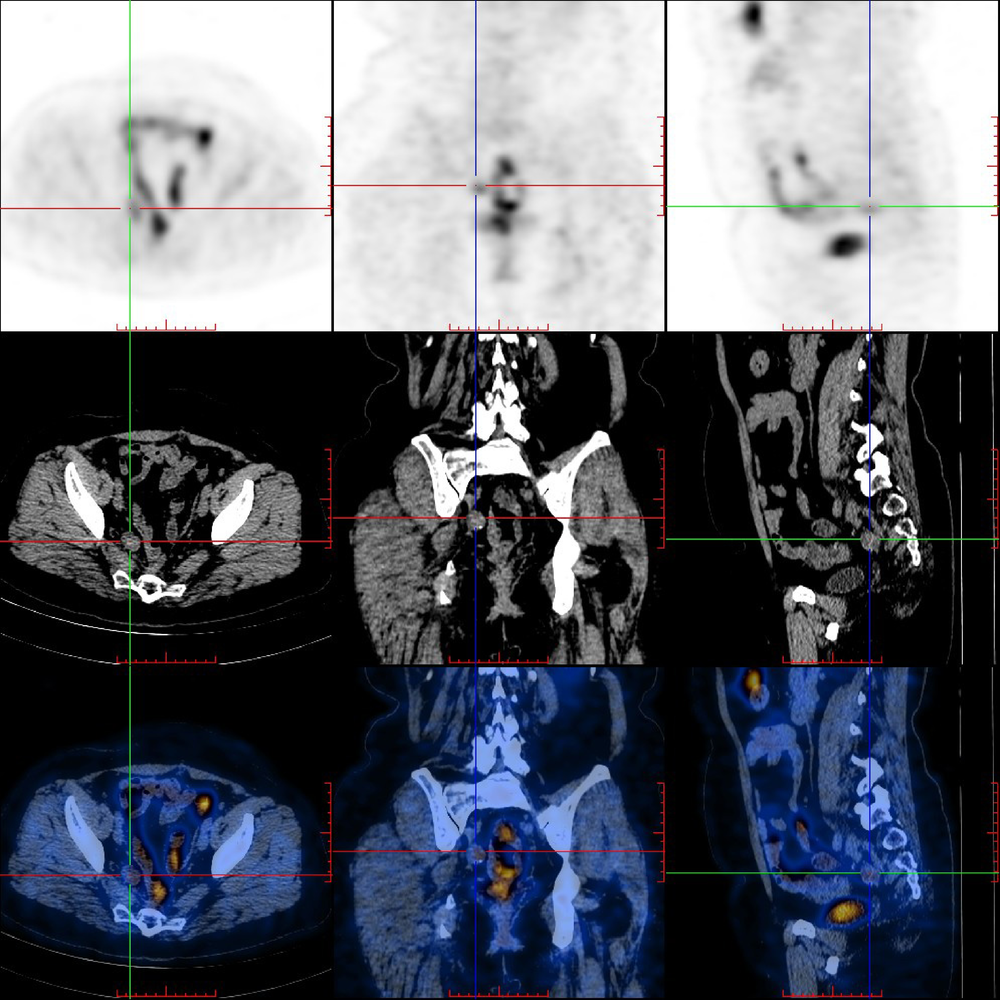
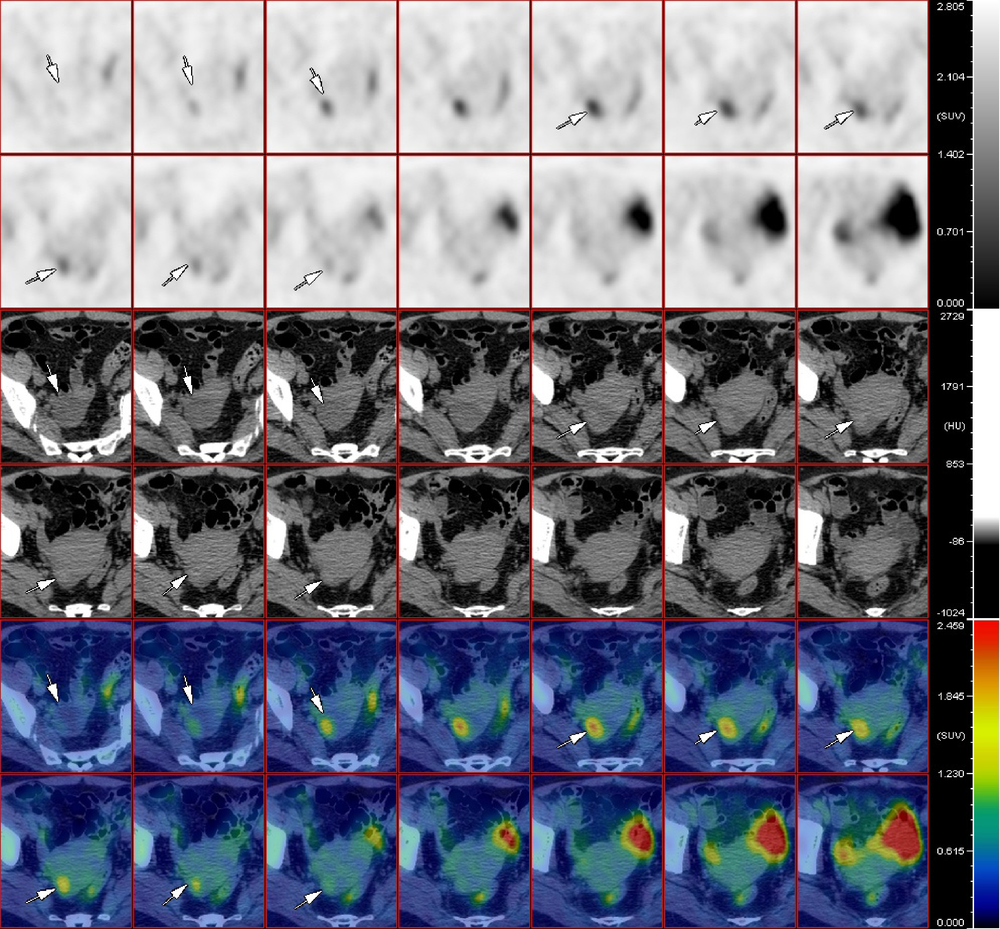
北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 1071-1077. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.06.017
18F-FDG PET/CT联合多种肿瘤标志物在结直肠中分化腺癌术后复发及转移中的应用价值
张旭初,张建华,王荣福( ),范岩,付占立,闫平,赵光宇,白艳霞
),范岩,付占立,闫平,赵光宇,白艳霞
- 北京大学第一医院核医学科,北京 100034
Diagnostic value of 18F-FDG PET/CT and tumor markers (CEA, CA19-9, CA24-2) in recurrence and metastasis of postoperative colorectal moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma
Xu-chu ZHANG,Jian-hua ZHANG,Rong-fu WANG( ),Yan FAN,Zhan-li FU,Ping YAN,Guang-yu ZHAO,Yan-xia BAI
),Yan FAN,Zhan-li FU,Ping YAN,Guang-yu ZHAO,Yan-xia BAI
- Department of Nuclear Medicine, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
摘要:
目的 探讨18F-FDG PET/CT与肿瘤标志物(CEA、CA19-9、CA24-2)在结直肠中分化腺癌患者术后探测及提示复发和转移灶中的应用。方法 对55例结直肠中分化腺癌患者进行 18F-FDG PET/CT显像及肿瘤标志物筛查,并与病理及临床随访结果进行比较。结果 对18F-FDG PET/CT对于结直肠中分化腺癌术后复发及转移灶的诊断效能为:灵敏度95.74%(45/47),特异性75.00%(6/8),阳性预测值95.74%(45/47),阴性预测值75.00%(6/8),准确率92.73%(51/55),其中假阳性2例,假阴性2例。