北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 414-421. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.03.007
体位性心动过速综合征儿童及青少年在直立试验中血流动力学变化
陶春燕1,李红霞1,李雪迎2,唐朝枢3,金红芳1,杜军保1△( )
)
- 1. 北京大学第一医院儿科, 北京 100034
2. 北京大学第一医院医学统计室, 北京 100034
3. 北京大学基础医学院生理与病理生理学系, 北京 100191
4. 教育部分子心血管学重点实验室, 北京 100191
Hemodynamic changes in standing-up test of children and adolescents with postural tachycardia syndrome
Chun-yan TAO1,Hong-xia LI1,Xue-ying LI2,Chao-shu TANG3,Hong-fang JIN1,Jun-bao DU1△( )
)
- 1. Department of Pediatrics, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
2. Department of Statistics, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
3. Department of Physiology and Pathophysiology, Peking University School of Basic Medical Sciences, Beijing 100191, China
4. Key Laboratory of Molecular Cardiovascular Science, the Ministry of Education, Beijing 100191, China
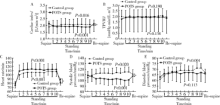
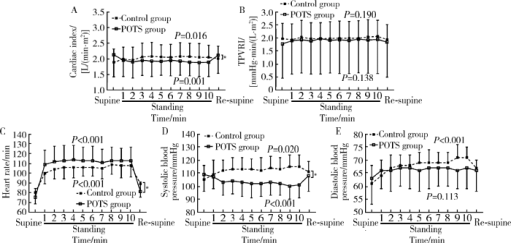
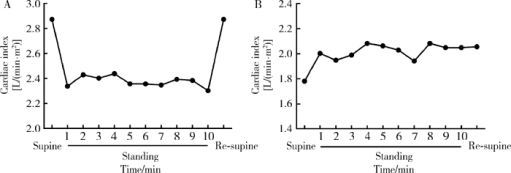
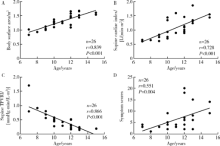
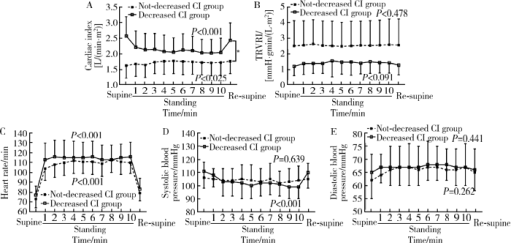
摘要: 目的 分析体位性心动过速综合征(postural tachycardia syndrome, POTS)儿童及青少年直立试验过程中血流动力学变化及不同心脏指数(cardiac index, CI)患者血流动力学指标的差异。方法 回顾性分析26例POTS患者与12例健康对照者间直立试验过程中总外周血管阻力指数(total peripheral vascular resistance index, TPVRI)、心率和血压的变化,并比较两组间各指标变化趋势。根据每位POTS患者直立试验过程中CI变化趋势将患者分为CI降低组(14例)与CI未降低组(12例), 分析两组患者在直立试验过程中CI、TPVRI、心率、血压变化,并比较两组间各指标变化趋势。结果 POTS患者在直立试验过程中CI显著下降(F=6.936, P=0.001), 心率明显增快(F=113.926, P <0.001),收缩压明显降低(F=6.049, P <0.001),而TPVRI (F=2.031, P=0.138)和舒张压(F=2.018, P=0.113)无明显变化。健康对照组CI在直立后显著升高(F=3.646, P=0.016),同时心率明显增快(F=43.970, P<0.001),收缩压(F=4.043, P=0.020)和舒张压(F=8.627, P<0.001)均明显升高,TPVRI (F=1.688, P=0.190)无明显变化。POTS患者与健康对照组比较,CI (F=6.221, P=0.001)、心率(F=6.203, P<0.001)和收缩压(F=7.946, P<0.001)随时间变化趋势显著不同,而TPVRI和舒张压在两组间的变化趋势差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。CI降低组与CI未降低组POTS患者在直立试验中CI变化趋势差异有统计学意义(F=14.723, P<0.001), 前者直立后收缩压明显降低(F=8.010, P<0.001),而后者却无明显变化(F=0.612, P=0.639), TPVRI、心率和舒张压在CI降低组与CI未降低组间随时间变化趋势差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。年龄是POTS患者直立后CI呈下降趋势的独立影响因素(P=0.013, OR=2.233; 95% CI:1.183~4.216)。结论 POTS患者在直立试验过程中存在明显的血流动力学变化,不同患者心输出量变化可能不同,年龄是心输出量下降的独立影响因素。
中图分类号:
- R725.4
| [1] |
Goodman BP . Evaluation of postural tachycardia syndrome (POTS)[J]. Auton Neurosci, 2018,215:12-19.
doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2018.04.004 |
| [2] |
Johnson JN, Mack KJ, Kuntz NL , et al. Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome: a clinical review[J]. Pediatr Neurol, 2010,42(2):77-85.
doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2009.07.002 |
| [3] | Stewart JM, Pianosi P, Shaban MA , et al. Postural hyperventilation as a cause of postural tachycardia syndrome: increased systemic vascular resistance and decreased cardiac output when upright in all postural tachycardia syndrome variants[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2018,7(13):e008854. |
| [4] |
Li H, Han Z, Chen S, et al. Total peripheral vascular resistance, cardiac output ,plasma C-type natriuretic peptide level in children with postural tachycardia syndrome[J]. J Pediatr, 2015, 166(6): 1385- 1389. e1-2.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2015.03.032 |
| [5] |
Zheng X, Chen Y, Du J . Recent advances in the understanding of the mechanisms underlying postural tachycardia syndrome in children: practical implications for treatment[J]. Cardiol Young, 2017,27(3):413-417.
doi: 10.1017/S1047951116002559 |
| [6] |
Medow MS, Stewart JM . The postural tachycardia syndrome[J]. Cardiol Rev, 2007,15(2):67-75.
doi: 10.1097/01.crd.0000233768.68421.40 |
| [7] | 中华医学会儿科学分会心血管学组, 《中华儿科杂志》编辑委员会, 北京医学会儿科学分会心血管学组, 等. 2016儿童晕厥诊断指南(2016年修订版)[J]. 中华儿科杂志, 2016,54(4):246-250. |
| [8] | 中华医学会儿科学分会心血管学组, 《中华儿科杂志》编辑委员会. 儿童晕厥诊断指南[J]. 中华儿科杂志, 2009,47(2):99-101. |
| [9] |
Garland EM, Celedonio JE, Raj SR . Postural tachycardia syndrome: beyond orthostatic intolerance[J]. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep, 2015,15(9):60.
doi: 10.1007/s11910-015-0583-8 |
| [10] |
Stewart JM, Medow MS, Glover JL , et al. Persistent splanchnic hyperemia during upright tilt in postural tachycardia syndrome[J]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2006,290(2):H665-H673.
doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00784.2005 |
| [11] |
Fu Q, Vangundy TB, Galbreath MM , et al. Cardiac origins of the postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2010,55(25):2858-2868.
doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.02.043 |
| [12] | Jacob G, Biaggioni I, Mosqueda-Garcia R , et al. Relation of blood volume and blood pressure in orthostatic intolerance[J]. Am J Med Sci, 1998,315(2):95-100. |
| [13] |
Farquhar WB, Taylor JA, Darling SE , et al. Abnormal baroreflex responses in patients with idiopathic orthostatic intolerance[J]. Circulation, 2000,102(25):3086-3091.
doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.102.25.3086 |
| [14] |
Zhang Q, Liao Y, Tang C , et al. Twenty-four-hour urinary sodium excretion and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome[J]. J Pediatr, 2012,161(2):281-284.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2012.01.054 |
| [15] | 蔺婧, 刘平, 王瑜丽 , 等. 儿童体位性心动过速综合征治疗随访的单中心研究[J]. 中华实用儿科临床杂志, 2015,30(13):983-987. |
| [16] | 蔺婧, 刘平, 王瑜丽 , 等. 直立试验心率变化预测口服补液盐治疗体位性心动过速综合征的效果[J]. 中华儿科杂志, 2015,53(1):25-29. |
| [17] |
Li H, Wang Y, Liu P , et al. Body mass index (BMI) is associated with the therapeutic response to oral rehydration solution in children with postural tachycardia syndrome[J]. Pediatr Cardiol, 2016,37(7):1313-1318.
doi: 10.1007/s00246-016-1436-1 |
| [18] |
Lu W, Yan H, Wu S , et al. Hemocytometric measures predict the efficacy of oral rehydration for children with postural tachycardia syndrome[J]. J Pediatr, 2017,187:220-224.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2017.04.034 |
| [19] |
Raj SR, Robertson D . Blood volume perturbations in the postural tachycardia syndrome[J]. Am J Med Sci, 2007,334(1):57-60.
