北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2026, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (1): 153-159. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2026.01.020
1 812例唾液腺结石患者的人口学特征和临床特点
杨雨婷, 屈留洋, 郑丹妮, 凌晓彤, 许晓韵, 柳登高*( )
)
- 北京大学口腔医学院 · 口腔医院医学影像科,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心,口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,国家卫生健康委员会口腔数字医学重点实验室,国家药品监督管理局口腔材料重点实验室,北京 100081
Demographic characteristic and clinical features in 1 812 patients with salivary gland stones
Yuting YANG, Liuyang QU, Danni ZHENG, Xiaotong LING, Xiaoyun XU, Denggao LIU*( )
)
- Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NHC Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NMPA Key Laboratory for Dental Materials, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
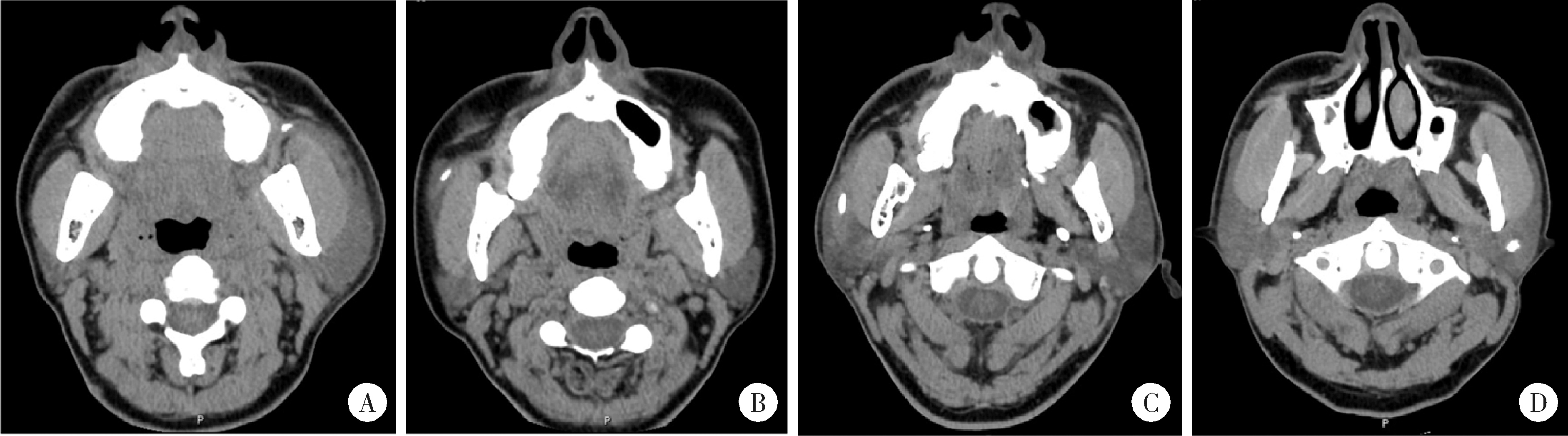
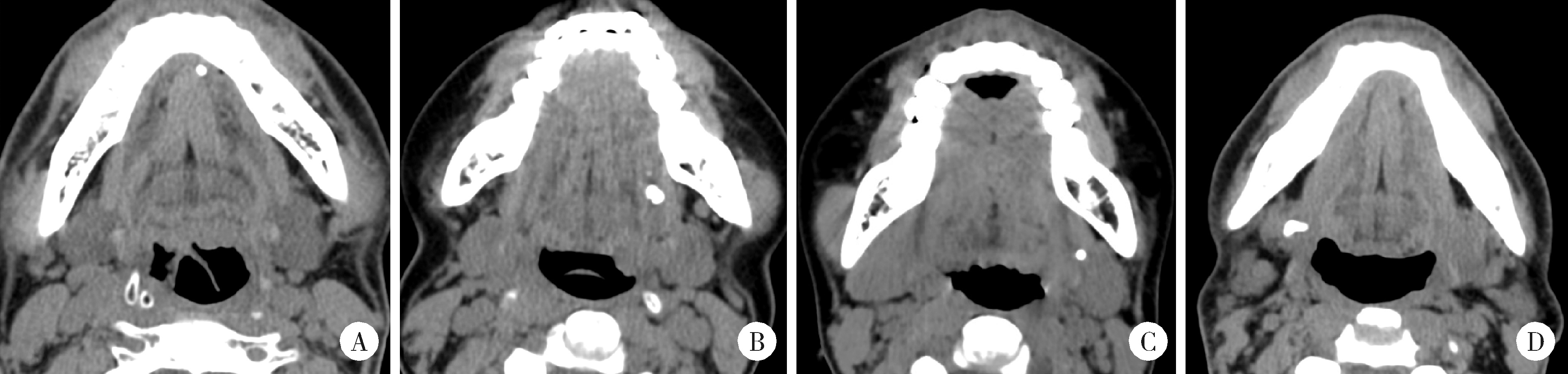
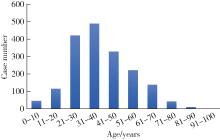
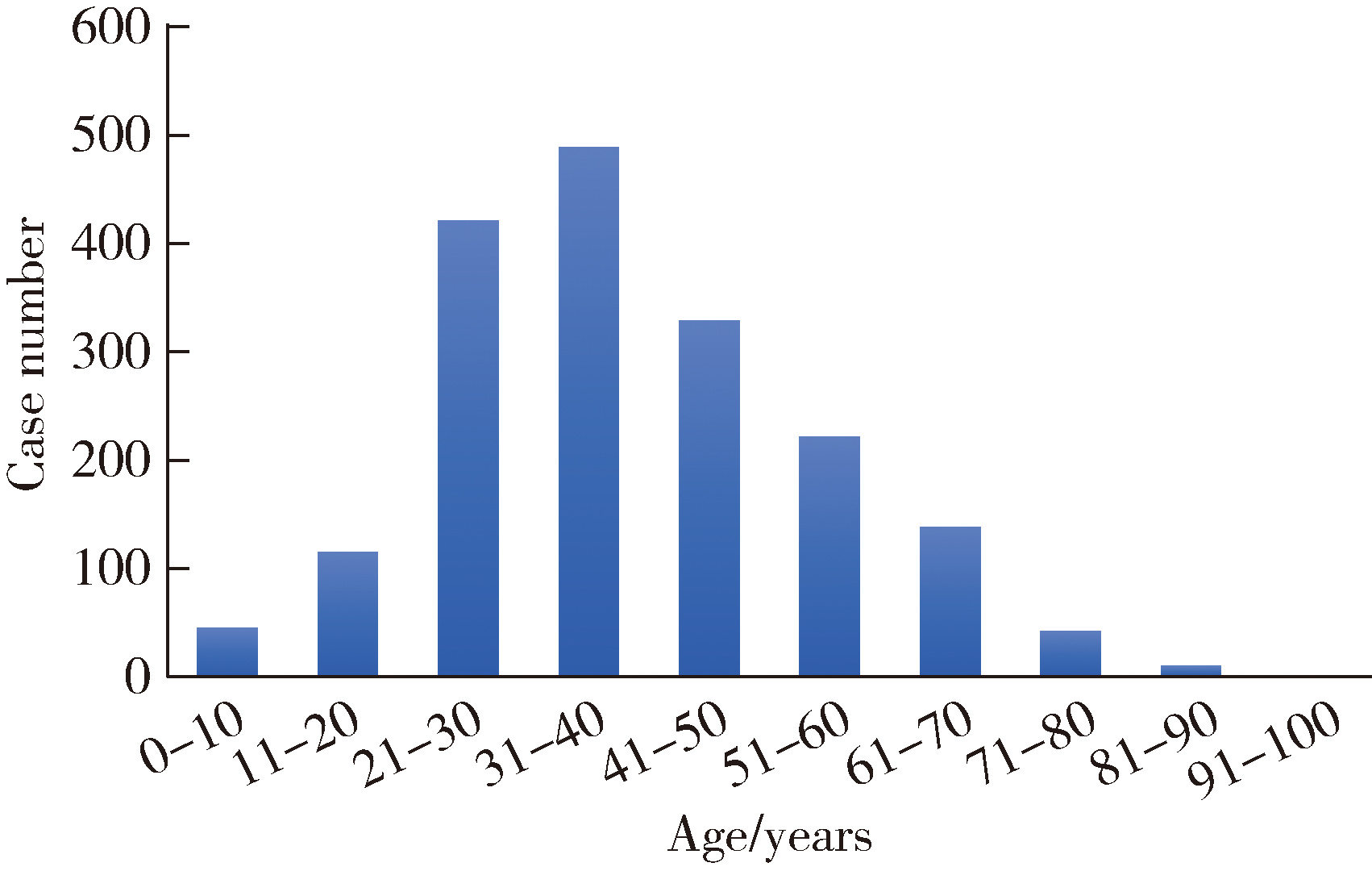
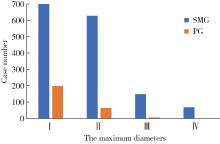
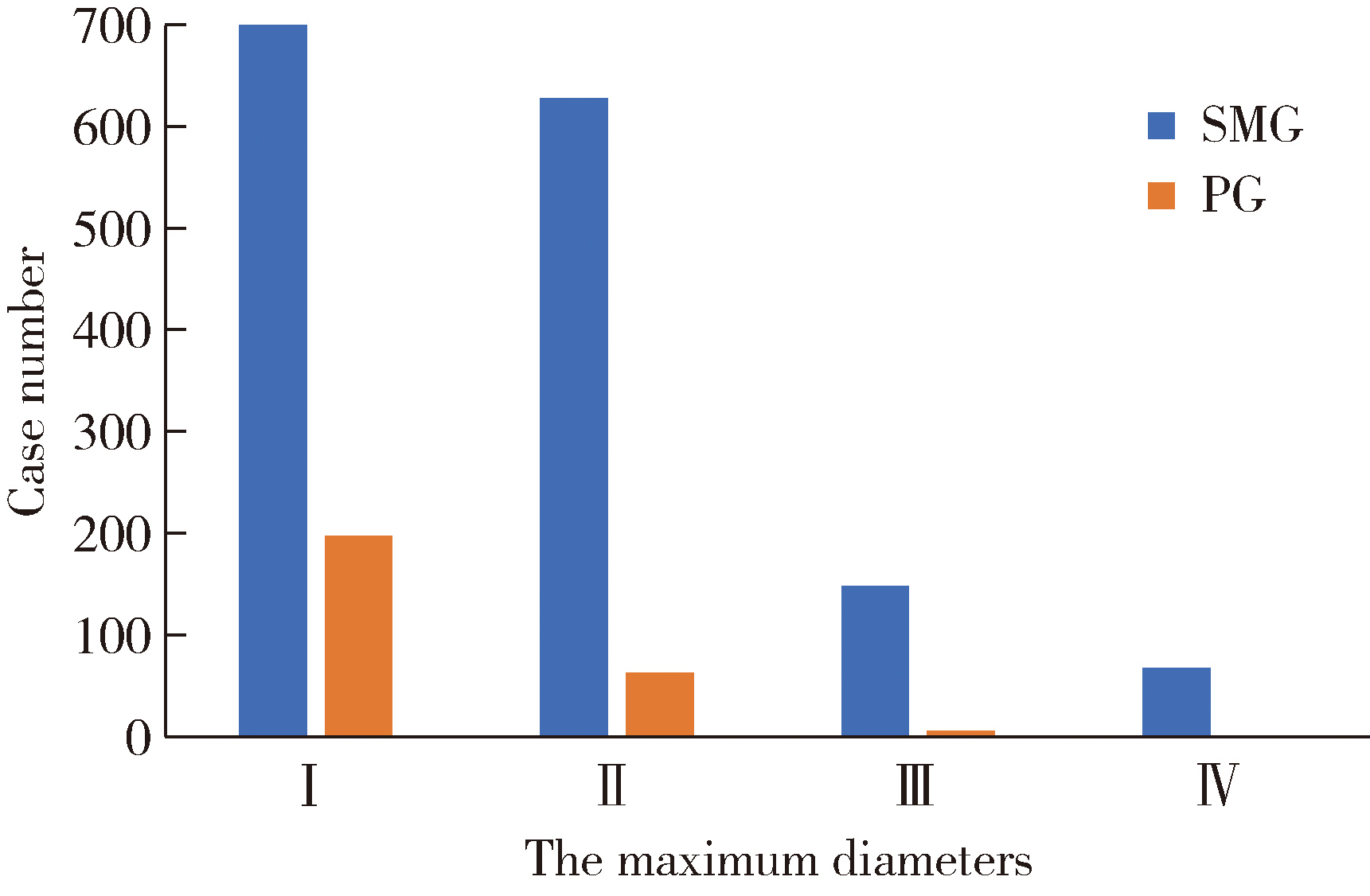
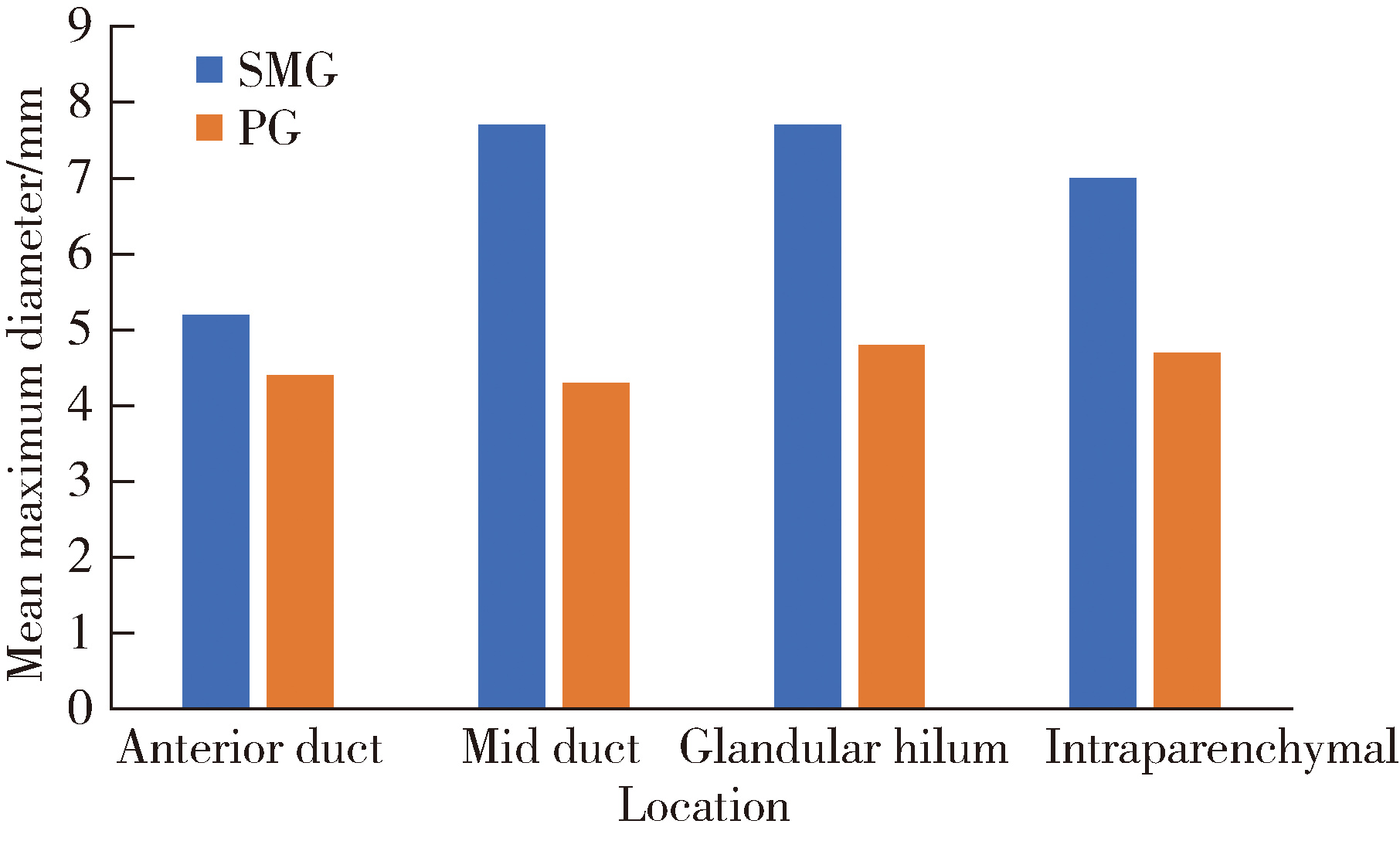
