北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 177-181. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.01.030
颈5-6神经根阻滞技术用于肩关节镜术后镇痛的随机对照研究
- 北京大学第三医院麻醉科,北京 100191
C5-6 nerve root block technique for postoperative analgesia of shoulder arthroscope: a randomized controlled trial
Ying DENG,Yan LI,Yao YAO,Dan-dan FENG,Mao XU( )
)
- Department of Anesthesiology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
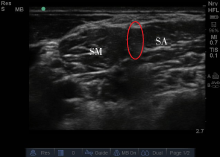
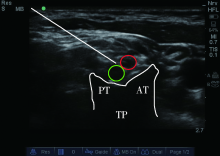
目的:比较超声引导下肌间沟臂丛神经阻滞和颈5-6神经根阻滞用于肩关节镜术后镇痛的效果。方法:选取北京大学第三医院运动医学研究所择期全身麻醉行肩关节镜下韧带断裂修复手术患者40例,美国麻醉医师协会(American society of anesthesiologists, ASA)分级Ⅰ~Ⅱ级。随机分为肌间沟臂丛阻滞组(I组)和颈5-6神经根阻滞组(C组),每组20例。40例患者均在全身麻醉前进行超声引导下单次神经阻滞,I组经肌间沟入路行臂丛神经阻滞,推注0.2%罗哌卡因10 mL;C组经侧颈部入路行颈5-6神经根阻滞,推注0.2%罗哌卡因10 mL。记录穿刺后感觉及运动阻滞起效时间,手术时间,术后持续镇痛时间,术后1、6、12、24 h数字疼痛强度量表(numerical rating scale,NRS)评分及患者手指运动情况。记录药物不良反应及患者满意度,主要终点为神经阻滞后到术后1 d患者术侧肩关节静息及运动疼痛情况,次要终点为患肢手指运动情况及患者满意度。结果:I组镇痛持续时间(571.50±70.11) min,C组(615.60±112.15) min,两组差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。C组术后1、6、12 h静态及动态NRS评分均低于I组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),24 h两组间静态及动态NRS评分差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。神经阻滞后患肢手部肌力,C组为5(4,5)级,I组为4(2,4)级,两组间差异有统计学意义(P<0.01);手部支配区感觉评分,桡神经C组为1(0,2),I组为 2(1,2),正中神经C组为0(0,2),I组为2(1,2),尺神经C组为0(0,1),I组为1(1,2),两组间差异均有统计学意义(P<0.01);术侧肩部感觉评分,C组为2(1,2),I组为2(1,2),两组间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);患者满意度评分, I组为8(6,9),C组为9(8,10),差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。结论:肌间沟臂丛神经阻滞和颈5-6神经根阻滞都可以满足肩关节镜术后镇痛需求,但颈5-6神经根阻滞后患肢前臂及手部活动不受限,麻木感更为局限,患者满意度更高。
中图分类号:
- R614.4
| [1] |
Hussain N, Goldar G, Raqina N . Suprascapular and interscalene nerve block for shoulder surgery: a systematic review and meta analysis[J]. Anesthesiology, 2017,127(6):998-1013.
doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000001894 |
| [2] |
Marhofer P, Harrop-Griffiths W, Willschke H , et al. Fifteen years of ultrasound guidance in regional anaesthesia: part 2. recent developments in block techniques[J]. Br J Anaesth, 2010,104(6):673-683.
doi: 10.1093/bja/aeq086 pmid: 20418267 |
| [3] |
Madison SJ, Humsi J, Loland VJ , et al. Ultrasound-guided root/trunk (interscalene) block for hand and forearm anesthesia[J]. Reg Anesth Pain Med, 2013,38(3):226-232.
doi: 10.1097/AAP.0b013e3182890d50 pmid: 23528646 |
| [4] |
Dhir S, Sondekoppam RV, Sharma R . A comparison of combined suprascapular and axillary nerve blocks to interscalene nerve block for analgesia in arthroscopic shoulder surgery: an equivalence stu-dy[J]. Reg Anesth Pain Med, 2016,41(5):564-571.
doi: 10.1097/AAP.0000000000000436 pmid: 27380105 |
| [5] |
Riazi S, Carmichael N, Awad L , et al. Effect of local anaesthetic volume (20 vs. 5 mL) on the efficacy and respiratory consequences of ultrasound-guided interscalene brachial plexus block[J]. Br J Anaesth, 2008,101(4):549-556.
doi: 10.1093/bja/aen229 pmid: 18682410 |
| [6] |
Lang RS, Kentor ML, Vallejo M , et al. The impact of local anesthetic distribution on block onset in ultrasound-guided interscalene block[J]. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand, 2012,56(9):1146-1151.
doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.2012.02745.x pmid: 22845687 |
| [7] |
Sinha SK, Abrams JH, Barnett JT , et al. Decreasing the local anesthetic volume from 20 to 10 mL for ultrasound-guided interscalene block at the cricoid level does not reduce the incidence of hemidiaphragmatic paresis[J]. Reg Anesth Pain Med, 2011,36(1):17-20.
doi: 10.1097/AAP.0b013e3182030648 pmid: 21751435 |
| [8] |
Vandepitte C, Gautier P, Xu D , et al. Effective volume of ropi-vicaine 0.75% through a catheter required for interscalene brachial plexus blockade[J]. Anesthesiology, 2013,118(4):863-867.
doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3182850dc7 |
| [9] | Winnie AP . Interscalene brachial plexus block[J]. Anesth Analg, 1970,49:455-466. |
| [10] |
Mendelsohn AH, Deconde A, Lambert HW , et al. Cervical variations of the phrenic nerve[J]. Laryngoscope, 2011,121(9):1920-1923.
