北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 673-677. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.04.013
MRI对肾细胞癌静脉瘤栓侵犯下腔静脉壁的术前评估
吴静云1,米悦2,刘水1,姚林2,唐琦2,何志嵩2,王霄英1,△( )
)
- 1. 北京大学第一医院医学影像科,北京 100034
2. 北京大学第一医院泌尿外科,北京 100034
Evaluating inferior vena cava wall invasion in renal cell carcinoma tumor thrombus with MRI
Jing-yun WU1,Yue MI2,Shui LIU1,Lin YAO2,Qi TANG2,Zhi-song HE2,Xiao-ying WANG1,△( )
)
- 1.Department of Radiology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
2.Department of Urology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
摘要:
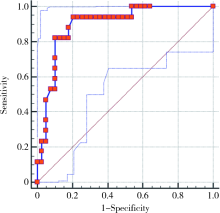
目的:评价MRI对肾细胞癌下腔静脉瘤栓侵犯下腔静脉壁的诊断价值。方法:回顾性分析2010—2018年在北京大学第一医院行肾根治性切除术及下腔静脉取栓术的肾细胞癌患者,术前行1.5 T或3.0 T MRI检查的56例患者被纳入本研究。由两位影像科医生测量术前MRI图像瘤栓所在水平肾静脉及下腔静脉最大径、下腔静脉瘤栓的长度,并评判瘤栓是否充满下腔静脉腔达两侧缘、瘤栓边缘是否光滑、瘤栓与下腔静脉壁分界是否清晰、下腔静脉壁正常信号是否改变等征象。基于病理证实下腔静脉壁受累与否将患者分为两组,对临床资料及MRI征象进行单因素分析及多因素回归分析。结果:56例患者中男性43例、女性13例,平均年龄(55.64±0.43)岁,有17例(30.4%)病理证实下腔静脉壁受累, 大部分为透明细胞癌。下腔静脉壁受累组与非受累组比较,下腔静脉瘤栓的长度更长[(7.91±3.59) cm vs. (5.94±3.57) cm,P=0.049]、瘤栓充满下腔静脉腔(P=0.002)、瘤栓边缘不光滑(P=0.005)、瘤栓与下腔静脉壁分界不清晰(P=0.001)、下腔静脉壁正常信号改变(P<0.001)出现的概率更大,结合这五个指标诊断下腔静脉壁受累的敏感性及特异性为94.12%和79.49%。结论:MRI可作为评估下腔静脉瘤栓侵犯静脉壁的方法,结合下腔静脉瘤栓的长度及MRI征象可以获得较高的诊断敏感性及特异性。
中图分类号:
- R737.11
| [1] | Motzer RJ, Jonasch E, Agarwal N , et al. Kidney cancer, version 2.2017: NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in oncology[J]. J Natl Compr Canc Netw, 2017,15(6):804-834. |
| [2] | Ljungberg B, Bensalah K, Canfield S , et al. EAU guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: 2014 update[J]. Eur Urol, 2015,67(5):913-924. |
| [3] | Hatcher PA, Anderson EE, Paulson DF , et al. Surgical management and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma invading the vena cava[J]. J Urol, 1991,145(1):20-23. |
| [4] | Lawindy SM, Kurian T, Kim T , et al. Important surgical consi-derations in the management of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) with inferior vena cava (IVC) tumour thrombus[J]. BJU Int, 2012,110(7):926-939. |
| [5] | Guo HF, Song Y, Na YQ , et al. Value of abdominal ultrasound scan, CT and MRI for diagnosing inferior vena cava tumour thrombus in renal cell carcinoma[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2009,122(19):2299-2302. |
| [6] | Neves RJ, Zincke H . Surgical treatment of renal cancer with vena cava extension[J]. Br J Urol, 1987,59(5):390-395. |
| [7] | Ciancio G, Livingstone AS, Soloway M . Surgical management of renal cell carcinoma with tumor thrombus in the renal and inferior vena cava: the University of Miami experience in using liver transplantation techniques[J]. Eur Urol, 2007,51(4):988-994. |
| [8] | Kwon TW, Kim H, Moon KM , et al. Surgical treatment of inferior vena cava tumor thrombus in patients with renal cell carcinoma[J]. J Korean Med Sci, 2010,25(1):104-109. |
| [9] | Hatakeyama S, Yoneyama T, Hamano I , et al. Prognostic benefit of surgical management in renal cell carcinoma patients with thrombus extending to the renal vein and inferior vena cava: 17-year experience at a single center[J]. BMC Urol, 2013(13):47. |
| [10] | Chen X, Li S, Xu Z , et al. Clinical and oncological outcomes in Chinese patients with renal cell carcinoma and venous tumor thrombus extension: single-center experience[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2015(13):14. |
| [11] | Whitson JM, Reese AC, Meng MV . Population based analysis of survival in patients with renal cell carcinoma and venous tumor thrombus[J]. Urol Oncol, 2013,31(2):259-263. |
| [12] | 中华医学会泌尿外科学分化中国肾癌联盟, 中国肾癌伴下腔静脉癌栓诊疗写作组. 肾癌伴静脉癌栓诊治专家共识[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2018,39(12):881-884. |
| [13] | Psutka SP, Boorjian SA, Thompson RH , et al. Clinical and radiographic predictors of the need for inferior vena cava resection du-ring nephrectomy for patients with renal cell carcinoma and caval tumour thrombus[J]. BJU Int, 2015,116(3):388-396. |
