北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 1048-1051. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.06.012
男性膀胱过度活动症的尿动力学分型及临床疗效随访
王涛,许克新,张维宇,胡浩,张晓威,王焕瑞,刘献辉,陈京文,张晓鹏( )
)
- 北京大学人民医院泌尿外科,北京 100044
Urodynamic classification of male patients with symptoms of overactive bladder and the outcome classification
Tao WANG,Ke-xin XU,Wei-yu ZHANG,Hao HU,Xiao-wei ZHANG,Huan-rui WANG,Xian-hui LIU,Jing-wen CHEN,Xiao-peng ZHANG( )
)
- Department of Urology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
摘要:
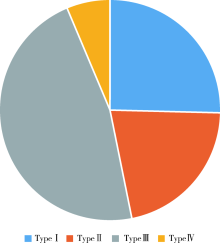
目的 介绍男性膀胱过度活动症(overactive bladder,OAB)的尿动学分型并探究其临床疗效的差异。方法 收集2015年1月至2017年1月北京大学人民医院泌尿外科诊断为OAB并且接受尿动力学检查的男性患者共126例,根据患者的主诉(是否可感知尿急)及尿动力学检查结果(是否有逼尿肌过度活动和终止不自主收缩的能力)将膀胱过度活动症分为四型,分析患者的基本信息、伴随疾病情况、治疗前后的OAB症状评分表(OAB symptom score,OABSS)以及国际前列腺症状评分(international prostate symptom score,IPSS)是否存在差异。结果 根据分型方法,Ⅰ型32例(25.40%),Ⅱ型27例(21.43%),Ⅲ型59例(46.83%),Ⅳ型8例(6.35%),四型患者的身高差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),Ⅳ型患者的年龄、体质量、伴随疾病数目显著大于其余三型,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ型患者的年龄、体质量、伴随疾病数目的差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),Ⅳ型患者治疗前后OABSS和IPSS量表差值显著小于其余三型,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),Ⅲ型患者治疗前后OABSS和IPSS量表差值显著大于其余三型,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型患者治疗前后OABSS和IPSS量表差值的差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论 在四型男性OAB患者中,Ⅲ型治疗效果最好,Ⅳ型治疗效果最差,此分型方法对男性OAB的个体化诊疗以及指导预后具有重要意义。
中图分类号:
- R694
| [1] | Abrams P, Cardoz L, Fall M , et al. The standardisation of terminology in lower urinary tract function: report from the standardisation sub-committee of the International Continence Society[J]. Neurourol Urodyn, 2002,21(2):167-178. |
| [2] | Kurosch M, Mager R, Gust K , et al. Diagnosis of overactive bladder (OAB)[J]. Urologe A, 2015,54(3):421-427. |
| [3] | Chen SL, Ng SC, Huang YH, Chen GD . Are patients with bladder oversensitivity different from those with urodynamically proven detrusor overactivity in female overactive bladder syndrome?[J]. J Chin Med Assoc, 2017,80(10):644-650. |
| [4] | D’Ancona CA, Bassani JW, Querne FA , et al. New method for minimally invasive urodynamic assessment in men with lower urinary tract symptoms[J]. Urology, 2008,71(1):75-78. |
| [5] | Flisser AJ, Walmsley K, Blaivas JG . Urodynamic classification of patients with symptoms of overactive bladder[J]. J Urol, 2003,169(2):529-533. |
| [6] | Fall M, Geirsson G, Lindstrom S . Toward a new classification of overactive bladders[J]. Neurourol Urodyn, 1995,14(6):635-646. |
| [7] | Yamaguchi O, Nishizawa O, Takeda M , et al. Clinical guidelines for overactive bladder[J]. Int J Urol, 2009,16(2):126-142. |
| [8] | Höfner K . Terminology and pathophysiology of overactive bladder (OAB)[J]. Aktuelle Urol, 2016,47(6):468-474. |
| [9] | Daly D, Chapple C . Relationship between overactive bladder (OAB) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): concurrent disorders with a common pathophysiology?[J]. BJU Int, 2013,111(4):530-531. |
