北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 1068-1073. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.06.018
北京社区人群促红细胞生成素相关因素及其与10年心血管疾病风险的关系
陈楚云,孙蓬飞,赵静,贾佳,范芳芳,王春燕,李建平,姜一梦,霍勇,张岩*( )
)
- 北京大学第一医院心血管内科, 北京 100034
Related factors of endogenous erythropoietin and its association with 10-year risks of cardiovascular disease in a community-based Chinese study
Chu-yun CHEN,Peng-fei SUN,Jing ZHAO,Jia JIA,Fang-fang FAN,Chun-yan WANG,Jian-ping LI,Yi-meng JIANG,Yong HUO,Yan ZHANG*( )
)
- Department of Cardiology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
摘要:
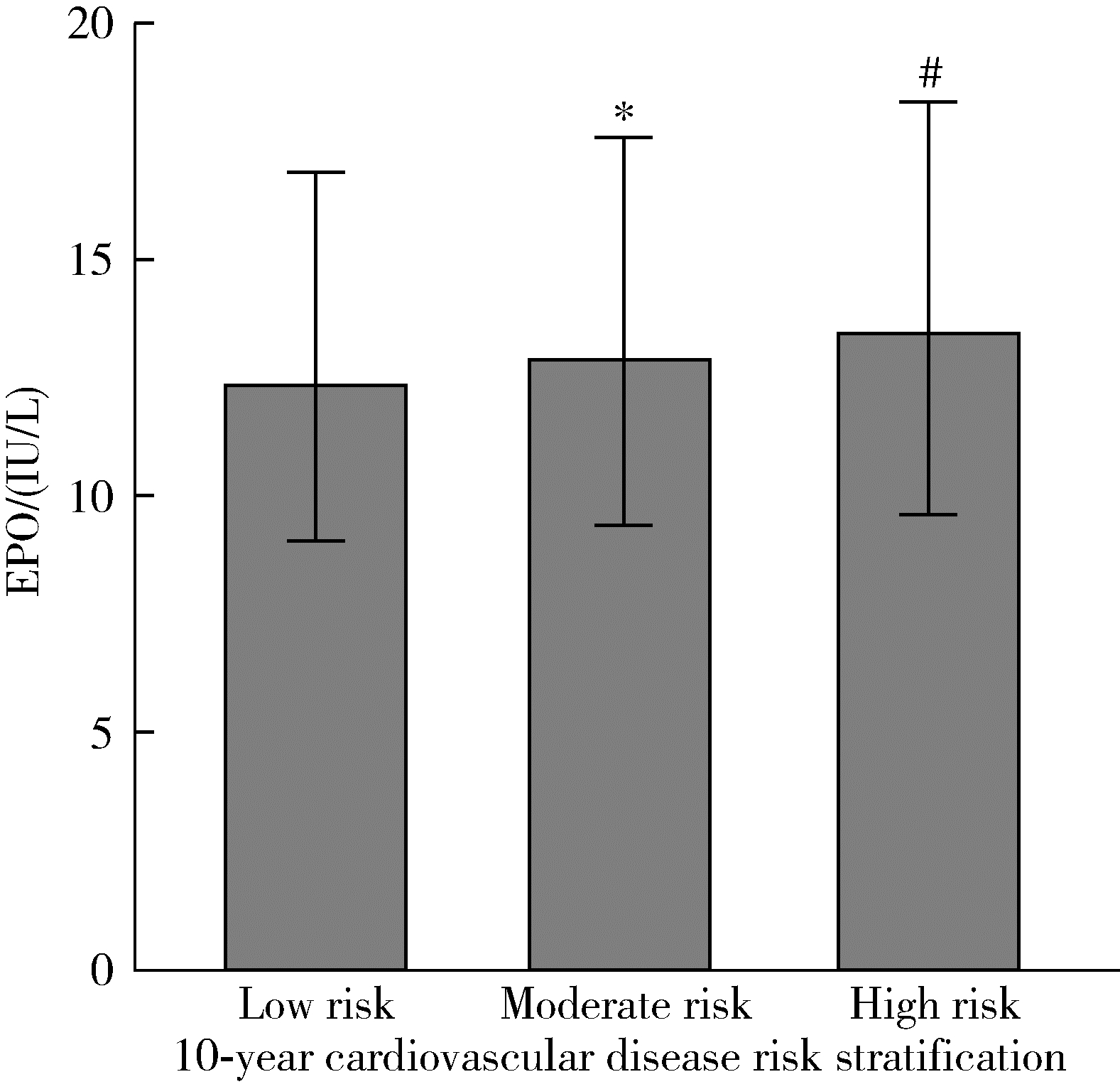
目的: 了解北京社区人群内源性促红细胞生成素(erythropoietin, EPO)的相关因素及其与10年心血管疾病发病风险的关系。方法: 数据来源于2011年12月至2012年4月北京大学第一医院动脉粥样硬化队列的基线资料, 采用多因素线性回归模型分析内源性EPO的相关因素, 应用中国动脉粥样硬化性心血管疾病风险预测(prediction for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk in China, China-PAR)模型计算研究对象10年心血管疾病发病风险, 以5%、10%为切点定义低、中、高风险分层。结果: 共纳入4 013名基线无心脑血管疾病、无贫血、肾功能未见异常的研究对象, 女性占比62.2%(2 496人), 平均年龄(55.9±8.2)岁, 平均EPO水平为12.8(9.3~17.4) IU/L。10年心血管疾病风险高危者占比25.1% (998人)。多因素回归结果显示, 血红蛋白(β=-0.05, 95%CI: -0.07~-0.04)和肾小球滤过率≥90 mL/(min·1.73 m2)(β=-0.05, 95%CI: -0.07~-0.04)与EPO水平呈显著负相关, 高血压(β=0.08, 95%CI: 0.05~0.12)和肥胖(β=0.14, 95%CI: 0.09~0.18)与内源性EPO水平升高显著相关。10年心血管疾病风险与内源性EPO水平呈显著正相关(β=0.07, 95%CI: 0.05~0.09), 中危者以及高危者内源性EPO水平均显著高于与低危者(P均 < 0.05)。结论: 北京市社区居民内源性EPO水平与血红蛋白、肾功能、肥胖及高血压呈显著相关性, 10年心血管疾病风险中、高危者内源性EPO水平显著高于低危者, 可能是心血管疾病风险标志物。
