北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (1): 175-182. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.01.026
全髋关节置换术治疗脊柱骨骺发育不良患者Tönnis 3级髋关节骨关节炎的早期疗效
柯岩1,张蔷2,马云青2,李儒军1,陶可1,Δ( ),桂先革3,李克鹏4,张洪2,林剑浩1
),桂先革3,李克鹏4,张洪2,林剑浩1
- 1.北京大学人民医院骨关节科,北京 100044
2.解放军总医院第四医学中心骨一科,北京 100037
3.浙江医院骨一科,杭州 310013
4.保定市第二中心医院骨科,河北保定 072750
Short-term outcomes of total hip arthroplasty in the treatment of Tönnis grade 3 hip osteoarthritis in patients with spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia
KE Yan1,ZHANG Qiang2,MA Yun-qing2,LI Ru-jun1,TAO Ke1,Δ( ),GUI Xian-ge3,LI Ke-peng4,ZHANG Hong2,LIN Jian-hao1
),GUI Xian-ge3,LI Ke-peng4,ZHANG Hong2,LIN Jian-hao1
- 1. Institute of Arthritis, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
2. First Section of Orthopaedics, The Fourth Medical Center, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100037, China
3. First Section of Orthopaedics, Zhejiang Hospital, Hangzhou 310013, China
4. Department of Orthopaedics, Baoding Second Central Hospital, Baoding 072750, Hebei, China
摘要:
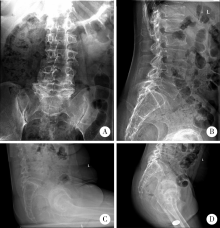
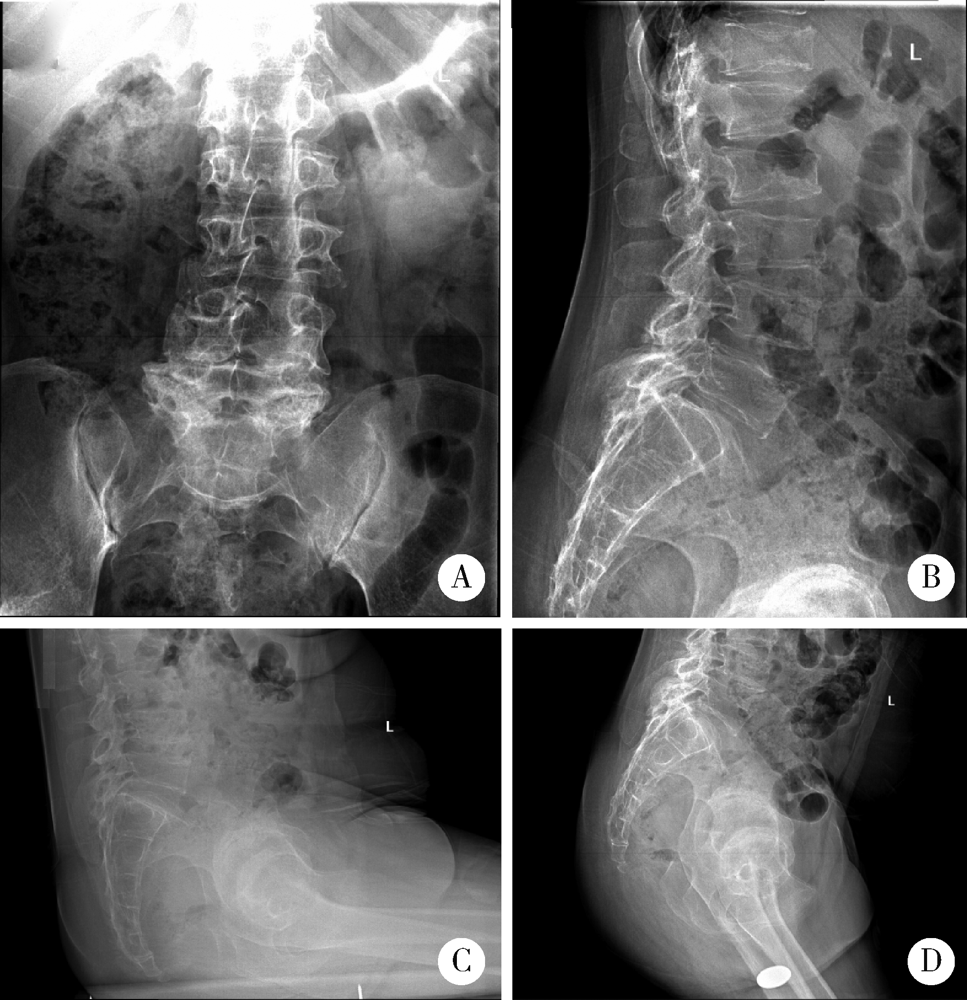
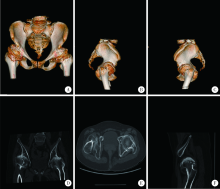
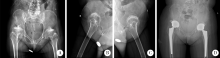
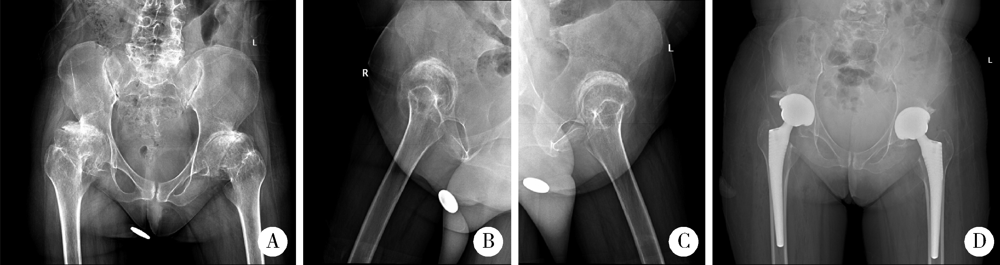
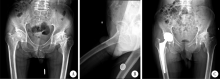
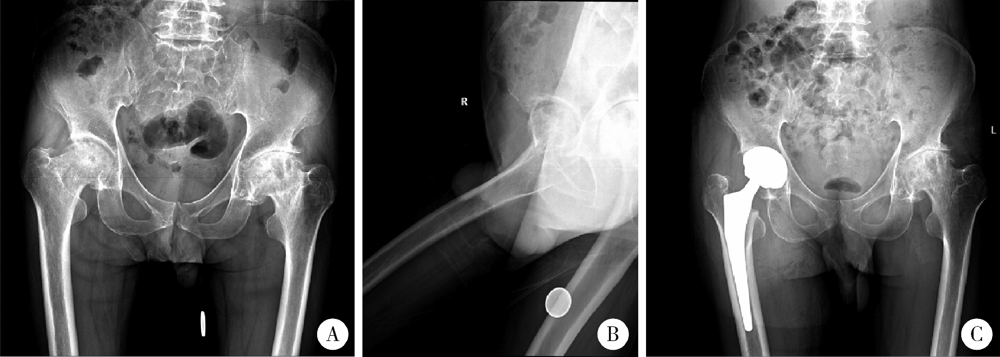
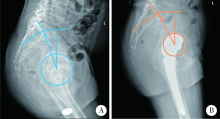
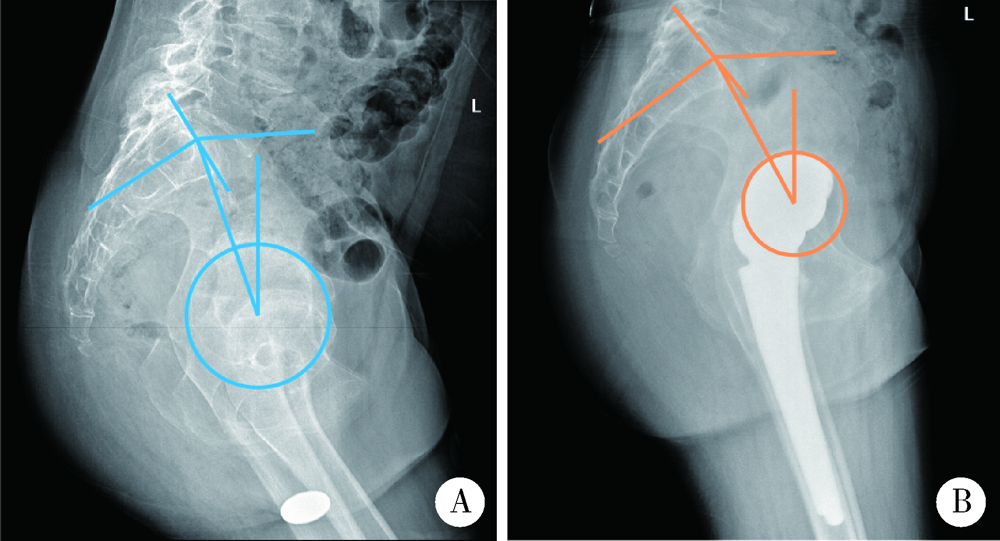
目的: 脊柱骨骺发育不良(spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia,SED)患者因骨骼、关节发育异常,生物力学改变和早年手术干预等往往导致严重的髋关节骨关节炎。本研究探讨人工全髋关节置换术治疗SED患者Tönnis 3级髋关节骨关节炎的早期疗效及可能的影响。方法: 2017年1月至2019年6月,将由高年资医生完成人工全髋关节置换术治疗的374例髋关节骨关节炎患者作为研究对象,其中因SED行人工全髋关节置换术的患者9例(男6例,女3例,12髋)符合纳入排除标准,观察人工全髋关节置换术对该类患者的早期疗效。结果: 所有患者均选用强生陶瓷内衬-陶瓷股骨头,均获得随访,平均随访时间20个月,除1例出现肌间静脉血栓外,其余患者均未出现无菌性松动、脱位、骨折、血管神经损伤、深静脉血栓和感染等并发症。