北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2018, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (6): 1014-1021. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2018.06.013
间充质干细胞治疗系统性红斑狼疮有效性的meta分析
- 1. 昆明医科大学第一附属医院风湿免疫科, 昆明 650032
2. 云南省阜外心血管病医院心血管内科,昆明 650000
3. 云南舜喜再生医学工程有限公司研究中心, 昆明 650000
Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells on systemic lupus erythematosus:a meta-analysis
Shuang LIU1,Yu-long GUO2,Jing-yi YANG3,Wei WANG1,Jian XU1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650032, China
2. Department of Cardiology, Yunnan Provincial Fuwai Cardiovascular Disease Hospital, Kunming 650000, China
3. Yunnan Shunxi Regeneration Medical Engineering Co., Ltd, Kunming 650000, China
摘要:
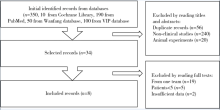
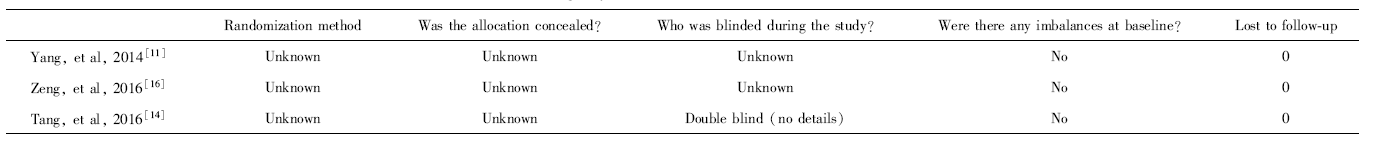
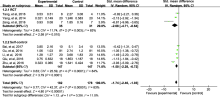
目的: 间充质干细胞(mesenchymal stem cell,MSC)用于治疗难治性系统性红斑狼疮(systemic lupus erythematosus,SLE)和狼疮性肾炎已有10余年的历史,但相关研究多为自身对照研究,随机对照研究(randomized controlled trial,RCT)较少,循证医学证据不足。本研究采用荟萃分析方法系统评价MSC治疗SLE的有效性。方法: 计算机检索PubMed数据库、Cochrane Library数据库、万方数据库、维普全文数据库发表的采用MSC治疗SLE的RCT和自身对照研究,截止日期至2018年6月1日。由2位研究者独立按照纳入与排除标准实施文献筛选和数据收集。以SLE疾病活动评分、24 h尿蛋白定量和补体C3定量为研究终点,应用Revman 5.3软件进行荟萃分析。结果: 共纳入8项研究,共213例患者,其中3项研究为RCT,包含66例患者。分析结果显示,MSC可降低SLE疾病活动评分[标准化均数差(standard mean difference,SMD)=-1.76,95%CI:-2.00~-1.51,P<0.001],可降低蛋白尿水平(SMD=-1.74,95%CI:-2.46~-1.03,P<0.001),改善补体C3水平(SMD=1.28,95%CI:0.93~1.62,P<0.001)。共有4项研究报道了不良事件。结论: MSC可用于治疗难治性SLE和狼疮性肾炎,现有证据表明,其可改善疾病活动程度、蛋白尿和补体水平,确切疗效仍需进一步大规模高质量的RCT证实。
中图分类号:
- R593.24
| [1] | 中华医学会风湿病学分会. 系统性红斑狼疮诊断及治疗指南[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2010,14(5):342-346. |
| [2] |
van Vollenhoven RF, Mosca M, Bertsias G , et al. Treat-to-target in systemic lupus erythematosus: recommendations from an international task force[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2014,73(6):958-967.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-205139 pmid: 24739325 |
| [3] |
He J, Zhang X, Wei Y , et al. Low-dose interleukin-2 treatment selectively modulates CD4(+) T cell subsets in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Nat Med, 2016,22(9):991-993.