中图分类号:
- R754
| 1 | 吴超群, 李希, 路甲鹏, 等. 中国居民心血管疾病危险因素分布报告[J]. 中国循环杂志, 2021, 36 (1): 4- 13. |
| 2 | 赵林林, 吴乃石. EPO在心肌缺血再灌注损伤的相关作用及保护机制的研究进展[J]. 现代诊断与治疗, 2022, 33 (9): 1289- 1291. |
| 3 |
Suresh S , Rajvanshi PK , Noguchi CT . The many facets of erythropoietin physiologic and metabolic response[J]. Front Physiol, 2019, 10, 1534.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01534 |
| 4 | 常晋瑞, 赵妍, 曹健, 等. 促红细胞生成素在心肌缺血和缺血再灌注损伤中应用及其保护作用机制的研究进展[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志, 2019, 35 (15): 1695- 1698. |
| 5 |
Minamino T , Higo S , Araki R , et al. Low-dose erythropoietin in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction(EPO-AMI-Ⅱ): A randomized controlled clinical trial[J]. Circ J, 2018, 82 (4): 1083- 1091.
doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-17-0889 |
| 6 | 秦永根, 蔡立刚, 董佳丽, 等. 小剂量促红细胞生成素联合基础疗法对AMI患者心肌损伤、氧化应激机制的影响[J]. 中国现代医生, 2023, 61 (12): 94- 98. |
| 7 |
Nagai T , Nishimura K , Honma T , et al. Prognostic significance of endogenous erythropoietin in long-term outcome of patients with acute decompensated heart failure[J]. Eur J Heart Fail, 2016, 18 (7): 803- 813.
