北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 510-518. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.03.020
腹膜透析患者营养不良-炎症-心血管疾病与认知功能恶化的关系
- 1. 邯郸市中心医院肾内一科,河北邯郸 056001
2. 北京大学第一医院肾内科,北京大学肾脏病研究所,卫生部重点实验室,教育部慢性肾脏病防治重点实验室,北京 100034
Association of malnutrition-inflammation-cardiovascular disease with cognitive deterioration in peritoneal dialysis patients
Li-ping DUAN1,Zhao-xia ZHENG1,Yu-hui ZHANG2,Jie DONG2△( )
)
- 1. Handan Central Hospital, Department 1 of Nephrology, Handan 056001, Hebei, China
2. Renal Division, Department of Medicine; Institute of Nephrology, Peking University First Hospital; Key Laboratory of Renal Disease, Ministry of Health of China; Key Laboratory of Chronic Kidney Disease Prevention and Treatment, Ministry of Education, Beijing 100034, China
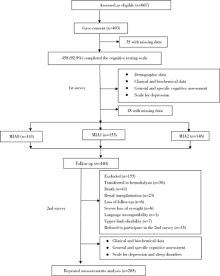
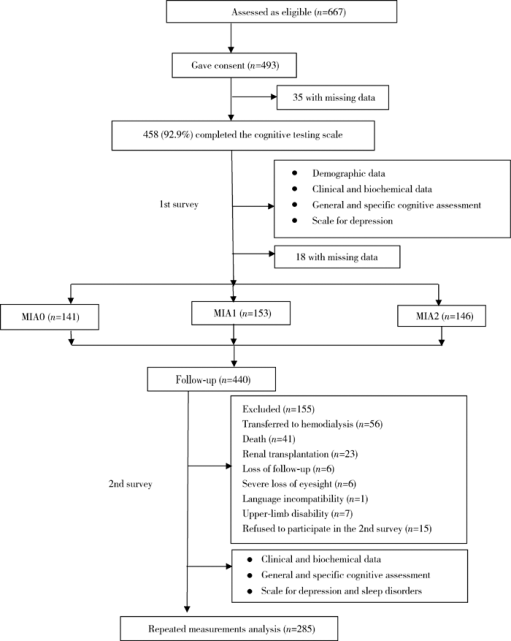
摘要: 目的 探讨腹膜透析(peritoneal dialysis, PD)患者存在的营养不良-炎症状态-心血管疾病(动脉硬化)(malnutrition-inflammation-atherosclerosis,MIA)综合征与认知功能恶化的关系。方法 采用前瞻性纵向队列研究,于2013年3—11月,对符合入选标准的腹膜透析患者完成总体和特定认知功能测定,结合基线是否有心血管疾病病史,白蛋白≤35 g/L,超敏C-反应蛋白(high-sensitive C-reactive protein, hs-CRP)≥3 mg/L,将患者分为MIA0(全为否)、MIA1(1项为是)、MIA2(≥2项为是)3个组,并于随访2年后对患者重复认知功能测定。采用卡方检验、单因素方差分析、Kruskal-Wallis H 检验比较基线及2年后组间一般资料、生化指标,以及总体和特定认知功能参数。进一步的组间多重两两比较采用Bonferroni方法调整显著性值。以每一项总体和特异认知功能得分差值为因变量,以年龄、性别、教育水平、体重指数、抑郁分数、糖尿病、血钠和MIA(MIA0为对照,MIA1和MIA2为哑变量)为自变量,以多元线性回归分析影响认知功能恶化的因素,每一项认知领域的分析都以其相应的基线参数进行校正。结果 随访2年后,认知障碍(cognitive impairment, CI)的发生率从20.0%上升到24.7%。MIA2和MIA1组修正的简易智力状态检查量表(the modified mini-mental state examination, 3MS)得分下降绝对值明显高于MIA0组(-3.9±12.0 vs. 1.1±6.7, P<0.01;-2.3±11.8 vs. 1.1±6.7, P<0.05),而特定认知功能测定包括执行功能(连线试验A和B,P=0.401,P=0.176)、即时记忆(P=0.437)、延迟记忆(P=0.104)、视觉空间能力(P=0.496)和语言能力(P=0.171)的变化3组间差异无统计学意义。经多元线性回归分析,年龄、教育水平、糖尿病、抑郁等均是一项或多项认知功能恶化的危险因素,存在MIA综合征一项因素是整体认知恶化的独立危险因素(P=0.022),存在MIA综合征两项及以上因素者不仅是整体认知恶化的独立危险因素(P<0.001),而且是延迟记忆、视觉功能及语言功能恶化的独立危险因素(P=0.002,P=0.007,P=0.004)。结论 腹膜透析患者存在MIA综合征一项及以上因素是总体认知功能恶化的高危人群;存在MIA综合征因素越多,患者的特异认知功能领域影响越广泛。
中图分类号:
- R459.5
| [1] |
Griva K, Stygall J, Hankins M , et al. Cognitive impairment and 7-year mortality in dialysis patients[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2010,56(4):693-703.
doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2010.07.003 |
| [2] |
Shea YF, Lam MF, Lee MS , et al. Prevalence of cognitive impairement among peritoneal dialysis patients, impact on peritonitis and role of assisted dialysis[J]. Perit Dial Int, 2016,36(3):284-290.
doi: 10.3747/pdi.2014.00247 |
| [3] |
Kalirao P, Pederson S, Foley RN , et al. Cognitive impairment in peritoneal dialysis patients[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2011,57(4):612-620.
doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2010.11.026 |
| [4] |
Kurella M, Chertow GM, Luan J , et al. Cognitive impairment in chronic kidney disease[J]. J Am Geriatr Soc, 2004,52(11):1863-1869.
doi: 10.1111/jgs.2004.52.issue-11 |
| [5] |
Dong J, Pi HC , Xiong ZY, et a1. Depression and cognitive impairment in peritoneal dialysis: A multi-center cross-sectional study[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2016,67(1):111-118.
doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.06.025 |
| [6] |
Zhang YH, Yang ZK, Wang JW , et al. Cognitive changes in peritoneal dialysis patients: a multi-center prospective cohort study[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2018,72(5):691-700.
doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2018.04.020 |
| [7] |
Kurella M, Mapes DL , Port FK, et a1. Correlates and outcomes of dementia among dialysis patients: the dialysis outcomes and practice patterns study[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2006,21(9):2543-2548.
doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfl275 |
| [8] |
Weiner DE, Scott TM , Giang LM, et a1. Cardiovascular disease and cognitive function in maintenance hemodialysis patients[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2011,58(5):773-781.
doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2011.03.034 |
| [9] |
Roberts RO, Geda YE , Knopman DS, et a1. Association of C-reactive protein with mild cognitive impairment[J]. Alzheimers Dement, 2009,5(5):398-405.
doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2009.01.025 |
| [10] |
Radi c ' J , Ljutic D , Radi c ' M , et al. Cognitive-psychomotor functions and nutritional status in maintenance hemodialysis patients: are they related[J]. Ther Apher Dial, 2011,15(6):532-539.
doi: 10.1111/tap.2011.15.issue-6 |
| [11] |
Tamura MK, Yaffe K . Dementia and cognitive impairment in ESRD: diagnostic and therapeutic strategies[J]. Kidney Int, 2011,79(1):14-22.
doi: 10.1038/ki.2010.336 |
| [12] |
Etgen T, Chonchol M, Förstl H , et al. Chronic kidney disease and cognitive impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Am J Nephrol, 2012,35(5):474-482.
doi: 10.1159/000338135 |
| [13] | 段丽萍, 郑朝霞, 吕宁 , 等. 腹膜透析患者营养不良-炎症-心血管疾病和认知功能的关系[J]. 中国血液净化, 2016,15(11):600-604. |
| [14] |
Smith SC, Jackson R, Pearson TA , et al. Principles for national and regional guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention: a scientific statement from the World Heart and Stroke Forum[J]. Circulation, 2004,109(25):3112-3121.
doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000133427.35111.67 |
| [15] | Teng EL, Chui HC . The modified mini-mental state (3MS) examination[J]. J Clin Psychiatry, 1987,48(8):314-318. |
| [16] |
Kurella M, Chertow GM, Fried LF , et al. Chronic kidney disease and cognitive impairment in the elderly: the health, aging, and body composition study[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2005,16(7):2127-2133.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2005010005 |
| [17] |
Lin FR, Yaffe K, Xia J , et al. Hearing loss and cognitive decline in older adults[J]. JAMA Intern Med, 2013,173(4):293-299.
doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.1868 |
| [18] | Randolph C . Repeatable battery for the assessment of neuropsychological status (RBANS)[Z]. San Antonio, TX: The Psychological Corporation, 1998. |
| [19] | Cheng Y, Wu W, Wang J , et al. Reliability and validity of the repeatable battery for the assessment of neuropsychological status in community-dwelling elderly[J]. Arch Med Sci, 2011,7(5):850-857. |
| [20] | 张保华, 谭云龙, 张五芳 , 等. 重复性成套神经心理状态测验的信度、效度分析[J]. 中国心理卫生杂志, 2008,22(12):865-869. |
| [21] | 杨贵刚, 田菊, 谭云龙 , 等. 重复性成套神经心理状态测验在北京地区正常人群中的应用[J]. 中国心理卫生杂志, 2010,24(12):926. |
| [22] |
Zung WW . A self-rating depression scale[J]. Arch Gen Psychiatry, 1965,12:63-70.
doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1965.01720310065008 |
| [23] |
Papagianni A, Kalovoulos M, Kirmizis D , et al. Carotid atherosclerosis is associated with inflammation and endothelial cell adhesion molecules in chronic haemodialysis patients[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2003,18(1):113-119.
doi: 10.1093/ndt/18.1.113 |
| [24] | Bartens W, Nauck M, Schollmeyer P , et al. Elevated lipoprotein(a)and fibrinogen levels [corrected] increase the cardiovascular risk in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients[J]. Perit Dial Int, 1996,16(1):27-33. |
| [25] |
Irish A . Cardiovascular disease, fibrinogen and theacute phase response: associations with lipids and blood pressure in patients with chronic renal disease[J]. Atherosclerosis, 1998,137(1):133-139.
doi: 10.1016/S0021-9150(97)00273-6 |
| [26] | Pi HC, Xu YF, Xu R , et al. Cognitive impairment and structural neuroimaging abnormalities among patients with chronic kidney disease [J]. Kidney Blood Press Res, 2016,41(6):986-996. |
| [1] | 侯婉音,董捷. 腹膜透析患者获得性肾囊肿出血3例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 546-550. |
| [2] | 陈楚云,孙蓬飞,赵静,贾佳,范芳芳,王春燕,李建平,姜一梦,霍勇,张岩. 北京社区人群促红细胞生成素相关因素及其与10年心血管疾病风险的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1068-1073. |
| [3] | 鲍雷,蔡夏夏,张明远,任磊磊. 维生素D3对2型糖尿病小鼠轻度认知障碍的改善作用及机制研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 587-592. |
| [4] | 闫晓晋,刘云飞,马宁,党佳佳,张京舒,钟盼亮,胡佩瑾,宋逸,马军. 《中国儿童发展纲要(2011-2020年)》实施期间中小学生营养不良率变化及其政策效应分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 593-599. |
| [5] | 乔婕,芦丽霞,何玉婷,门春翠,楚新新,武蓓,赵慧萍,王梅. 真菌性腹膜透析导管出口感染合并隧道感染1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 748-754. |
| [6] | 张紫薇,花语蒙,刘爱萍. 中国中老年人群抑郁症状、缺血性心血管疾病10年风险对心血管疾病的联合影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 465-470. |
| [7] | 张云静,乔丽颖,祁萌,严颖,亢伟伟,刘国臻,王明远,席云峰,王胜锋. 乳腺癌患者新发心血管疾病预测模型的建立与验证:基于内蒙古区域医疗数据[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 471-479. |
| [8] | 张明露,刘秋萍,巩超,王佳敏,周恬静,刘晓非,沈鹏,林鸿波,唐迅,高培. 阿司匹林用于心血管病一级预防的不同策略比较:一项马尔可夫模型研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 480-487. |
| [9] | 董尔丹. 心血管受体的信号转导与疾病[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 796-802. |
| [10] | 郭子宁, 梁志生, 周仪, 张娜, 黄捷. 基于国际疾病分类的心血管疾病亚型的基因组学研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 453-459. |
| [11] | 刘秋萍,陈汐瑾,王佳敏,刘晓非,司亚琴,梁靖媛,沈鹏,林鸿波,唐迅,高培. 基于马尔可夫模型的社区人群心血管病筛查策略的效果评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 460-466. |
| [12] | 陈家丽,金月波,王一帆,张晓盈,李静,姚海红,何菁,李春. 老年发病类风湿关节炎的临床特征及其心血管疾病危险因素分析:一项大样本横断面临床研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 1040-1047. |
| [13] | 徐涛,韩敬丽,姚伟娟. 雄激素剥夺治疗相关心血管疾病的机制与临床对策[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 607-609. |
| [14] | 刘欢,何映东,刘金波,黄薇,赵娜,赵红薇,周晓华,王宏宇. 血管健康指标对新发心脑血管事件的预测价值:北京血管健康分级标准的初步验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(3): 514-520. |
| [15] | 任川,吴晓月,赵威,陶立元,刘萍,高炜. 心肺适能对动脉粥样硬化性心血管疾病高危患者的保护作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 152-157. |
|
||