目的: 基于较大样本量及完善的临床与影像学资料,分析唾液腺结石病的人口学特征和临床发病特点。方法: 回顾性收集2020年1月至2024年12月于北京大学口腔医院唾液腺内镜中心就诊的唾液腺结石患者的临床及影像资料,统计患者的性别、年龄、病程及受累腺体,测量结石的数目、大小、位置及长短径之比,分析唾液腺结石病的人群特征、临床与影像学特点。结果: 共收集1 812例唾液腺结石患者,男性855例,女性957例,年龄4~97岁,平均年龄(39.0±15.0)岁,中位病程6.0个月。结石多累及单侧腺体(98.4%),多为单发(64.3%),平均直径(6.5±4.6) mm。本组病例包括下颌下腺结石1 541例(85.0%),腮腺结石267例(14.7%),其余4例患者的下颌下腺及腮腺均受累。下颌下腺结石多位于腺外主导管(50.2%),其次为腺门部(41.5%),仅少数位于腺内(8.2%);腮腺结石大部分位于腺外主导管(75.2%)。下颌下腺结石的平均直径显著大于腮腺结石[(6.9±4.8) mm vs. (4.5±2.5) mm],下颌下腺结石患者的平均年龄显著低于腮腺结石患者[(38.0±15.0)岁vs. (48.0±16.0)岁]。腮腺结石的复发率(3.4%)和下颌下腺结石的复发率(2.1%)都较低,复发间隔2个月至10年不等,平均(33.8±31.4)个月。本组病例中,21例(1.2%)患者的结石来源于异物钙化,包括9例下颌下腺结石和12例腮腺结石患者。