北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 670-675. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.04.007
结石相关输尿管狭窄的上尿路修复手术技术与临床结局
余霄腾*, 黄奕瑄*, 李新飞, 陈昶甫, 赵方舟, 应鸿刚, 陶子豪, 张一鸣, 徐丽清, 李志华, 杨昆霖, 周利群, 李学松, 赵峥*( )
)
- 北京大学第一医院泌尿外科, 北京大学泌尿外科研究所, 国家泌尿男生殖系研究肿瘤中心, 北京 100034
Surgical techniques and clinical outcomes of upper urinary tract reconstruction for stone-related ureteral strictures
Xiaoteng YU, Yixuan HUANG, Xinfei LI, Changfu CHEN, Fangzhou ZHAO, Honggang YING, Zihao TAO, Yiming ZHANG, Liqing XU, Zhihua LI, Kunlin YANG, Liqun ZHOU, Xuesong LI, Zheng ZHAO*( )
)
- Department of Urology, Peking University First Hospital, Institute of Urology, Peking University, National Urological Cancer Center, Beijing 100034, China
摘要:
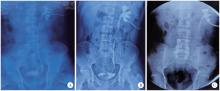
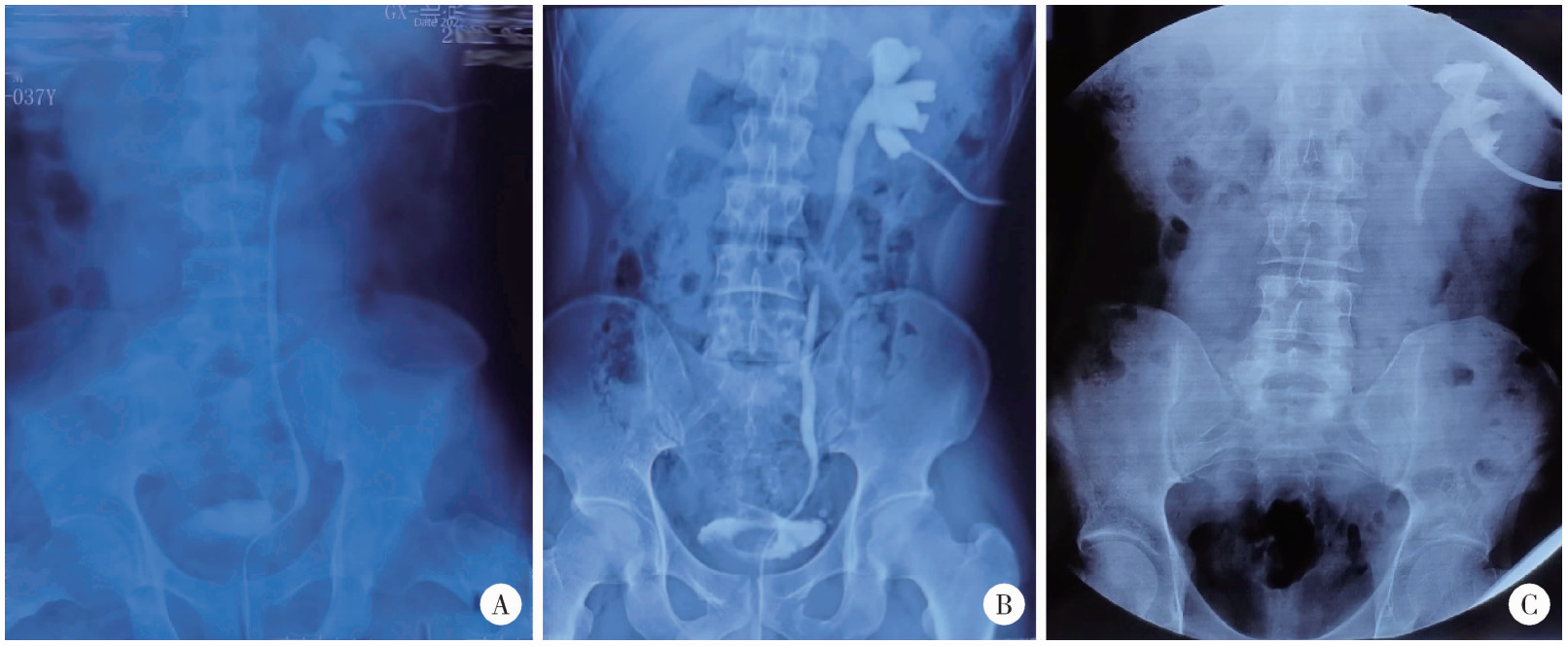
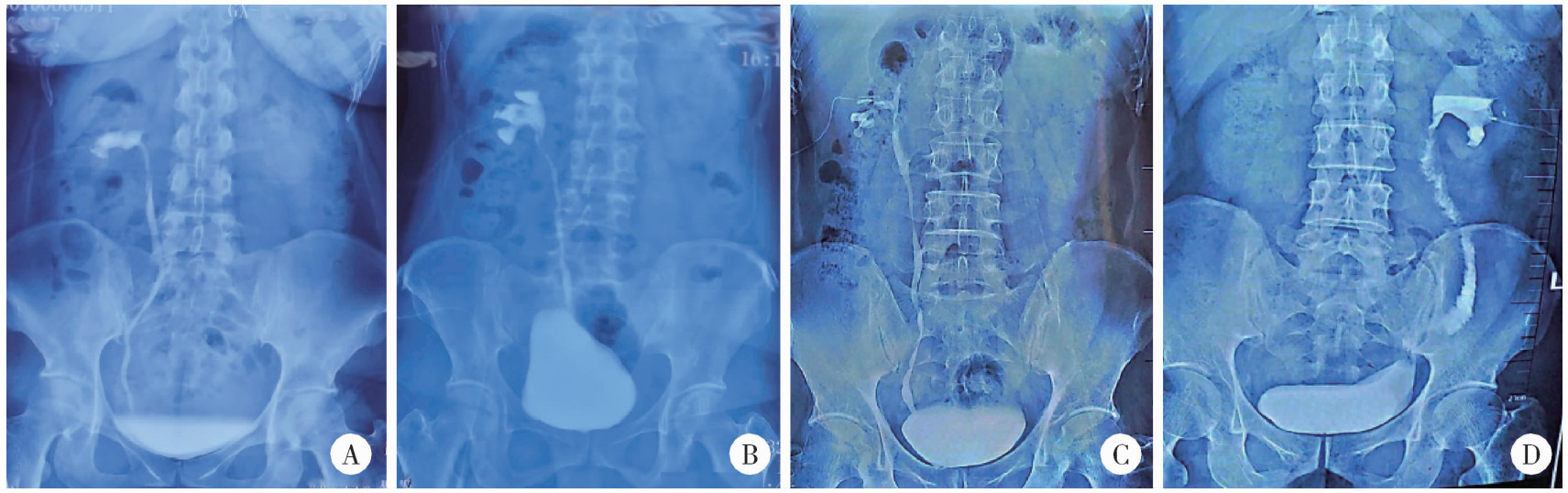
