北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (1): 9-15. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.01.003
生长停滞特异性蛋白6在人牙周膜细胞迁移及成骨分化中的作用
张胜男1,安娜2,Δ( ),欧阳翔英1,Δ(
),欧阳翔英1,Δ( ),刘颖君2,王雪奎1
),刘颖君2,王雪奎1
- 1.北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,牙周科, 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
2.北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,综合二科 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
Role of growth arrest-specific protein 6 in migration and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells
ZHANG Sheng-nan1,AN Na2,Δ( ),OUYANG Xiang-ying1,Δ(
),OUYANG Xiang-ying1,Δ( ),LIU Ying-jun2,WANG Xue-kui1
),LIU Ying-jun2,WANG Xue-kui1
- 1. Department of Periodontology, , Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of General Dentistry Ⅱ, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
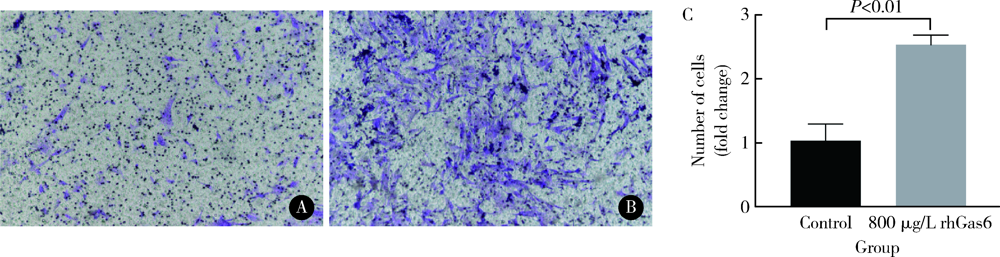
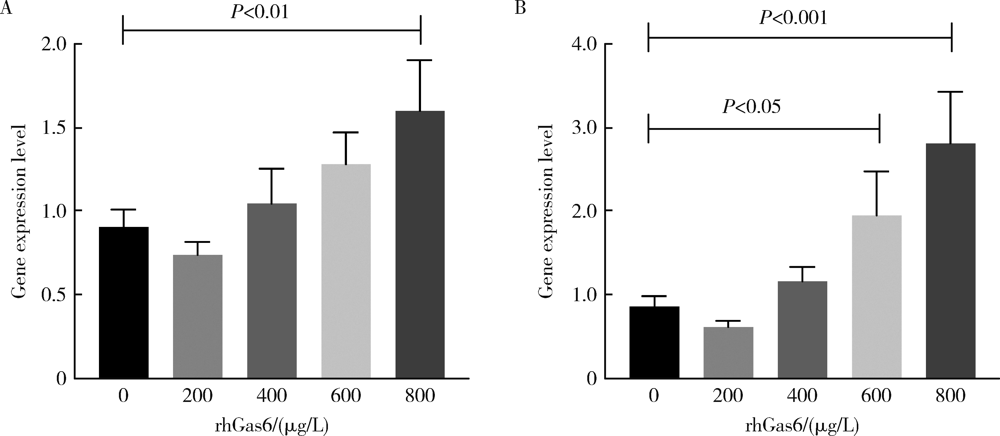
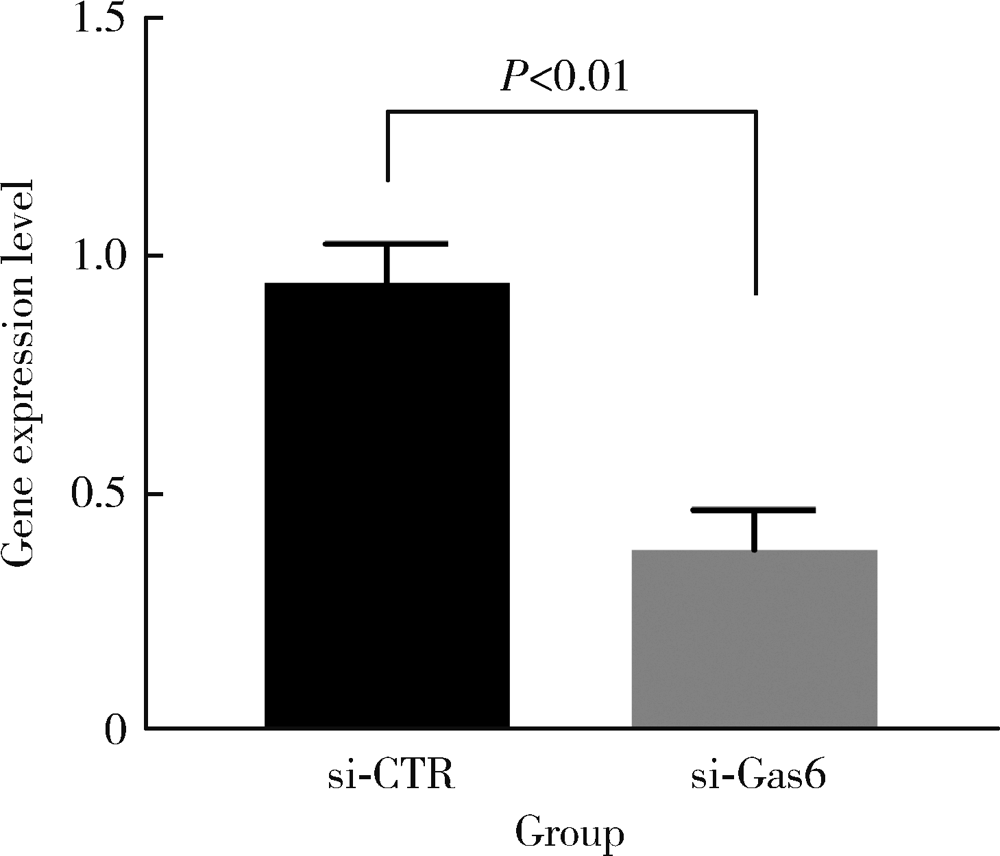
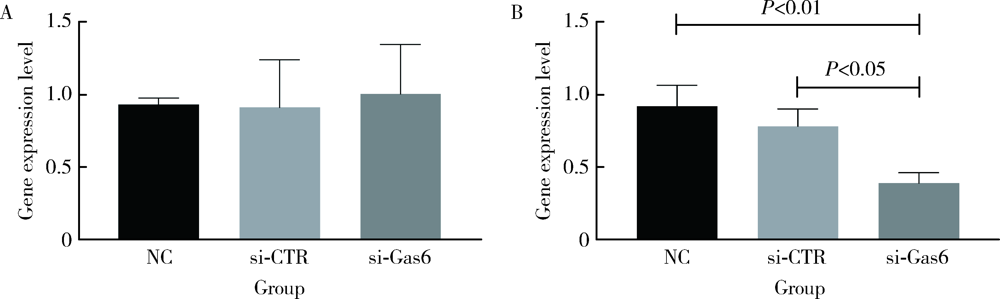
目的: 探讨AXL受体酪氨酸激酶配体——生长停滞特异性蛋白6(growth arrest-specific protein 6,Gas6)在人牙周膜细胞(human periodontal ligament cells,hPDLCs)迁移及成骨诱导液培养下成骨分化中发挥的作用。方法: 在对hPDLCs进行体外培养的培养液中加入不同浓度的外源性人重组Gas6(recombinant human Gas6,rhGas6), 通过细胞增殖实验(CCK-8)检测rhGas6对hPDLCs细胞增殖的影响,通过细胞划痕实验和细胞迁移实验(Transwell)检测rhGas6对hPDLCs迁移的影响。