北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (5): 865-870. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.05.014
膀胱内灌注电灼联合水扩张法治疗女性间质性膀胱炎
- 中国医科大学附属第一医院泌尿外科, 沈阳 110001
Treatment of intravesical instillation with fulguration-hydrodistention on female interstitial cystitis
Peng XIN,Hao ZHANG,Zhen-ming JIANG*( )
)
- Department of Urology, The First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110001, China
摘要:
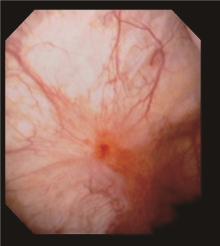
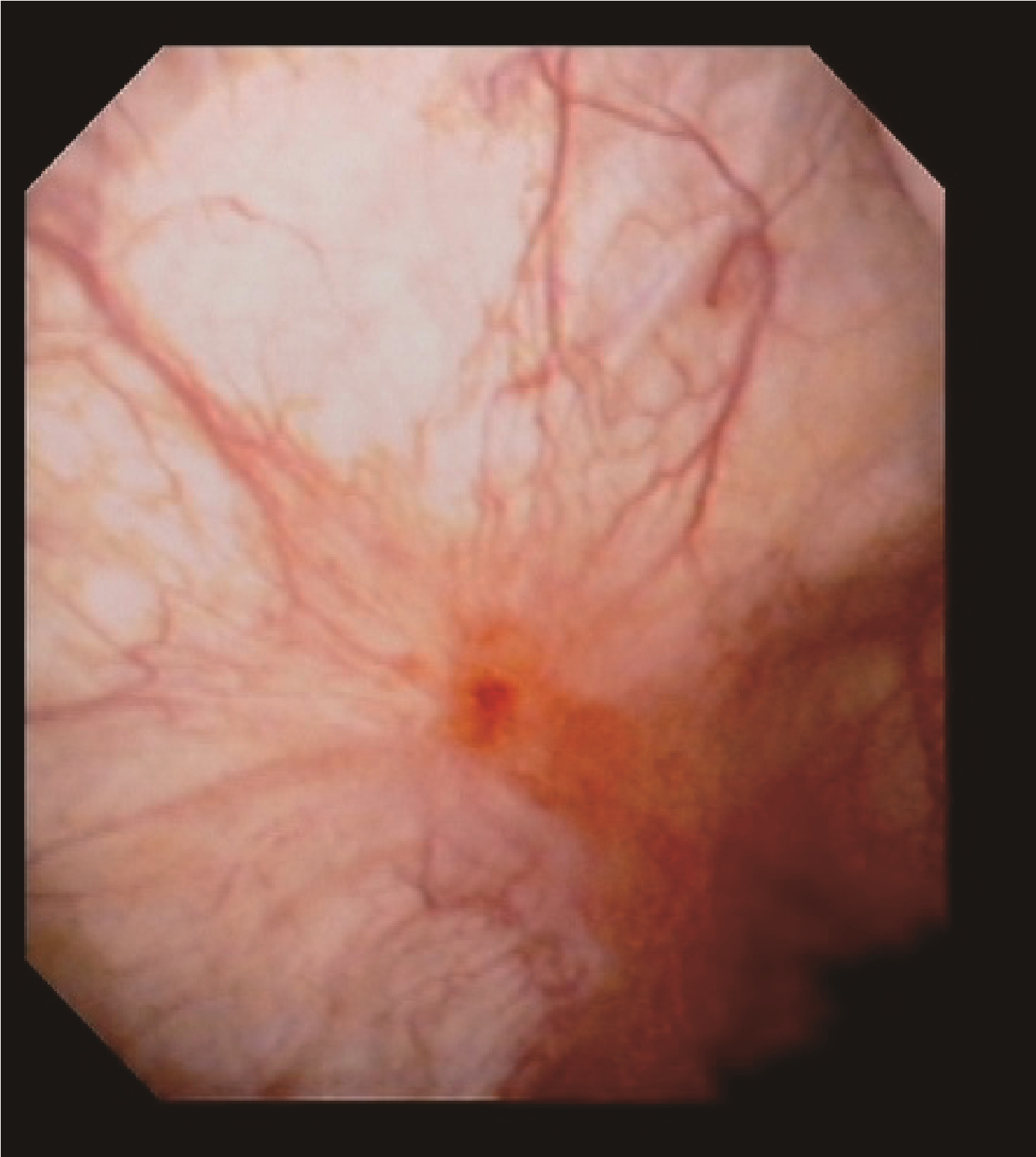
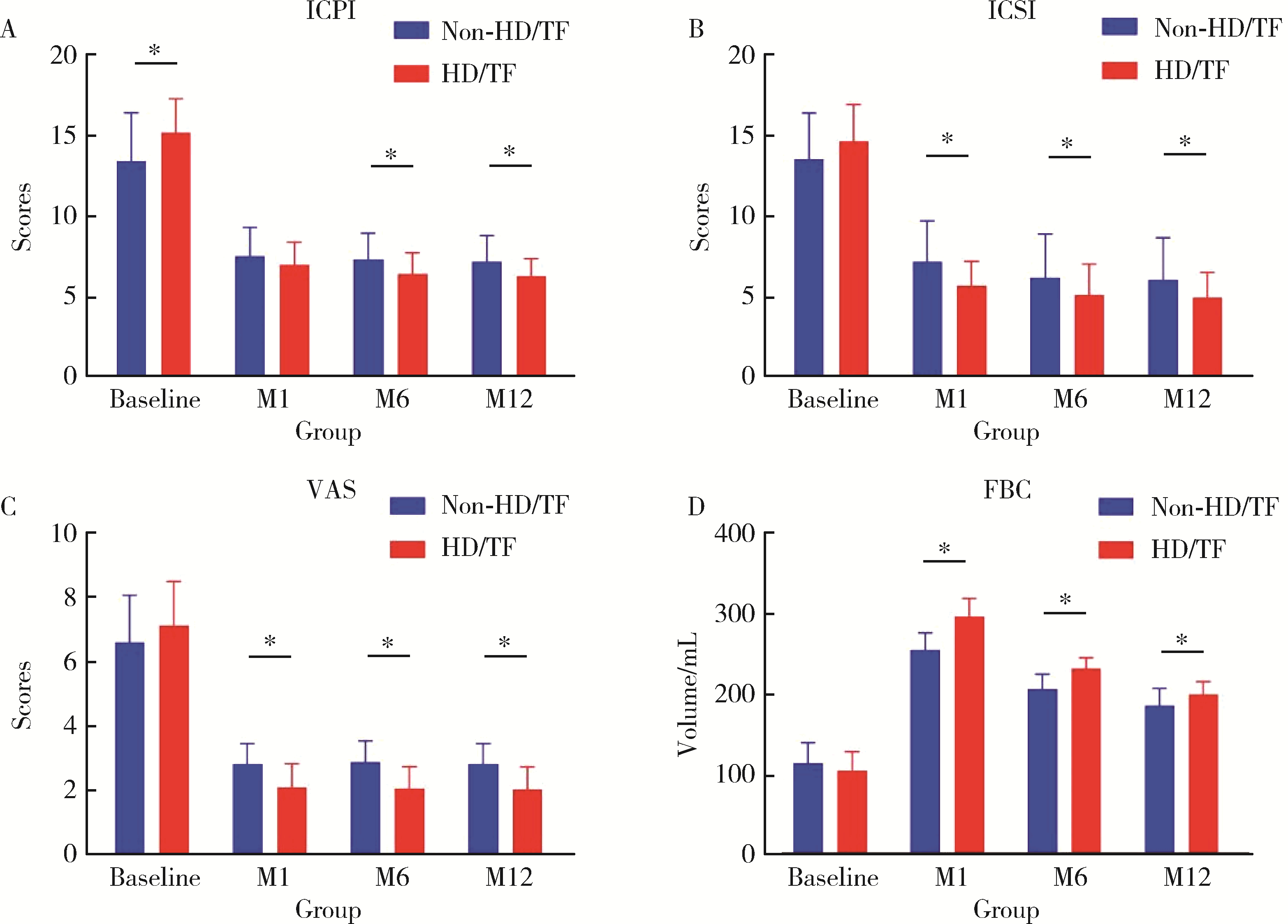
目的: 探讨肝素/碱化利多卡因(利多卡因与碳酸氢钠混合)协同膀胱内灌注联合水扩张及经尿道电灼治疗女性间质性膀胱炎(interstitial cystitis, IC)的有效性和安全性。方法: 选择2012年1月至2020年12月于中国医科大学附属第一医院泌尿外科就诊,符合美国泌尿外科协会指南的诊断标准,新诊断为IC的女性患者的病例资料进行回顾性分析,诊断时对可疑病变进行膀胱镜检查和活检。所有患者均接受持续12个月的2%(质量分数)利多卡因10 mL + 5%(质量分数)碳酸氢钠5 mL +肝素25 000 IU的膀胱内灌注治疗,根据患者的意愿,选择接受或不接受水扩张及经尿道电灼治疗,将患者分为水扩张和经尿道电灼(hydrodistension and transurethral fulguration, HD/TF)组和非HD/TF组,记录患者治疗前和治疗后1、6、12个月O’Leary-Sant间质性膀胱炎症状指标评分(interstitial cystitis patient symptom index scores, ICSI)、问题指标评分(interstitial cystitis patient problem index scores, ICPI)、耻骨上疼痛视觉模拟评分(visual analog scale, VAS)、功能性膀胱容量(functional bladder capacity,FBC)等。