北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (2): 243-253. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.02.007
人表皮生长因子受体2低表达乳腺癌的临床病理学特征及预后
朱晓娟1,张虹1,*( ),张爽1,李东1,李鑫1,徐玲2,李挺1
),张爽1,李东1,李鑫1,徐玲2,李挺1
- 1. 北京大学第一医院病理科,北京 100034
2. 北京大学第一医院乳腺疾病中心,北京 100034
Clinicopathological features and prognosis of breast cancer with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 low expression
Xiao-juan ZHU1,Hong ZHANG1,*( ),Shuang ZHANG1,Dong LI1,Xin LI1,Ling XU2,Ting LI1
),Shuang ZHANG1,Dong LI1,Xin LI1,Ling XU2,Ting LI1
- 1. Department of Pathology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
2. Breast Disease Center, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
摘要:
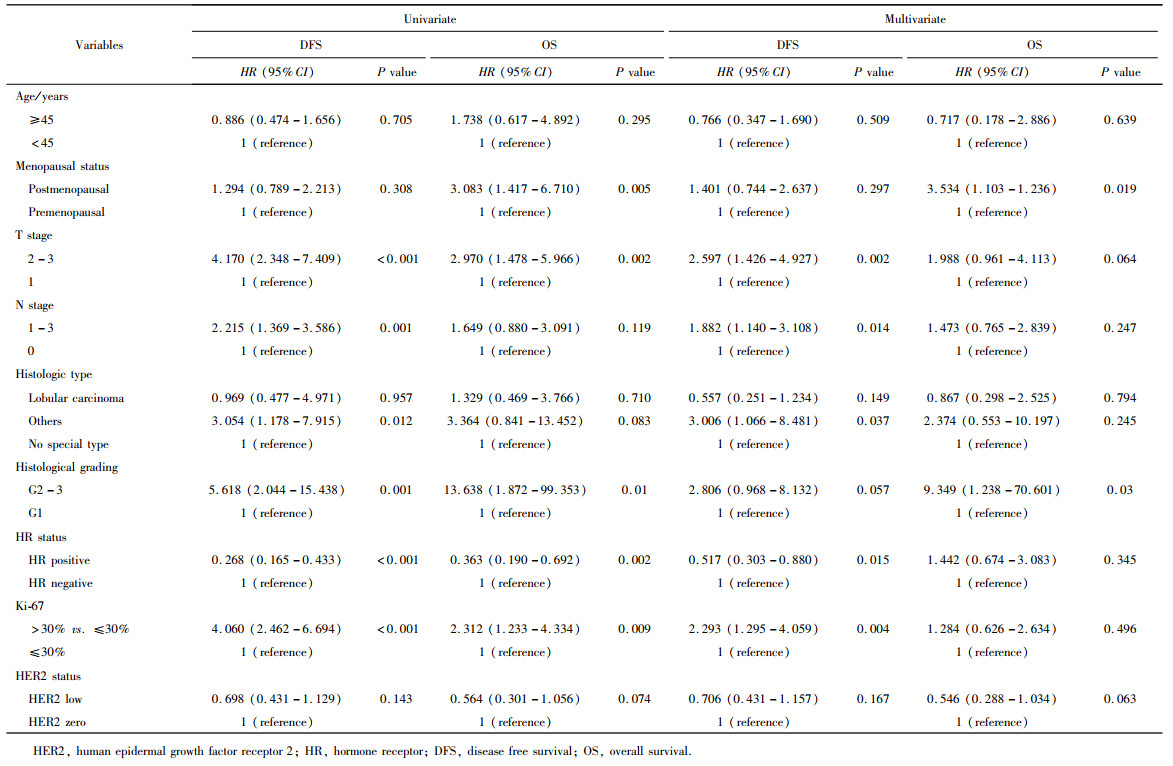
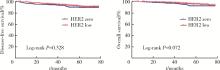
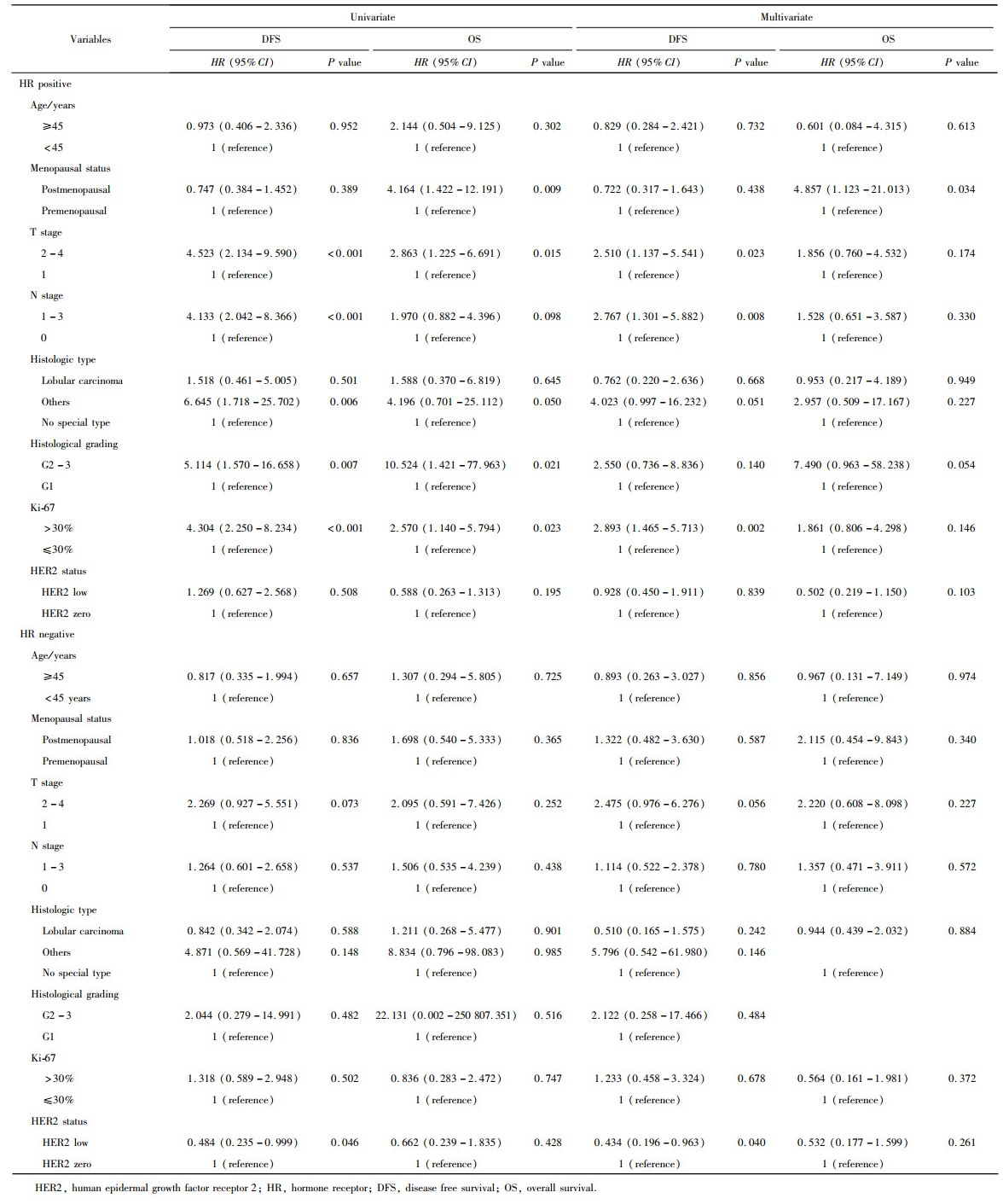
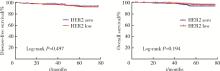
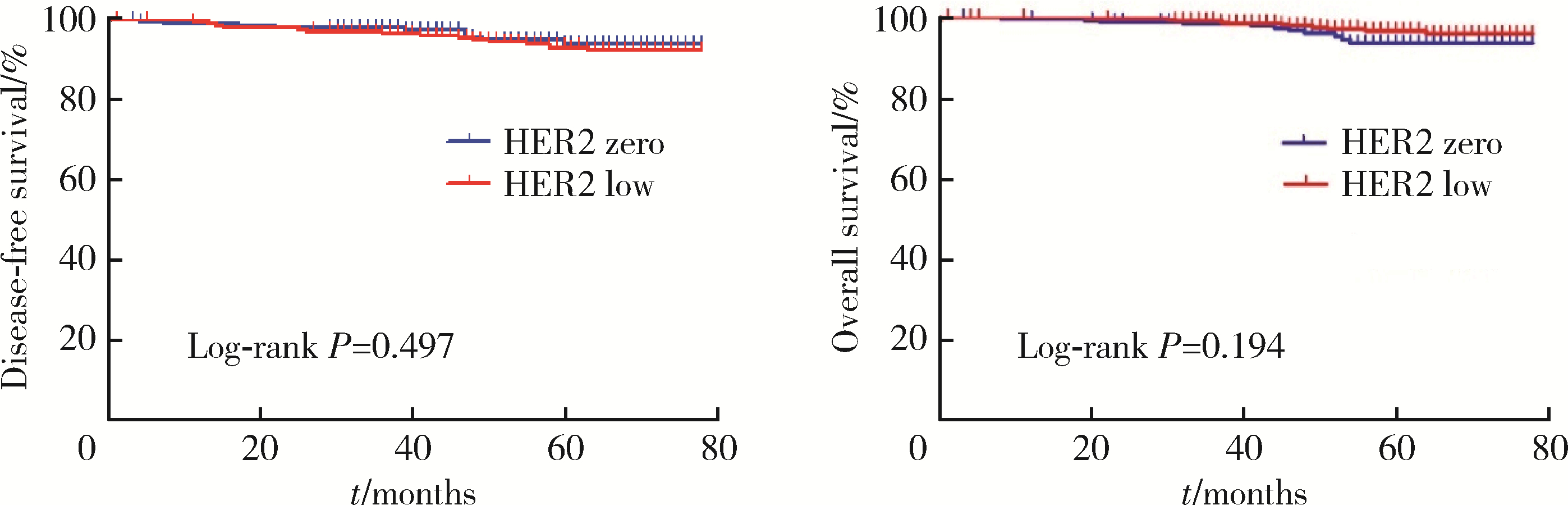
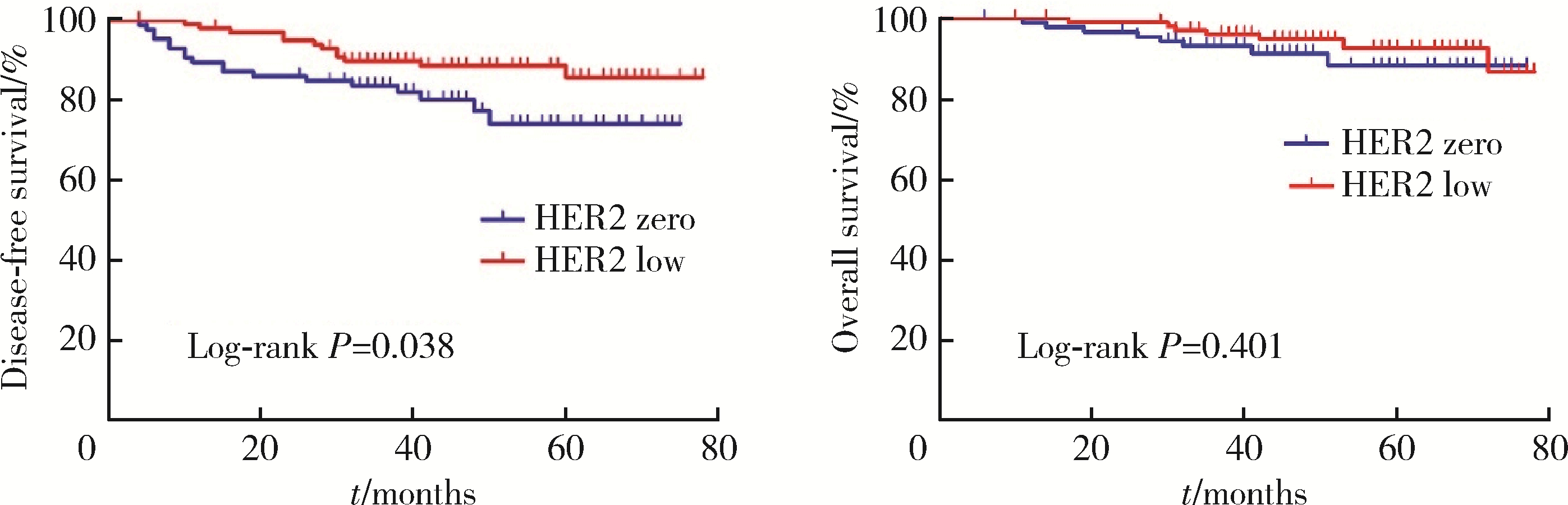
目的: 新型抗人表皮生长因子受体2(human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, HER2)抗体偶联药物临床试验的成功, 使HER2低表达乳腺癌是否将成为新的乳腺癌类型而受到关注。本研究分析比较HER2低表达与HER2零表达两组乳腺癌患者间的临床病理特征及生存数据, 探讨其临床生物学上的差异性。方法: 2014年1月至2017年12月北京大学第一医院乳腺疾病中心收治的1 250例女性原发性非转移性乳腺癌中, 969例HER2阴性(免疫组织化学染色评分为0、1+、2+, 且荧光原位杂交未扩增), 分析其中HER2低表达(1+或2+且荧光原位杂交未扩增)和HER2零表达(0分)两组患者间临床病理特征及预后情况。对两组患者进行无病生存期(disease free survival, DFS)和总生存期(overall survival, OS)预后评价, 采用Kaplan-Meier曲线计算生存率, Log-rank检验比较生存差异, 单因素和多因素Cox回归分析预后影响因素。