doi: 10.1002/ejhf.537 |
| 8 | Onoda H, Imamura T, Ueno H, et al. Prognostic impact of elevated erythropoietin levels in patients with severe aortic stenosis receiving trans-catheter aortic valve implantation[J/OL]. J Cardiol, 2023[2023-10-10]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0914508723001648?via%3Dihub. |
| 9 |
Mas-Peiro S , Seppelt PC , De Rosa R , et al. Potential role and prognostic value of erythropoietin levels in patients with severe aortic stenosis undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2020, 7, 605257.
doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2020.605257 |
| 10 | 李锴印, 范芳芳, 贾佳, 等. 中心动脉收缩压与中国动脉粥样硬化性心血管病风险预测研究模型评估的心血管病10年风险的关系[J]. 中华高血压杂志, 2023, 31 (1): 45- 51. |
| 11 |
Levey AS , Stevens LA , Schmid CH , et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2009, 150 (9): 604- 612.
doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-150-9-200905050-00006 |
| 12 |
Sun P , Jia J , Fan F , et al. Hemoglobin and erythrocyte count are independently and positively associated with arterial stiffness in a community-based study[J]. J Hum Hypertens, 2021, 35 (3): 265- 273.
doi: 10.1038/s41371-020-0332-6 |
| 13 | 唐迅, 张杜丹, 何柳, 等. China-PAR模型在北方农村人群中预测动脉粥样硬化性心血管疾病发病风险的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49 (3): 439- 445. |
| 14 | 艾合买提·阿布都卡地尔, 黄莺. 心血管疾病高危人群的早期筛查模型[J]. 中国心血管杂志, 2019, 24 (5): 474- 476. |
| 15 | 何靖楠, 宁尚勇, 韩晓燕, 等. 北京社区老年人群促红细胞生成素水平及贫血相关因素研究[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2012, 4 (2): 158- 160. |
| 16 | Kristjansdottir HL , Lewerin C , Lerner UH , et al. High Plasma erythropoietin predicts incident fractures in elderly men with normal renal function: The MrOS Sweden Cohort[J]. J Bone Miner Res, 2020, 35 (2): 298- 305. |
| 17 | Nahm CH , Lee MH , Fujii T , et al. Lipocalin-2, soluble transferrin receptor, and erythropoietin in anemia during mild renal dysfunction[J]. Int J Gen Med, 2023, 16, 3603- 3612. |
| 18 | Panjeta M , Tahirović I , Sofić E , et al. Interpretation of erythropoietin and haemoglobin levels in patients with various stages of chronic kidney disease[J]. J Med Biochem, 2017, 36 (2): 145- 152. |
| 19 | Schmieder RE , Langenfeld MR , Hilgers KF . Endogenous rythropoietin correlates with blood pressure in essential[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 1997, 29 (3): 376- 382. |
| 20 | Grote BN , Verweij N , Klip IT , et al. Erythropoietin in the general population: reference ranges and clinical, biochemical and genetic correlates[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10 (4): e125215. |
| 21 | Muhammad TG , Haroon ZH , Younas M , et al. Correlation of serum erythropoietin levels with different stages of diabetic reti-nopathy[J]. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak, 2023, 33 (4): 380- 384. |
| 22 | Hämäläinen P , Saltevo J , Kautiainen H , et al. Erythropoietin, ferritin, haptoglobin, hemoglobin and transferrin receptor in metabolic syndrome: A case control study[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2012, 11, 116. |
| 23 | Reinhardt M , Dey S , Tom Noguchi C , et al. Non-hematopoietic effects of endogenous erythropoietin on lean mass and body weight regulation[J]. Obesity, 2016, 24 (7): 1530- 1536. |