结果: 共收集到患者79例,其中有4例(5.1%)患者因病理诊断为癌或治疗失败而行膀胱切除术被剔除,其余患者均在治疗后1、6、12个月成功随访。重复测量方差分析显示:治疗后ICPI、ICSI和VAS较治疗前均显著降低(P < 0.05),FBC显著增加(P < 0.05)。治疗后1、6、12个月随访期间FBC持续下降,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);在治疗后1个月和6个月随访时ICSI持续降低,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),而治疗后的6个月与治疗后12个月的ICSI差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。HD/TF组在治疗后1个月和6个月随访时ICPI持续降低,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),而治疗后6个月与12个月的ICPI差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。治疗后1、6、12个月其余各项指标之间比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。与非HD/TF组相比,HD/TF组的ICPI、ICSI、VAS和FBC改善更早,且VAS和FBC的变化更显著(P < 0.05)。结论: 肝素/碱化利多卡因协同膀胱内灌注加水扩张和经尿道电灼治疗IC是一种有效的治疗选择。膀胱内肝素/碱化利多卡因协同灌注可能成为首选治疗方法,可显著减轻患者和医保系统的经济负担,如果患者能接受,可考虑经尿道电灼联合水扩张的治疗方法。
中图分类号:
- R694.3
| 1 |
Hanno PM , Erickson D , Moldwin R , et al. Diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: AUA guideline amendment[J]. J Urol, 2015, 193 (5): 1545- 1553.
doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2015.01.086 |
| 2 |
Engeler DS , Baranowski AP , Dinis-Oliveira P , et al. The 2013 EAU guidelines on chronic pelvic pain: Is management of chronic pelvic pain a habit, a philosophy, or a science? 10 years of development[J]. Eur Urol, 2013, 64 (3): 431- 439.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2013.04.035 |
| 3 |
Generali JA , Cada DJ . Amitriptyline: Interstitial cystitis (painful bladder syndrome)[J]. Hosp Pharm, 2014, 49 (9): 809- 810.
doi: 10.1310/hpj4909-809 |
| 4 |
Sun Y , Fang Z , Ding Q , et al. Effect of amitriptyline in treatment interstitial cystitis or bladder pain syndrome according to two criteria: Does ESSIC criteria change the response rate[J]. Neurourol Urodyn, 2014, 33 (3): 341- 344.
doi: 10.1002/nau.22407 |
| 5 |
Sant GR , Propert KJ , Hanno PM , et al. A pilot clinical trial of oral pentosan polysulfate and oral hydroxyzine in patients with interstitial cystitis[J]. J Urol, 2003, 170 (3): 810- 815.
doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000083020.06212.3d |
| 6 |
Nickel JC , Herschorn S , Whitmore KE , et al. Pentosan polysulfate sodium for treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Insights from a randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled study[J]. J Urol, 2015, 193 (3): 857- 862.
doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2014.09.036 |
| 7 |
Vollstedt A , Tennyson L , Turner K , et al. Evidence for early cyclosporine treatment for hunner lesion interstitial cystitis[J]. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg, 2022, 28 (1): e1- e5.
doi: 10.1097/SPV.0000000000001108 |
| 8 |
Ogawa T , Ishizuka O , Ueda T , et al. Pharmacological management of interstitial cystitis /bladder pain syndrome and the role cyclosporine and other immunomodulating drugs play[J]. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol, 2018, 11 (5): 495- 505.
doi: 10.1080/17512433.2018.1457435 |
| 9 |
Crescenze IM , Tucky B , Li J , et al. Efficacy, side effects, and monitoring of oral cyclosporine in interstitial cystitis-bladder pain syndrome[J]. Urology, 2017, 107, 49- 54.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2017.05.016 |
| 10 |
Malde S , Palmisani S , Al-Kaisy A , et al. Guideline of guidelines: Bladder pain syndrome[J]. BJU Int, 2018, 122 (5): 729- 743.
doi: 10.1111/bju.14399 |
| 11 |
Nickel JC , Ehrlich GD , Krol JE , et al. The bacterial microbiota of Hunner lesion interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome[J]. BJU Int, 2022, 129 (1): 104- 112.
doi: 10.1111/bju.15519 |
| 12 |
Meng E , Hsu YC , Chuang YC . Advances in intravesical therapy for bladder pain syndrome (BPS)/interstitial cystitis (IC)[J]. Low Urin Tract Symptoms, 2018, 10 (1): 3- 11.
doi: 10.1111/luts.12214 |
| 13 |
Lim YN , Dwyer P , Murray C , et al. Long-term outcomes of intravesical dimethyl sulfoxide/heparin/hydrocortisone therapy for interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome[J]. Int Urogynecol J, 2017, 28 (7): 1085- 1089.