采用双侧检验, P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。结果: 969例HER2阴性乳腺癌中, HER2低表达者606例(62.54%)、HER2零表达者363例(37.46%)。与HER2零表达组相比, HER2低表达组的N分期(P=0.001)和TNM分期更高(P=0.044), 非特殊型组织学类型占比(82.7% vs. 79.1%, P=0.009)和组织学分级更高(P=0.048), 激素受体阳性率偏高(83.2% vs. 75.2%, P=0.003), Ki-67增殖指数>30%者的比例偏低(30.4% vs. 36.6%, P=0.044)。两组间DFS及OS差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。969例患者中, 激素受体阳性777例, 激素受体阴性(即三阴性乳腺癌)192例。激素受体阳性的777例中, HER2低表达504例(64.9%), HER2零表达273例(35.1%), 两组比较, HER2低表达组的发病年龄小(P=0.016), 未绝经者占比高(P=0.029), 淋巴结受累更多(P=0.002), TNM分期更高(P=0.031), 小叶癌和黏液癌组织学类型较少见(3.6% vs. 7.3%, 4.8% vs. 10.6%, P < 0.001), DFS和OS差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。192例激素受体阴性(三阴性乳腺癌)中, HER2低表达102例(53.1%), HER2零表达90例(46.9%), 两组比较, HER2低表达组的发病年龄大(P=0.001), 未绝经所占比例低(P=0.029), 组织学分级更低(P < 0.001), Ki-67增殖指数更低(P < 0.001), 雄激素受体阳性率高(58.8% vs. 34.4%, P < 0.001), DFS比较好(P=0.038), OS差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论: HER2低表达乳腺癌占所有乳腺癌约一半的比例, 发病远高于HER2阳性乳腺癌, 其临床病理特征存在异质性, 激素受体表达状态对HER2低表达乳腺癌的临床生物学有影响。
中图分类号:
- R737.9
| 1 | Yarden Y . Biology of HER2 and its importance in breast cancer[J]. Oncology, 2001, 61 (Suppl 2): 1- 13. |
| 2 |
Choong GM , Cullen GD , O'Sullivan CC , et al. Evolving stan-dards of care and new challenges in the management of HER2-positive breast cancer[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2020, 70 (5): 355- 374.