术前髋关节Harris评分平均35.55分,美国西部Ontario和McMaster大学骨关节炎指数评分(the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities osteoarthritis index,WOMAC)平均56.56分,SF-12生活质量量表评分平均41.56分,视觉模拟评分(visual analogue scale, VAS)平均7.44分;末次随访时Harris评分平均89.56分,WOMAC骨关节炎指数评分平均41.11分,SF-12评分平均56.33分,VAS评分平均2.67分。与全髋关节置换术术前相比,SED患者术后骨盆入射角、骨盆倾斜角和骶骨倾斜角等骨盆相关参数均有所增加,术前平均骨盆入射角为68.95°±4.60°、平均骨盆倾斜角为52.75°±1.06°、平均骶骨倾斜角为17.45°±1.77°,而术后则相应变为76.98°±5.12°、60.51°±4.35°和18.10°±2.02°。患者术后双下肢均基本等长。结论: 人工全髋关节置换是治疗SED患者Tönnis 3级髋关节骨关节炎的一种有效手术方式,且早期疗效满意。
中图分类号:
- R687.4
| [1] |
Terhal PA, Nievelstein RJ, Verver EJ, et al. A study of the clinical and radiological features in a cohort of 93 patients with a COL2A1 mutation causing spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita or a related phenotype[J]. Am J Med Genet A, 2015,167A(3):461-475.
doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.36922 pmid: 25604898 |
| [2] |
Kocyigit H, Arkun R, Ozkinay F, et al. Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda with progressive arthropathy[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2000,19(3):238-241.
doi: 10.1007/s100670050166 pmid: 10870664 |
| [3] | 杨波, 金今, 翁习生, 等. 6例脊柱骨骺发育不良患者的诊断及治疗[J]. 中国骨与关节外科, 2008,1(4):285-289. |
| [4] | Chiavetta JB, Parvizi J, Shaughnessy WJ, et al. Total hip arthroplasty in patients with dwarfism [J]. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2004, 86-A(2):298-304. |
| [5] |
Wyles CC, Panos JA, Houdek MT, et al. Total hip arthroplasty reduces pain and improves function in patients with spondyloepi-physeal dysplasia: A long-term outcome study of 50 cases[J]. J Arthroplasty, 2019,34(3):517-521.
doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2018.10.028 pmid: 30528131 |
| [6] |
