北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 144-151. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.01.023
三种数字化分析算法测量咬合接触分布及面积的对比研究
- 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,口腔医学数字化研究中心,口腔修复教研室 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
Preliminary study on three digital analysis methods for analyzing the distribution and area of occlusal contacts
Ning XIAO,Yu-chun SUN,Yi-jiao ZHAO( ),Yong WANG(
),Yong WANG( )
)
- Center of Digital Dentistry, Department of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
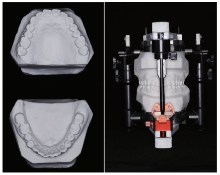
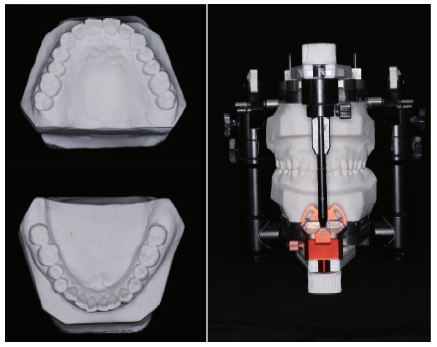
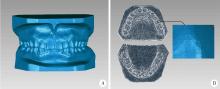
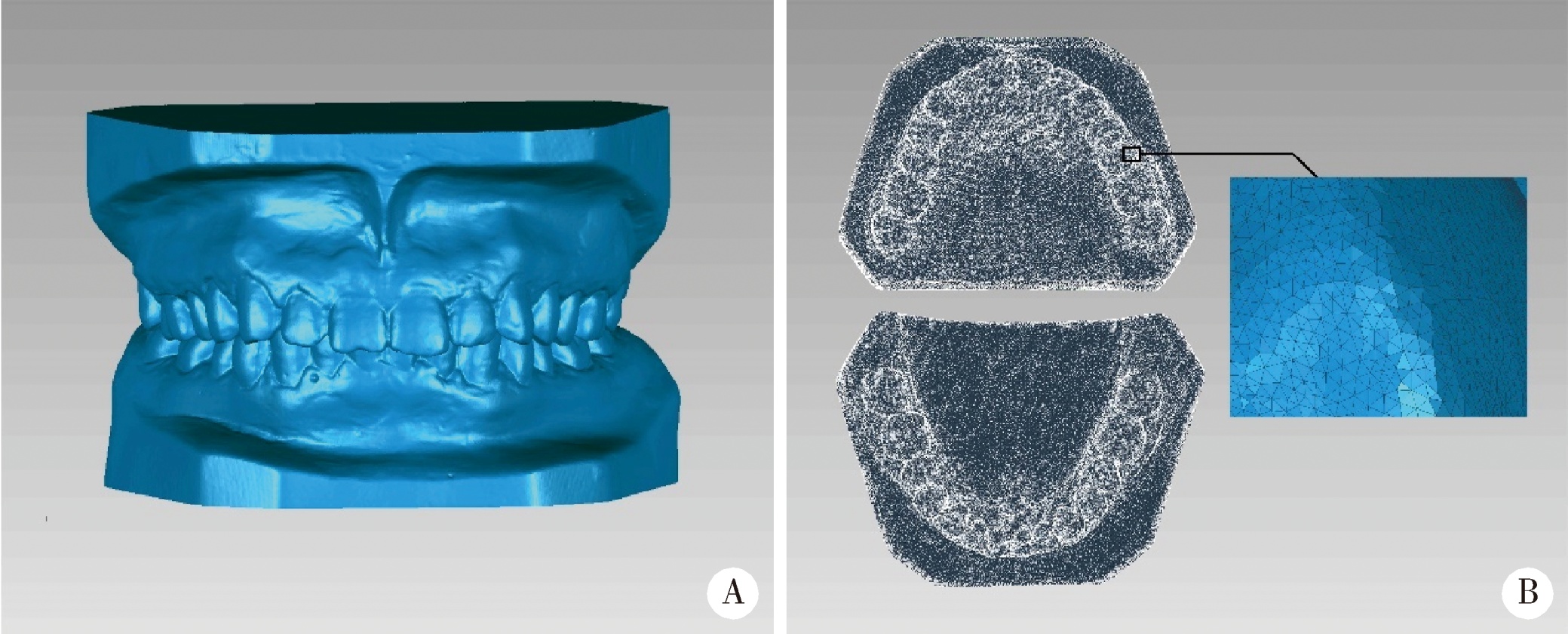
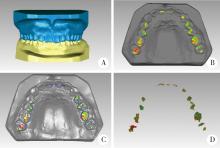
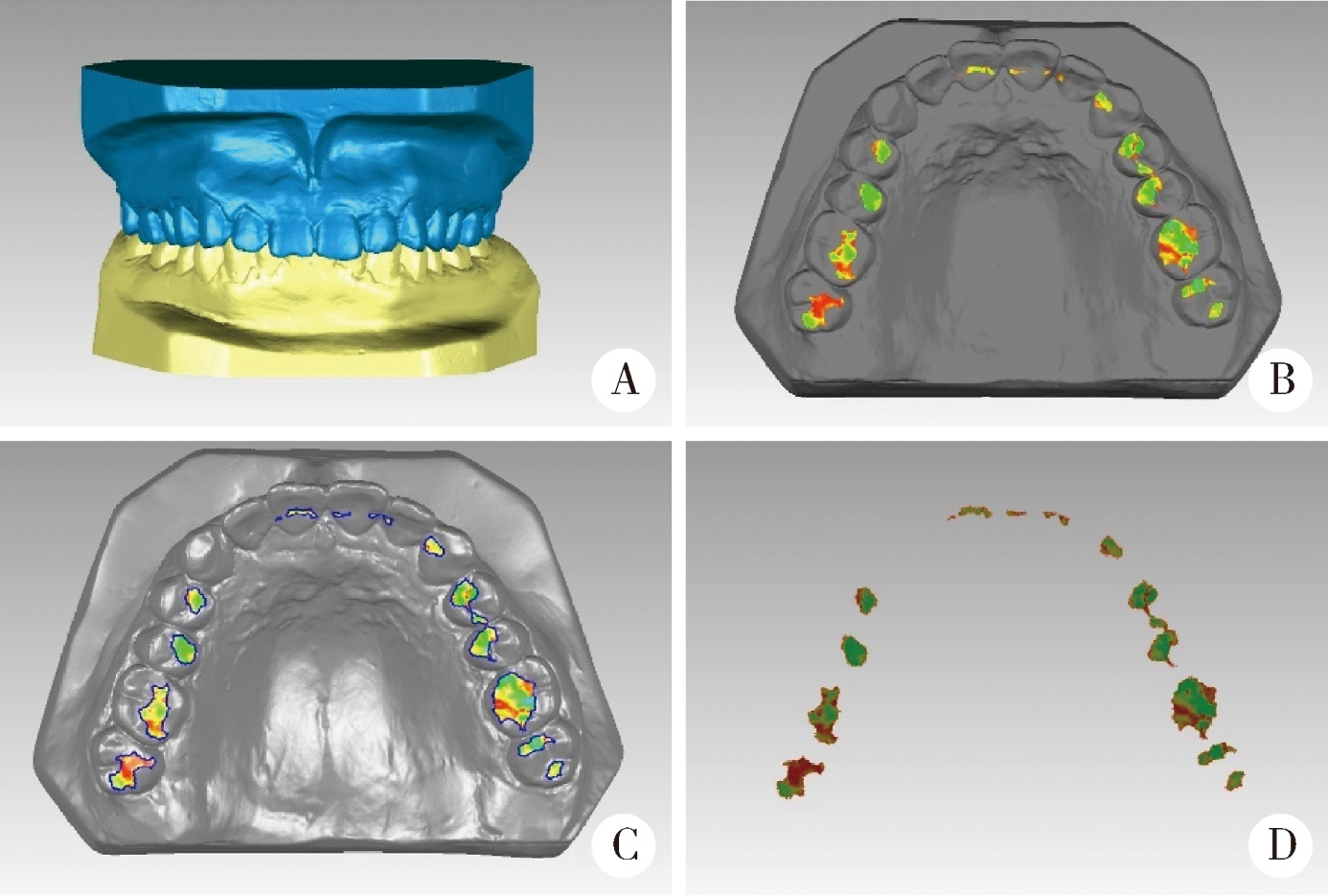
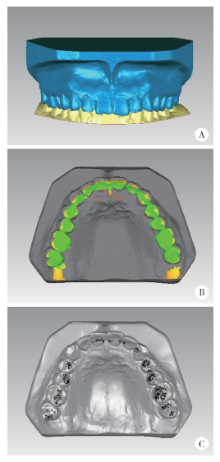
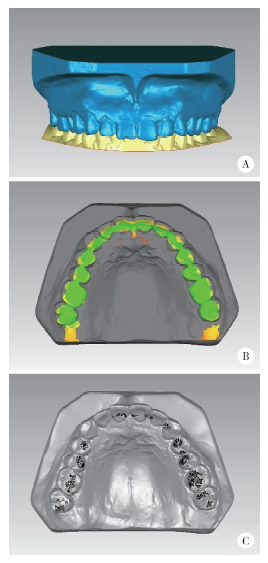
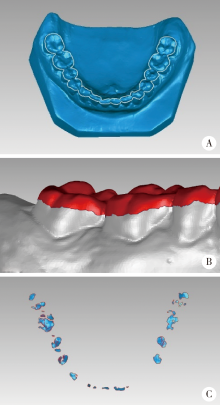
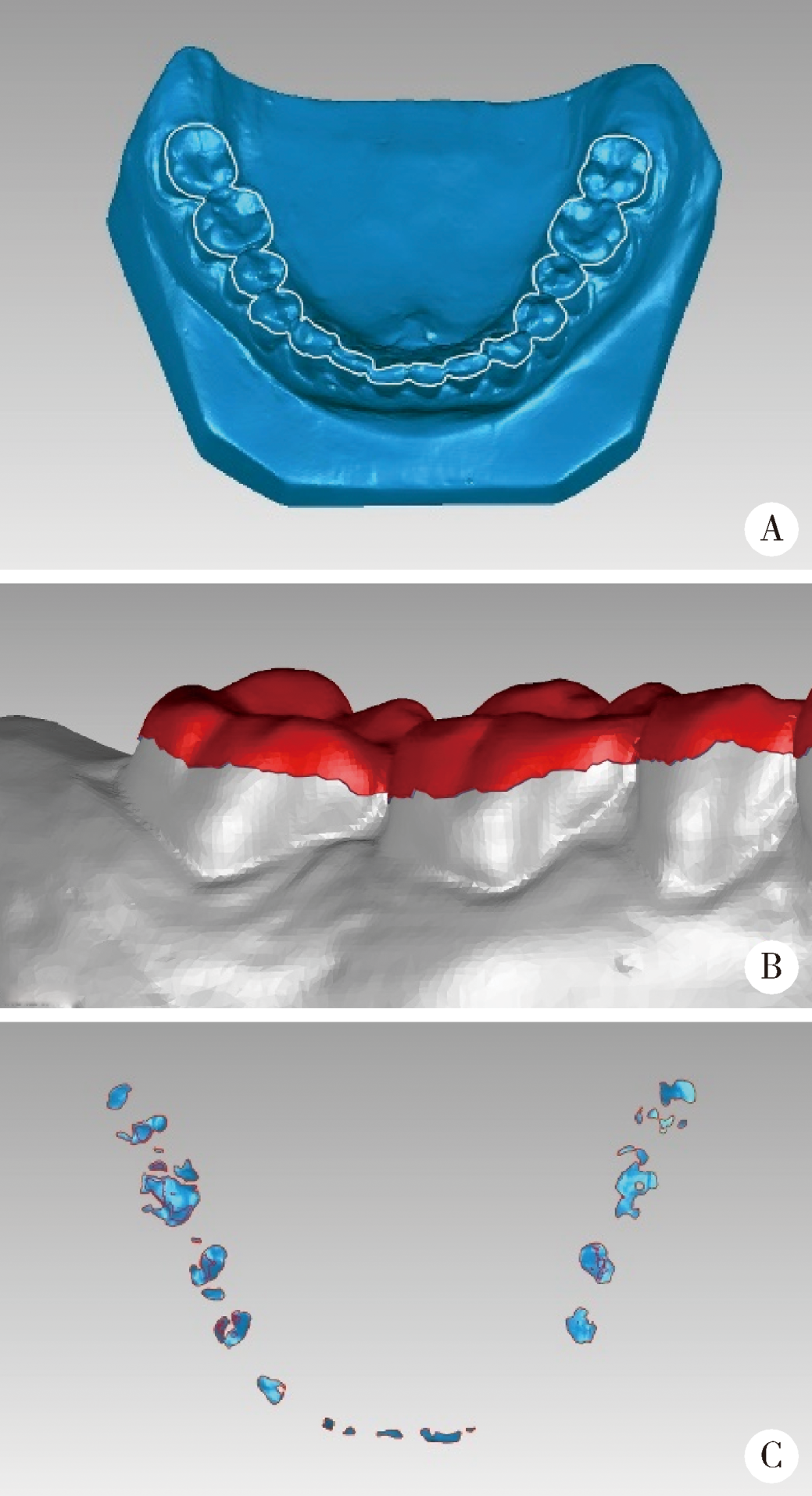
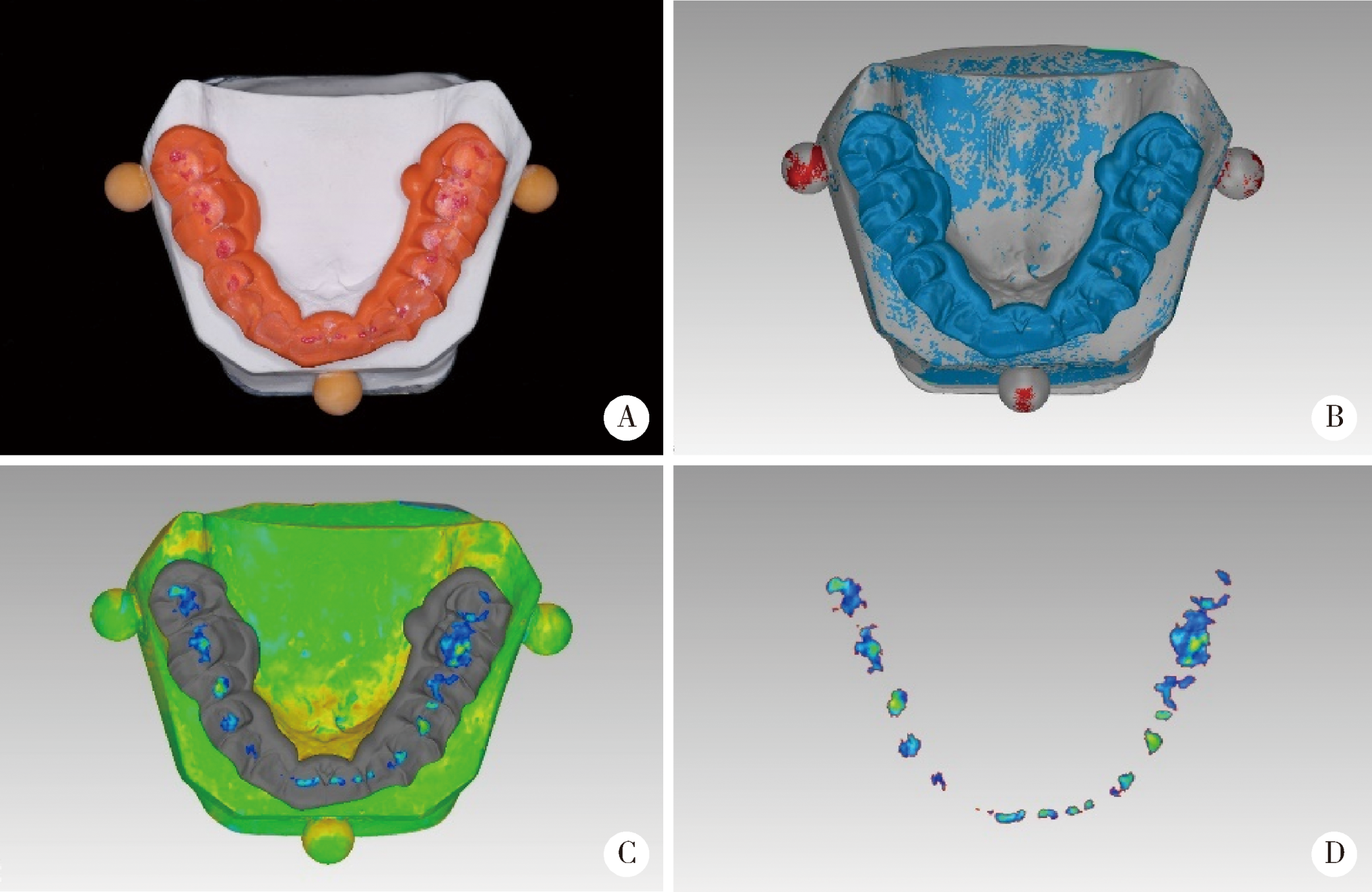
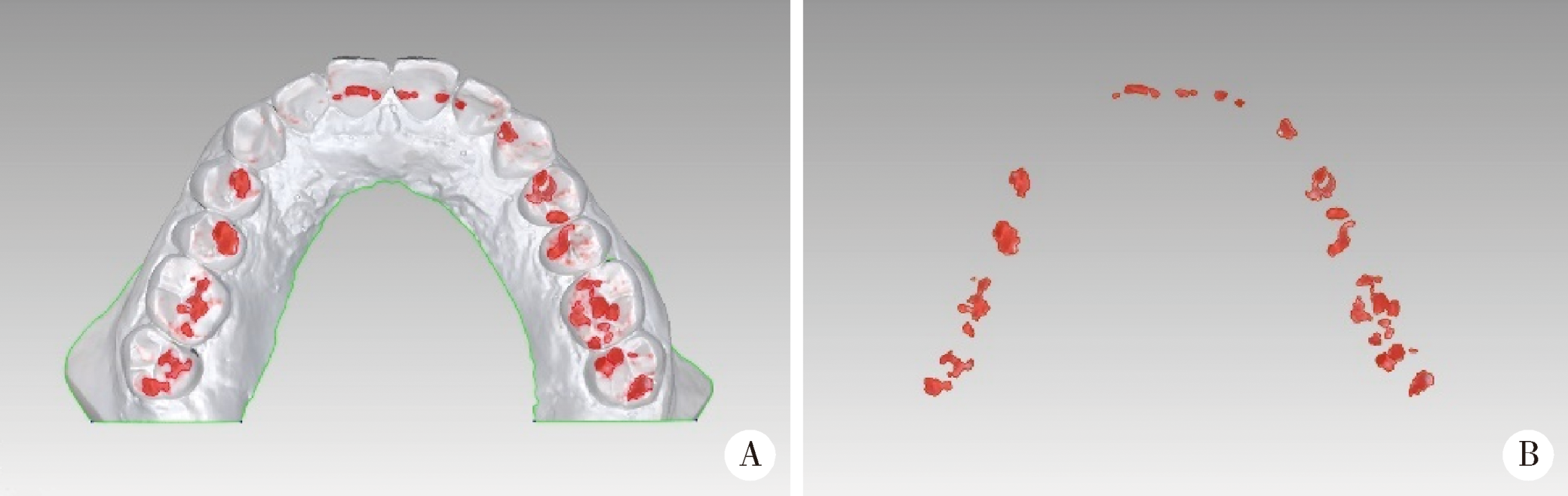
