北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (5): 907-912. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.05.019
树脂冠修复乳前牙的临床效果评价
陈小贤1,钟洁1,闫文娟1,张红梅1,姜霞1,黄芊1,薛世华1,刘星纲2,∆( )
)
- 1.北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,门诊部儿童口腔科 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100034
2.首都医科大学附属北京口腔医院修复科,北京 100050
Clinical performance of rensin-bonded composite strip crowns in primary incisors
Xiao-xian CHEN1,Jie ZHONG1,Wen-juan YAN1,Hong-mei ZHANG1,Xia JIANG1,Qian HUANG1,Shi-hua XUE1,Xing-gang LIU2,∆( )
)
- 1. Department of Pediatric Dentistry, First Clinical Division, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100034, China
2. Department of Prosthodontics, Beijing Stomatological Hospital & School of Stomatology, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100050, China
摘要:
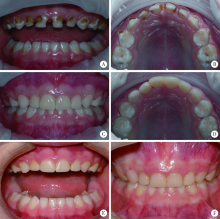
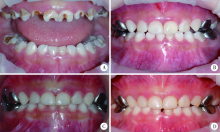
目的:评价对活髓乳前牙复面洞和多面洞龋坏采用Strip crowns透明成形冠进行复合树脂全冠修复的临床效果。方法:纳入的研究对象为2016年1—12月接受全身麻醉下牙齿治疗,且因乳前牙复面洞或多面洞龋坏需行树脂全冠修复的患儿。术中使用选择性酸蚀技术、Universal Bond粘接剂、3M Z350树脂制作全冠。术后6、12和18个月复查,由非治疗医师采用改良的美国公共卫生署(United States Public Health Service,USPHS)标准进行单盲评价。结果:共有127例儿童的418颗牙齿纳入统计,年龄为1.17~5.75岁(平均3.22岁),其中70例男性,57例女性。树脂冠6个月时的保留率为97.8%,12个月时的保留率为93.6%,18个月时的保留率为89.2%。18个月时共有28颗(6.7%)树脂冠完全脱落,17颗(4.1%)部分脱落,4颗(1.0%)树脂冠发生继发龋,6颗(1.4%)牙齿出现牙髓感染。修复体外观及邻接关系恢复较好,色泽协调性佳,可明显改善美观。93.1%的树脂冠牙龈健康,有29颗(6.9%)牙龈轻度红肿。有47颗(11.2%)树脂冠因菌斑堆积出现颜色变化,抛光可去除着色。树脂冠脱落主要与进食咬物相关。结论:树脂冠是修复乳前牙大面积龋坏和多面洞龋坏的较好方式,功能运动是导致脱落的重要原因。由于制作树脂冠技术敏感性高,需要儿童全程配合,更适用于年龄较大且可配合的儿童以及接受镇静或全身麻醉的儿童。
中图分类号:
- R783.3
| [1] | 王兴. 第四次全国口腔健康流行病学调查报告 [M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2018: 8. |
| [2] | Jeong M, Kim A, Shim Y, et al. Restoration of strip crown with a resin-bonded composite cement in early childhood caries[J]. Case Rep Dent, 2013(2):660-672. |
| [3] | Waggoner WF. Restorative dentistry for the primary dentition[M] // Pinkham JR. Pediatric dentistry: Infancy through adolescence. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: W. B. Saunders, 1994: 298-325. |
| [4] |
Waggoner WF. Restoring primary anterior teeth: updated for 2014[J]. Pediatr Dent, 2015,37(2):163-170.
pmid: 25905657 |
| [5] |
Almeida AG, Roseman MM, Sheff M, et al. Future caries susceptibility in children with early childhood caries following treatment under general anesthesia[J]. Pediatr Dent, 2000,22(4):302-306.
pmid: 10969437 |
| [6] |
Cuvillon P, Nouvellon E, Marret E, et al. American Society of Anesthesiologists’ physical status system: a multicentre Francophone study to analyses reasons for classification disagreement[J]. Eur J Anaesthesiol, 2011,28(10):742-747.
doi: 10.1097/EJA.0b013e328348fc9d pmid: 21912242 |
| [7] | 中华口腔医学会. 口腔医学行业标准规范及指南 [M]. 北京: 人民军医出版社, 2015. |
| [8] |
Ryge G. Clinical criteria[J]. Int Dent J, 1980,30(4):347-358.
pmid: 6935165 |
| [9] |
Kupietzky A, Waggoner WF, Galea J. The clinical and radiographic success of bonded resin composite strip crowns for primary incisors[J]. Pediatr Dent, 2003,25(6):577-581.
pmid: 14733473 |
| [10] |
Al-Eheideb AA, Herman NG. Outcomes of dental procedures performed on children under general anesthesia[J]. J Clin Pediatr Dent, 2003,27(2):181-183.
doi: 10.17796/jcpd.27.2.k3307186n7086r11 pmid: 12597693 |
| [11] | 李永吉, 滕立群, 张英华, 等. 透明成形冠在大面积龋损乳前牙修复中的应用[J]. 广东牙病防治, 2011,19(6):299-301. |
| [12] |
Kupietzky A, Waggoner WE, Galea J. Long-term photographic and radiographic assessment of bonded resin composite strip crowns for primary incisors: results after 3 years[J]. Pediatr Dent, 2005,27(3):221-225.