Treble NJ, Jensen FO, Bankier A, et al. Development of the hip in multiple epiphyseal dysplasia. Natural history and susceptibility to premature osteoarthritis[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1990,72(6):1061-1064.
doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.72B6.2246289 pmid: 2246289 |
| [7] |
Modi RM, Kheir MM, Tan TL, et al. Survivorship and complications of total hip arthroplasty in patients with dwarfism[J]. Hip Int, 2017,27(5):460-464.
doi: 10.5301/hipint.5000484 pmid: 28497456 |
| [8] |
Tönnis D. Diagnosis and therapy of hip dysplasia in the older child[J]. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb, 1990,128(4):369-372.
doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1039880 pmid: 2147315 |
| [9] |
Karimi D, Kallemose T, Troelsen A, et al. Hip malformation is a very common finding in young patients scheduled for total hip arthroplasty[J]. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg, 2018,138(4):581-589.
doi: 10.1007/s00402-018-2900-6 pmid: 29429067 |
| [10] |
Zhu S, Qian W, Jiang C, Enhanced recovery after surgery for hip and knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Postgrad Med J, 2017,93(1106):736-742.
doi: 10.1136/postgradmedj-2017-134991 pmid: 28751437 |
| [11] | 马明太, 芦浩, 张培训, 等. 老年髋部骨折手术风险评估表的制定[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2018,20(12):1031-1037. |
| [12] |
Necas L, Hrubina M, Melisik M, et al. Cementless hip arthroplasty and transverse shortening femoral osteotomy with the S-ROM stem for Crowe type IV developmental dysplasia[J]. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol, 2019,29(5):1025-1033.
doi: 10.1007/s00590-019-02400-y pmid: 30761426 |
| [13] |
Gala L, Kim PR, Beaulé PE. Natural history of lateral femoral cutaneous nerve neuropraxia after anterior approach total hip arthroplasty[J]. Hip Int, 2019,29(2):161-165.
