北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (5): 896-901. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.05.022
穿刺活检单针阳性前列腺癌术后病理升级的危险因素分析及列线图模型构建
李志存, 吴天俣, 梁磊, 范宇, 孟一森*( ), 张骞*(
), 张骞*( )
)
- 北京大学第一医院泌尿外科,北京大学泌尿外科研究所,泌尿生殖系疾病(男)分子诊治北京市重点实验室,国家泌尿男生殖系肿瘤中心,北京 100034
Risk factors analysis and nomogram model construction of postoperative pathological upgrade of prostate cancer patients with single core positive biopsy
Zhicun LI, Tianyu WU, Lei LIANG, Yu FAN, Yisen MENG*( ), Qian ZHANG*(
), Qian ZHANG*( )
)
- Department of Urology, Peking University First Hospital; Institution of Urology, Peking University; Beijing Key Laboratory of Urogenital Diseases (Male) Molecular Diagnosis and Treatment Center; National Urological Cancer Center, Beijing 100034, China
摘要:
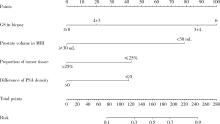
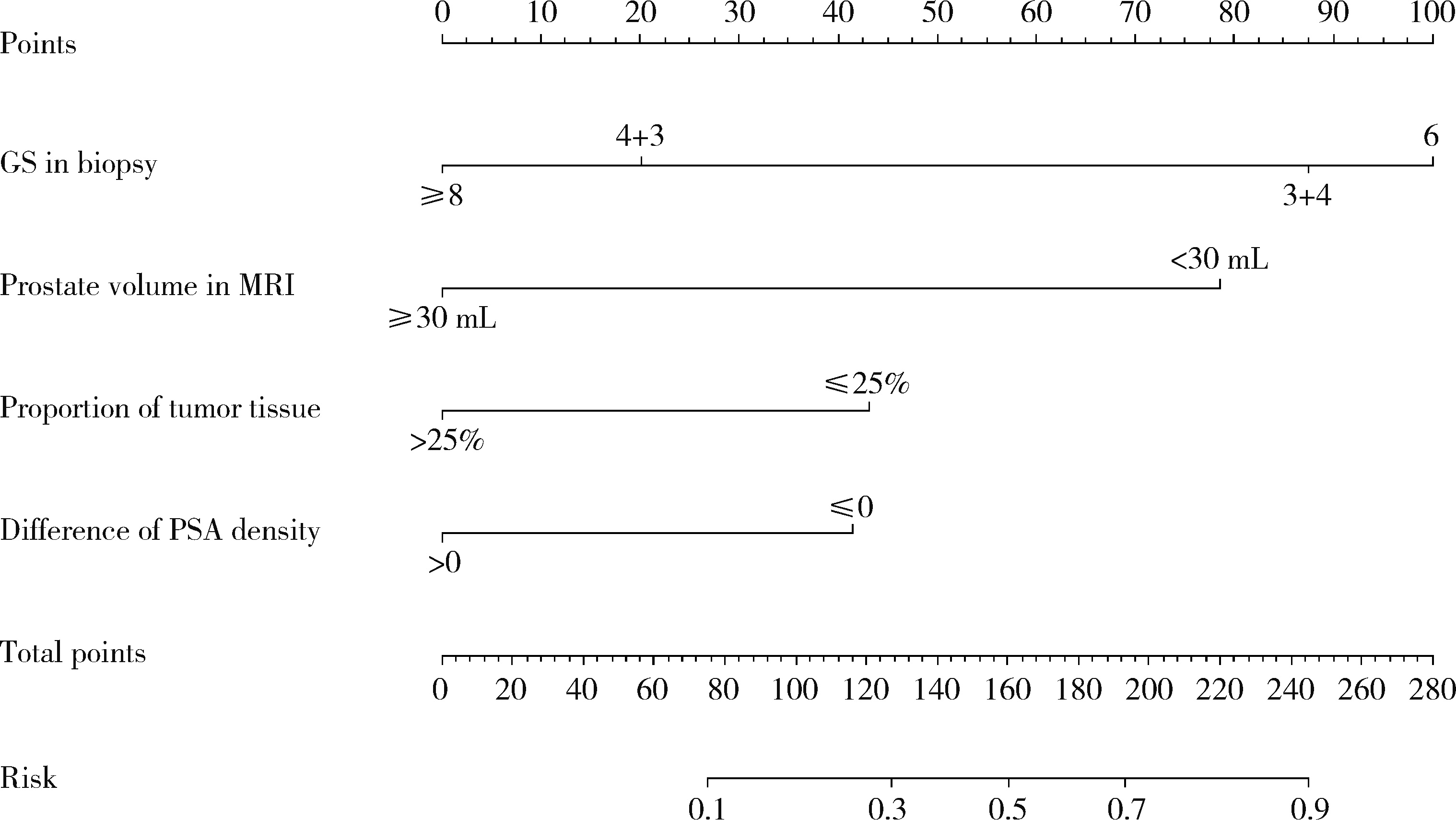
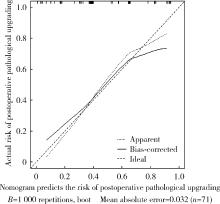
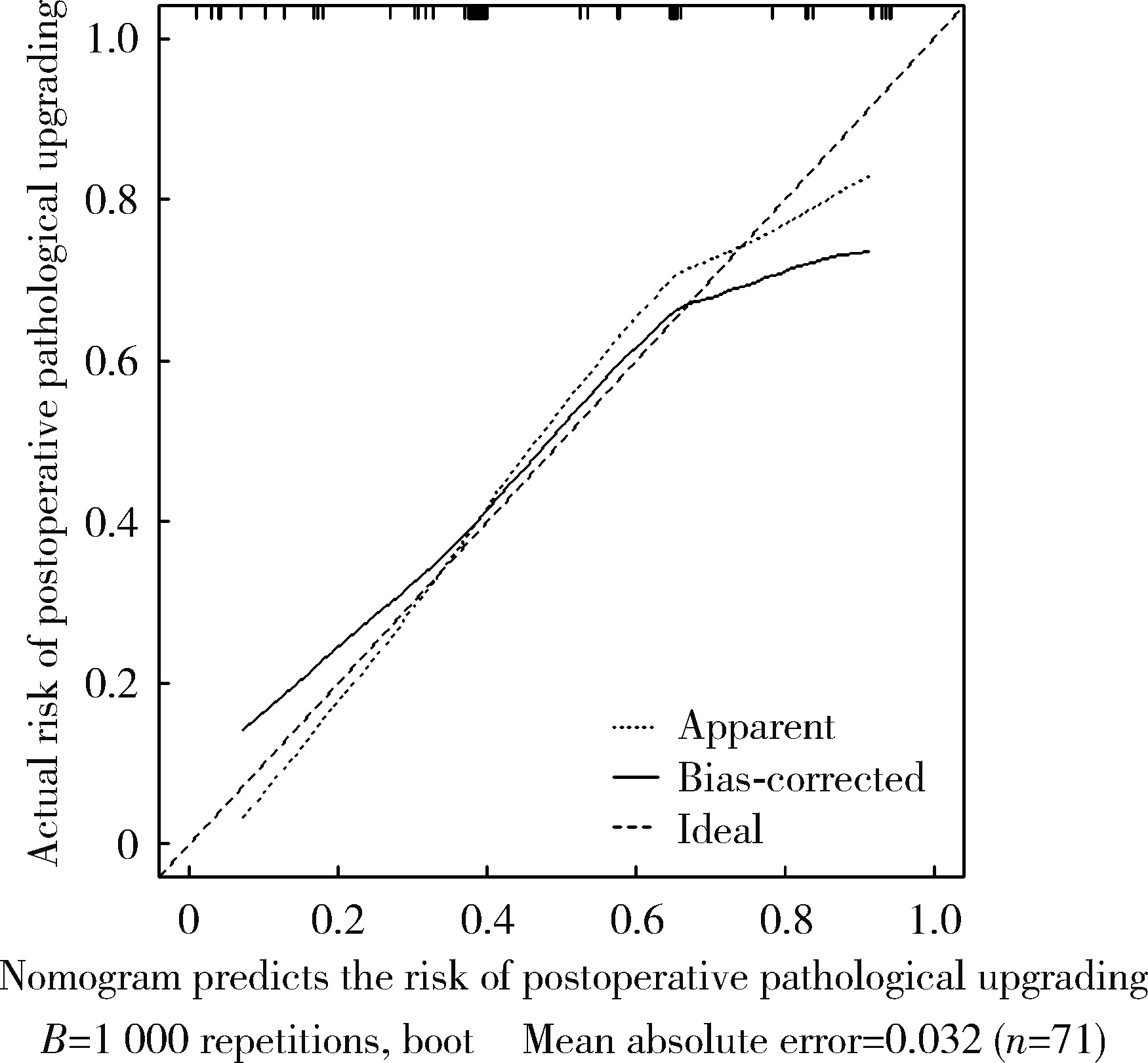
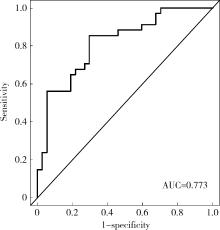
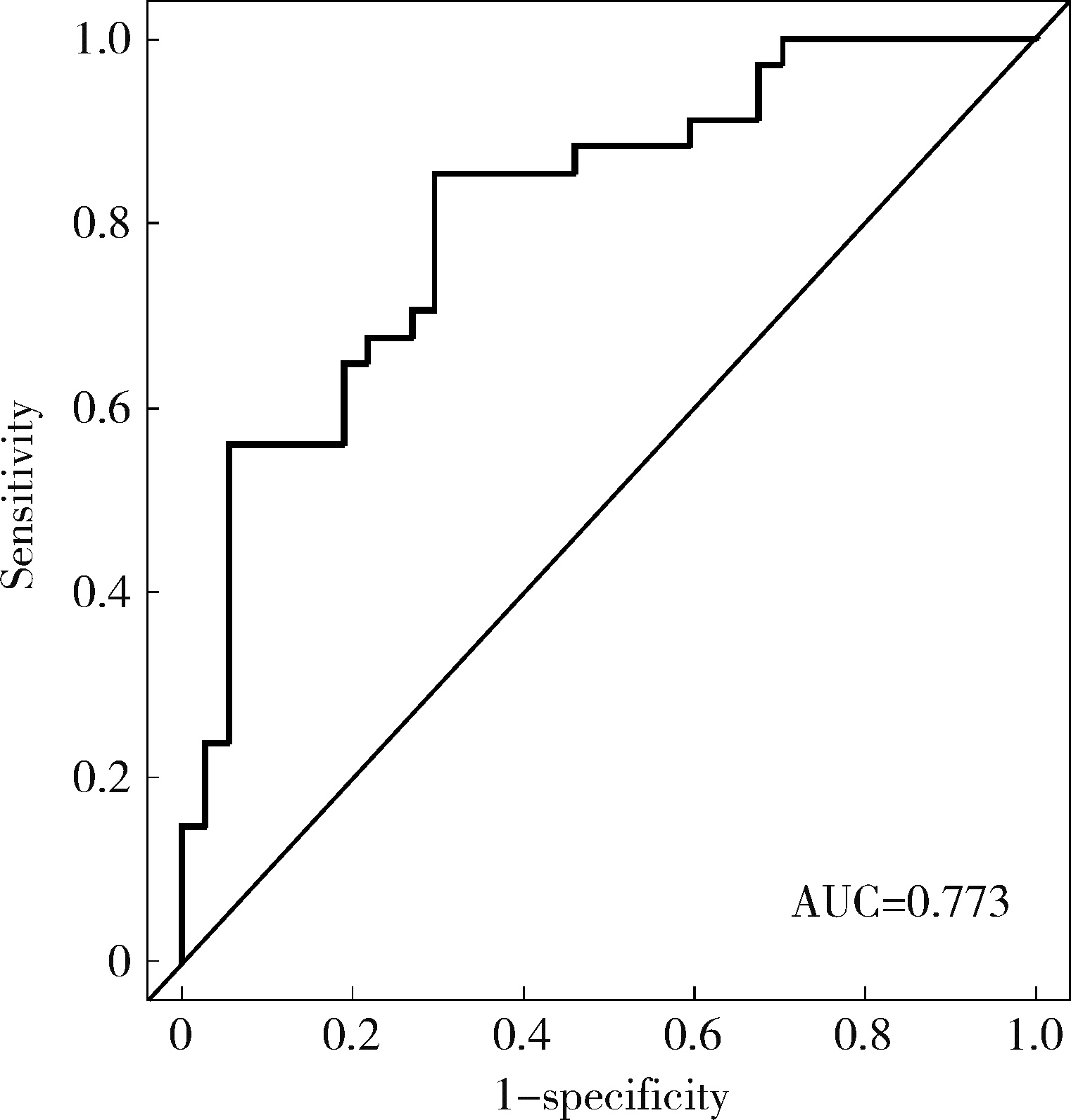
目的: 对穿刺活检单针阳性前列腺癌术后病理升级的危险因素进行分析,并尝试构建预测穿刺单针阳性前列腺癌患者术后病理升级的数学模型。方法: 回顾分析2015年1月至2020年8月期间于北京大学第一医院诊断为前列腺癌且接受根治性前列腺切除术的患者1 349例,选取其中穿刺活检单针阳性患者的临床资料,将其分为术后病理较穿刺病理升级组及未升级组,比较两组的年龄、体重指数、临床分期、前列腺影像报告和数据系统(prostate imaging reporting and data system,PI-RADS)评分、磁共振成像(magnetic resonance imaging,MRI)报告的前列腺体积、前列腺穿刺活检的Gleason评分、穿刺前及术前血清前列腺特异性抗原(prostate specific antigen,PSA)、手术方式、术后病理分期的差异,将单因素分析中P < 0.1的术前变量纳入多因素Logistic回归并绘制列线图,通过受试者工作特征曲线对模型进行评价。