目的:研究三种数字化分析算法测量石膏牙颌模型三维咬合接触分布及面积的检测效果,并与传统咬合分析方法进行比较,探究各数字化分析算法的特点和应用。方法:选取一副正常受试者的上、下颌石膏牙颌模型,使用3shape E4牙颌模型三维扫描仪进行数字化扫描得到数字模型,在三维测量分析软件Geomagic Studio 2013及Geomagic Qualify 2013中采用“三维偏差色阶图法”、“点云统计分析法”和“虚拟咬合纸法”三种数字化分析算法获得相应的三维咬合接触分布及面积,同时使用牙合记录硅橡胶法及咬合纸扫描法两种传统咬合分析方法获得咬合接触分布和面积。各方法的咬合检测阈值为100 μm,量化评价各数字化分析算法与传统咬合分析方法的检测结果。结果:上述五种方法所得的全牙列咬合接触分布的定性评价结果基本一致,三维偏差色阶图法、点云统计分析法、虚拟咬合纸法、牙合记录硅橡胶法和咬合纸扫描法所得到的总咬合接触面积分别为133.10 mm 2、142.08 mm 2、128.95 mm 2、163.31 mm 2、100.55 mm 2。三种数字化分析算法间的检测结果差异性不大,数字化方法与传统方法检测的总咬合接触面积有一定差异。结论:三种数字化分析算法均可提供较为可靠、准确的牙颌模型咬合接触分布及面积量化分析结果,可为口腔临床修复体数字化设计制作及咬合分析提供参考。
中图分类号:
- R783
| [1] | 马斐斐, 胡秀莲, 林野 . 口腔种植修复与咬合[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 2013,29(1):121-123. |
| [2] | Foz AM, Artese HP, Horliana AC , et al. Occlusal adjustment associated with periodontal therapy: A systematic review[J]. J Dent, 2012,40(12):1025-1035. |
| [3] | 曾艳, 王嘉德 . 牙体牙髓病临床问题解析Ⅱ. 牙齿的慢性损伤性疾病[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2009,44(7):441-443. |
| [4] | 谢秋菲 . 牙体解剖与口腔生理学 [M]. 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2013. |
| [5] | Abduo J, Bennamoun M, Tennant M , et al. Effect of prosthodontic planning on intercuspal occlusal contacts: Comparison of digital and conventional planning[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2015,60:143-150. |