doi: 10.3322/caac.21634 |
| 3 |
Swain SM , Baselga J , Kim SB , et al. Pertuzumab, trastuzumab, and docetaxel in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 2015, 372 (8): 724- 734.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1413513 |
| 4 |
Wolff AC , Hammond ME , Hicks DG , et al. Recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Patho-logists clinical practice guideline update[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2013, 31 (31): 3997- 4013.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.50.9984 |
| 5 |
Gilcrease MZ , Woodward WA , Nicolas MM , et al. Even low-level HER2 expression may be associated with worse outcome in node-positive breast cancer[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2009, 33 (5): 759- 767.
doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31819437f9 |
| 6 |
Modi S , Park H , Murthy RK , et al. Antitumor activity and safety of trastuzumab deruxtecan in patients with HER2-low-expressing advanced breast cancer: Results from a phase Ⅰb study[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2020, 38 (17): 1887- 1896.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.02318 |
| 7 |
Tarantino P , Hamilton E , Tolaney SM , et al. HER2-low breast cancer: Pathological and clinical landscape[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2020, 38 (17): 1951- 1962.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.02488 |
| 8 |
Hammond ME , Hayes DF , Dowsett M , et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College Of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2010, 28 (16): 2784- 2795.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.25.6529 |
| 9 |
Schalper KA , Kumar S , Hui P , et al. A retrospective population-based comparison of HER2 immunohistochemistry and fluorescence in situ hybridization in breast carcinomas: Impact of 2007 American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists criteria[J]. Arch Pathol Lab Med, 2014, 138 (2): 213- 219.
doi: 10.5858/arpa.2012-0617-OA |
| 10 |
Xin L , Wu Q , Zhan C , et al. Multicenter study of the clinico-pathological features and recurrence risk prediction model of early-stage breast cancer with low-positive human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 expression in China (Chinese Society of Breast Surgery 021)[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2022, 135 (6): 697- 706.
doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002056 |
| 11 |
Schettini F , Chic N , Brasó-Maristany F , et al. Clinical, patholo-gical, and PAM50 gene expression features of HER2-low breast cancer[J]. NPJ Breast Cancer, 2021, 7 (1): 1.
doi: 10.1038/s41523-020-00208-2 |
| 12 |
Denkert C , Seither F , Schneeweiss A , et al. Clinical and molecular characteristics of HER2-low-positive breast cancer: Pooled analysis of individual patient data from four prospective, neoadjuvant clinical trials[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2021, 22 (8): 1151- 1161.
doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00301-6 |
| 13 |
Rossi V , Sarotto I , Maggiorotto F , et al. Moderate immunohistochemical expression of HER-2 (2+) without HER-2 gene amplification is a negative prognostic factor in early breast cancer[J]. Oncologist, 2012, 17 (11): 1418- 1425.
doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2012-0194 |
| 14 |
Won HS , Ahn J , Kim Y , et al. Clinical significance of HER2-low expression in early breast cancer: A nationwide study from the Korean Breast Cancer Society[J]. Breast Cancer Res, 2022, 24 (1): 22.