doi: 10.1002/lary.21894 pmid: 22024845 |
| [11] |
Lee J, Kim K, Kim S . Threatment of a symptomatic cervical perineural cyst with ultrasound-guided cervical selective nerve root block: a case report[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2018,97(37):e12412.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012412 |
| [12] |
van Geffen GJ, Moayeri N, Bruhn J , et al. Correlation between ultrasound imaging, cross-sectional anatomy, and histology of the brachial plexus: a review[J]. Reg Anesth Pain Med, 2009,34(5):490-497.
doi: 10.1097/AAP.0b013e3181add8a3 pmid: 19920425 |
| [13] |
Kapral S, Greher M, Huber G , et al. Ultrasonographic guidance improves the success rate of interscalene brachial plexus blockade[J]. Reg Anesth Pain Med, 2008,33(3):253-258.
doi: 10.1016/j.rapm.2007.10.011 pmid: 18433677 |
| [14] |
Shin HJ, Na HS, Oh AY ,et a1. A prospective,randomized and controlled study of interscalene brachiaI plexus block for arthroscopic shoulder surgery: a comparison of C5 and con-ventional approach, a CONSORT-compliant article[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2016,95(37):e4921.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004921 |
| [15] |
Marhofer P, Greher M, Kapral S . Ultrasound guidance in regional anaesthesia[J]. Br J Anaesth, 2005,94(1):7-17.
doi: 10.1093/bja/aer111 pmid: 15277302 |
| [16] | 周玉弟, 姜慧丽, 汤洋 , 等. 超声引导下选择性颈神经根阻滞在肩关节镜术后镇痛中的应用[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志, 2017,12(33):1167-1170. |
| [17] |
Junq HS, Seo KH, Kanq JH . Optimal dose of perineural dexmedetomidine for inerscalene brachial plexus block to control post-operative pain in patients undergoing arthroscopic shoulder sur-gery: a prospective, double-blind,randomized controlled study[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2018,97(16):e0440.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010440 |
| [18] |
Marhofer D, Marhofer P, Triffterer L , et al. Dislocation rates of perineural catheters: a volunteer study[J]. Br J Anaesth, 2013,111(5):800-806.
doi: 10.1093/bja/aet198 pmid: 23748198 |
| [19] |
张大志, 刘永盛, 周海滨 . 舒芬太尼与地塞米松对罗哌卡因神经阻滞作用影响的比较研究[J]. 中国药物警戒, 2012,9(12):710-712.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8629.2012.12.003 |
| [1] | 王江静,魏顺依,敖英芳,杨渝平. 前交叉韧带重建术后三种不同药物镇痛早期疗效的对比[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 293-298. |
| [2] | 王菲,赵阳阳,关明,王晶,许向亮,刘宇,翟新利. 静脉给药镇静技术在2 582例口腔外科门诊手术中的临床应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 181-186. |
| [3] | 李岩,王辉,邓莹,姚瑶,李民. 静脉输注右美托咪定对臂丛阻滞效果的随机对照研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(5): 845-849. |
| [4] | 孟甜,张智勇,张晓,陈宇寰,李京琦,陈全,刘文曙,高巍. 口服洛索洛芬钠片在拔除阻生齿中的超前镇痛[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(1): 165-169. |
| [5] | 赵旻暐, 王宁, 曾琳, 李民, 赵中凯, 张菡, 田华. 膝关节置换术后连续收肌管阻滞与股神经阻滞的疗效比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(1): 142-147. |
| [6] | 伊军,许莉,林惠华. 不同背景量连续胫神经阻滞用于跟骨手术术后镇痛的临床效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(2): 283-286. |
| [7] | 池里群, 卢新, 王雷, 刘叔平, 丁楠, 张洪影, 鄂文. 细胞色素P450 3A4基因多态性分子检测指导分娩镇痛舒芬太尼用药[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(4): 653-656. |
| [8] | 刘慧丽,马彩虹,张小青,杨艳,宋雪凌,郭向阳. 宫-腹腔镜检查患者联合应用帕瑞昔布钠和罗哌卡因对术后疼痛的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(6): 901-905. |
| [9] | 赵红*, 叶铁虎, 龚志毅. 氯诺昔康用于全子宫切除术后患者自控镇痛的非劣效性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(1): 119-122. |
| [10] | 梁汉生, 冯艺, 刘怡昭, 安海燕, 杨拔贤. 氟比洛芬酯联合戳口局部浸润对腹腔镜胆囊切除术后镇痛的临床观察[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2011, 43(5): 753-756. |
| [11] | 董长江, 谭宏宇, 朱文智, 姚月勤, 范志毅. 氟比洛芬酯联合舒芬太尼用于腹部肿瘤术后镇痛的效果及其安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2011, 43(2): 307-310. |
| [12] | 万有, , 韩济生, John E. Pintar. 孤啡肽基因敲除小鼠电针镇痛作用增强[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2009, 41(3): 376-379. |
| [13] | 董稳, 刘瑞昌, 刘克英, 关明, 杨旭东. 氯诺昔康和舒芬太尼用于颌面外科术后自控静脉镇痛的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2009, 41(1): 109-111. |
| [14] | 葛立宏. 儿童口腔科治疗中的焦虑和疼痛控制[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2009, 41(1): 6-9. |
| [15] | 潘丽峰, 王东信, 李军. 不同麻醉和镇痛方法对老年患者非心脏手术后早期认知功能的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2006, 38(5): 510-514. |
|
||