| [6] | Moreno-Hay I, Okeson JP . Does altering the occlusal vertical dimension produce temporomandibular disorders? A literature review[J]. J Oral Rehabil, 2015,42(11):875-882. |
| [7] | 韩科, 张豪 . 牙合学理论与临床实践 [M]. 北京: 人民军医出版社, 2014. |
| [8] | 宋倩, 王辉, 冯春雷 , 等. 咬合纸指导调牙合可靠性的定量研究[J]. 牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志, 2016,26(2):86-90. |
| [9] | Koos B, Godt A, Schille C , et al. Precision of an instrumentation-based method of analyzing occlusion and its resulting distribution of forces in the dental arch[J]. J Orofac Orthop, 2010,71(6):403-410. |
| [10] | Forrester SE, Presswood RG, Toy AC , et al. Occlusal measurement method can affect SEMG activity during occlusion[J]. J Oral Rehabil, 2011,38(9):655-660. |
| [11] | 赵一姣, 王勇, 吕培军 . 一种基于数字化牙颌模型的三维咬合分析方法[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2008,40(1):109-111. |
| [12] | Gintaute A, Keeling AJ, Osnes CA , et al. Precision of maxillo-mandibular registration with intraoral scanners in vitro [J]. J Prosthodont Res, 2019, pii: S1883- 1958(19) 30145-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpor.2019.05.006.[Epub ahead of print]. |
| [13] | Lee H, Cha J, Chun YS , et al. Comparison of the occlusal contact area of virtual models and actual models: a comparative in vitro study on Class Ⅰ and Class Ⅱ malocclusion models[J]. Bmc Oral Health, 2018,18(1):109. |