| [14] | Hallscheidt PJ, Fink C, Haferkamp A , et al. Preoperative staging of renal cell carcinoma with inferior vena cava thrombus using multidetector CT and MRI: prospective study with histopathological correlation[J]. J Comput Assist Tomogr, 2005,29(1):64-68. |
| [15] | Gupta NP, Ansari MS, Khaitan A , et al. Impact of imaging and thrombus level in management of renal cell carcinoma extending to veins[J]. Urol Int, 2004,72(2):129-134. |
| [16] | Cuevas C, Raske M, Bush WH , et al. Imaging primary and se-condary tumor thrombus of the inferior vena cava: multi-detector computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol, 2006,35(3):90-101. |
| [17] | Lawrentschuk N, Gani J, Riordan R , et al. Multidetector computed tomography vs magnetic resonance imaging for defining the upper limit of tumour thrombus in renal cell carcinoma: a study and review[J]. BJU Int, 2005,96(3):291-295. |
| [18] | Adams LC, Ralla B, Bender YY , et al. Renal cell carcinoma with venous extension: prediction of inferior vena cava wall invasion by MRI[J]. Cancer imaging, 2018,18(1):17. |
| [19] | Aslam Sohaib SA, Teh J , et al. Assessment of tumor invasion of the vena caval wall in renal cell carcinoma cases by magnetic resonance imaging[J]. J Urol, 2002,167(3):1271-1275. |
| [20] | Oto A, Herts BR, Remer EM , et al. Inferior vena cava tumor thrombus in renal cell carcinoma: staging by MR imaging and impact on surgical treatment[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 1998,171(6):1619-1624. |
| [21] | Laissy JP, Menegazzo D, Debray MP , et al. Renal carcinoma: diagnosis of venous invasion with Gd-enhanced MR venography[J]. Eur Radiol, 2000,10(7):1138-1143. |
| [22] | Alayed A, Krishna Sk, Breau RH , et al. Diagnostic accuracy of MRI for detecting inferior vena cava wall invasion in renal cell carcinoma tumor thrombus using quantitative and subjective analysis[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2019,212(3):562-569. |
| [23] | Myneni L, Hricak H, Carroll PR . Magnetic resonance imaging of renal carcinoma with extension into the vena cava: staging accuracy and recent advances[J]. Br J Urol, 1991,68(6):571-578. |
| [1] | 黄教悌,胡菁,韩博. 治疗相关神经内分泌前列腺癌机制研究与靶向治疗新进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 557-561. |
| [2] | 张树栋,谢睿扬. 机器人手术时代的肾癌合并腔静脉瘤栓治疗策略[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 562-564. |
| [3] | 邢念增,王明帅,杨飞亚,尹路,韩苏军. 前列腺免活检创新理念的临床实践及其应用前景[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 565-566. |
| [4] | 田宇轩,阮明健,刘毅,李德润,吴静云,沈棋,范宇,金杰. 双参数MRI改良PI-RADS评分4分和5分病灶的最大径对临床有意义前列腺癌的预测效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 567-574. |
| [5] | 颜野,李小龙,夏海缀,朱学华,张羽婷,张帆,刘可,刘承,马潞林. 前列腺癌根治术后远期膀胱过度活动症的危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 589-593. |
| [6] | 于书慧,韩佳凝,钟丽君,陈聪语,肖云翔,黄燕波,杨洋,车新艳. 术前盆底肌电生理参数对前列腺癌根治性切除术后早期尿失禁的预测价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 594-599. |
| [7] | 李雨清,王飚,乔鹏,王玮,关星. 经耻骨后尿道中段悬吊带术治疗女性复发性压力性尿失禁的中长期疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 600-604. |
| [8] | 陈克伟,刘茁,邓绍晖,张帆,叶剑飞,王国良,张树栋. 肾血管平滑肌脂肪瘤伴下腔静脉瘤栓的临床诊治[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 617-623. |
| [9] | 刘帅,刘磊,刘茁,张帆,马潞林,田晓军,侯小飞,王国良,赵磊,张树栋. 伴静脉癌栓的肾上腺皮质癌的临床治疗及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [10] | 杨捷,冯杰莉,张树栋,马潞林,郑清. 经食管超声心动图在肾切除术联合Mayo Ⅲ~Ⅳ级静脉瘤栓取栓术不同手术方式中的临床作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 631-635. |
| [11] | 王滨帅,邱敏,张前进,田茂锋,刘磊,王国良,陆敏,田晓军,张树栋. 6例肾尤文肉瘤伴静脉瘤栓的诊治[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 636-639. |
| [12] | 舒帆,郝一昌,张展奕,邓绍晖,张洪宪,刘磊,王国良,田晓军,赵磊,马潞林,张树栋. 肾部分切除术治疗囊性肾癌的功能学和肿瘤学结果:单中心回顾性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 667-672. |
| [13] | 周泽臻,邓绍晖,颜野,张帆,郝一昌,葛力源,张洪宪,王国良,张树栋. 非转移性T3a肾细胞癌患者3年肿瘤特异性生存期预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 673-679. |
| [14] | 李红光,韩玮华,吴训,冯继玲,李刚,孟娟红. 关节腔冲洗联合液态浓缩生长因子注射治疗单侧颞下颌关节骨关节炎的初步研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 338-344. |
| [15] | 苏俊琪,王晓颖,孙志强. 舌鳞状细胞癌根治性切除术后患者预后预测列线图的构建与验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 120-130. |
|
||