北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (5): 902-906. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.05.018
沙利霉素对口腔鳞癌细胞增殖和凋亡的影响
苏雷震1,2,3,陈洁1,2,李显1,3,季平1,3,∆( )
)
- 1.重庆医科大学附属口腔医院口腔颌面外科,重庆 401120
2.口腔疾病与生物医学重庆市重点实验室,重庆 401120
3.重庆市高校市级口腔生物医学工程重点实验室,重庆 401120
Effects of salinomycin on proliferation and apoptosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma
Lei-zhen SU1,2,3,Jie CHEN1,2,Xian LI1,3,Ping JI1,3,∆( )
)
- 1. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery,Stomatological Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 401120, China
2. Chongqing Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases and Biomedical Sciences, Chongqing 401120, China
3. Municipal Key Laboratory of Oral Biomedical Engineering of Higher Education, Chongqing 401120, China
摘要:
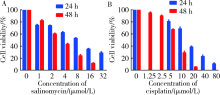
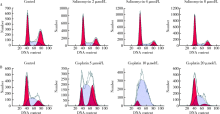
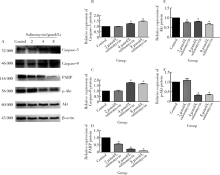
目的:探讨沙利霉素(salinomycin)对口腔鳞癌细胞增殖和凋亡的影响,并初步探讨沙利霉素对信号通路的影响。方法:培养口腔鳞状细胞癌细胞系CAL-27,将1、2、4、8、16、32 μmol/L沙利霉素和1.25、2.5、5、10、20、40、80 μmol/L顺铂与CAL-27细胞共同培养,24 h和48 h后用细胞计数试剂盒-8(cell counting kit-8,CCK-8)法检测沙利霉素和顺铂对CAL-27细胞增殖的影响;0、2、4、8 μmol/L沙利霉素和0、5、10、20 μmol/L顺铂与CAL-27细胞共培养48 h后,通过流式细胞术检测沙利霉素和顺铂对CAL-27细胞周期的影响,蛋白免疫印迹法(Western blot)检测CAL-27细胞中天冬氨酸特异性半胱氨酸蛋白酶-3(cysteine-containing aspartate-specific proteases-3,Caspase-3)、天冬氨酸特异性半胱氨酸蛋白酶-9(cysteine-containing aspartate-specific proteases-9,Caspase-9)、脱氧核糖核酸(deoxyribonucleic acid,DNA)修复酶(poly ADP-ribose polymerase,PARP)、蛋白激酶B(protein kinase B, Akt)和磷酸化蛋白激酶B (phosphorylated protein kinase B,p-Akt)的表达。结果:CCK-8实验表明沙利霉素和顺铂均能显著抑制口腔鳞状细胞癌CAL-27细胞增殖,且抑制作用呈时间依赖性和药物浓度依赖性,但是相对于临床一线化疗药物顺铂而言,沙利霉素对CAL-27细胞增殖的抑制效果更加显著(P<0.001)。细胞周期检测表明,与加入二甲基亚砜(dimethyl sulfoxide,DMSO)的对照组相比,8 μmol/L沙利霉素与CAL-27细胞共同培养48 h后,细胞休眠期/DNA合成前期的CAL-27细胞比例明显升高(40.40%±1.99% vs.64.46%±0.90%,P<0.05), DNA合成期和DNA合成后期/有丝分裂期的CAL-27细胞比例出现降低(24.32%±2.30% vs.18.73%±0.61%,P<0.05,35.01%±1.24% vs.16.54%±1.31%,P<0.05);顺铂对CAL-27细胞周期没有特异性改变。蛋白免疫印迹法结果显示,沙利霉素在上调CAL-27细胞中Caspase-3和 Caspase-9蛋白表达(P<0.05)的同时下调PARP、Akt和p-Akt蛋白的表达(P<0.05)。结论:相对于顺铂而言,沙利霉素对CAL-27细胞增殖有更强的抑制作用,并且能将口腔鳞状细胞癌CAL-27细胞周期阻滞在细胞休眠期/DNA合成前期,同时能够诱导CAL-27细胞发生凋亡,这一机制可能和Akt/p-Akt 信号通路相关。
中图分类号:
- R739.8
| [1] |
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram1 I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012[J]. Int J Cancer, 2015,136(5):E359-E386.
doi: 10.1002/ijc.29210 pmid: 25220842 |
| [2] | 孟宪瑞, 刘进忠. 口腔癌的早期诊断[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2008,35(3):329-331. |
| [3] |
Abrahão R, Anantharaman D, Gaborieau V, et al. The influence of smoking, age and stage at diagnosis on the survival after larynx,hypopharynx and oral cavity cancers in Europe: The ARCAGE study[J]. Int J Cancer, 2018,143(1):32-44.
doi: 10.1002/ijc.31294 pmid: 29405297 |
| [4] |
Cho H, Nishiike S, Yamamoto Y, et al. Docetaxel, cisplatin,and fluorouracil for patients with inoperable recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2015,42(5):396-400.
doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2015.02.009 pmid: 25721854 |
| [5] |
Gupta PB, Onder TT, Jiang G, et al. Identification of selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput screening[J]. Cell, 2009,138(4):645-659.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.06.034 pmid: 19682730 |
| [6] |
Zhang B, Wang X, Cai F, et al. Effects of salinomycin on human ovarian cancer cell line OV2008 are associated with modulating p38 MAPK[J]. Tumor Biol, 2012,33(6):1855-1862
doi: 10.1007/s13277-012-0445-9 |
| [7] |
Wu D, Zhang Y, Huang J, et al. Salinomycin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell in vitro and suppresses tumor growth in vivo[J]. Biochem Bioph Res Co, 2014,443(2):712-717.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.12.032 |
| [8] |
Dhaheri AI, Attoub S, Arafat K, et al. Salinomycin induces apoptosis and senescence in breast cancer: Up regulation of p21, down regulation of survivin and histone H3 and H4 hyperacetylation[J]. BBA-GEN Subjects, 2013,1830(4):3121-3135.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.01.010 |
| [9] |
Arafat K, Iratni R, Takahashi T, et al. Inhibitory effects of salinomycin on cell survival, colony growth, migration, and invasion of human non-small cell lung cancer A549 and LNM35: Involvement of NAG-1[J]. PLoS One, 2013,8(6):e66931.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066931 pmid: 23805285 |
| [10] |
Parajuli B, Lee HG, Kwon SH, et al. Salinomycin inhibits Akt/NF-κB and induces apoptosis in cisplatin resistant ovarian cancer cells[J]. Cancer Epidemiology, 2013,37(4):512-517.
doi: 10.1016/j.canep.2013.02.008 |
| [11] | 亓放, 张宝泉, 徐炎, 等. 顺铂诱导的喉癌细胞凋亡及其对细胞周期的影响[J]. 中华医学杂志, 1999,79(4):298-301. |
| [12] | 徐志巧, 庞国明. 实用肿瘤临床药物手册[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2013: 282. |
| [13] |
Fuchs D, Heinold A, Opelz G, et al. Salinomycin induces apoptosis and overcomes apoptosis resistance in human cancer cells[J]. Biochem Bioph Res Co, 2009,390(3):743-749.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.10.042 |
| [14] |
Nuutinen U, Postila V, Matto M, et al. Inhibition of PI3-kinase-Akt pathway enhances dexamethasolle-induced apoptosis in a human follicular lymphoma cell line[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2006,312(3):322-330.
doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.10.023 pmid: 16309671 |
| [15] |
Jeong SJ, Dasgupta A, Jung KJ, et al. PI3K/AKT inhibition induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in HTLV-1 transformed cells[J]. Virology, 2008,370(2):264-272.
doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.09.003 pmid: 17931677 |
| [1] | 刘耘充,吴宗龙,葛力源,杜坦,吴雅倩,宋一萌,刘承,马潞林. 肾透明细胞癌中核蛋白1对阿昔替尼耐药的作用及机制[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 781-792. |
| [2] | 娄雪,廖莉,李兴珺,王楠,刘爽,崔若玫,徐健. 类风湿关节炎患者外周血TWEAK基因启动子区甲基化状态及其表达[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1020-1025. |
| [3] | 高亚东,朱安,李璐迪,张涛,王硕,单丹萍,李盈姿,王旗. 吴茱萸碱对HepG2细胞毒性及其机制[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1107-1114. |
| [4] | 耿良,吕静,范敬. 肺瘤平膏联合环磷酰胺化疗对肺癌的抑瘤作用和酸性微环境的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(2): 247-253. |
| [5] | 陶船思博,董凡,王佃灿,郭传瑸. 红外热成像技术诊断口腔鳞状细胞癌颈淋巴结转移[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(5): 959-963. |
| [6] | 刘洋,高岩,陈学杰,华红. 脱落细胞DNA 定量分析在口腔潜在恶性疾病诊断中的准确性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(1): 16-20. |
| [7] | 孙静,宋卫东,闫思源,席志军. 氯喹抑制肾癌细胞活性促进舒尼替尼诱导的细胞凋亡[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(5): 778-784. |
| [8] | 李满,李圆,孙麟,宋君来,吕聪. 高迁移率族蛋白B1通过调节Bcl-2和Bax蛋白表达促进氧糖剥夺/复氧星形胶质细胞的凋亡[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(5): 785-791. |
| [9] | 王昊,陈亮,叶小云. 雷公藤甲素对TM4细胞氧化应激及PI3K/AKT通路的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(4): 607-612. |
| [10] | 王玉洁,郭向阳,王军. 重复异丙酚麻醉对新生大鼠海马细胞凋亡及远期学习记忆能力的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(2): 310-314. |
| [11] | 杨光,程庆砾,李春霖,贾雅丽,岳文,裴雪涛,刘洋,赵佳慧,杜婧,敖强国. 高糖减弱肾组织干细胞条件培养液对缺氧损伤肾小管上皮细胞的修复作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(1): 125-130. |
| [12] | 曹珮,姜学军,席志军. 舒尼替尼通过抑制Akt/mTOR信号通路诱导肾癌细胞自噬[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(4): 584-589. |
| [13] | 李刚,张洪宪,王云鹏,张径,洪锴,田晓军,马潞林. 间苯三酚对大鼠肾缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(5): 743-748. |
| [14] | 郑少强, 陈雪, 王雅杰, 安立新. 七氟烷对幼鼠脑细胞凋亡和远期学习记忆功能的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(4): 674-678. |
| [15] | 温静,程庆砾,马强,齐云,赵佳慧,杜婧,王小丹,刘胜,李美花,张晓英. 肾组织干细胞对人肾小管上皮细胞损伤修复的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(4): 619-. |
|
||