结论: 唾液腺结石病好发于中年人群,无明显的性别差异,绝大多数为单侧腺体受累,单发结石较多见;下颌下腺结石与腮腺结石在好发部位、大小、结石形状(长宽比)及患者年龄等方面均存在明显差异;唾液腺结石的复发率较低,少数结石由异物钙化引起;这些发病特点,可为阐明唾液腺结石病的发病机制及优化诊疗策略提供依据。
中图分类号:
- R781.75
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
doi: 10.1016/S0901-5027(05)80127-4 |
| 3 |
doi: 10.1038/sj.bdj.4800141a |
| 4 |
doi: 10.1067/moe.2000.109075a |
| 5 |
doi: 10.1016/S0030-6665(05)70175-4 |
| 6 |
doi: 10.1038/sj.bdj.2014.1054 |
| 7 |
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2022.10.007 |
| 8 |
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2023.12.001 |
| 9 |
doi: 10.1001/jama.1962.03050390017005 |
| 10 |
doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(83)90341-9 |
| 11 |
doi: 10.1002/lary.25377 |
| 12 |
doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2005.10.063 |
| 13 |
doi: 10.1002/bjs.4789 |
| 14 |
doi: 10.1007/s001060050476 |
| 15 |
doi: 10.1177/0194599812452837 |
| 16 |
doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2009.08.012 |
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
doi: 10.1259/dmfr.20210361 |
| 19 |
伊里夏提·卡米力. 颌下腺导管腺门结石形成的解剖学因素研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆医科大学, 2014.
