北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (1): 54-61. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.01.009
105例口腔颅颌面部纤维性结构不良的临床病理分析
薛江1,张建运1,时瑞瑞2,谢晓艳3,白嘉英1,李铁军1,△( )
)
- 1.北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院 口腔病理科, 北京 100081
2.北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院 中心实验室, 北京 100081
3.北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院 口腔颌面医学影像科,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室,口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室, 北京 100081
Clinicopathological analysis of 105 patients with fibrous dysplasia of cranio-maxillofacial region
XUE Jiang1,ZHANG Jian-yun1,SHI Rui-rui2,XIE Xiao-yan3,BAI Jia-ying1,LI Tie-jun1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Oral Pathology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Central Laboratory, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
3. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
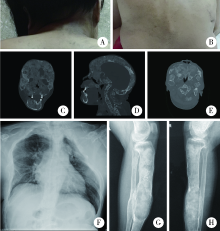
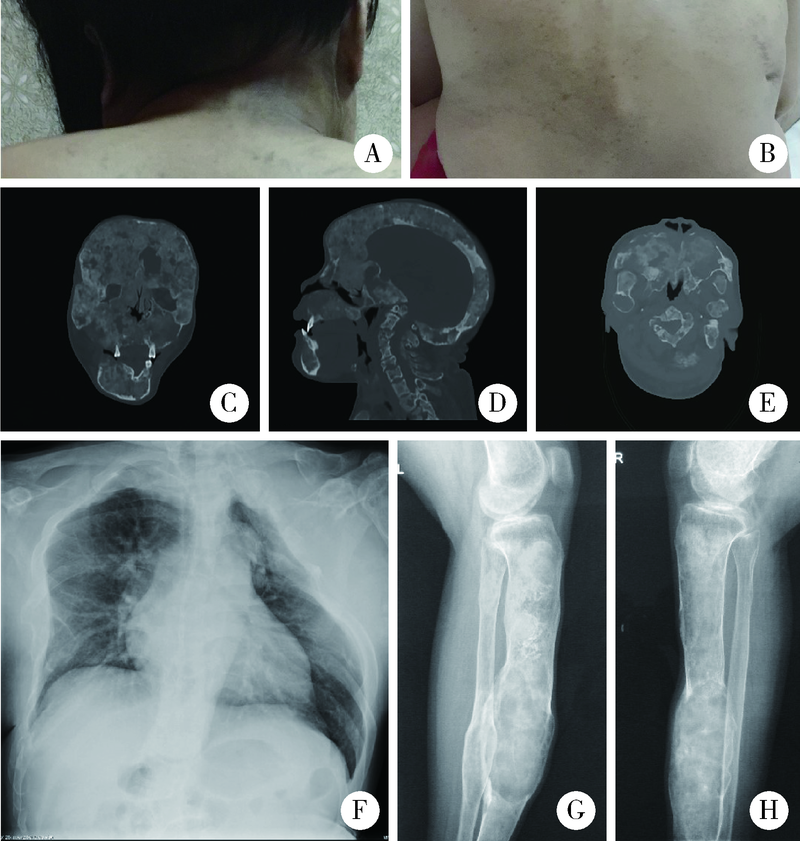
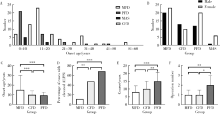
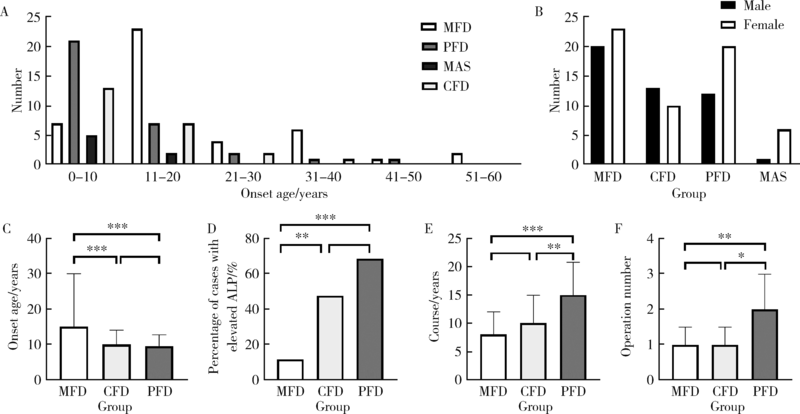
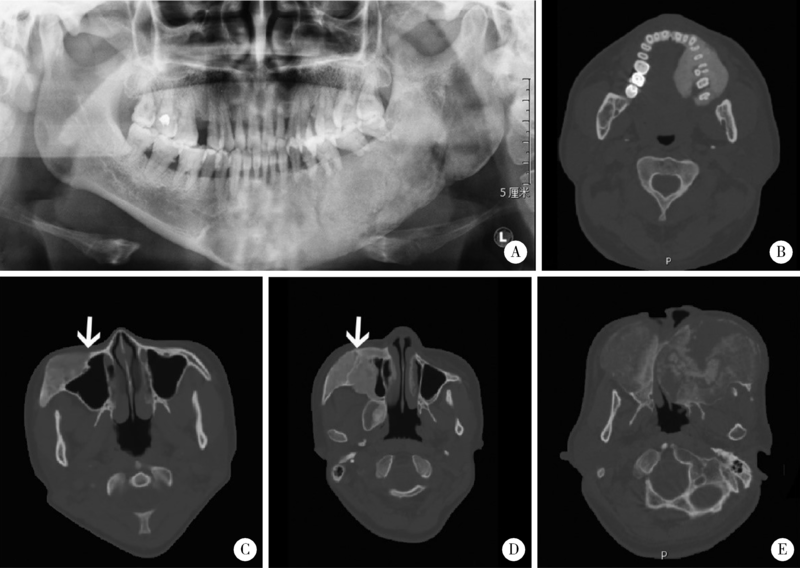
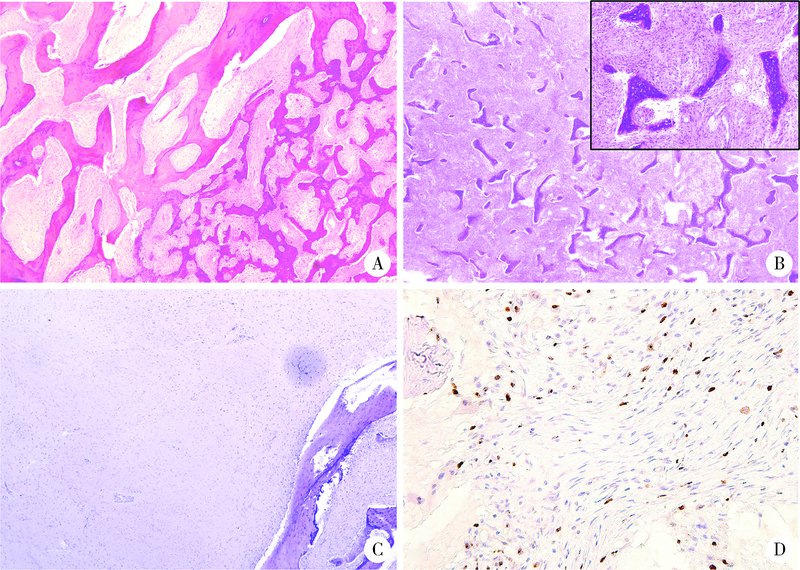
目的: 比较不同类型口腔颅颌面部纤维性结构不良(fibrous dysplasia,FD)的临床病理特点,为临床诊治及预后判断提供依据。方法: 收集2013年1月至2020年12月于北京大学口腔医院确诊为FD或McCune-Albright综合征(McCune-Albright syndrome, MAS)的患者105例,分析其临床资料、影像学和病理学特点,分别归类为单骨型、多骨型、MAS型及口腔颅颌面部特有的口腔颅面型纤维性结构不良(craniofacial fibrous dysplasia,CFD)四型,对各型的临床病理特征、治疗及随访资料等进行分析。结果: 105例患者的男女比为1 ∶1.3,发病年龄0~56岁(中位数为12岁)。本组病例中,单骨型43例(40.95%), 其中上颌骨29例,下颌骨12例,颧骨2例;多骨型32例(30.48%);MAS型7例(6.67%);发生在颅上颌部位的FD,经影像学分析确诊CFD型23例(21.90%)。CFD在患者性别、术前血清碱性磷酸酶水平等方面有别于其他类型的FD。病理学上,各型FD的形态特点类似,但多骨型及MAS型患者可能出现以纤维成分增生为主的特征。结论: 口腔颅颌面部FD的临床和病理特点有别于身体其他部位发生的FD病变,CFD的临床和病理特点与发生于颅颌面部的单骨型或多骨型FD也有显著差异,应注意区分,以进一步明确CFD在临床处置及预后等方面的特殊性。
中图分类号:
- R739.8
| [1] |
Dumitrescu CE, Collins MT. McCune-Albright syndrome[J]. Orphanet J Rare Dis, 2008, 3:12.
doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-3-12 pmid: 18489744 |
| [2] | 叶为民, 竺涵光, 郑家伟, 等. 46例颌面部骨纤维异常增殖症临床分析[J]. 中国口腔颌面外科杂志, 2008, 6(3):170-173. |
| [3] | El-Naggar AK, Chan JK, Grandis JR, et al. WHO classification of head and neck tumours [M]. Lyon: IARC Press, 2017: 253-254. |
| [4] | 张壁, 韩其滨, 赵吉宏, 等. 30例颌面部骨纤维异常增殖症诊治的临床分析[J]. 口腔医学研究, 2010, 26(5):713-715. |
| [5] |
Sweeney K, Kaban LB. Natural history and progression of craniofacial fibrous dysplasia: A retrospective evaluation of 114 patients from Massachusetts General Hospital[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2020, 78(11):1966-1980.
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2020.05.036 |
| [6] |
Cheng J, Wang Y, Yu H, et al. An epidemiological and clinical analysis of craniomaxillofacial fibrous dysplasia in a Chinese population[J]. Orphanet J Rare Dis, 2012, 7:80.
doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-7-80 pmid: 23074969 |
| [7] |
Javaid MK, Boyce A, Appelman-Dijkstra N, et al. Best practice management guidelines for fibrous dysplasia/McCune-Albright syndrome: A consensus statement from the FD/MAS international consortium[J]. Orphanet J Rare Dis, 2019, 14(1):139.
doi: 10.1186/s13023-019-1102-9 |
| [8] | World Health Organization. WHO classification of tumours of soft tissue and bone [M]. 5th ed. Lyon: IARC Press, 2020: 472-474. |
| [9] |
Ma J, Liang L, Gu B, et al. A retrospective study on craniofacial fibrous dysplasia: Preoperative serum alkaline phosphatase as a prognostic marker?[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2013, 41(7):644-647.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2012.12.007 |
| [10] | Chen YR, Wong FH, Hsueh C, et al. Computed tomography characteristics of non-syndromic craniofacial fibrous dysplasia[J]. Chang Gung Med J, 2002, 25(1):1-8. |
| [11] |
Burke AB, Collins MT, Boyce AM. Fibrous dysplasia of bone: Craniofacial and dental implications[J]. Oral Dis, 2017, 23(6):697-708.
doi: 10.1111/odi.12563 pmid: 27493082 |
| [12] |
Akintoye SO, Lee JS, Feimster T, et al. Dental characteristics of fibrous dysplasia and McCune-Albright syndrome[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod, 2003, 96(3):275-282.
doi: 10.1016/S1079-2104(03)00225-7 |
| [13] |
Waldron CA. Fibro-osseous lesions of the jaws[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 1993, 51(8):828-835.
doi: 10.1016/S0278-2391(10)80097-7 |
| [14] |
Gupta D, Garg P, Mittal A. Computed tomography in craniofacial fibrous dysplasia: A case series with review of literature and classification update[J]. Open Dent J, 2017, 11:384-403.
doi: 10.2174/1874210601711010384 |
| [15] | 李铁军. 口腔组织学与病理学 [M]. 3版. 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2020: 360-361. |
| [16] |
Slootweg PJ. Maxillofacial fibro-osseous lesions: Classification and differential diagnosis[J]. Semin Diagn Pathol, 1996, 13(2):104-112.