目的: 总结结石相关输尿管狭窄患者接受上尿路修复重建的手术技术及临床结局。方法: 连续性纳入2014年3月至2023年11月在北京大学第一医院的71例接受上尿路修复手术的结石相关输尿管狭窄患者的病例资料进行回顾性分析, 收集患者临床特征、实验室检查结果、影像学特点、手术方式及随访情况。手术成功定义为术后症状缓解、肾积水程度改善或未再加重、肾功能处于正常范围且保持稳定。结果: 上、中、下段输尿管狭窄患者分别为36、9、15例, 另有11例患者为多段狭窄。中位狭窄长度为5.0(3.0~15.0) cm。上段输尿管狭窄最常用的修复方式为口腔黏膜补片输尿管成形术(13/36, 36.1%)和阑尾补片输尿管成形术(8/36, 22.2%); 中段输尿管狭窄患者根据狭窄长度, 可选用球囊扩张术(1/9, 11.1%)、输尿管狭窄段切除再吻合(1/9, 11.1%)、自体黏膜补片输尿管成形术(3/9, 33.3%)和回肠代输尿管术(4/9, 44.4%); 下段输尿管狭窄患者最常用的修复方式为输尿管膀胱再植术(10/15, 66.7%); 所有多段狭窄患者均接受回肠代输尿管术。中位随访时间为14.2(6.1~107.1)个月, 总体成功率97.2%。结论: 结石相关输尿管狭窄个体差异大, 根据具体狭窄位置和长度选择合适的手术方法可获得较满意的临床预后。
中图分类号:
- R699
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
黄健, 张旭. 中国泌尿外科和男科疾病诊断治疗指南2022版[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2022: 803- 806.
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
程嗣达, 李新飞, 熊盛炜, 等. 机器人辅助腹腔镜上尿路修复手术: 单一术者108例经验总结[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 771- 779.
doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.04.032 |
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
朱照伟, 赵品, 王声政, 等. 腹腔镜或机器人肾盂瓣成形术治疗复杂上段输尿管狭窄[J/OL]. 泌尿外科杂志(电子版), 2023, 15(1): 29-33.
