北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 657-662. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.04.011
吲哚菁绿标记的荧光实时显影技术在腹腔镜肾部分切除术中的应用
张树栋1,洪鹏1,王滨帅1,邓绍晖1,张帆1,陶立元2,曹财广3,胡振华3,马潞林1,△( )
)
- 1.北京大学第三医院泌尿外科,北京 100191
2.北京大学第三医院临床流行病学研究中心,北京 100191
3.中国科学院自动化研究所,中国科学院分子影像重点实验室,北京 100190
Usefulness of the indocyanine green fluorescence imaging technique in laparoscopic partial nephrectomy
Shu-dong ZHANG1,Peng HONG1,Bin-shuai WANG1,Shao-hui DENG1,Fan ZHANG1,Li-yuan TAO2,Cai-guang CAO3,Zhen-hua HU3,Lu-lin MA1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Urology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Clinical Research Center of Epidemiology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
3. Chinese Academy of Sciences Automation Research Institute,Chinese Academy of Sciences Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging, Beijing 100190, China
摘要:
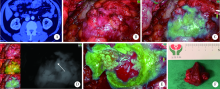
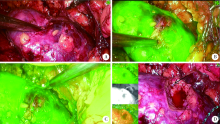
目的: 评估吲哚菁绿(indocyanine green,ICG)标记的荧光实时显影技术在腹腔镜肾部分切除术中应用的可行性和效果。方法: 回顾性分析北京大学第三医院在2019年7月至2020年1月由单一术者所行25例患者ICG标记的近红外荧光腹腔镜肾部分切除术的临床资料,通过荧光显影,精准定位肿瘤,辨认切缘,并在实时显像下完整切除肿瘤,其中1例为双肾肿瘤,共进行26例次手术。收集患者围手术期的临床资料进行统计分析,计量资料采用中位数(范围)表示,计数资料采用百分率表示。男19例,女6例,年龄29~77岁,平均年龄54岁,体重指数25.4(20.0~35.4) kg/m2,肿瘤位于肾上极11个(42%)、中部6个(23%)、下极9个(35%),肿瘤大小为2.75 (1.30~5.20) cm,R.E.N.A.L评分为7.5 (5.0~10.0)。肿瘤术前临床分期:T1aN0M0 23个(88.5%),T1bN0M0 2个(7.7%),T2aN0M0 1个(3.8%)。结果: 25位患者共行26例次手术,患者术中注射ICG无过敏、感染等并发症发生,无术中输血和中转开放者,所有手术切缘均阴性。手术时间为136 (50~247) min,热缺血时间为14 (7~30) min。术中估计失血量为50 (10~400) mL,住院日为5.5 (3.0~31.0) d。术后出现肾周血肿1例,尿漏1例,呼吸衰竭伴下肢静脉血栓1例,经相应治疗后均痊愈,其余无严重并发症发生。随访时间为4~10个月,无肿瘤复发和转移。结论: ICG标记的荧光实时显影技术应用于腹腔镜肾部分切除术安全、有效,有助于肿瘤的精准定位和切除。
中图分类号:
- R737.11
| [1] |
Lane BR, Gill IS. 7-year oncological outcomes after laparoscopic and open partial nephrectomy[J]. J Urol, 2010,183(2):473-479.
pmid: 20006866 |
| [2] | Teishima J, Takayama Y, Iwagum S, et al. Usefulness of persona-lized three-dimensional printed model on the satisfaction of pre-operative education for patients undergoing robot-assisted partial nephrectomy and their families[J]. Int Urol Nephrol, 2018,50(6):1061-1066. |
| [3] |
Hekman MCH, Rijpkema M, Langenhuijsen JF, et al. Intraoperative imaging techniques to support complete tumor resection in partial nephrectomy[J]. Eur Urol Focus, 2018,4(6):960-968.
pmid: 28753888 |
| [4] | 朱刚, 邢金春, 翁国斌, 等. 全息影像术中导航在泌尿外科腹腔镜和机器人手术中的应用价值[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2020,41(2):131-135. |
| [5] | Kutikov A, Uzzo RG. The R.E.N.A.L. nephrometry score: a comprehensive standardized system for quantitating renal tumor size, location and depth[J]. J Urol, 2009,182(3):844-853. |
| [6] | 张树栋. 复杂情况腹腔镜肾部分切除术的方法探讨(附光盘)[J]. 现代泌尿外科杂志, 2016,21(5):325-328. |
| [7] | 张树栋, 马潞林, 黄毅, 等. 改良Pfannenstiel 切口取肾的经腹途径腹腔镜肾癌根治术[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014,46(4):638-641. |
| [8] | Garisto J, Bertolo R, Dagenais J, et al. Robotic versus open partial nephrectomy for highly complex renal masses: comparison of perioperative, functional, and oncological outcomes[J]. Urol Oncol, 2018, 471.e1-471.e9. |
| [9] | 张树栋. 肾门区肿瘤腹腔镜保留肾单位手术的决策(附光盘)[J]. 现代泌尿外科杂志, 2018,23(5):323-327. |
| [10] |
Reinhart MB, Huntington CR, Blair LJ, et al. Indocyanine green: Historical context, current complications,and future considerations[J]. Surg Innov, 2016,23(2):166-175.