pmid: 8734416 |
| [17] |
Riminucci M, Liu B, Corsi A, et al. The histopathology of fibrous dysplasia of bone in patients with activating mutations of the Gs alpha gene: Site-specific patterns and recurrent histological hallmarks[J]. J Pathol, 1999, 187(2):249-258.
pmid: 10365102 |
| [18] |
Sissons HA, Steiner GC, Dorfman HD. Calcified spherules in fibro-osseous lesions of bone[J]. Arch Pathol Lab Med, 1993, 117(3):284-290.
pmid: 8442673 |
| [19] | Dorfman HD. New knowledge of fibro-osseous lesions of bone[J]. Int J Surg Pathol, 2010, 18(3 Suppl):62S-65S. |
| [20] |
Sargolzaei S, Ghelejkhani A, Baghban AA. Diagnostic and bio-logical significance of immunohistochemical expression of osteopontin and Ki67 in fibro-osseous lesions of jaws[J]. J Islam Dent Assoc IRAN, 2017, 29(2):70-78.
doi: 10.30699/jidai.29.2.70 |
| [21] |
Shi RR, Li XF, Zhang R, et al. GNAS mutational analysis in differentiating fibrous dysplasia and ossifying fibroma of the jaw[J]. Mod Pathol, 2013, 26(8):1023-1031.
doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2013.31 |
| [22] |
Li Z, Raynald, Wang Z, et al. Malignant transformation of craniofacial fibrous dysplasia: A systematic review of overall survival[J]. Neurosurg Rev, 2020, 43(3):911-921.
doi: 10.1007/s10143-019-01089-1 |
| [1] | 邢念增,王明帅,杨飞亚,尹路,韩苏军. 前列腺免活检创新理念的临床实践及其应用前景[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 565-566. |
| [2] | 田宇轩,阮明健,刘毅,李德润,吴静云,沈棋,范宇,金杰. 双参数MRI改良PI-RADS评分4分和5分病灶的最大径对临床有意义前列腺癌的预测效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 567-574. |
| [3] | 刘帅,刘磊,刘茁,张帆,马潞林,田晓军,侯小飞,王国良,赵磊,张树栋. 伴静脉癌栓的肾上腺皮质癌的临床治疗及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [4] | 赖展鸿,李嘉辰,贠泽霖,张永刚,张昊,邢晓燕,邵苗,金月波,王乃迪,李依敏,李玉慧,栗占国. 特发性炎性肌病完全临床应答相关因素的单中心真实世界研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 284-292. |
| [5] | 徐训敏,邵校,姬爱平. 口腔急诊科死亡病例分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 185-189. |
| [6] | 冯璐,翟佳羽,赵金霞. IgG4相关性疾病患者就诊情况及其临床特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1028-1032. |
| [7] | 薛子璇,唐世英,邱敏,刘承,田晓军,陆敏,董靖晗,马潞林,张树栋. 青年肾肿瘤伴瘤栓的临床病理特征及预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 802-811. |
| [8] | 魏慧,次旦央宗,益西拉姆,白玛央金. 高原地区不同类型过敏性紫癜藏族患者发病的相关危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 923-928. |
| [9] | 时云飞,王豪杰,刘卫平,米岚,龙孟平,刘雁飞,赖玉梅,周立新,刁新婷,李向红. 血管免疫母细胞性T细胞淋巴瘤临床与分子病理学特征分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 521-529. |
| [10] | 马利加,胡攀攀,刘晓光. 脊柱转移癌伴软脊膜转移1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 563-566. |
| [11] | 李挺. 建设当代临床病理学科[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 197-200. |
| [12] | 周桥. 肿瘤病理学研究的进展和展望[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 201-209. |
| [13] | 朱晓娟,张虹,张爽,李东,李鑫,徐玲,李挺. 人表皮生长因子受体2低表达乳腺癌的临床病理学特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 243-253. |
| [14] | 赖玉梅,李忠武,李欢,吴艳,时云飞,周立新,楼雨彤,崔传亮. 68例肛管直肠黏膜黑色素瘤临床病理特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 262-269. |
| [15] | 沈棋,刘亿骁,何群. 肾黏液样小管状和梭形细胞癌的临床病理特点及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 276-282. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 183
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 905
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||