北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (4): 710-715. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.04.015
LAPTM4B-35蛋白作为肝癌血清学诊断新标志物的探讨
- 北京大学基础医学院细胞生物学系, 北京 100191
Serum LAPTM4B-35 protein as a novel diagnostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma
PANG Yong,ZHANG Sha,YANG Hua,ZHOU Rou-li( )
)
- Department of Cell Biology, Peking University School of Basic Medical Sciences, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
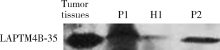
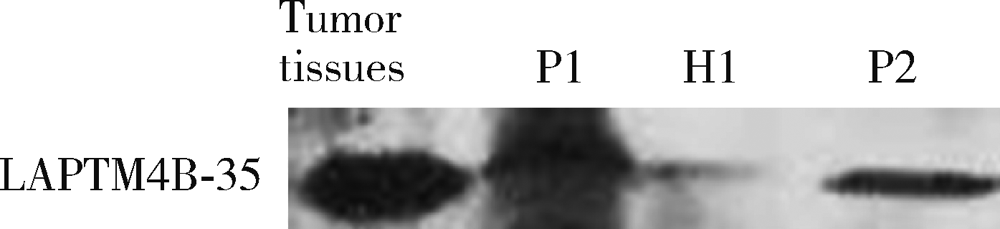
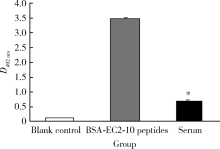
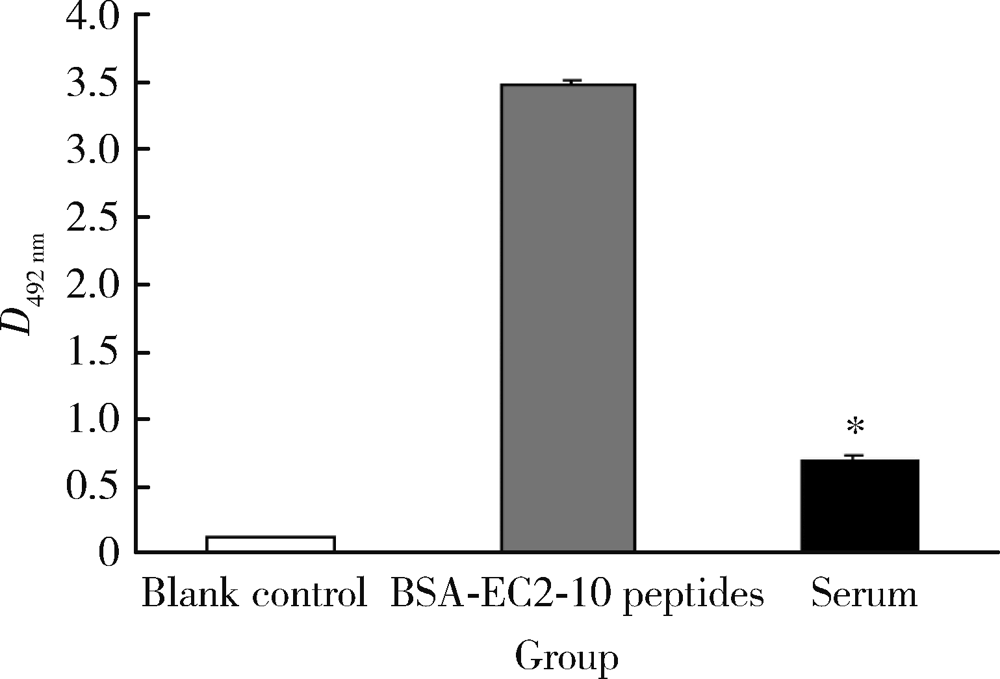
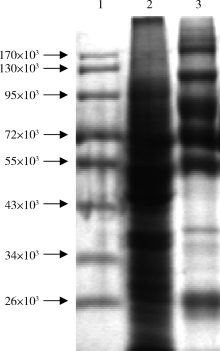
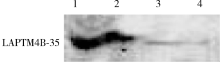
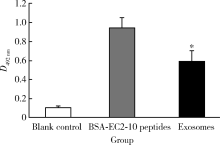
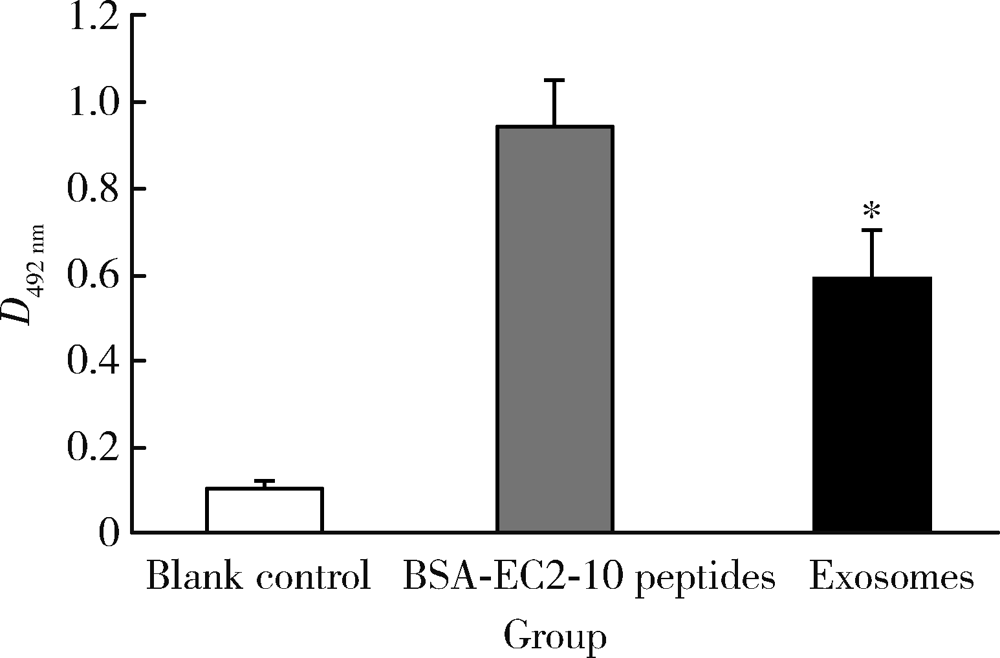
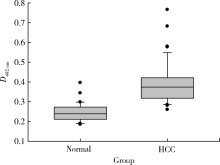
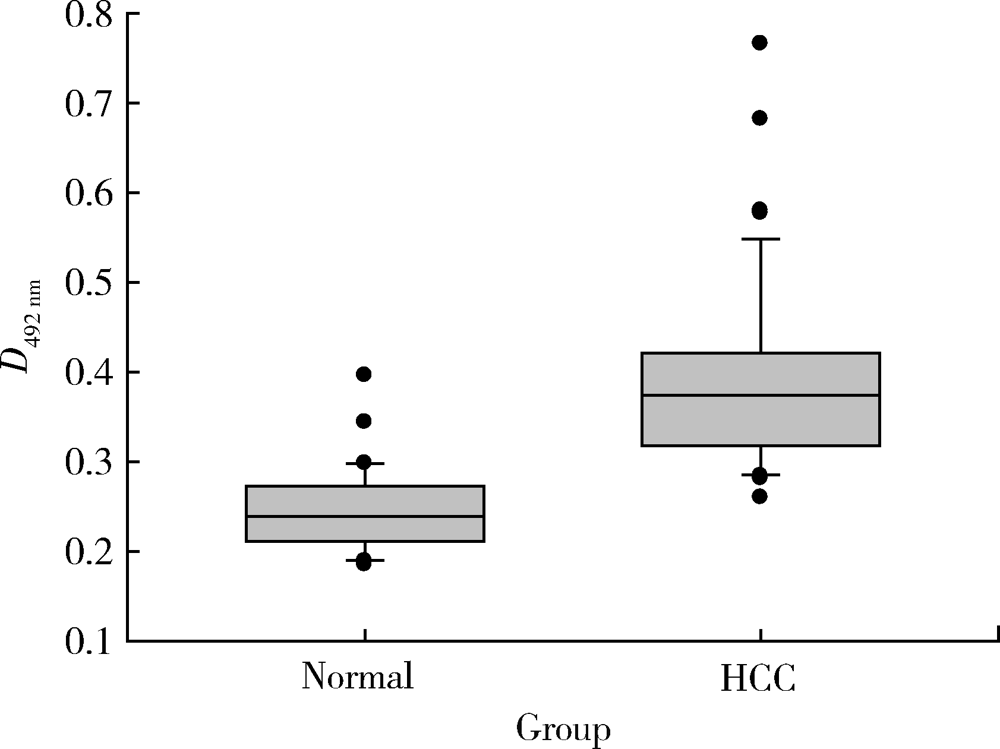
目的: LAPTM4B-35是北京大学基础医学院发现和鉴定的一个肿瘤驱动基因LAPTM4B所编码的蛋白质同型分子(isoform)之一,其在多种恶性肿瘤中[如肝癌、肺癌(包括非小细胞肺癌和小细胞肺癌)、胃癌、结直肠癌、胰腺癌、胆囊癌、胆管癌、乳腺癌、前列腺癌、宫颈癌、子宫内膜癌等]均超高表达。实验室和临床资料均证明,LAPTM4B-35蛋白的过表达促进肿瘤生长、转移和多药耐药,LAPTM4B-35的蛋白表达水平与肝癌的复发相关。本文的目的在于鉴定患者体内的肝癌细胞和体外培养的肝癌细胞系是否释放出LAPTM4B-35蛋白到血液和细胞培养液中,以及其可能的存在形式,为建立肝细胞癌等肿瘤的血清学诊断新方法奠定基础。方法: 采用免疫印迹分析(Western blot)、酶联免疫吸附实验(enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay,ELISA)鉴定LAPTM4B-35蛋白,应用超滤和超离心方法从肝癌细胞培养上清液中分离、纯化外排体(exosome)。结果: 特异性抗体的ELISA结果表明,肝细胞癌患者的血液中存在LAPTM4B-35蛋白,体外培养的肝癌细胞以外排体形式释放LAPTM4B-35蛋白到培养基的上清液中。ELISA夹心法检测表明,肝细胞癌患者(n=43)血淸中LAPTM4B-35蛋白的平均水平和中位值均显著高于正常人(n=33)。结论: 肝癌细胞以外排体形式释放到其外环境中的LAPTM4B-35蛋白有望成为肝细胞癌血清学诊断的新标志物。