| [14] | 陈磊, 张豪, 冯海兰 , 等. 正常受试者单侧咀嚼运动中的牙合接触模式[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2009,41(1):90-94. |
| [15] | Abduo J . Geometrical effects of conventional and digital prosthodontic planning wax-ups on lateral occlusal contact number, contact area, and steepness[J]. J Oral Sci, 2017,59(3):431-438. |
| [16] | Iwase Y, Saitoh I, Okamoto A , et al. Do occlusal contact areas of maximum closing position during gum chewing and intercuspal position coincide?[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 2011,56(12):1616-1623. |
| [17] | Schelb E, Kaiser DA, Brukl CE . Thickness and marking characteristics of occlusal registration strips[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 1985,54(1):122-126. |
| [18] | Cohen-Levy J, Cohen N . Computerized analysis of occlusal contacts after lingual orthodontic treatment in adults[J]. Int Orthod, 2011,9(4):410-431. |
| [19] | Qadeer S, Kerstein R, Kim RJ , et al. Relationship between arti-culation paper mark size and percentage of force measured with compu-terized occlusal analysis[J]. J Adv Prosthodont, 2012,4(1):7-12. |
| [20] | Kerstein RB . Articulating paper mark misconceptions and compu-terized occlusal analysis technology: A clinical brief[J]. Dent Implantol Update, 2008,19(6):41-46. |
| [21] | Toledo MF, Jóias RP, Marques-Iasi YS , et al. Thickness and marking quality of different occlusal contact registration strips[J]. J Appl Oral Sci, 2014,22(6):516-521. |
| [22] | Malta Barbosa J, Urtula AB, Hirata R , et al. Thickness evaluation of articulating papers and foils[J]. J Esthet Restor Dent, 2018,30(1):70-72. |
| [23] | Saraçoġlu A, Ozpinar B . In vivo and in vitro evaluation of occlusal indicator sensitivity[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2002,88(5):522-526. |
| [24] | Matsui Y, Ohno K, Michi K , et al. A computerized method for evaluating balance of occlusal load[J]. J Oral Rehabil, 1996,23(8):530-535. |
| [25] | Imamura Y, Sato Y, Kitagawa N , et al. Influence of occlusal loading force on occlusal contacts in natural dentition[J]. J Prosthodont Res, 2015,59(2):113-120. |
| [26] | Augusti D, Augusti G, Re D , et al. Effect of different dental articulating papers on SEMG activity during maximum clenching[J]. J Electromyogr Kinesiol, 2015,25(4):612-618. |