doi: 10.1097/MAJ.0b013e318063c6c0 |
| [20] | Karataş Z, Alp H, Sap F , et al. Usability of QTc dispersion for the prediction of orthostatic intolerance syndromes[J]. Eur J Paediatr Neurol, 2012,16(5):467-474. |
| [21] |
Wang Y, Zhang C, Chen S , et al. Frequency domain indices of heart rate variability are useful for differentiating vasovagal syncope and postural tachycardia syndrome in children[J]. J Pediatr, 2019,207:59-63.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2018.11.054 |
| [22] |
Lin J, Jin H, Du J . Assessment of therapeutic biomarkers in the treatment of children with postural tachycardia syndrome and vasovagal syncope[J]. Cardiol Young, 2014,24(5):792-796.
doi: 10.1017/S1047951114000316 |
| [23] |
Altun B, Arici M . Salt and blood pressure: time to challenge[J]. Cardiology, 2006,105(1):9-16.
doi: 10.1159/000088265 |
| [24] |
Hart EC, Joyner MJ, Wallin BG , et al. Sex, ageing and resting blood pressure: gaining insights from the integrated balance of neural and haemodynamic factors[J]. J Physiol, 2012,590(9):2069-2079.
doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.224642 |
| [25] | Bevan JA . Control of peripheral vascular resistance: evidence based on the in vitro study of resistance arteries[J]. Clin Invest Med, 1987,10(6):568-572. |
| [1] | 王敏, 李倩. 青少年抑郁症患者心理弹性影响因素的路径分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 809-814. |
| [2] | 赵双云, 邹思雨, 李雪莹, 沈丽娟, 周虹. 中文版口腔健康素养量表简版(HeLD-14)在学龄前儿童家长中应用的信度和效度评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 828-832. |
| [3] | 陈心心, 唐哲, 乔艳春, 荣文笙. 北京市密云区4岁儿童患龋状况及其与龋活跃性检测的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [4] | 岳芷涵,韩娜,鲍筝,吕瑾莨,周天一,计岳龙,王辉,刘珏,王海俊. 儿童早期体重指数轨迹与超重风险关联的前瞻性队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 390-396. |
| [5] | 费秀文,刘斯,汪波,董爱梅. 成人及儿童组织坏死性淋巴结炎临床特征及治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 533-540. |
| [6] | 沈鹤军,侍崇艳,郑清,黄玉,景涛. 我国高中生静坐时长与健康素养现状及其影响因素调查[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 239-246. |
| [7] | 俞光岩. 儿童唾液腺疾病[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 1-3. |
| [8] | 闫晓晋,刘云飞,马宁,党佳佳,张京舒,钟盼亮,胡佩瑾,宋逸,马军. 《中国儿童发展纲要(2011-2020年)》实施期间中小学生营养不良率变化及其政策效应分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 593-599. |
| [9] | 弭小艺,侯杉杉,付子苑,周末,李昕璇,孟召学,蒋华芳,周虹. 中文版童年不良经历问卷在学龄前儿童父母中应用的信效度评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 408-414. |
| [10] | 崔孟杰,马奇,陈曼曼,马涛,王鑫鑫,刘婕妤,张奕,陈力,蒋家诺,袁雯,郭桐君,董彦会,马军,星一. 不同生长模式与7~17岁儿童青少年代谢综合征的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 415-420. |
| [11] | 党佳佳,蔡珊,钟盼亮,王雅琪,刘云飞,师嫡,陈子玥,张依航,胡佩瑾,李晶,马军,宋逸. 室外夜间人工光暴露与中国9~18岁儿童青少年超重肥胖的关联[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 421-428. |
| [12] | 陈敬,肖伍才,单蕊,宋洁云,刘峥. DRD2基因rs2587552多态性对儿童肥胖干预效果的影响:一项前瞻性、平行对照试验[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 436-441. |
| [13] | 郑丹枫,李君禹,李佳曦,张英爽,钟延丰,于淼. 青少年特发性脊柱侧凸椎旁肌的病理特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 283-291. |
| [14] | 李辉,高阳旭,王书磊,姚红新. 恶性肿瘤患儿完全植入式静脉输液港手术并发症[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1167-1171. |
| [15] | 刘京,陆爱东,左英熹,吴珺,黄志卓,贾月萍,丁明明,张乐萍,秦炯. 儿童急性淋巴细胞白血病合并癫痫发作75例临床特征和预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 948-953. |
|
||