中图分类号:
- R735.7
| [1] |
Shao GZ, Zhou RL, Zhang QY, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of LAPTM4B, a novel gene upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Oncogene, 2003, 22(32):5060-5069.
doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206832 |
| [2] |
Yang H, Xiong FX, Lin M, et al. LAPTM4B-35 is a novel diagnostic marker and a prognostic factor of hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. J Surgical Oncology, 2010, 101(5):363-369.
doi: 10.1002/jso.v101:5 |
| [3] |
Yang H, Xiong FX, Lin M, et al. LAPTM4B-35 overexpression is a risk factor for tumor recurrence and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2010, 136(2):275-281.
doi: 10.1007/s00432-009-0659-4 pmid: 19690886 |
| [4] | 何静, 邵根泽, 周柔丽, 等. 肝癌中高表达的新基因LAPTM4B对细胞增殖及成瘤性的影响 [J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2003, 35(4):348-352. |
| [5] |
Li L, Shan Y, Yang H, et al. Upregulation of LAPTM4B-35 promotes malignant transformation and tumorigenesis in L02 human liver cell line [J]. Anat Rec (Hoboken), 2011, 294(7):1135-1142.
doi: 10.1002/ar.v294.7 |
| [6] |
Liu XR, Xiong FX, Wei XH, et al. LAPTM4B-35, a novel tetratransmembrane protein and its PPRP motif play critical roles in proliferation and metastatic potential of HCC cells [J]. Cancer Sci, 2009, 100(12):2335-2340.
doi: 10.1111/cas.2009.100.issue-12 |
| [7] |
Li L, Wei XH, Pan YP, et al. LAPTM4B: A novel cancer-asso-ciated gene motivates multi-drug resistance through efflux and activating PI3K/Akt signaling [J]. Oncogene, 2010, 29(43):5785-5795.
doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.303 pmid: 20711237 |
| [8] |
Yang H, Xiong FX, Wei XH, et al. LAPTM4B-35 promotes growth and metastasis of hepatocelluar carcinoma [J]. Cancer Lett, 2010, 264(2):209-217.
doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2008.01.025 |
| [9] | 刘歆荣, 周柔丽, 张青云, 等. 人肝癌相关新基因编码产物LAPTM4B的鉴定及其生物学特性 [J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2003, 35(4):340-347. |
| [10] |
Keller S, Sanderson MP, Stoeck A, et al. Exosomes: from biogenesis and secretion to biological function [J]. Immunol Lett, 2006, 107(2):102-108.
doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2006.09.005 |
| [11] |
Simons M, Raposo G. Exosomes: vesicular carriers for intercellular communication [J]. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 2009, 21(4):575-581.
doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.03.007 |
| [12] |
Simpson RJ. Exosomes: proteomic insights and diagnostic potential [J]. Expert Rev Proteomics, 2009, 6(3):267-283.
doi: 10.1586/epr.09.17 |
| [13] |
Mitchell PJ, Welton J, Staffurth J. Can urinary exosomes act as treatment response markers in prostate cancer? [J]. J Transl Med, 2009, 7:4.
doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-7-4 pmid: 19138409 |
| [14] |
Nilsson J, Skog J, Nordstrand A, et al. Prostate cancer-derived urine exosomes: a novel approach to biomarkers for prostate cancer [J]. Br J Cancer, 2009, 100(10):1603-1607.
doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605058 |
| [15] | Théry C, Amigorena S, Raposo G, et al. Isolation and characte-rization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids [J]. Curr Protoc Cell Biol, 2006, Chapter 3: Unit 3.22. |
| [16] |
Navabi H, Croston D, Hobot J, et al. Preperation of human ova-rian cancer ascites-derived exosomes for a clinical trial [J]. Blood Cells Mol Dis, 2005, 35(2):149-152.
doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2005.06.008 |
| [17] |
Houali K, Wang X, Shimizu Y, et al. A new diagnostic marker for secreted Epstein-Barr virus encoded LMP1 and BARF1, oncoproteins in the serum and saliva of patients with nasopharyn-geal carcinoma [J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2007, 13(17):4993-5000.
pmid: 17785549 |
| [18] |
Viaud S, Théry C, Ploix S, et al. Dendritic cell-derived exosomes for cancer immunotherapy: what’s next? [J]. Cancer Res, 2010, 70(4):1281-1285.
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3276 |
| [19] | Koga K, Matsumoto K, Akiyoshi T, et al. Purification, characte-rization and biological significance of tumor-derived exosomes [J]. Anticancer Res, 2005, 25(6A):3703-3707. |
| [20] | Zhou RL. LAPTM4B: a novel diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma [M]// Wan-Yee Lau. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Basic research. Philippines: InTech Press, 2012: 1-34. |
| [21] |
Yang Z, Senninger N, Flammang I, et al. Clinical impact of circulating LAPTM4B-35 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2019, 145(5):1165-1178.
doi: 10.1007/s00432-019-02863-w |
| [1] | 李志存, 吴天俣, 梁磊, 范宇, 孟一森, 张骞. 穿刺活检单针阳性前列腺癌术后病理升级的危险因素分析及列线图模型构建[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 896-901. |
| [2] | 刘家骏, 刘国康, 朱玉虎. 免疫相关性重症肺炎1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 932-937. |
| [3] | 黄教悌,胡菁,韩博. 治疗相关神经内分泌前列腺癌机制研究与靶向治疗新进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 557-561. |
| [4] | 田宇轩,阮明健,刘毅,李德润,吴静云,沈棋,范宇,金杰. 双参数MRI改良PI-RADS评分4分和5分病灶的最大径对临床有意义前列腺癌的预测效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 567-574. |
| [5] | 姚凯烽,阮明健,李德润,田宇轩,陈宇珂,范宇,刘毅. 靶向穿刺联合区域系统穿刺对PI-RADS 4~5分患者的前列腺癌诊断效能[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 575-581. |
| [6] | 欧俊永,倪坤明,马潞林,王国良,颜野,杨斌,李庚午,宋昊东,陆敏,叶剑飞,张树栋. 肌层浸润性膀胱癌合并中高危前列腺癌患者的预后因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [7] | 王滨帅,邱敏,张前进,田茂锋,刘磊,王国良,陆敏,田晓军,张树栋. 6例肾尤文肉瘤伴静脉瘤栓的诊治[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 636-639. |
| [8] | 虞乐,邓绍晖,张帆,颜野,叶剑飞,张树栋. 具有低度恶性潜能的多房囊性肾肿瘤的临床病理特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [9] | 舒帆,郝一昌,张展奕,邓绍晖,张洪宪,刘磊,王国良,田晓军,赵磊,马潞林,张树栋. 肾部分切除术治疗囊性肾癌的功能学和肿瘤学结果:单中心回顾性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 667-672. |
| [10] | 方杨毅,李强,黄志高,陆敏,洪锴,张树栋. 睾丸鞘膜高分化乳头状间皮肿瘤1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 741-744. |
| [11] | 柴晓东,孙子文,李海爽,朱靓怡,刘小旦,刘延涛,裴斐,常青. 髓母细胞瘤分子亚型中CD8+T淋巴细胞浸润的临床病理特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 512-518. |
| [12] | 林国中,马长城,吴超,司雨,杨军. 微通道技术在颈椎管肿瘤微创切除术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 318-321. |
| [13] | 俞光岩. 儿童唾液腺疾病[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 1-3. |
| [14] | 薛蔚,董樑,钱宏阳,费笑晨. 前列腺癌新辅助治疗与辅助治疗的现状及进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 775-780. |
| [15] | 薛子璇,唐世英,邱敏,刘承,田晓军,陆敏,董靖晗,马潞林,张树栋. 青年肾肿瘤伴瘤栓的临床病理特征及预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 802-811. |
|
||