|
| 20 |
doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2022.08.005 |
| 21 |
doi: 10.1016/S0003-9969(02)00211-X |
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
doi: 10.4103/0976-237X.111599 |
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
doi: 10.1001/archotol.127.1.66 |
| 28 |
doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2016.02.008 |
| 29 |
doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000000851 |
| 30 |
doi: 10.1002/hed.25560 |
| [1] | 杨源源, 张珊珊, 俞光岩, 杨辉俊, 杨宏宇. 部分下颌下腺切除术治疗下颌下腺良性肿瘤的临床效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(2): 334-339. |
| [2] | 杨玉淑, 齐晅, 丁萌, 王炜, 郭惠芳, 高丽霞. 抗唾液腺蛋白1抗体联合抗腮腺分泌蛋白抗体对干燥综合征的诊断价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 845-852. |
| [3] | 柳登高,郑丹妮,赵雅宁,张亚琼,叶欣,张丽琪,谢晓艳,张雷,张祖燕,俞光岩. 疑难唾液腺结石病的治疗研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 8-12. |
| [4] | 俞光岩,苏家增,柳登高,吴立玲,丛馨. 下颌下腺保存治疗新技术体系的建立与应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 842-845. |
| [5] | 李炳雨,唐祖南,胡耒豪,章文博,于尧,俞光岩,彭歆. 腮腺微小肿瘤的临床病理研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 335-339. |
| [6] | 陈超伦,苏家增,俞光岩. 酸刺激对腮腺和下颌下腺唾液流率及成分的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 89-94. |
| [7] | 俞光岩,柳登高,李巍,洪霞,张严妍,朱文瑄,张可夫,李潇,栗占国,刘燕鹰,陈艳,高岩,苏家增. 3类新型慢性唾液腺炎的诊断和治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 13-17. |
| [8] | 朱忆颖,闵赛南,俞光岩. 局部注射环孢素A对非肥胖糖尿病小鼠下颌下腺分泌功能及炎症的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 750-757. |
| [9] | 王怡平,蔡志刚,彭歆,张杰,孙志鹏,李巍,张雷,俞光岩. 下颌下腺质量和体积的实体体外检测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 126-132. |
| [10] | 俞光岩. 多发性唾液腺肿大的鉴别诊断及处理[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 1-4. |
| [11] | 李玉冰,孙丽莎,孙志鹏,谢晓艳,张建运,张祖燕,赵燕平,马绪臣. 腮腺CT影像报告与数据系统的初步研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 83-89. |
| [12] | 丛馨,闵赛南,吴立玲,蔡志刚,俞光岩. 激活毒蕈碱乙酰胆碱受体调控下颌下腺分泌的机制研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(3): 390-396. |
| [13] | 宿骞,彭歆,周传香,俞光岩. 原发性腮腺淋巴瘤的临床病理特点及预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(1): 35-42. |
| [14] | 俞光岩,洪霞,李巍,张严妍,高岩,陈艳,张祖燕,谢晓艳,栗占国,刘燕鹰,苏家增,朱文瑄,孙志鹏. IgG4相关唾液腺炎的临床病理特点及诊断[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(1): 1-3. |
| [15] | 俞光岩,吴立玲,蔡志刚,吕岚,丛馨. 血管化自体下颌下腺移植治疗重症干眼20年研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(1): 1-4. |
|
||