, 1986, 314 (10): 614- 619.
doi: 10.1056/NEJM198603063141004 |
| 5 |
Houssiau FA , Vasconcelos C , D'Cruz D , et al. Immunosuppressive therapy in lupus nephritis: The Euro-Lupus Nephritis Trial, a randomized trial of low-dose versus high-dose intravenous cyclophosphamide[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2002, 46 (8): 2121- 2131.
doi: 10.1002/art.10461 |
| 6 |
Hussenbocus YA , Jin ZY , Pan WY , et al. Low dosage use of cyclophosphamide improves the survival of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2022, 41 (7): 2043- 2052.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-022-06117-y |
| 7 |
Durcan L , O'Dwyer T , Petri M . Management strategies and future directions for systemic lupus erythematosus in adults[J]. Lancet, 2019, 393 (10188): 2332- 2343.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30237-5 |
| 8 |
Zhang XW , Li C , Ma XX , et al. Short-interval lower-dose intravenous cyclophosphamide as induction and maintenance therapy for lupus nephritis: A prospective observational study[J]. Clinical Rheumatol, 2014, 33 (7): 939- 945.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-014-2590-6 |
| 9 |
Hanaoka H , Kiyokawa T , Iida H , et al. Comparison of renal response to four different induction therapies in Japanese patients with lupus nephritis class Ⅲ or Ⅳ: A single-centre retrospective study[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12 (4): e0175152.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175152 |
| 10 |
Thomas G , Mancini J , Jourde-Chiche N , et al. Mortality associa-ted with systemic lupus erythematosus in France assessed by multiple-cause-of-death analysis[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2014, 66 (9): 2503- 2511.
doi: 10.1002/art.38731 |
| 11 | Wang Z , Wang Y , Zhu R , et al. Long-term survival and death causes of systemic lupus erythematosus in China: A systemic review of observational studies[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2015, 94 (17): e794. |
| 12 |
Wang H , Zhou Y , Yu L , et al. Major infection in newly diagnosed systemic lupus erythematosus: An inception cohort study[J]. Lupus Sci Med, 2022, 9 (1): e000725.
doi: 10.1136/lupus-2022-000725 |
| 13 |
Ghobadi MZ , Izadi S , Teymoori-RM , et al. Potential role of viral infection and B cells as a linker between innate and adaptive immune response in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Immunol Res, 2021, 69 (2): 196- 204.
doi: 10.1007/s12026-021-09186-4 |
| 14 |
Mok CC , Tse SM , Chan KL , et al. Effect of immunosuppressive therapies on survival of systemic lupus erythematosus: A propensity score analysis of a longitudinal cohort[J]. Lupus, 2018, 27 (5): 722- 727.
doi: 10.1177/0961203317739129 |
| 15 |
Tian M , Song XH , Dong LP , et al. Systematic evaluation of different doses of cyclophosphamide induction therapy for lupus nephritis[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2017, 96 (51): e9408.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009408 |
| 16 |
Giambalvo S , Garaffoni C , Silvagni E , et al. Factors associated with fertility abnormalities in women with systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2022, 21 (4): 103038.
doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2022.103038 |
| 17 |
Katsifis GE , Tzioufas AG . Ovarian failure in systemic lupus erythematosus patients treated with pulsed intravenous cyclophosphamide[J]. Lupus, 2004, 13 (9): 673- 678.
doi: 10.1191/0961203304lu2012oa |
| 18 |
Ponticelli C , Escoli R , Moroni G . Does cyclophosphamide still play a role in glomerular diseases?[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2018, 17 (10): 1022- 1027.
doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2018.04.007 |
| [1] | 武志慧, 胡明智, 赵巧英, 吕凤凤, 张晶莹, 张伟, 王永福, 孙晓林, 王慧. miR-125b-5p修饰脐带间充质干细胞对系统性红斑狼疮的免疫调控机制[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 860-867. |
| [2] | 柯涵炜, 王起, 许克新. 优化环磷酰胺剂量在间质性膀胱炎/膀胱疼痛综合征啮齿动物模型中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 908-912. |
| [3] | 乔佳佳,田聪,黄晓波,刘军. 肾结石合并系统性红斑狼疮行经皮肾镜碎石取石术的安全性和有效性评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 745-749. |
| [4] | 任立敏,赵楚楚,赵义,周惠琼,张莉芸,王友莲,沈凌汛,范文强,李洋,厉小梅,王吉波,程永静,彭嘉婧,赵晓珍,邵苗,李茹. 系统性红斑狼疮低疾病活动度及缓解状况的真实世界研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 273-278. |
| [5] | 赵祥格,刘佳庆,黄会娜,陆智敏,白自然,李霞,祁荆荆. 干扰素-α介导系统性红斑狼疮外周血CD56dimCD57+自然杀伤细胞功能的损伤[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 975-981. |
| [6] | 姚海红,杨帆,唐素玫,张霞,何菁,贾园. 系统性红斑狼疮及成人Still病合并巨噬细胞活化综合征的临床特点及诊断指标[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
| [7] | 罗芷筠,吴佳佳,宋优,梅春丽,杜戎. 伴神经精神系统病变的系统性红斑狼疮相关巨噬细胞活化综合征2例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1111-1117. |
| [8] | 李敏,侯林卿,金月波,何菁. 系统性红斑狼疮合并视网膜病变的临床及免疫学特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1106-1111. |
| [9] | 张琳崎,赵静,王红彦,王宗沂,李英妮,汤稷旸,李思莹,曲进锋,赵明威. 抗ENO1抗体与狼疮性视网膜病变的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1099-1105. |
| [10] | 朱琳,张维宇,许克新. 环磷酰胺诱导SD大鼠膀胱疼痛综合征模型的有效性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 735-740. |
| [11] | 杜莹珏,刘维超,陈茜,程永静. 秋水仙碱致慢性肾脏病患者肌肉病变1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1188-1190. |
| [12] | 邹健梅,武丽君,罗采南,石亚妹,吴雪. 血清25-羟维生素D与系统性红斑狼疮活动的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 938-941. |
| [13] | 夏芳芳,鲁芙爱,吕慧敏,杨国安,刘媛. 系统性红斑狼疮伴间质性肺炎的临床特点及相关因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 266-272. |
| [14] | 耿研,李伯睿,张卓莉. 系统性红斑狼疮患者有症状关节病变的肌肉骨骼超声特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 163-168. |
| [15] | 王玉华,张国华,张令令,罗俊丽,高兰. 系统性红斑狼疮合并自发性肾上腺出血1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6): 1178-1181. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 187
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 486
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||