doi: 10.1007/s00192-016-3232-0 |
| 14 |
Generali JA , Cada DJ . Intravesical heparin: Interstitial cystitis (painful bladder syndrome)[J]. Hosp Pharm, 2013, 48 (10): 822- 824.
doi: 10.1310/hpj4810-822 |
| 15 | Li B, Leng Q, Li C, et al. Comparison of intravesical instillation of hyaluronic acid with intradetrusor botulinum toxin A injection or cystoscopic hydrodistention for ketamine-associated cystitis[J]. J Int Med Res, 2020, 48(11): 300060520973100. |
| 16 |
Lv YS , Zhou HL , Mao HP , et al. Intravesical hyaluronic acid and alkalinized lidocaine for the treatment of severe painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis[J]. Int Urogynecol J, 2012, 23 (12): 1715- 1720.
doi: 10.1007/s00192-012-1802-3 |
| 17 | Downey A , Hennessy DB , Curry D , et al. Intravesical chondroitin sulphate for interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome[J]. Ulster Med J, 2015, 84 (3): 161- 163. |
| 18 | Nickel JC , Jain P , Shore N , et al. Continuous intravesical lidocaine treatment for interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Safety and efficacy of a new drug delivery device[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2012, 4 (143): 143ra100. |
| 19 |
Niimi A , Nomiya A , Yamada Y , et al. Hydrodistension with or without fulguration of hunner lesions for interstitial cystitis: Long-term outcomes and prognostic predictors[J]. Neurourol Urodyn, 2016, 35 (8): 965- 969.
doi: 10.1002/nau.22837 |
| 20 |
Ham BK , Kim JH , Oh MM , et al. Effects of combination treatment of intravesical resiniferatoxin instillation and hydrodistention in patients with refractory painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis: A pilot study[J]. Int Neurourol J, 2012, 16 (1): 41- 46.
doi: 10.5213/inj.2012.16.1.41 |
| 21 | Evans RJ , Overholt T , Colaco M , et al. Injection location does not impact botulinum toxin A efficacy in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome patients[J]. Can J Urol, 2020, 27 (1): 10125- 10129. |
| 22 | Rahnamai MS , Marcelissen T , Apostolidis A , et al. The efficacy of botulinum toxin A and sacral neuromodulation in the management of interstitial cystitis (IC)/bladder pain syndrome (BPS), what do we know? ICI-RS 2017 think thank, Bristol[J]. Neurourol Urodyn, 2018, 37 (Suppl 4): S99- S107. |
| 23 |
Peters KM , Jayabalan N , Bui D , et al. Effect of sacral neuro-modulation on outcome measures and urine chemokines in interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome patients[J]. Low Urin Tract Symptoms, 2015, 7 (2): 77- 83.
doi: 10.1111/luts.12054 |
| 24 |
Xu R , Schachar J , Evans RJ , et al. Hydrodistention does not alter bladder gene expression profiles in patients with non-Hunner lesion interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome[J]. Neurourol Urodyn, 2021, 40 (5): 1126- 1132.
doi: 10.1002/nau.24680 |
| 25 |
Walker SJ , Plair A , Hemal K , et al. Bladder hydrodistention does not result in a significant change in bladder capacity for interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome patients[J]. Urology, 2019, 132, 81- 86.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2019.06.031 |
| 26 |
Huang MC , Hsieh CH , Chang WC , et al. Assessment of treatment outcomes of interstitial cystitis with hydrodistention and bladder training by O'Leary-Sant interstitial cystitis symptom and problem indices[J]. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol, 2018, 57 (5): 718- 721.
doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2018.08.019 |
| 27 |
Yu WR , Jhang JF , Ho HC , et al. Cystoscopic hydrodistention characteristics provide clinical and long-term prognostic features of interstitial cystitis after treatment[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11 (1): 455.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80252-x |
| 28 |
Lee SW , Kim WB , Lee KW , et al. Long-term outcomes of ulcerative interstitial cystitis after complete transurethral resection with therapeutic hydrodistention[J]. Int Urol Nephrol, 2021, 53 (2): 219- 227.
doi: 10.1007/s11255-020-02637-1 |
| 29 |
Keller J , Chiou HY , Lin HC . Increased risk of bladder cancer following diagnosis with bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis[J]. Neurourol Urodyn, 2013, 32 (1): 58- 62.
doi: 10.1002/nau.22283 |
| [1] | 柯涵炜, 王起, 许克新. 优化环磷酰胺剂量在间质性膀胱炎/膀胱疼痛综合征啮齿动物模型中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 908-912. |
| [2] | 朱琳,张维宇,许克新. 环磷酰胺诱导SD大鼠膀胱疼痛综合征模型的有效性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 735-740. |
| [3] | 王佳文,刘敬超,孟令峰,张威,刘晓东,张耀光. 间质性膀胱炎/膀胱疼痛综合征患者生活质量及相关因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 653-658. |
|
||