doi: 10.1038/nm.4148 pmid: 27500725 |
| [4] | 王丹丹, 孙凌云 . 间充质干细胞移植治疗重症自身免疫病[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2015,35(10):831-834. |
| [5] | 梁军, 孙凌云 . 间充质干细胞治疗系统性红斑狼疮的基础和临床研究[J]. 浙江医学, 2017,39(21):1836-1841. |
| [6] |
Carrion F, Nova E, Ruiz C , et al. Autologous mesenchymal stem cell treatment increased T regulatory cells with no effect on disease activity in two systemic lupuserythematosus patients[J]. Lupus, 2010,19(3):317-322.
doi: 10.1177/0961203309348983 |
| [7] |
Deng D, Zhang P, Guo Y , et al. A randomised double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of allogeneic umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell for lupus nephritis[J]. Ann RheumDis, 2017,76(8):1436-1439.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211073 |
| [8] | Hochberg MC . Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 1997,40(9):1725. |
| [9] |
Petri M, Orbai A, Alarcón GS , et al. Derivation and validation of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2012,64(8):2677-2686.
doi: 10.1002/art.34473 |
| [10] |
Gladman DD, Iba ED, Urowitz MB . Systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index 2000[J]. J Rheumatol, 2002,29(2):288-291.
doi: 10.1097/00124743-200202000-00018 pmid: 11838846 |
| [11] |
杨桂鲜, 潘丽萍, 陈志琴 , 等. 脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗狼疮性肾炎的临床疗效[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2014,30(17):2779-2781.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2014.17.029 |
| [12] |
白茹, 戚燕, 吕昭萍 , 等. 脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗难治性系统性红斑狼疮3年随访[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2017,33(6):905-909.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2017.06.020 |
| [13] |
李俊霞, 林强, 陈建 , 等. 脐带间充质干细胞对增殖型狼疮性肾炎的临床疗效观察[J]. 中华细胞与干细胞杂志: 电子版, 2016,6(3):174-178.
doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-1221.2016.03.007 |
| [14] |
唐帮丽, 邓丹琪, 张佩莲 , 等. 脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗狼疮性肾炎的疗效与机制[J]. 昆明医科大学学报, 2016,37(7):93-98.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4706.2016.07.022 |
| [15] |
Gu F, Wang D, Zhang H , et al. Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for lupus nephritis patients refractory to conventional therapy[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2014,33(11):1611-1619.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-014-2754-4 pmid: 25119864 |
| [16] | 曾雯, 胡英, 杨霞 , 等. 间充质干细胞联合吗替麦考酚酯治疗狼疮性肾炎的临床效果[J]. 中国当代医药, 2016,23(7):67-70. |
| [17] |
朱宁, 毛静, 张小莲 , 等. 脐带间充质干细胞移植在系统性红斑狼疮患者中的应用研究[J]. 疑难病杂志, 2016,15(1):44-47.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6450.2016.01.011 |
| [18] | 裘影影, 何建强, 汤郁 , 等. 脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗难治性系统性红斑狼疮患者的疗效分析[J]. 中国实用医药, 2016,11(25):68-69. |
| [19] |
Sun L, Akiyama K, Zhang H , et al. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation reverses multiorgan dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus mice and humans[J]. Stem Cells, 2009,27(6):1421-1432.
doi: 10.1002/stem.68 pmid: 19489103 |
| [20] | 杨桂鲜, 潘丽萍, 曹礼应 , 等. 脐带间充质干细胞治疗难治性系统性红斑狼疮的临床研究[J]. 云南医药, 2018,39(1):38-41. |
| [21] | 杨桂鲜, 潘丽萍, 陈志琴 , 等. 脐带间充质干细胞治疗系统性红斑狼疮的量效关系[J]. 云南医药, 2015,36(6):579-584. |
| [22] |
杨桂鲜, 潘丽萍, 宋薇 , 等. 脐带间充质干细胞治疗难治性系统性红斑狼疮临床分析[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2014,30(5):735-738.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2014.05.019 |
| [23] | 杨桂鲜, 潘丽萍, 周巧艳 , 等. 脐带间充质干细胞移植辅助治疗系统性红斑狼疮的疗效观察[J]. 四川大学学报(医学版), 2014,45(2):338-341. |
| [24] |
Klimczak A, Kozlowska U . Mesenchymal stromal cells and tissue-specific progenitor cells: their role in tissue homeostasis[J]. Stem Cells Int, 2016,4285215. doi: 10.1155/2016/4285215.