CEA组、CA19-9组、CA24-2组及肿瘤标记物联合组灵敏度分别为68.09%(32/47)、28.57%(12/42)、40.00%(16/40)及74.47%(35/47),特异性为50.00%(4/8)、66.67%(4/6)、71.73%(5/7)及50.00%(4/8),阳性预测值为88.89%(32/36)、85.71%(12/14)、88.89%(16/18)及89.74%(35/39),阴性预测值为26.67%(4/19)、11.42%(4/34)、17.24%(5/29)及25.00%(4/16),准确率为65.45%(36/55)、32.65%(16/49)、44.68%(21/47)及70.91%(39/55)结论 18F-FDG PET/CT对于结直肠癌术后中分化腺癌患者复发及转移灶的探测具有较高的灵敏度及特异性,各项肿瘤标志物对病灶转移及复发均有一定的提示作用,多项肿瘤标志物联合应用更准确。
中图分类号:
- R735.5
| [1] | 吴菲, 林国桢, 张晋昕 . 我国恶性肿瘤发病现状及趋势[J]. 中国肿瘤, 2012,21(2):81-85. |
| [2] | 阮丽琴, 李太原, 周凤凤 . 不同年龄组的结直肠癌临床流行病学分析[J]. 实用临床医学, 2016,17(4):86-87. |
| [3] | 张小龙, 高枫, 陈利生 , 等. 结直肠癌病理组织学类型分析[J]. 广西医学, 2008,30(11):1671-1672. |
| [4] | 陈美玲 . 291例结直肠癌患者的临床病理分析[J]. 大家健康(学术版), 2015,9(8):66-67. |
| [5] | 邱大胜, 胡晓燕, 彭辽河 , 等. 18F-FDG-PET/CT对结直肠癌术后血清CEA升高患者的诊断价值 [J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2013,32(12):1739-1742. |
| [6] | 路晓雯, 刘林祥, 崔新建 , 等. 18F-FDG PET/CT对结直肠癌术后血清CEA升高病例的临床诊断价值 [J]. 泰山医学院学报, 2010,31(2):83-85. |
| [7] | 潘睿. 中国慢性病前瞻性研究队列恶性肿瘤发病与死亡分析[C], 2017. |
| [8] |
黄利娟, 陈继贵, 刘丽 , 等. 结直肠癌患者血清肿瘤标志物水平与预后关系[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2011,27(5):563-566.
