北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (3): 447-452. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.03.002
荞麦、燕麦、豌豆复配对糖尿病大鼠血糖的影响
- 北京大学公共卫生学院营养与食品卫生学系, 北京 100191
Effects of the composite of buckwheat-oat-pea on blood glucose in diabetic rats
YIN Xue-qian,ZHANG Xiao-xuan,WEN Jing,LIU Si-qi,LIU Xin-ran,ZHOU Ruo-yu,WANG Jun-boΔ( )
)
- Department of Nutrition and Food Hygiene, Peking University School of Public Health, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
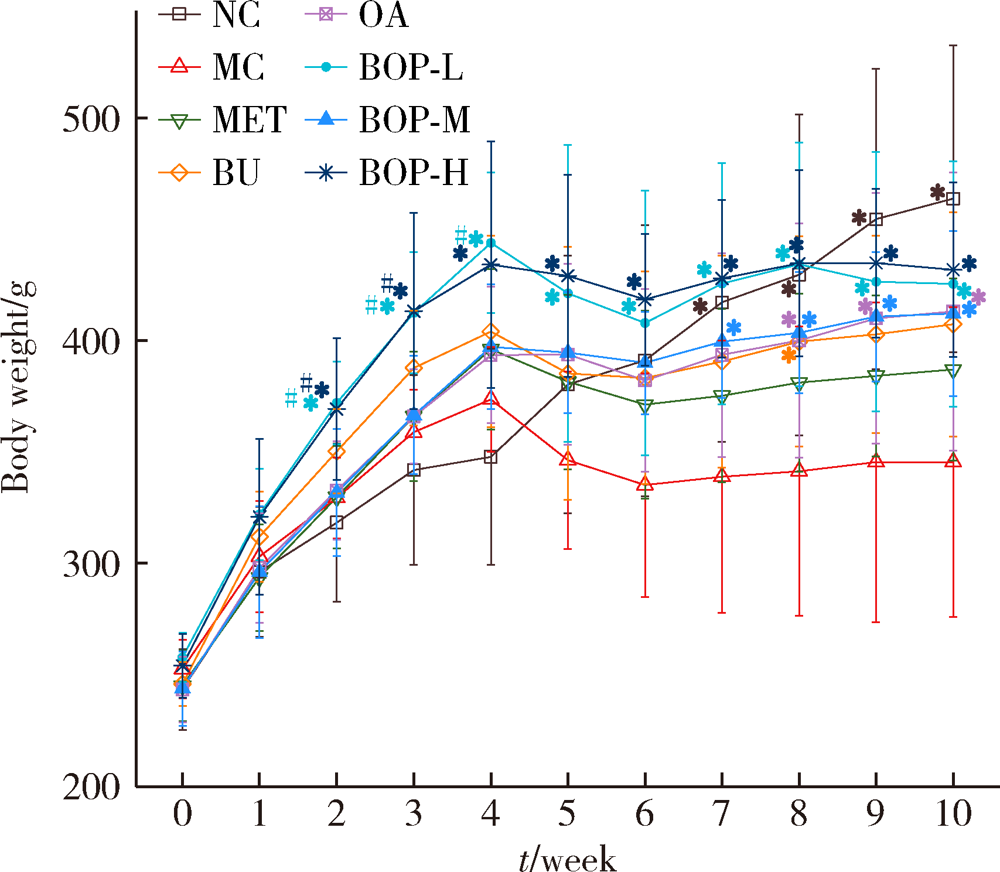
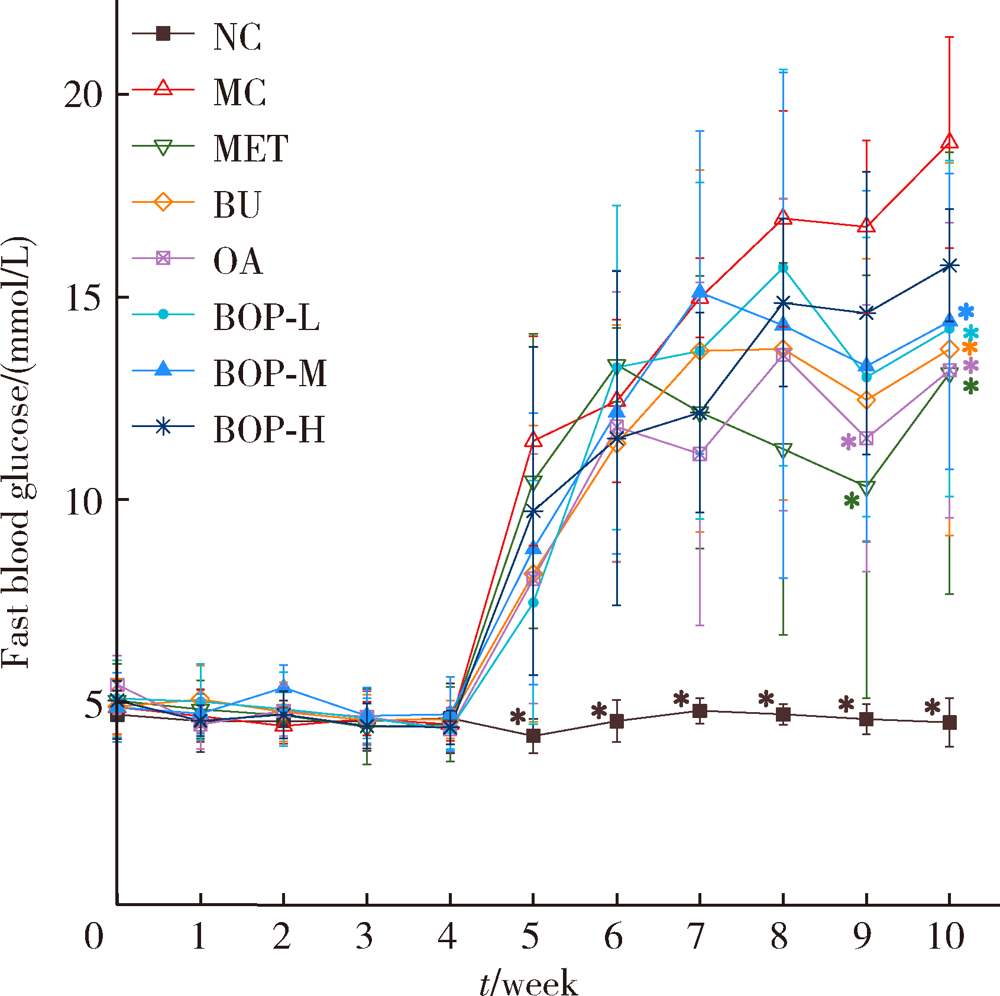
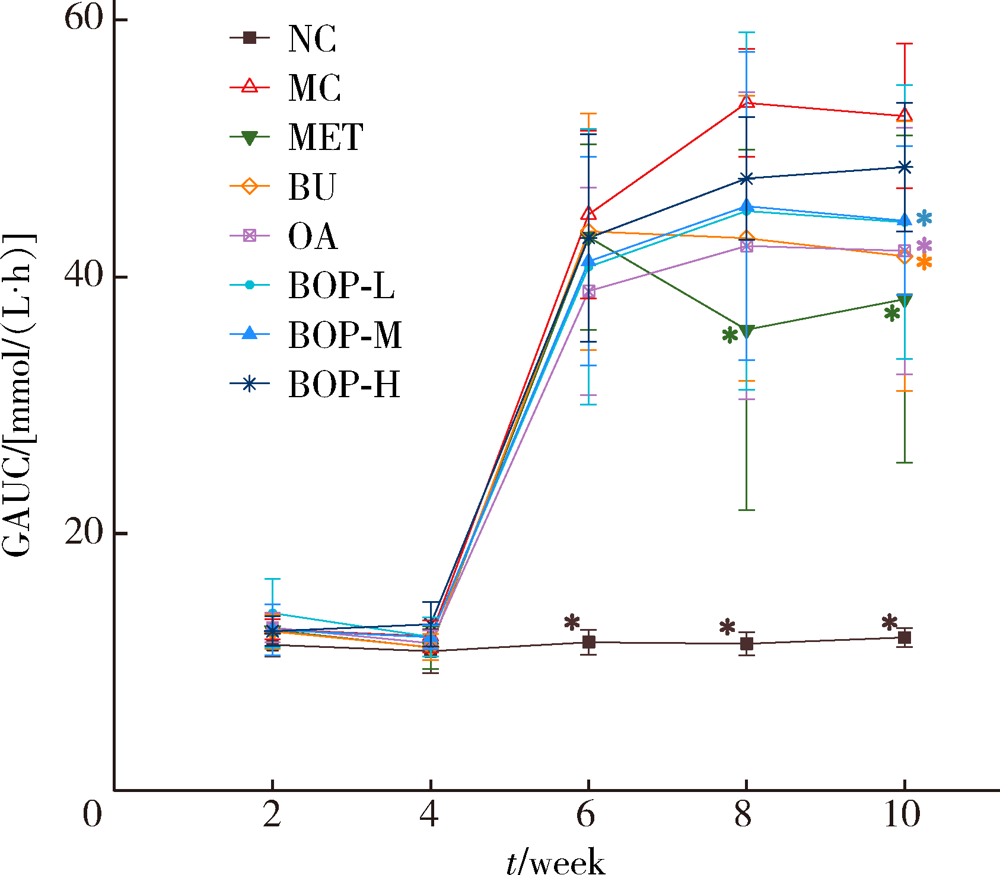
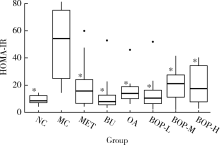
目的: 研究荞麦、燕麦、豌豆(质量比为6 ∶1 ∶1)复配式杂粮(buckwheat-oat-pea composite flour, BOP)对糖尿病大鼠血糖的影响。方法: 64只雄性SD大鼠按照空腹血糖(fasting blood glucose, FBG)和体质量分为8组,包括空白对照组、模型对照组、二甲双胍组、荞麦组、燕麦组、低剂量组(BOP-L)、中剂量组(BOP-M)、高剂量组(BOP-H)。