doi: 10.1155/2016/4285215 pmid: 4707334 |
| [25] |
Sun LY, Zhang HY, Feng XB , et al. Abnormality of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Lupus, 2007,16(2):121-128.
doi: 10.1177/0961203306075793 |
| [26] |
Nie Y, Lau C, Lie A , et al. Defective phenotype of mesenchymal stem cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Lupus, 2010,19(7):850-859.
doi: 10.1177/0961203310361482 pmid: 20118163 |
| [27] |
Li X, Liu L, Meng D , et al. Enhanced apoptosis and senescence of bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Stem Cells Dev, 2012,21(13):2387-2394.
doi: 10.1089/scd.2011.0447 pmid: 22375903 |
| [28] |
Gu Z, Tan W, Feng G , et al. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling me-diates the senescence of bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cells from systemic lupus erythematosus patients through the p53/p21 pathway[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2014,387(1-2):27-37.
doi: 10.1007/s11010-013-1866-5 pmid: 24130040 |
| [29] |
Wang D, Feng X, Lu L , et al. A CD8 T cell/indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase axis is required for mesenchymal stem cell suppression of human systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2014,66(8):2234-2245.
doi: 10.1002/art.38674 pmid: 24756936 |
| [30] |
Feng X, Che N, Liu Y , et al. Restored immunosuppressive effect of mesenchymal stem cells on B cells after olfactory 1/early B cell factor-associated zinc-finger protein down-regulation in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2014,66(12):3413-3423.
doi: 10.1002/art.v66.12 |
| [31] |
Fathollahi A, Gabalou NB, Aslani S . Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in systemic lupus erythematous, a mesenchymal stem cell disorder[J]. Lupus, 2018,27(7):1053-1064.
doi: 10.1177/0961203318768889 |
| [32] |
Choi EW, Shin IS, Park SY , et al. Reversal of serologic, immunologic, and histologic dysfunction in mice with systemic lupus erythematosus by long-term serial adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2012,64(1):243-253.
doi: 10.1002/art.33313 pmid: 21904997 |
| [33] |
Choi EW, Lee M, Song JW , et al. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation can restore lupus disease-associated miRNA expression and Th1/Th2 ratios in a murine model of SLE[J]. Sci Rep, 2016(6):38237.
doi: 10.1038/srep38237 pmid: 27924862 |
| [34] |
Zhou K, Zhang H, Jin O , et al. Transplantation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell ameliorates the autoimmune pathogenesis in MRL/lpr mice[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2008,5(6):417-424.
doi: 10.1038/cmi.2008.52 |
| [35] |
Tang Y, Xie H, Chen J , et al. Activated NF-kappaB in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from systemic lupus erythematosus patients inhibits osteogenic differentiation through downregulating Smad signaling[J]. Stem Cells Dev, 2013,22(4):668-678.
doi: 10.1089/scd.2012.0226 |
| [36] |
Sun L, Wang D, Liang J , et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in severe and refractory systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2010,62(8):2467-2475.
doi: 10.1002/art.v62:8 |
| [37] |
Zhang Z, Feng R, Niu L , et al. Humanumbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells inhibit T follicular helper cell expansion through the activation of iNOS in lupus-prone B6.MRL-Fas(lpr) mice[J]. Cell Transplant, 2017,26(6):1031-1042.
doi: 10.3727/096368917X694660 pmid: 28105982 |
| [38] |
Deng W, Chen W, Zhang Z , et al. Mesenchymal stem cells promote CD206 expression and phagocytic activity of macrophages through IL-6 in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Clin Immunol, 2015,161(2):209-216.
doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2015.07.011 pmid: 26209923 |
| [39] |
Che N, Li X, Zhou S , et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells suppress B-cell proliferation and differentiation[J]. Cell Immunol, 2012,274(1-2):46-53.
doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2012.02.004 pmid: 22414555 |
| [40] |
Le Blanc K, Ringden O . Immunomodulation by mesenchymal stem cells andclinical experience[J]. J Intern Med, 2007,262(5):509-525.
doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2011.07.035 pmid: 17949362 |
| [41] |
Chamberlain G, Fox J, Ashton B , et al. Concise review: mesenchymal stem cells: their phenotype, differentiation capacity, immunological features, and potential for homing[J]. Stem Cells, 2007,25(11):2739-2749.
doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2007-0197 |
| [42] |
Alunno A, Bistoni O, Montanucci P , et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of autoimmune diseases: beware of cell-to-cell contact[J]. Ann RheumDis, 2018,77(3):e14.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211790 pmid: 28611081 |
| [43] |
Lalu MM, Mcintyre L, Pugliese C , et al. Safety of cell therapy with mesenchymal stromal cells (SafeCell): a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials[J]. PLoS One, 2012,7(10):e47559.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047559 |
| [44] | 汤郁, 雷芳, 宋东明 , 等. 脐带间充质干细胞治疗结缔组织病不良反应分析[J]. 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版), 2014,34(12):1687-1689. |
| [1] | 武志慧, 胡明智, 赵巧英, 吕凤凤, 张晶莹, 张伟, 王永福, 孙晓林, 王慧. miR-125b-5p修饰脐带间充质干细胞对系统性红斑狼疮的免疫调控机制[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 860-867. |
| [2] | 乔佳佳,田聪,黄晓波,刘军. 肾结石合并系统性红斑狼疮行经皮肾镜碎石取石术的安全性和有效性评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 745-749. |
| [3] | 任立敏,赵楚楚,赵义,周惠琼,张莉芸,王友莲,沈凌汛,范文强,李洋,厉小梅,王吉波,程永静,彭嘉婧,赵晓珍,邵苗,李茹. 系统性红斑狼疮低疾病活动度及缓解状况的真实世界研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 273-278. |
| [4] | 罗芷筠,吴佳佳,宋优,梅春丽,杜戎. 伴神经精神系统病变的系统性红斑狼疮相关巨噬细胞活化综合征2例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1111-1117. |
| [5] | 姚海红,杨帆,唐素玫,张霞,何菁,贾园. 系统性红斑狼疮及成人Still病合并巨噬细胞活化综合征的临床特点及诊断指标[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
| [6] | 赵祥格,刘佳庆,黄会娜,陆智敏,白自然,李霞,祁荆荆. 干扰素-α介导系统性红斑狼疮外周血CD56dimCD57+自然杀伤细胞功能的损伤[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 975-981. |
| [7] | 张琳崎,赵静,王红彦,王宗沂,李英妮,汤稷旸,李思莹,曲进锋,赵明威. 抗ENO1抗体与狼疮性视网膜病变的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1099-1105. |
| [8] | 李敏,侯林卿,金月波,何菁. 系统性红斑狼疮合并视网膜病变的临床及免疫学特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1106-1111. |
| [9] | 邵苗,郭惠芳,雷玲彦,赵清,丁艳杰,林进,吴锐,于峰,李玉翠,苗华丽,张莉芸,杜燕,焦瑞英,庞丽霞,龙丽,栗占国,李茹. 短间期小剂量环磷酰胺治疗系统性红斑狼疮耐受性的多中心对照研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1112-1116. |
| [10] | 韩超,周祝兴,陈有荣,董子慧,余家阔. 绵羊外周血间充质干细胞的生物学特性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1151-1157. |
| [11] | 袁昌巍,王盈进,张书杰,沈胜利,段鸿洲. 显微外科手术与血管内栓塞治疗硬脊膜动静脉瘘临床疗效比较的meta分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 304-314. |
| [12] | 帅婷,刘娟,郭艳艳,金婵媛. 敲减长链非编码RNA MIR4697HG抑制骨髓间充质干细胞成脂向分化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 320-326. |
| [13] | 邹健梅,武丽君,罗采南,石亚妹,吴雪. 血清25-羟维生素D与系统性红斑狼疮活动的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 938-941. |
| [14] | 尤鹏越,刘玉华,王新知,王思雯,唐琳. 脱细胞猪心包膜生物相容性及成骨性能的体内外评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 776-784. |
| [15] | 夏芳芳,鲁芙爱,吕慧敏,杨国安,刘媛. 系统性红斑狼疮伴间质性肺炎的临床特点及相关因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 266-272. |
|
||