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
包军胜, 范阳, 冯宁翰, 等. 机器人辅助腹腔镜自体组织补片修复输尿管狭窄中国专家共识[J]. 微创泌尿外科杂志, 2024, 13(2): 93- 99.
|
| 18 |
柴帅帅, 李兵, 肖行远. 自体组织补片修复复杂输尿管狭窄的手术要点及围手术期管理中国专家共识(2024版)[J]. 现代泌尿外科杂志, 2024, 29(5): 388- 393.
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
肖行远, 柴帅帅, 董满顺, 等. 阑尾输尿管成形术治疗右侧输尿管狭窄的初步临床经验: 基于8例患者的研究[J]. 泌尿外科杂志(电子版), 2024, 16(4): 8- 12.
|
| 21 |
朱照伟, 赵品, 张雪培. 长段输尿管狭窄外科治疗思考: 不同自体组织成形术的优劣及微创与开放的抉择[J]. 现代泌尿外科杂志, 2025, 30(4): 279- 283.
|
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
|
| [1] | 王焕瑞, 赖世聪, 胡浩浦, 丁泽华, 徐涛, 胡浩. 腹腔镜与输尿管软镜联合定位治疗复杂输尿管狭窄的疗效分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(4): 784-788. |
| [2] | 黄万伟, 沙显燊, 张艺宝, 伍国豪, 骆峰, 陈智慧, 叶东明, 李学松, 赖彩永. 完全3D腹腔镜回肠代双侧输尿管联合膀胱扩大术修复放射治疗后双侧输尿管狭窄并膀胱挛缩[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(4): 789-795. |
| [3] | 陈思鹭, 王海菊, 吴宇财, 李志华, 黄燕波, 何宇辉, 许洋洋, 李学松, 贯华. 成人肾积水病因分析:一项单中心横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 913-918. |
| [4] | 王明瑞, 王起, 胡浩, 赖金惠, 唐鑫伟, 万春艳, 许克新, 徐涛. 覆膜金属输尿管支架治疗盆腔脂肪增多症所致肾积水的疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 919-922. |
| [5] | 应沂岑,杜毅聪,李志华,张一鸣,李新飞,王冰,张鹏,朱宏建,周利群,杨昆霖,李学松. 机器人辅助腹腔镜下颊黏膜补片输尿管成形术治疗复杂输尿管狭窄[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 640-645. |
| [6] | 秦彩朋,王飞,杜依青,张晓威,李清,刘士军,徐涛. 无症状无积水输尿管结石4例患者的诊治[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 939-942. |
| [7] | 王磊,韩天栋,江卫星,李钧,张道新,田野. 主动迁移技术与原位碎石技术在输尿管软镜治疗1~2 cm输尿管上段结石中的安全性和有效性比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 553-557. |
| [8] | 柳登高,郑丹妮,赵雅宁,张亚琼,叶欣,张丽琪,谢晓艳,张雷,张祖燕,俞光岩. 疑难唾液腺结石病的治疗研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 8-12. |
| [9] | 张春龙,王明瑞,王起,许克新,徐涛,胡浩. 覆膜金属输尿管支架维持性治疗输尿管镜碎石术后难治性输尿管狭窄的远期疗效评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 674-679. |
| [10] | 韩冠鹏,许洋洋,李志华,孟畅,朱宏建,杨昆霖,周利群,李学松. 造血干细胞移植后输尿管狭窄1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 762-765. |
| [11] | 黄炳伟,王杰,张鹏,李喆,毕泗成,王强,岳才博,杨昆霖,李学松,周利群. 吲哚菁绿在复杂上尿路修复手术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 651-656. |
| [12] | 马闰卓,夏海缀,陆敏,张智荧,张启鸣,卢剑,王国良,马潞林. 输尿管镜活体组织检查对上尿路尿路上皮癌根治性手术的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(4): 665-672. |
| [13] | 王晶,陈俊鹏,王洋,许向亮,郭传瑸. 数字化下颌运动记录及咀嚼肌肌电图在下颌骨肿瘤患者口颌功能评价中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(3): 571-578. |
| [14] | 郝一昌,陈昆,刘余庆,卢剑,肖春雷,马潞林. 输尿管软镜下钬激光切除术治疗肾盂癌6例报道及文献复习[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(5): 816-821. |
| [15] | 郝一昌,侯小飞,赵磊,肖春雷,刘茁,张帆,马潞林. 全腹腔镜移植输尿管膀胱再植术处理肾移植术后输尿管狭窄[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(4): 705-710. |
|
||