| [10] | Vahabi B, Drake MJ . Physiological and pathophysiological implications of micromotion activity in urinary bladder function[J]. Acta Physiol (Oxf), 2015,213(2):360-370. |
| [11] | Bothig R, Domurath B, Kaufmann A , et al. Neuro-urological diagnosis and therapy of lower urinary tract dysfunction in patients with spinal cord injury: S2k Guideline of the German-Speaking Medical Society of Paraplegia (DMGP)[J]. Urologe A, 2017,56(6):785-792. |
| [12] | Mehnert U, Nehiba M . Neuro-urological dysfunction of the lower urinary tract in CNS diseases: pathophysiology, epidemiology, and treatment options[J]. Urologe A, 2012,51(2):189-197. |
| [13] | Gill BC, Pizarro-Berdichevsky J, Bhattacharyya PK , et al. Real-time changes in brain activity during sacral neuromodulation for overactive bladder[J]. J Urol, 2017,198(6):1379-1385. |
| [14] | Sakakibara R, Panicker J, Fowler CJ , et al. Is overactive bladder a brain disease? The pathophysiological role of cerebral white matter in the elderly[J]. Int J Urol, 2014,21(1):33-38. |
| [15] | Elser DM . Stress urinary incontinence and overactive bladder syndrome: current options and new targets for management[J]. Postgrad Med, 2012,124(3):42-49. |
| [1] | 柯涵炜, 王起, 许克新. 优化环磷酰胺剂量在间质性膀胱炎/膀胱疼痛综合征啮齿动物模型中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 908-912. |
| [2] | 颜野,李小龙,夏海缀,朱学华,张羽婷,张帆,刘可,刘承,马潞林. 前列腺癌根治术后远期膀胱过度活动症的危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 589-593. |
| [3] | 吴一凡,玉应香,谢岚,张志达,常翠青. 不同体重指数青年男性的静息能量消耗特点及预测方程评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 247-252. |
| [4] | 林浩,李菁华,杨潇,陈晓婷,史宇晖,常春,郝元涛,曹望楠. 中国成都男男性行为人群HIV暴露前预防用药行为-认知偏差现状及其影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 511-520. |
| [5] | 朱琳,张维宇,许克新. 环磷酰胺诱导SD大鼠膀胱疼痛综合征模型的有效性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 735-740. |
| [6] | 王起,张维宇,刘献辉,王明瑞,赖金惠,胡浩,徐涛,许克新. 骶神经调节术治疗膀胱逼尿肌无力的疗效分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 671-674. |
| [7] | 杜强,洪锴,潘伯臣. 两种检测男性生殖道沙眼衣原体和解脲支原体方法的对比[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 785-788. |
| [8] | 李远骋, 崔闻心, 郭雪儿, 朱璠, 刘思辰, 贾碧波, 汪培, 马迎华. 青年学生男男性行为人群中人类免疫缺陷病毒阳性与阴性者获得性免疫缺陷综合征(艾滋病)相关知识与行为比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 511-517. |
| [9] | 张维宇,夏秋翔,胡浩,陈京文,孙屹然,许克新,张晓鹏. 门诊女性下尿路症状患者尿动力学检查结果分析及逼尿肌无力患者的随访[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(5): 856-862. |
| [10] | 代晓微,徐影,郑连文,李凌云,李丹丹,谭鑫,高飞,王艳,吴桂杰. 1 324例少精子症和无精子症患者的染色体核型分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(5): 774-777. |
| [11] | 吴桂杰,马帅,郑连文,徐影,孟繁鹤,代晓微. 1例复杂染色体易位伴男性不育患者的家系核型分析及文献复习[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(4): 729-731. |
| [12] | 张维宇,张晓鹏,陈京文,孙屹然,王佳,胡浩,许克新. 年龄因素对女性尿失禁患者尿动力学参数的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(5): 825-829. |
| [13] | 张维宇,胡浩,王起,陈京文,许克新. 女性压力性尿失禁患者术前尿动力学检查的意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(4): 655-658. |
| [14] | 赵连明,姜辉,洪锴,林浩成,唐文豪,刘德风,毛加明,廉颖,马潞林. Y染色体AZFc区缺失患者的治疗结局分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(4): 607-611. |
| [15] | 叶海云,许清泉,黄晓波,马凯,王晓峰. 卡介苗膀胱灌注治疗致结核性前列腺脓肿1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(6): 1039-1041. |
|
||