| [27] | Sharma A, Rahul GR, Poduval ST , et al. History of materials used for recording static and dynamic occlusal contact marks: a literature review[J]. J Clin Exp Dent, 2013,5(1):e48-e53. |
| [28] | 易新竹 . 牙合学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2012. |
| [29] | Makino E, Nomura M, Motegi E , et al. Effect of orthodontic treatment on occlusal condition and masticatory function[J]. Bull Tokyo Dent Coll, 2014,55(4):185-197. |
| [30] | Horie T, Kanazawa M, Komagamine Y , et al. Association between near occlusal contact areas and mixing ability[J]. J Oral Rehabil, 2014,41(11):829-835. |
| [31] | 刘洋 . 调牙合——临床实用技术图解 [M]. 南京: 江苏凤凰科学技术出版社, 2018. |
| [32] | Brizuela-Velasco A, Álvarez-Arenal Á, Ellakuria-Echevarria J , et al. Influence of articulating paper thickness on occlusal contacts registration: A preliminary report[J]. Int J Prosthodont, 2015,28(4):360-362. |
| [33] | Komiyama O, Obara R, Iida T , et al. Comparison of direct and indirect occlusal contact examinations with different clenching intensities[J]. J Oral Rehabil, 2015,42(3):185-191. |
| [34] | 程明轩, 姜婷, 孙玉春 , 等. 比较口内扫描和模型扫描对数字化牙列模型咬合定量分析的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018,50(1):136-140. |