用小干扰RNA(siRNA)下调hPDLCs 中Gas6基因表达,然后进行成骨诱导,利用实时荧光定量聚合酶链式反应(real-time PCR)检测runt相关转录因子2(runt-related transcription factor 2,Runx2)和碱性磷酸酶(alkaline phosphatase,ALP)基因表达变化,用ALP染色检测其对矿化结节形成的影响。结果: 不同浓度rhGas6对24、48、72 h的hPDLCs增殖的影响与对照组差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。划痕后24 h,800 μg/L rhGas6组愈合面积百分比(31.06%±13.70%)大于对照组(21.79%±9.51%),但差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);迁移实验中,24 h后800 μg/L rhGas6组迁移细胞数显著多于对照组(P<0.01)。加入rhGas6并成骨诱导后,800 μg/L组Runx2、ALP基因表达量显著高于对照组(1.60±0.30 vs. 0.91±0.10, 2.81±0.61 vs. 0.86±0.12,P<0.01)。敲低Gas6后,ALP表达显著低于对照组(0.39±0.07 vs. 0.92±0.14,P<0.01),Runx2表达无明显变化(P>0.05)。成骨诱导7 d后Gas6敲低组矿化结节形成显著少于对照组(0.25±0.04 vs. 1.00±0.11,P<0.001), 14 d后Gas6敲低组矿化结节形成少于对照组,但两组间差异无统计学意义(0.86±0.04 vs. 1.00±0.16,P>0.05)。结论: 下调Gas6基因后成骨诱导早期的矿化结节形成减少,ALP表达减少,加入rhGas6后Runx2、ALP表达增多,细胞迁移数量增多,提示Gas6在牙周膜细胞迁移及成骨分化中可能存在促进作用。
中图分类号:
- R781.42
| [1] |
Jönsson D, Nebel D, Bratthall G, et al. The human periodontal ligament cell: A fibroblast-like cell acting as an immune cell[J]. J Periodontal Res, 2011,46(2):153-157.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.2010.01331.x |
| [2] |
Somerman MJ, Young MF, Foster RA, et al. Characteristics of human periodontal ligament cells in vitro[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 1990,35(3):241-247.
doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(90)90062-f pmid: 2161648 |
| [3] |
Liu F, Wang X, Zheng B, et al. USF2 enhances the osteogenic differentiation of PDLCs by promoting ATF4 transcriptional activities[J]. J Periodontal Res, 2020,55(1):68-76.
doi: 10.1111/jre.12689 pmid: 31448831 |
| [4] |
Manokawinchoke J, Pavasant P, Sawangmake C, et al. Intermittent compressive force promotes osteogenic differentiation in human periodontal ligament cells by regulating the transforming growth factor-β pathway[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2019,10(10):761.
doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1992-4 pmid: 31591384 |
| [5] |
Xu Y, Ren C, Zhao X, et al. MicroRNA-132 inhibits osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells via GDF5 and the NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2019,215(12):152722.
doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2019.152722 pmid: 31718857 |
| [6] |
Liu S, Zhou M, Li J, et al. LIPUS inhibited the expression of inflammatory factors and promoted the osteogenic differentiation capacity of hPDLCs by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. J Periodontal Res, 2020,55(1):125-140.
doi: 10.1111/jre.12696 pmid: 31541455 |
| [7] |
Schneider C, King RM, Philipson L. Genes specifically expressed at growth arrest of mammalian cells[J]. Cell, 1988,54(6):787-793.
doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91065-3 pmid: 3409319 |
| [8] |
Manfioletti G, Brancolini C, Avanzi G, et al. The protein encoded by a growth arrest-specific gene (gas6) is a new member of the vitamin K-dependent proteins related to protein S, a negative coregulator in the blood coagulation cascade[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 1993,13(8):4976-4985.
doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4976 pmid: 8336730 |
| [9] | 刘颖君, 欧阳翔英, 安娜, 等. 生长停滞特异性蛋白6在牙龈卟啉单胞菌脂多糖诱导内皮细胞黏附分子及趋化因子表达中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018,50(1):20-25. |
| [10] |
Collett G, Wood A, Alexander MY, et al. Receptor tyrosine kinase Axl modulates the osteogenic differentiation of pericytes[J]. Circ Res, 2003,92(10):1123-1129.
doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000074881.56564.46 pmid: 12730092 |
| [11] |
Katagiri M, Hakeda Y, Chikazu D, et al. Mechanism of stimulation of osteoclastic bone resorption through Gas6/Tyro 3, a receptor tyrosine kinase signaling, in mouse osteoclasts[J]. J Biol Chem, 2001,276(10):7376-7382.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M007393200 pmid: 11084030 |
| [12] |
Kim YS, Jung SH, Jung DH, et al. Gas6 stimulates angiogenesis of human retinal endothelial cells and of zebrafish embryos via ERK1/2 signaling[J]. PLoS One, 2014,9(1):e83901.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083901 pmid: 24409287 |
| [13] |
Mao S, Wu Y, Wang R, et al. Overexpression of GAS6 promotes cell proliferation and invasion in bladder cancer by activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2020,13:4813-4824.
doi: 10.2147/OTT.S237174 pmid: 32547108 |
| [14] |
Lemke G. Biology of the TAM receptors[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 2013,5(11):a009076.
doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a009076 pmid: 24186067 |
| [15] |
Xu J, Li Z, Hou Y, et al. Potential mechanisms underlying the Runx2 induced osteogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2015,7(12):2527-2535.
pmid: 26885254 |
| [16] |
Ciceri P, Elli F, Braidotti P, et al. Iron citrate reduces high phosphate-induced vascular calcification by inhibiting apoptosis[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2016,254:93-101.
doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.09.071 pmid: 27716569 |
| [17] |
Badi I, Mancinelli L, Polizzotto A, et al. miR-34a promotes vascular smooth muscle cell calcification by downregulating SIRT1 (Sirtuin 1) and Axl (AXL receptor tyrosine kinase)[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2018,38(9):2079-2090.
doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311298 pmid: 30026277 |
| [18] |
Goruppi S, Ruaro E, Varnum B, et al. Gas6-mediated survival in NIH3T3 cells activates stress signalling cascade and is independent of Ras[J]. Oncogene, 1999,18(29):4224-4236.
doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202788 pmid: 10435635 |
| [19] | Hasanbasic I, Cuerquis J, Varnum B, et al. Intracellular signaling pathways involved in Gas6-Axl-mediated survival of endothelial cells[J]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2004,287(3):1207-1213. |
| [20] |
Allen MP, Linseman DA, Udo H, et al. Novel mechanism for gonadotropin-releasing hormone neuronal migration involving Gas6/Ark signaling to p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2002,22(2):599-613.
doi: 10.1128/mcb.22.2.599-613.2002 pmid: 11756555 |
| [21] |
Li H, Deng Y, Tan M, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound upregulates osteogenesis under inflammatory conditions in periodontal ligament stem cells through unfolded protein response[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2020,11(1):215.
doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01732-5 pmid: 32493507 |
| [22] |
Chang M, Lin H, Fu H, et al. MicroRNA-195-5p regulates osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament cells under mechanical loading[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2017,232(12):3762-3774.
doi: 10.1002/jcp.25856 pmid: 28181691 |
| [1] | 简远志,王菲,尹宁,周若宇,王军波. 基于胚胎干细胞模型的Cry1Ab蛋白发育毒性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 213-222. |
| [2] | 潘媛,顾航,肖涵,赵笠君,汤祎熳,葛雯姝. 泛素特异性蛋白酶42调节人脂肪干细胞成骨向分化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 9-16. |
| [3] | 薛江,张建运,时瑞瑞,谢晓艳,白嘉英,李铁军. 105例口腔颅颌面部纤维性结构不良的临床病理分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 54-61. |
| [4] | 杜文瑜,杨静文,姜婷. 甲磺酸去铁胺促进大鼠颅骨临界骨缺损血管化骨再生的早期连续观察[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1171-1177. |
| [5] | 谢静,赵玉鸣,饶南荃,汪晓彤,方滕姣子,李晓霞,翟越,李静芝,葛立宏,王媛媛. 3种口腔颌面部来源的间充质干细胞成血管内皮分化潜能的比较研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(5): 900-906. |
| [6] | 隋华欣,吕培军,王勇,冯驭驰. 低能量激光照射对人脂肪来源干细胞/海藻酸钠/明胶三维生物打印体成骨能力的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(5): 868-875. |
| [7] | 刘颖君,欧阳翔英,王宇光,吕培军,安娜. 生长停滞特异性蛋白6在牙龈卟啉单胞菌脂多糖诱导内皮细胞黏附因子及趋化因子表达中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(1): 20-25. |
| [8] | 刘婧寅,陈飞,葛严军,魏菱,潘韶霞,冯海兰. 选择性激光熔化种植体对早期骨矿化沉积率的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(1): 117-122. |
| [9] | 隋华欣, 吕培军, 王宇光, 王勇, 孙玉春. 低能量激光照射对人脂肪基质细胞增殖分化的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(2): 337-343. |
| [10] | 陈飞,潘韶霞,冯海兰. 转化生长因子β1和血管内皮生长因子在浓缩生长因子各层中的分布及含量特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(5): 860-865. |
| [11] | 凌龙,赵玉鸣,葛立宏. 不同炎症状态下犬年轻恒牙牙髓干细胞增殖及成骨分化能力的改变[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(5): 878-883. |
| [12] | 秦雪嫣,赵华翔,张倩,陈峰,林久祥. NELL-1: 高效特异的新型生长因子[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(2): 380-383. |
| [13] | 俞光岩, 曹彤, 邹晓晖, 张学慧, 傅歆, 彭双清, 邓旭亮, 李盛林, 刘鹤, 肖苒, 欧阳宏伟, 彭晖, 陈晓, 赵增明,王晓颖……. 基于人胚胎干细胞健康安全评价体系的构建[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(1): 1-4. |
| [14] | 张晓,刘云松,吕珑薇,陈彤,吴刚,周永胜. 骨形态发生蛋白2/7异二聚体对人脂肪间充质干细胞成骨分化的促进作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(1): 37-44. |
| [15] | 宋杨,王晓飞,王宇光,孙玉春,吕培军△. 人脂肪间充质干细胞与生物材料共混物三维打印体的体内成骨[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(1): 45-50. |
|
||