doi: 10.11847/zgggws-2011-27-05-16 |
| [9] | Van Cutsem E, Cervantes A, Adam R , et al. ESMO consensus guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer[J]. Ann Oncol, 2016,27(8):1386-1422. |
| [10] | 王贵玉 . 结直肠癌NCCN、NICE及ESMO指南的对比分析和解读[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2015,25(11):849-853. |
| [11] | Schmoll HJ, Van Cutsem E, Stein A , et al. ESMO Consensus Guidelines for management of patients with colon and rectal can-cer. A personalized approach to clinical decision making[J]. Ann Oncol, 2012,23(10):2479-2516. |
| [12] | Chan K, Welch S, Walker-Dilks C , et al. Evidence-based guideline recommendations on the use of positron emission tomography imaging in colorectal cancer[J]. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol), 2012,24(4):232-249. |
| [13] | 王晶晶, 陈康, 徐万菊 . 直肠癌患者手术前后血清CA199和CA242水平测定及预后评价[J]. 中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2009,14(21):1667-1668. |
| [14] | 刘传, 清水汪, 王宁 , 等. 结直肠癌术前血清CEA、CA199表达水平与临床病理关系的研究[J]. 医学研究杂志, 2012,41(3):27-30. |
| [15] | 周华胜, 梁光林 . 癌胚抗原测定在直肠癌手术前后及药物化疗过程中的追踪研究[J]. 河北医学, 2010,16(4):455-456. |
| [16] | Lim YK, Kam MH, Eu KW . Carcinoembryonic antigen screening: how far should we go?[J]. Singapore Med J, 2009,50(9):862-865. |
| [17] | 陈恺杰 . 3种血清肿瘤标志物在诊断大肠癌中的价值[J]. 广东医学院学报, 2005,23(4):384-385. |
| [18] | 高志海, 田志军, 安燚 . 五种肿瘤标志物联合检测在胃和结直肠癌诊断及随访中的临床意义[J]. 医学综述, 2012,18(10):1595-1597. |
| [1] | 钟华, 李原, 徐丽玲, 白明欣, 苏茵. 18F-FDG PET/CT在风湿免疫病中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 853-859. |
| [2] | 李志存, 吴天俣, 梁磊, 范宇, 孟一森, 张骞. 穿刺活检单针阳性前列腺癌术后病理升级的危险因素分析及列线图模型构建[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 896-901. |
| [3] | 刘家骏, 刘国康, 朱玉虎. 免疫相关性重症肺炎1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 932-937. |
| [4] | 黄教悌,胡菁,韩博. 治疗相关神经内分泌前列腺癌机制研究与靶向治疗新进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 557-561. |
| [5] | 田宇轩,阮明健,刘毅,李德润,吴静云,沈棋,范宇,金杰. 双参数MRI改良PI-RADS评分4分和5分病灶的最大径对临床有意义前列腺癌的预测效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 567-574. |
| [6] | 姚凯烽,阮明健,李德润,田宇轩,陈宇珂,范宇,刘毅. 靶向穿刺联合区域系统穿刺对PI-RADS 4~5分患者的前列腺癌诊断效能[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 575-581. |
| [7] | 欧俊永,倪坤明,马潞林,王国良,颜野,杨斌,李庚午,宋昊东,陆敏,叶剑飞,张树栋. 肌层浸润性膀胱癌合并中高危前列腺癌患者的预后因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [8] | 王滨帅,邱敏,张前进,田茂锋,刘磊,王国良,陆敏,田晓军,张树栋. 6例肾尤文肉瘤伴静脉瘤栓的诊治[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 636-639. |
| [9] | 虞乐,邓绍晖,张帆,颜野,叶剑飞,张树栋. 具有低度恶性潜能的多房囊性肾肿瘤的临床病理特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [10] | 舒帆,郝一昌,张展奕,邓绍晖,张洪宪,刘磊,王国良,田晓军,赵磊,马潞林,张树栋. 肾部分切除术治疗囊性肾癌的功能学和肿瘤学结果:单中心回顾性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 667-672. |
| [11] | 方杨毅,李强,黄志高,陆敏,洪锴,张树栋. 睾丸鞘膜高分化乳头状间皮肿瘤1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 741-744. |
| [12] | 柴晓东,孙子文,李海爽,朱靓怡,刘小旦,刘延涛,裴斐,常青. 髓母细胞瘤分子亚型中CD8+T淋巴细胞浸润的临床病理特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 512-518. |
| [13] | 林国中,马长城,吴超,司雨,杨军. 微通道技术在颈椎管肿瘤微创切除术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 318-321. |
| [14] | 俞光岩. 儿童唾液腺疾病[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 1-3. |
| [15] | 任晓萌,李凯一,李春蕾. 基于转录组测序探索口腔扁平苔藓局部激素治疗敏感性相关分子特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 32-38. |
|
||