| [35] | Ayuso-Montero R, Mariano-Hernandez Y, Khoury-Ribas L , et al. Reliability and validity of T-scan and 3D intraoral scanning for measuring the occlusal contact area[J]. J Prosthodont, 2019. doi: 10.1111/jopr.13096. |
| [36] | Gupta S, Tarannum F, Gupta NK , et al. Effect of head posture on tooth contacts in dentate and complete denture wearers using computerized occlusal analysis system[J]. J Indian Prosthodont Soc, 2017,17(3):250-254. |
| [37] | Nishimori H, Iida T, Kamiyama H , et al. Comparing the occlusal contact area of individual teeth during low-level clenching[J]. J Oral Sci, 2017,59(3):337-342. |
| [1] | 邢念增,王明帅,杨飞亚,尹路,韩苏军. 前列腺免活检创新理念的临床实践及其应用前景[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 565-566. |
| [2] | 田宇轩,阮明健,刘毅,李德润,吴静云,沈棋,范宇,金杰. 双参数MRI改良PI-RADS评分4分和5分病灶的最大径对临床有意义前列腺癌的预测效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 567-574. |
| [3] | 唐祖南,胡耒豪,陈震,于尧,章文博,彭歆. 增强现实技术在口腔颌面颈部解剖识别中的应用评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 541-545. |
| [4] | 吕梁,张铭津,温奧楠,赵一姣,王勇,李晶,杨庚辰,柳大为. 应用三维软组织空间线角模板法评价颏部对称性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 106-110. |
| [5] | 毛渤淳,田雅婧,王雪东,李晶,周彦恒. 骨性Ⅱ类高角患者拔牙矫治前后的面部软硬组织变化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 111-119. |