doi: 10.1177/1120700019827201 pmid: 30810069 |
| [14] |
Zeng WN, Liu JL, Jia XL, et al. Midterm results of total hip arthroplasty in patients with high hip dislocation after suppurative hip arthritis[J]. J Arthroplasty, 2019,34(1):102-107.
doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2018.09.081 pmid: 30342951 |
| [15] |
Brokelman RB, Haverkamp D, van Loon C, et al. The validation of the visual analogue scale for patient satisfaction after total hip arthroplasty[J]. Eur Orthop Traumatol, 2012,3(2):101-105.
doi: 10.1007/s12570-012-0100-3 pmid: 22798966 |
| [16] |
Piazzolla A, Solarino G, Bizzoca D, et al. Spinopelvic parameter changes and low back pain improvement due to femoral neck anteversion in patients with severe unilateral primary hip osteoarthritis undergoing total hip replacement[J]. Eur Spine J, 2018,27(1):125-134.
doi: 10.1007/s00586-017-5033-7 pmid: 28303384 |
| [17] |
Ochi H, Baba T, Homma Y, et al. Importance of the spinopelvic factors on the pelvic inclination from standing to sitting before total hip arthroplasty[J]. Eur Spine J, 2016,25(11):3699-3706.
doi: 10.1007/s00586-015-4217-2 pmid: 26329653 |
| [18] |
Zhang Z, He JW, Fu WZ, et al. Identification of three novel mutations in the COL2A1 gene in four unrelated Chinese families with spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenital[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2011,413(4):504-508.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.08.090 pmid: 21924244 |
| [19] | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 《中国居民营养与慢性病状况报告(2015)》新闻发布会文字实录[J]. 中国实用乡村医生杂志, 2015,22(15):1-5. |
| [20] | 赵文华. 关注我国劳动力人口营养与健康状况[J]. 中华健康管理学杂志, 2015,9(6):393-394. |
| [21] |
Dawson P, Dunne L, Raza H, et al. Total hip arthroplasty for the treatment of osteoarthritis secondary to acetabular fractures treated by open reduction and internal fixation[J]. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol, 2019,29(5):1049-1054.
doi: 10.1007/s00590-019-02406-6 pmid: 30796512 |
| [22] |
Flecher X, Ollivier M, Argenson JN. Lower limb length and offset in total hip arthroplasty[J]. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res, 2016,102(1 Suppl):S9-20.
doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2015.11.001 pmid: 26797005 |
| [23] | 马千里, 吴敏瑞, 郑玉云, 等. 改良骨性定点测量法在全髋关节置换术中处理双下肢不等长的研究[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2018,20(12):1038-1043. |
| [24] |
Amirfeyz R, Taylor A, Smithson SF, et al. Orthopaedic manifestations and management of spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia Strudwick type[J]. J Pediatr Orthop B, 2006,15(1):41-44.
doi: 10.1097/01202412-200601000-00009 pmid: 16280719 |
| [25] |
Mac-Thiong JM, Labelle H, Berthonnaud E, et al. Sagittal spinopelvic balance in normal children and adolescents[J]. Eur Spine J, 2007,16(2):227-234.
doi: 10.1007/s00586-005-0013-8 pmid: 16311754 |
| [26] |
Arima H, Dimar JR 2nd, Glassman SD, et al. Differences in lumbar and pelvic parameters among African American, Caucasian and Asian populations[J]. Eur Spine J, 2018,27(12):2990-2998.
doi: 10.1007/s00586-018-5743-5 pmid: 30143898 |
| [27] | 张志奇, 古明晖, 廖威明, 等. 人体骨盆矢状面解剖参数在髋关节置换中的作用[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2013,93(15):1190-1191. |
| [28] |
Gu M, Zhang Z, Kang Y, et al. Roles of sagittal anatomical parameters of the pelvis in primary total hip replacement for patients with ankylosing spondylitis[J]. J Arthroplasty, 2015,30(12):2219-2223.
doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2015.06.027 pmid: 26164560 |
| [29] | 中华医学会骨科学分会. 中国骨科大手术静脉血栓栓塞症预防指南[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2016,36(2):65-71. |
| [30] |
Healy WL, Iorio R, Clair AJ, et al. Complications of total hip arthroplasty: standardized list, definitions, and stratification developed by the hip society[J]. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 2016,474(2):357-364.
doi: 10.1007/s11999-015-4341-7 pmid: 26040966 |
| [1] | 李森磊,杨先腾,田晓滨,孙立. 直接前入路和前外侧入路全髋关节置换术后的早期功能恢复对比[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 268-272. |
|
||