空白对照组大鼠喂养基础饲料,模型对照组和二甲双胍组大鼠喂养高脂饲料,荞麦组、燕麦组、BOP-L、BOP-M、BOP-H组大鼠分别喂养含10%(质量分数)荞麦粉、10%(质量分数)燕麦粉、3.3%(质量分数)BOP、10%(质量分数)BOP、30%(质量分数)BOP的高脂饲料,各组高脂饲料的脂肪供能比均为45%。30 d后,高脂饲料喂养大鼠腹腔注射30 mg/kg链脲佐菌素(每周一次,连续两周)建立糖尿病模型。模型建立成功后,继续喂养28 d。实验期间定期观察各组大鼠体质量、单位体质量进食量及饮水量、食物利用率、24 h尿量、FBG、血糖曲线下面积(glucose area under curve, GAUC)。实验结束时,检测空腹股动脉血清血糖及胰岛素,计算稳态模型胰岛素抵抗指数(homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance, HOMA-IR)。结果: 经过高脂饲料联合链脲佐菌素诱导,与空白对照组相比,模型对照组大鼠单位体质量进食量及饮水量、24 h尿量、FBG、GAUC、HOMA-IR均明显升高(P<0.05),体质量、食物利用率降低(P<0.05)。与模型对照组相比,三个BOP组大鼠体质量、食物利用率均出现显著升高(P<0.05),单位体质量饮水量及HOMA-IR显著降低(P<0.05);BOP-L及BOP-M组大鼠单位体质量进食量、24 h尿量及FBG显著降低(P<0.05),BOP-M组大鼠GAUC也显著降低(P<0.05)。造模成功后,三个BOP组与荞麦组或燕麦组大鼠血糖等指标差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论: BOP具有降低糖尿病大鼠血糖和胰岛素抵抗,减轻糖尿病症状的作用,具有进一步开发利用的价值。
中图分类号:
- R587.1
| [1] | International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas[EB/OL]. (2019-11-14) [2020-08-24]. https://www.diabetesatlas.org. |
| [2] |
Li L, Lietz G, Seal C. Buckwheat and CVD risk markers: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Nutrients, 2018,10(5):619.
doi: 10.3390/nu10050619 |
| [3] |
He LX, Zhao J, Huang YS, et al. The difference between oats and beta-glucan extract intake in the management of HbA1c, fasting glucose and insulin sensitivity: a meta-analysis of rando-mized controlled trials[J]. Food Funct, 2016,7(3):1413-1428.
doi: 10.1039/C5FO01364J |
| [4] | Al-Malki AL. Oat Attenuation of hyperglycemia-induced retinal oxidative stress and NF-kappaB activation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2013,2013:983923. |
| [5] |
Hashemi Z, Fouhse J, Im HS, et al. Dietary pea fiber supplementation improves glycemia and induces changes in the composition of gut microbiota, serum short chain fatty acid profile and expression of mucins in glucose intolerant rats[J]. Nutrients, 2017,9(11):1236.