结果: 共有71例患者符合纳入排除标准,其中术后病理升级组34例,未升级组37例,两组患者的年龄(P=0.585)、体重指数(P=0.165)、手术方式(P=0.08)、MRI前列腺体积(P=0.067)、临床分期(P=0.678)、PI-RADS评分(P=0.203)、穿刺前PSA(P=0.359)、术前PSA(P=0.739)、PSA密度差(P=0.063)、穿刺Gleason评分(P=0.068)差异均无统计学意义,两组患者穿刺阳性针中肿瘤组织占比(P=0.007)、术后病理分期(P < 0.001)及术后Gleason评分(P < 0.001)差异有统计学意义。将单因素分析中P < 0.1的术前变量,即MRI前列腺体积、PSA密度差、穿刺阳性针中的肿瘤组织占比、穿刺Gleason评分纳入多因素Logistic回归分析,只有MRI前列腺体积组间差异有统计学意义。进一步根据多因素Logistic回归结果绘制列线图,受试者工作特征曲线的曲线下面积为0.773。结论: 对于穿刺病理单针阳性的前列腺癌患者,若前列腺体积较小或穿刺阳性针中肿瘤组织占比较少,需警惕术后病理较穿刺病理升级的可能;对于可能出现病理升级的患者,需谨慎考虑术前的危险分层。本模型可初步用于预测穿刺活检单针阳性前列腺癌患者术后病理升级的可能性。
中图分类号:
- R737.25
| 1 | 郑荣寿, 陈茹, 韩冰峰, 等. 2022年中国恶性肿瘤流行情况分析[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2024, 46 (3): 221- 231. |
| 2 |
Siegel RL , Miller KD , Jemal A . Cancer statistics, 2020[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2020, 70 (1): 7- 30.
doi: 10.3322/caac.21590 |
| 3 | 徐毅, 毛祺琦, 刘犇, 等. 穿刺单针阳性前列腺癌的术后病理特征分析[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2018, 39 (10): 757- 760. |
| 4 | 陈小豹, 张潮鸿, 江玮, 等. 前列腺穿刺单针阳性的临床特点[J]. 中国男科学杂志, 2019, 33 (3): 30- 33. |
| 5 | 唐超来, 唐贤富, 郑兴明. 前列腺穿刺活检单针阳性患者行前列腺根治性切除术后的病理特征[J]. 国际泌尿系统杂志, 2020, 40 (4): 587- 590. |
| 6 |
Goldstein NS , Bégin LR , Grody WW , et al. Minimal or no cancer in radical prostatectomy specimens. Report of 13 cases of the "vanishing cancer phenomenon"[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 1995, 19 (9): 1002- 1009.
doi: 10.1097/00000478-199509000-00003 |
| 7 |
Ricardo Kupka da S , Dall'Oglio MF , Sant'Ana AC , et al. Can single positive core prostate cancer at biopsy be considered a low-risk disease after radical prostatectomy?[J]. Int Braz J Urol, 2013, 39 (6): 800- 807.
doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2013.06.05 |
| 8 | 刘希高, 谌诚, 李健, 等. 前列腺穿刺活检单针阳性患者前列腺内癌灶分布特点[J]. 中华男科学杂志, 2012, 18 (2): 155- 159. |
| 9 | 杜少静, 贺慧颖. 穿刺单针阳性前列腺癌患者根治术后62例临床病理分析[J]. 中华病理学杂志, 2016, 45 (7): 446- 450. |
| 10 |
郝一昌, 颜野, 张帆, 等. 穿刺活检单针阳性的前列腺癌手术策略选择及经验总结[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52 (4): 625- 631.
doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.04.005 |
| 11 | Dong F , Jones JS , Stephenson AJ , et al. Prostate cancer volume at biopsy predicts clinically significant upgrading[J]. J Urol, 2008, 179 (3): 896- 900. |
| 12 | Hwang I , Lim D , Jeong YB , et al. Upgrading and upstaging of low-risk prostate cancer among Korean patients: A multicenter study[J]. Asian J Androl, 2015, 17 (5): 811- 814. |
| [1] | 李钰锴, 王红彦, 罗靓, 李云, 李春. 抗磷脂抗体在白塞病合并血栓中的临床意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 1036-1040. |
| [2] | 田杨, 韩永正, 李娇, 王明亚, 曲音音, 房景超, 金辉, 李民, 王军, 徐懋, 王圣林, 郭向阳. 颈椎前路手术后硬膜外血肿的发生率和危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 1058-1064. |
| [3] | 王明瑞, 赖金惠, 姬家祥, 唐鑫伟, 胡浩浦, 王起, 许克新, 徐涛, 胡浩. 使用中文版威斯康星结石生活质量问卷预测肾结石患者生活质量降低的危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 1069-1074. |
| [4] | 刘园梅, 傅义程, 郝靖欣, 张福春, 刘慧琳. 老年髋部骨折患者住院期间发生术后心力衰竭的列线图预测模型的构建及验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 874-883. |
| [5] | 田宇轩,阮明健,刘毅,李德润,吴静云,沈棋,范宇,金杰. 双参数MRI改良PI-RADS评分4分和5分病灶的最大径对临床有意义前列腺癌的预测效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 567-574. |
| [6] | 姚凯烽,阮明健,李德润,田宇轩,陈宇珂,范宇,刘毅. 靶向穿刺联合区域系统穿刺对PI-RADS 4~5分患者的前列腺癌诊断效能[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 575-581. |
| [7] | 欧俊永,倪坤明,马潞林,王国良,颜野,杨斌,李庚午,宋昊东,陆敏,叶剑飞,张树栋. 肌层浸润性膀胱癌合并中高危前列腺癌患者的预后因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [8] | 颜野,李小龙,夏海缀,朱学华,张羽婷,张帆,刘可,刘承,马潞林. 前列腺癌根治术后远期膀胱过度活动症的危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 589-593. |
| [9] | 周泽臻,邓绍晖,颜野,张帆,郝一昌,葛力源,张洪宪,王国良,张树栋. 非转移性T3a肾细胞癌患者3年肿瘤特异性生存期预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 673-679. |
| [10] | 陈延,李况蒙,洪锴,张树栋,程建星,郑仲杰,唐文豪,赵连明,张海涛,姜辉,林浩成. 阴茎海绵体注射试验对阴茎血管功能影响的回顾性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 680-686. |
| [11] | 庞博,郭桐君,陈曦,郭华棋,石嘉章,陈娟,王欣梅,李耀妍,单安琪,余恒意,黄婧,汤乃军,王艳,郭新彪,李国星,吴少伟. 天津与上海35岁以上人群氮氧化物个体暴露水平及其影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 700-707. |
| [12] | 和静,房中则,杨颖,刘静,马文瑶,霍勇,高炜,武阳丰,谢高强. 血浆中脂质代谢分子与颈动脉粥样硬化斑块、传统心血管危险因素及膳食因素的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 722-728. |
| [13] | 蔡珊,张依航,陈子玥,刘云飞,党佳佳,师嫡,李佳欣,黄天彧,马军,宋逸. 北京市中小学生身体活动时间现状及影响因素的路径[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 403-410. |
| [14] | 张祖洪,陈天娇,马军. 中小学生青春发动时相与心血管代谢危险因素的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 418-423. |
| [15] | 林郁婷,王华丽,田宇,巩俐彤,常春. 北京市老年人认知功能的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 456-461. |
|
||