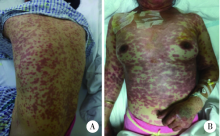
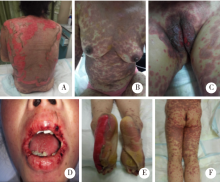
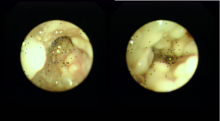
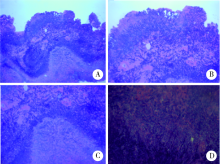
北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 977-980. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.05.032
继发呼吸道烟曲霉菌感染的中毒性表皮坏死松解型药疹1例
- 北京大学人民医院皮肤科,北京 100044
Drug-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis with secondary aspergillus fumigatus infection: a case report
Si ZHANG,Xiao-yang LIU,Jian-zhong ZHANG( ),Lin CAI,Cheng ZHOU(
),Lin CAI,Cheng ZHOU( )
)
- Department of Dermatological, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
中图分类号:
- R758.25
| [1] | Mazokopakis EE, Tzortzinis AA, Dalieraki-Ott EI , et al. Coexistence of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis with papillary thyroid carcinoma.a retrospective study[J]. Hormones (Athens), 2010,9(5):312-317. |
| [2] | Pazos C, Ponton J, Del Palaeio A . Contribution of (1,3)-beta-D-glucanchromogenie assay to diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring of invasive aspergillosis in neutropenia adult patients:a comparison with serial screening for circulating galactomannan[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 2005,43:299-305. |
| [3] | 黄晓鸥, 刘霆 . 联合检测半乳甘露聚糖和(1,3)-β- D葡聚糖诊断侵袭性曲霉菌感染的研究进展[J]. 中国呼吸与危重监护杂志, 2011,10(6):610-612. |
| [4] | Bohme A, Ruhnke M, Buehheidt D , et al. Treatment of invasive fungal infections in cancer patients-recommendations of the infectious diseases working party (AGlHO) of the German Society of Hematology and Oncology (DGHO)[J]. Ann Hematol, 2009,88(2):97-110. |
| [5] | Herbrecht R, Denning DW, Patterson TF , et al. Voriconazole versus amphotericin B for invasive aspergillosis.[J]. New Engl J Med, 2002,347(25):2080-2081. |
| [6] | Paradisi A, Abeni D, Bergamo F , et al. Etanercept therapy for toxic epidermal necrolysis[J]. J Am Acad Dermatol, 2014,71(2):278-283. |
| [7] | Espinel-Ingroff A, Cuenca-Estreila M, Fothergill A , et al. Wild-type MIC distributions and epidemiological cutoff values for amphotericin B and Aspergillus spp.for the CLSI broth microdilution method (M38-A2 document)[J]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2011,55(11):5150-5154. |
| [8] | Lockhart SR, Frade JP, Etienne KA , et al. Azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus isolates from the ARTEMIS global surveillance is primarily due to the TR/L98H mutation in the cyp51A gene[J]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2011,55(9):4465-4468. |
| [9] | Harr T, French LE . Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome[J]. Arch Dermatol, 2000,136(3):323-327. |
| [1] | 乔佳佳,田聪,黄晓波,刘军. 肾结石合并系统性红斑狼疮行经皮肾镜碎石取石术的安全性和有效性评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 745-749. |
| [2] | 朱金荣,赵亚娜,黄巍,赵微微,王悦,王松,苏春燕. 感染新型冠状病毒的血液透析患者的临床特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 267-272. |
| [3] | 刘鑫,石雪迎,李军. 新型冠状病毒感染相关缺血性结肠炎1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 362-365. |
| [4] | 王丽芳,石连杰,宁武,高乃姝,王宽婷. 干燥综合征合并冷凝集素病1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1130-1134. |
| [5] | 张陈光,陈旭岩,吴圣,冯莉莉,王琰,陈妤,段敏,王科,宋琳琳. 咽旁脓肿致颈内动脉假性动脉瘤1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1135-1138. |
| [6] | 乔婕,芦丽霞,何玉婷,门春翠,楚新新,武蓓,赵慧萍,王梅. 真菌性腹膜透析导管出口感染合并隧道感染1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 748-754. |
| [7] | 林浩,李菁华,杨潇,陈晓婷,史宇晖,常春,郝元涛,曹望楠. 中国成都男男性行为人群HIV暴露前预防用药行为-认知偏差现状及其影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 511-520. |
| [8] | 王哲,孙伟,杨雪,宋颖,姬爱平,白洁. 口腔急诊颌面部感染患者临床分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 543-547. |
| [9] | 叶一林,刘恒,潘利平,柴卫兵. 全膝关节置换术后假体周围痛风发作误诊1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 362-365. |
| [10] | 曹芳,钟明,刘从容. 宫体POLE突变型内膜样癌合并HPV感染相关性宫颈腺癌1例报道及文献回顾[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 370-374. |
| [11] | 邢晓燕,张筠肖,朱冯赟智,王一帆,周新尧,李玉慧. 皮肌炎合并巨噬细胞活化综合征5例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1214-1218. |
| [12] | 徐朝焰,林长艺,叶达梅,吴培埕,宋明辉,刘有添,邓琼,黄雪艳,范忠晓,游雪兰. 感染性关节炎诊断分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1234-1237. |
| [13] | 康志宇,王磊磊,韩永正,郭向阳. 北京冬季奥林匹克运动会运动员手术的麻醉管理[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 770-773. |
| [14] | 于博,赵扬玉,张喆,王永清. 妊娠合并感染性心内膜炎1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 578-580. |
| [15] | 张朴丽,杨红霞,张立宁,葛勇鹏,彭清林,王国春,卢昕. 血清YKL-40在诊断抗黑色素瘤分化相关基因5阳性皮肌炎合并严重肺损伤中的价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1055-1060. |
|
||