doi: 10.3390/nu9111236 |
| [6] | 何宇纳, 赵丽云, 于冬梅, 等. 中国成年居民粗杂粮摄入状况[J]. 营养学报, 2016,38(2):115-118. |
| [7] |
Ruggiero E, Bonaccio M, Di Castelnuovo A, et al. Consumption of whole grain food and its determinants in a general Italian population: Results from the INHES study[J]. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis, 2019,29(6):611-620.
doi: S0939-4753(19)30066-3 pmid: 30956028 |
| [8] | 韩珍华, 王瑞, 吕万勇. 糖尿病患者营养教育中粗杂粮摄入情况分析[J]. 海南医学, 2013,24(12):1842-1844. |
| [9] |
Qiu J, Liu Y, Yue Y, et al. Dietary tartary buckwheat intake attenuates insulin resistance and improves lipidprofiles in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial[J]. Nutr Res, 2016,36(12):1392-1401.
doi: S0271-5317(16)30673-X pmid: 27919453 |
| [10] | 杨兰兰, 徐曼, 董方虹, 等. 燕麦饮食干预在社区2型糖尿病饮食治疗中的应用研究[J]. 中国现代医学杂志, 2018,28(19):75-79. |
| [11] |
Li X, Cai X, Ma X, et al. Short- and long-term effects of wholegrain oat intake on weight management and glucolipid metabolism in overweight type-2 diabetics: a randomized control trial[J]. Nutrients, 2016,8(9):549.
doi: 10.3390/nu8090549 |
| [12] | 梁云. 荞麦早餐饮食对糖尿病患者餐后血糖的影响[J]. 临床合理用药杂志, 2018,11(17):116-117. |
| [13] | 方海滨, 亢春雨, 郭梦冉, 等. 薏米燕麦膨化食品对高血糖血脂大鼠模型的降糖降脂作用研究[J]. 河北农业大学学报, 2018,41(6):87-91. |
| [14] | 中国食品药品监督管理局. 辅助降血糖功能评价方法[EB/OL]. (2012-04-23) [2020-08-27]. http://www.cfda.com.cn/NewsDetail.aspx?id=53366. |
| [15] |
Perez-Ramirez IF, Becerril-Ocampo LJ, Reynoso-Camacho R, et al. Cookies elaborated with oat and common bean flours improved serum markers in diabetic rats[J]. J Sci Food Agric, 2018,98(3):998-1007.
doi: 10.1002/jsfa.2018.98.issue-3 |
| [16] | 杨月欣, 王光亚, 潘兴昌. 中国食物成分表[M]. 2版. 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2009. |
| [17] | Beitane I, Krumina-Zemture G, Sabovics M. Technological properties of pea and buckwheat flours and their blends[M]// Treija S, Skujeniece S. Research for rural development. Jelgava: Latvia Univ Life Sciences & Technologies, 2016: 137-142. |
| [18] |
Angioloni A, Collar C. Nutritional and functional added value of oat, Kamut, spelt, rye and buckwheat versus common wheat in breadmaking[J]. J Sci Food Agric, 2011,91(7):1283-1292.
doi: 10.1002/jsfa.4314 |
| [19] | 齐婧, 吕莹果. 多谷物面条的配方优化[J]. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018,39(3):58-64. |
| [20] | 刘淑梅, 韩淑英, 张宝忠, 等. 荞麦种子总黄酮对糖尿病高脂血症大鼠血脂、血糖及脂质过氧化的影响[J]. 中成药, 2003,25(8):60-61. |
| [21] |
Peng L, Zhang Q, Zhang Y, et al. Effect of tartary buckwheat, rutin, and quercetin on lipid metabolism in rats during high dietary fat intake[J]. Food Sci Nutr, 2020,8(1):199-213.
doi: 10.1002/fsn3.v8.1 |
| [22] |
Liu M, Zhang Y, Zhang H, et al. The anti-diabetic activity of oat β-d-glucan in streptozotocin-nicotinamide induced diabetic mice[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2016,91:1170-1176.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.06.083 |
| [23] |
Shen RL, Cai FL, Dong JL, et al. Hypoglycemic effects and biochemical mechanisms of oat products on streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2011,59(16):8895-8900.