| 24 | Chiang WF , Hsiao PJ , Wu KL , et al. Investigation of the relationship between lean muscle mass and erythropoietin resistance in maintenance haemodialysis patients: A cross-sectional study[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2022, 19 (9): 5704. |
| 25 | Yanamandra U , Senee H , Yanamadra S , et al. Erythropoietin and ferritin response in native highlanders aged 4-19 years from the Leh-Ladakh region of India[J]. Br J Haematol, 2019, 184 (2): 263- 268. |
| 26 | Cai G , Qiu J , Chen S , et al. Hematological, hormonal and fitness indices in youth swimmers: Gender-related comparisons[J]. J Hum Kinet, 2019, 70, 69- 80. |
| 27 | Ershler WB , Sheng S , Mckelvey J , et al. Serum erythropoietin and aging: A longitudinal analysis[J]. J Am Geriatr Soc, 2005, 53 (8): 1360- 1365. |
| 28 | Sinkeler SJ , Zelle DM , Homan van der Heide JJ , et al. Endogenous plasma erythropoietin, cardiovascular mortality and all-cause mortality in renal transplant recipients[J]. Am J Transplant, 2012, 12 (2): 485- 491. |
| 29 | Szummer K , Lindahl B , Sylven C , et al. Relationship of plasma erythropoietin to long-term outcome in acute coronary syndrome[J]. Int J Cardiol, 2010, 143 (2): 165- 170. |
| 30 | Grote BN , van der Wal HH , Klip IT , et al. High serum erythropoietin levels are related to heart failure development in subjects from the general population with albuminuria: Data from PREVEND[J]. Eur J Heart Fail, 2016, 18 (7): 814- 821. |
| [1] | 陈敬,单蕊,肖伍才,张晓蕊,刘峥. 青春期和成年早期自制力与抑郁症状和超重肥胖共病风险的关联:基于全国调查的十年前瞻性队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 397-402. |
| [2] | 刘佐相,陈晓薇,赵厚宇,詹思延,孙凤. 真实世界中2型糖尿病患者二甲双胍联用西格列汀的心血管安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 424-430. |
| [3] | 吴一凡,玉应香,谢岚,张志达,常翠青. 不同体重指数青年男性的静息能量消耗特点及预测方程评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 247-252. |
| [4] | 刘欢锐,彭祥,李森林,苟欣. 基于HER-2相关基因构建风险模型用于膀胱癌生存预后评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 793-801. |
| [5] | 党佳佳,蔡珊,钟盼亮,王雅琪,刘云飞,师嫡,陈子玥,张依航,胡佩瑾,李晶,马军,宋逸. 室外夜间人工光暴露与中国9~18岁儿童青少年超重肥胖的关联[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 421-428. |
| [6] | 陈敬,肖伍才,单蕊,宋洁云,刘峥. DRD2基因rs2587552多态性对儿童肥胖干预效果的影响:一项前瞻性、平行对照试验[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 436-441. |
| [7] | 汪雨欣,邓宇含,谭银亮,刘宝花. 应激性血糖升高对重症监护病房患者28 d全因死亡风险的预测价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 442-449. |
| [8] | 张紫薇,花语蒙,刘爱萍. 中国中老年人群抑郁症状、缺血性心血管疾病10年风险对心血管疾病的联合影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 465-470. |
| [9] | 张云静,乔丽颖,祁萌,严颖,亢伟伟,刘国臻,王明远,席云峰,王胜锋. 乳腺癌患者新发心血管疾病预测模型的建立与验证:基于内蒙古区域医疗数据[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 471-479. |
| [10] | 张明露,刘秋萍,巩超,王佳敏,周恬静,刘晓非,沈鹏,林鸿波,唐迅,高培. 阿司匹林用于心血管病一级预防的不同策略比较:一项马尔可夫模型研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 480-487. |
| [11] | 林浩,李菁华,杨潇,陈晓婷,史宇晖,常春,郝元涛,曹望楠. 中国成都男男性行为人群HIV暴露前预防用药行为-认知偏差现状及其影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 511-520. |
| [12] | 赵亚楠,范慧芸,王翔宇,罗雅楠,张嵘,郑晓瑛. 孤独症患者过早死亡风险及死亡原因[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 375-383. |
| [13] | 梁喆,范芳芳,张岩,秦献辉,李建平,霍勇. 中国高血压人群中H型高血压的比率和特征及与美国人群的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 1028-1037. |
| [14] | 马麟,吴静依,李双成,李鹏飞,张路霞. 抗高血压药物对二氧化氮长期暴露与慢性肾脏病关联的修饰效应[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 1047-1055. |
| [15] | 董尔丹. 心血管受体的信号转导与疾病[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 796-802. |
|
||