| [6] | 凌晓彤,屈留洋,郑丹妮,杨静,闫雪冰,柳登高,高岩. 牙源性钙化囊肿与牙源性钙化上皮瘤的三维影像特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 131-137. |
| [7] | 刘毅,袁昌巍,吴静云,沈棋,肖江喜,赵峥,王霄英,李学松,何志嵩,周利群. 靶向穿刺+6针系统穿刺对PI-RADS 5分患者的前列腺癌诊断效能[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 812-817. |
| [8] | 袁昌巍,李德润,李志华,刘毅,山刚志,李学松,周利群. 多参数磁共振成像中动态对比增强状态在诊断PI-RADS 4分前列腺癌中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 838-842. |
| [9] | 刘颖,霍然,徐慧敏,王筝,王涛,袁慧书. 磁共振血管壁成像评估颈动脉中重度狭窄患者斑块特征与脑血流灌注的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 646-651. |
| [10] | 傅强,高冠英,徐雁,林卓华,孙由静,崔立刚. 无症状髋关节前上盂唇撕裂超声与磁共振检查的对比研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 665-669. |
| [11] | 刘想,谢辉辉,许玉峰,张晓东,陶晓峰,柳林,王霄英. 人工智能对提高放射科住院医生诊断胸部肋骨骨折一致性的价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 670-675. |
| [12] | 黄莹,吴志远,周行红,蔡志刚,张杰. 股前外侧皮瓣修复上颌骨缺损术后面部软组织对称性感观分级[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 708-715. |
| [13] | 张雯,刘筱菁,李自力,张益. 基于解剖标志的鼻翼基底缩窄缝合术对正颌患者术后鼻唇部形态的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 736-742. |
| [14] | 欧蒙恩,丁云,唐卫峰,周永胜. 基台边缘-牙冠的平台转移结构中粘接剂流动的三维有限元分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 548-552. |
| [15] | 温奥楠,刘微,柳大为,朱玉佳,萧宁,王勇,赵一姣. 5种椅旁三维颜面扫描技术正确度的初步评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 343-350. |
|
||