doi: 10.1021/jf200678q |
| [24] | 张慧娟, 黄莲燕, 尹梦, 等. 燕麦多肽降血糖功能的研究[J]. 食品工业科技, 2017,38(10):360-363, 384. |
| [25] | 柳春, 王艳杰, 刘洋, 等. 苦荞麦提取物对糖尿病模型大鼠肾脏的保护作用及机制[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2016,36(3):557-559. |
| [26] |
Hu Y, Hou Z, Yi R, et al. Tartary buckwheat flavonoids ameliorate high fructose-induced insulin resistance and oxidative stress associated with the insulin signaling and Nrf2/HO-1 pathwaysin mice[J]. Food Funct, 2017,8(8):2803-2816.
doi: 10.1039/C7FO00359E |
| [27] |
Hashemi Z, Yang K, Yang H, et al. Cooking enhances beneficial effects of pea seed coat consumption on glucosetolerance, incretin, and pancreatic hormones in high-fat-diet-fed rats[J]. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab, 2015,40(4):323-333.
doi: 10.1139/apnm-2014-0380 pmid: 25794240 |
| [1] | 汪雨欣,邓宇含,谭银亮,刘宝花. 应激性血糖升高对重症监护病房患者28 d全因死亡风险的预测价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 442-449. |
| [2] | 郭洪萍,赵艾,薛勇,马良坤,张玉梅,王培玉. 孕期营养素摄入与妊娠期糖尿病孕妇血糖控制效果的相关性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 467-472. |
| [3] | 王兆年,高文静,王碧琦,曹卫华,吕筠,余灿清,逄增昌,丛黎明,汪华,吴先萍,刘彧,李立明. 成年双生子空腹血糖、糖化血红蛋白与全基因组DNA甲基化的相关性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(3): 425-431. |
| [4] | 何海珍,张婷,周景,王东平,王浩杰,宋阳,朱珠,王培玉,刘爱萍. 乌海市成人含糖饮料饮用与糖尿病的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(3): 469-473. |
| [5] | 朱振杰,许清泉,黄晓波,洪扬,杨庆亚,王澍,安立哲,徐涛. 糖尿病患者经皮肾镜取石术后发生全身炎症反应综合征的危险因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(4): 643-649. |
| [6] | 李志霞,武珊珊,杨智荣,詹思延,孙凤. 胰高血糖素样肽1受体激动剂类降糖药致2型糖尿病患者鼻咽炎和上呼吸道感染的网状meta分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(3): 454-459. |
| [7] | 孙可欣, 刘志, 曹亚英, 隽娟, 项骁, 杨成, 黄少平, 刘晓芬, 李娜, 唐迅, 李劲, 吴涛, 陈大方, 胡永华 . 北京某社区2型糖尿病患者血糖控制情况与肱踝脉搏波传导速度的相关性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(3): 431-436. |
| [8] | 徐可, 刘雪芹, 张春雨, 王颖, 李星, 吴晔, 杨艳玲, 肖慧捷. 果糖-1,6-二磷酸酶缺乏症基因诊断1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(5): 681-685. |
| [9] | 于卓人*, 刘丽笙, 栾庆先, 王兴宇, 李蓬, 沙月琴, 刘曦. 北京石景山区老年人群牙周炎与代谢综合征的相关性探讨[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(4): 633-638. |
| [10] | 王义, 贺利军, 周哲, 赵文峰, 那彦群. 30~50岁男性前列腺体积与体重指数、血压、血脂及血糖的相关性分析 [J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2011, 43(3): 460-462. |
| [11] | 李峥*, 沙月琴, 张博学, 朱凌, 康军. 社区牙周干预对2型糖尿病患者牙周健康及血糖代谢水平的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2011, 43(2): 285-289. |
| [12] | 关明, 刘瑞昌, 杨旭东, 董稳, 刘克英 . 婴儿唇腭裂修复术中输注不同浓度含糖液的效果分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2010, 42(1): 74-77. |
| [13] | 董爱梅, 袁振芳, 张虹, 高燕明, 郭晓蕙. 2型糖尿病合并胰岛细胞增生症1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2009, 41(5): 590-592. |
| [14] | 张婷婷, 徐冲, 俎鲁霞, 何金汗, 蒲申申, 郭晓蕙, 徐国恒. 高浓度葡萄糖刺激脂肪细胞脂肪分解的效应及其机制[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2008, 40(3): 273-279. |
| [15] | 汤秀英, 王昱, 郭晓蕙, 王书合, 柴立军, 张烨. 胰高血糖素样多肽-1对OLETF大鼠肺泡毛细血管基板的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2008, 40(2): 178-180. |
|
||