doi: 10.1186/s13058-022-01519-x |
| 15 |
Horisawa N , Adachi Y , Takatsuka D , et al. The frequency of low HER2 expression in breast cancer and a comparison of prognosis between patients with HER2-low and HER2-negative breast cancer by HR status[J]. Breast Cancer, 2022, 29 (2): 234- 241.
doi: 10.1007/s12282-021-01303-3 |
| 16 |
Dehghani M , Keshavarz P , Talei A , et al. The Effects of Low HER2/neu expression on the clinicopathological characteristics of triple-negative breast cancer patients[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2020, 21 (10): 3027- 3032.
doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.10.3027 |
| 17 |
Jacot W , Maran-Gonzalez A , Massol O , et al. Prognostic value of HER2-low expression in non-metastatic triple-negative breast cancer and correlation with other biomarkers[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2021, 13 (23): 6059.
doi: 10.3390/cancers13236059 |
| [1] | 赖玉梅,李忠武,李欢,吴艳,时云飞,周立新,楼雨彤,崔传亮. 68例肛管直肠黏膜黑色素瘤临床病理特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 262-269. |
| [2] | 沈棋,刘亿骁,何群. 肾黏液样小管状和梭形细胞癌的临床病理特点及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 276-282. |
| [3] | 宿骞,彭歆,周传香,俞光岩. 369例口腔颌面部非霍奇金淋巴瘤的临床病理特点及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 13-21. |
| [4] | 张铨,宋海峰,马冰磊,张喆楠,周朝晖,李傲林,刘军,梁磊,朱时雨,张骞. 术前预后营养指数可作为预测非转移性肾细胞癌预后的指标[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 149-155. |
| [5] | 邢晓燕,张筠肖,朱冯赟智,王一帆,周新尧,李玉慧. 皮肌炎合并巨噬细胞活化综合征5例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1214-1218. |
| [6] | 曹乐清,周婧睿,陈育红,陈欢,韩伟,陈瑶,张圆圆,闫晨华,程翼飞,莫晓冬,付海霞,韩婷婷,吕萌,孔军,孙于谦,王昱,许兰平,张晓辉,黄晓军. 异基因造血干细胞移植后晚发重症肺炎患者治疗与预后转归的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 1013-1020. |
| [7] | 方伟岗,田新霞,解云涛. 基因多态性对中国汉族女性乳腺癌遗传易感性的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 822-828. |
| [8] | 王跃,张爽,张虹,梁丽,徐玲,程元甲,段学宁,刘荫华,李挺. 激素受体阳性/人表皮生长因子受体2阴性乳腺癌临床病理特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 853-862. |
| [9] | 张崔建,何志嵩,周利群. 上尿路尿路上皮癌的淋巴清扫[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 592-594. |
| [10] | 邱敏,连岩岩,陆敏,王滨帅,田晓军,卢剑,刘承,张树栋,姜敏,马潞林. 多原发癌合并肾癌的治疗及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 680-685. |
| [11] | 博尔术,洪鹏,张宇,邓绍晖,葛力源,陆敏,李楠,马潞林,张树栋. 乳头状肾细胞癌的临床病理特征和预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 615-620. |
| [12] | 邓宇含,姜勇,王子尧,刘爽,汪雨欣,刘宝花. 基于长短期记忆网络和Logistic回归的重症监护病房脑卒中患者院内死亡风险预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 458-467. |
| [13] | 丁婷婷,曾楚雄,胡丽娜,余明华. 基于癌症基因组图谱数据库结直肠癌免疫细胞浸润预测模型的建立[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 203-208. |
| [14] | 蓝璘,贺洋,安金刚,张益. 颧骨缺损不同修复重建方法和预后的回顾性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 356-362. |
| [15] | 王飞,朱翔,贺蓓,朱红,沈宁. 自发缓解的滤泡性细支气管炎伴非特异性间质性肺炎1例报道并文献复习[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1196-1200. |
|