pmid: 26359355 |
| [11] |
Simone G, Gabriele Tuderti G, Anceschi U, et al. Ride the green light: Indocyanine green-marked off-clamp robotic partial nephrectomy for totally endophytic renal masses[J]. Eur Urol, 2019,75(6):1008-1014.
pmid: 30262342 |
| [12] | Ljungberg B, Albiges L, Abu-Ghanem Y, et al. European Association of Urology guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: The 2019 update[J]. Eur Urol, 2019,75(5):799-810. |
| [13] | Fernando A, Fowler S, O’Brien T. Nephron-sparing surgery across a nation-outcomes from the British Association of Urological Surgeons 2012 National Partial Nephrectomy Audit[J]. BJU Int, 2016,117(6):874-882. |
| [1] | 陈克伟,刘茁,邓绍晖,张帆,叶剑飞,王国良,张树栋. 肾血管平滑肌脂肪瘤伴下腔静脉瘤栓的临床诊治[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 617-623. |
| [2] | 舒帆,郝一昌,张展奕,邓绍晖,张洪宪,刘磊,王国良,田晓军,赵磊,马潞林,张树栋. 肾部分切除术治疗囊性肾癌的功能学和肿瘤学结果:单中心回顾性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 667-672. |
| [3] | 毛海,张帆,张展奕,颜野,郝一昌,黄毅,马潞林,褚红玲,张树栋. 基于MRI前列腺腺体相关参数构建腹腔镜前列腺癌术后尿失禁的预测模型[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 818-824. |
| [4] | 邱敏,宗有龙,王滨帅,杨斌,徐楚潇,孙争辉,陆敏,赵磊,卢剑,刘承,田晓军,马潞林. 腹腔镜肾部分切除术治疗中高复杂程度肾肿瘤的效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 833-837. |
| [5] | 张展奕,张帆,颜野,曹财广,李长剑,邓绍晖,孙悦皓,黄天亮,管允鹤,李楠,陆敏,胡振华,张树栋. 近红外荧光靶向探针用于前列腺神经血管束术中成像[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 843-850. |
| [6] | 刘慧丽,吕彦函,王晓晓,李民. 老年患者腹腔镜泌尿系肿瘤根治术后慢性疼痛的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 851-856. |
| [7] | 张铃福,侯纯升,徐智,王立新,凌晓锋,王港,崔龙,修典荣. 腹腔镜下经胆囊管胆管引流联合胆总管探查取石术治疗复杂胆管结石的临床效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1185-1189. |
| [8] | 周鑫,李文智. 肾细胞癌极致保肾时代的冷思考[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 595-598. |
| [9] | 安立哲,熊六林,陈亮,王焕瑞,陈伟男,黄晓波. 腹腔镜肾盂成形术联合肾盂镜超声碎石取石术治疗肾盂输尿管连接部梗阻合并肾结石[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 746-750. |
| [10] | 张帆,陈曲,郝一昌,颜野,刘承,黄毅,马潞林. 术前及术后膜性尿道长度与腹腔镜根治性前列腺切除术后控尿功能恢复的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 299-303. |
| [11] | 张帆,黄晓娟,杨斌,颜野,刘承,张树栋,黄毅,马潞林. 前列腺尖部深度与腹腔镜前列腺癌根治术后早期控尿功能恢复的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 692-696. |
| [12] | 邱敏,王璐,邓绍晖,拓鹏飞,郭巍,卢剑,刘承,马潞林. 肾周筋膜悬吊装置在后腹腔镜肾部分切除术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 789-792. |
| [13] | 邱敏,费月阳,邓绍晖,刘承,卢剑,何为,陆敏,田晓军,张树栋,马潞林. 后肾腺瘤的诊治经验及文献回顾[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 417-419. |
| [14] | 黄炳伟,王杰,张鹏,李喆,毕泗成,王强,岳才博,杨昆霖,李学松,周利群. 吲哚菁绿在复杂上尿路修复手术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 651-656. |
| [15] | 程嗣达,李新飞,熊盛炜,樊书菠,王杰,朱伟杰,李子奡,丁光璞,俞婷,李万强,孙永明,杨昆霖,张雷,郝瀚,李学松,周利群. 机器人辅助腹腔镜上尿路修复手术:单一术者108例经验总结[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 771-779. |
|
||