pmid: 16173227 |
| [13] |
Ram D, Fuks AB. Clinical performance of resin-bonded composite strip crowns in primary incisors: a retrospective study[J]. Int J Paediatr Dent, 2006,16(1):49-54.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-263X.2006.00680.x pmid: 16364093 |
| [14] |
Duhan H, Pandit IK, Srivastava N, et al. Clinical comparison of various esthetic restorative options for coronal build-up of primary anterior teeth[J]. Dent Res J, 2015,12(6):574-580.
doi: 10.4103/1735-3327.170578 |
| [15] |
Eidelman E, Faibis S, Peretz B. A comparison of restorations for children treated under general anesthesia or conscious sedation[J]. Pediatr Dent, 2000,22(1):33-37.
pmid: 10730284 |
| [16] |
Dietschi D, Campanile G, Holz J, et al. Comparison of the color stability of ten new-generation composites: an in vitro study[J]. Dent Mater, 1994,10(6):353-362.
doi: 10.1016/0109-5641(94)90059-0 pmid: 7498599 |
| [17] |
Ernst CP, Brandenbusch M, Meyer G, et al. Two-year clinical performance of a nanofiller vs a fine-particle hybrid resin composite[J]. Clin Oral Investig, 2006,10(2):119-125.
doi: 10.1007/s00784-006-0041-8 pmid: 16555069 |
| [18] |
El Shahawy OI, O’Connell AC. Successful restoration of severely mutilated primary incisors using a novel method to retain zirconia crowns—two year results[J]. J Clin Pediatr Dent, 2016,40(6):425-430.
doi: 10.17796/1053-4628-40.6.425 pmid: 27805887 |
| [1] | 赵双云, 邹思雨, 李雪莹, 沈丽娟, 周虹. 中文版口腔健康素养量表简版(HeLD-14)在学龄前儿童家长中应用的信度和效度评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 828-832. |
| [2] | 陈心心, 唐哲, 乔艳春, 荣文笙. 北京市密云区4岁儿童患龋状况及其与龋活跃性检测的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [3] | 岳芷涵,韩娜,鲍筝,吕瑾莨,周天一,计岳龙,王辉,刘珏,王海俊. 儿童早期体重指数轨迹与超重风险关联的前瞻性队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 390-396. |
| [4] | 费秀文,刘斯,汪波,董爱梅. 成人及儿童组织坏死性淋巴结炎临床特征及治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 533-540. |
| [5] | 俞光岩. 儿童唾液腺疾病[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 1-3. |
| [6] | 闫晓晋,刘云飞,马宁,党佳佳,张京舒,钟盼亮,胡佩瑾,宋逸,马军. 《中国儿童发展纲要(2011-2020年)》实施期间中小学生营养不良率变化及其政策效应分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 593-599. |
| [7] | 弭小艺,侯杉杉,付子苑,周末,李昕璇,孟召学,蒋华芳,周虹. 中文版童年不良经历问卷在学龄前儿童父母中应用的信效度评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 408-414. |
| [8] | 崔孟杰,马奇,陈曼曼,马涛,王鑫鑫,刘婕妤,张奕,陈力,蒋家诺,袁雯,郭桐君,董彦会,马军,星一. 不同生长模式与7~17岁儿童青少年代谢综合征的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 415-420. |
| [9] | 党佳佳,蔡珊,钟盼亮,王雅琪,刘云飞,师嫡,陈子玥,张依航,胡佩瑾,李晶,马军,宋逸. 室外夜间人工光暴露与中国9~18岁儿童青少年超重肥胖的关联[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 421-428. |
| [10] | 陈敬,肖伍才,单蕊,宋洁云,刘峥. DRD2基因rs2587552多态性对儿童肥胖干预效果的影响:一项前瞻性、平行对照试验[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 436-441. |
| [11] | 欧蒙恩,丁云,唐卫峰,周永胜. 基台边缘-牙冠的平台转移结构中粘接剂流动的三维有限元分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 548-552. |
| [12] | 李辉,高阳旭,王书磊,姚红新. 恶性肿瘤患儿完全植入式静脉输液港手术并发症[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1167-1171. |
| [13] | 甄敏,孟焕新,胡文杰,武登诚,危伊萍. 改良牙冠延长术后组织愈合的动物实验研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 927-935. |
| [14] | 刘京,陆爱东,左英熹,吴珺,黄志卓,贾月萍,丁明明,张乐萍,秦炯. 儿童急性淋巴细胞白血病合并癫痫发作75例临床特征和预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 948-953. |
| [15] | 崔雅茜,杜军保,张清友,廖莹,刘平,王瑜丽,齐建光,闫辉,徐文瑞,刘雪芹,孙燕,孙楚凡,张春雨,陈永红,金红芳. 儿童直立不耐受和坐位不耐受的疾病谱及治疗方式十年回顾[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 954-960. |
|
||