北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (3): 485-490. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.03.008
2015—2019年宁波市0~36月龄婴幼儿癫痫发病的流行病学研究
姚晓莹1,刘志科1,李宁2,马瑞2,赵薛飞2,张良2,许国章2,詹思延1,Δ( ),方挺2,Δ(
),方挺2,Δ( )
)
- 1.北京大学公共卫生学院流行病与卫生统计学系, 北京 100191
2.宁波市疾病控制与预防中心, 浙江宁波 315010
Epidemiological study of infantile epilepsy incidence density among infants under 36 months of age in Ningbo City from 2015 to 2019
YAO Xiao-ying1,LIU Zhi-ke1,LI Ning2,MA Rui2,ZHAO Xue-fei2,ZHANG Liang2,XU Guo-zhang2,ZHAN Si-yan1,Δ( ),FANG Ting2,Δ(
),FANG Ting2,Δ( )
)
- 1. Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Peking University School of Public Health, Beijing 100191, China
2. Ningbo Municipal Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Ningbo 315010, Zhejiang, China
摘要:
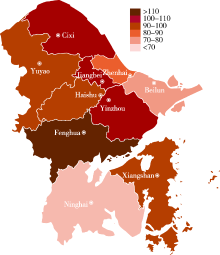
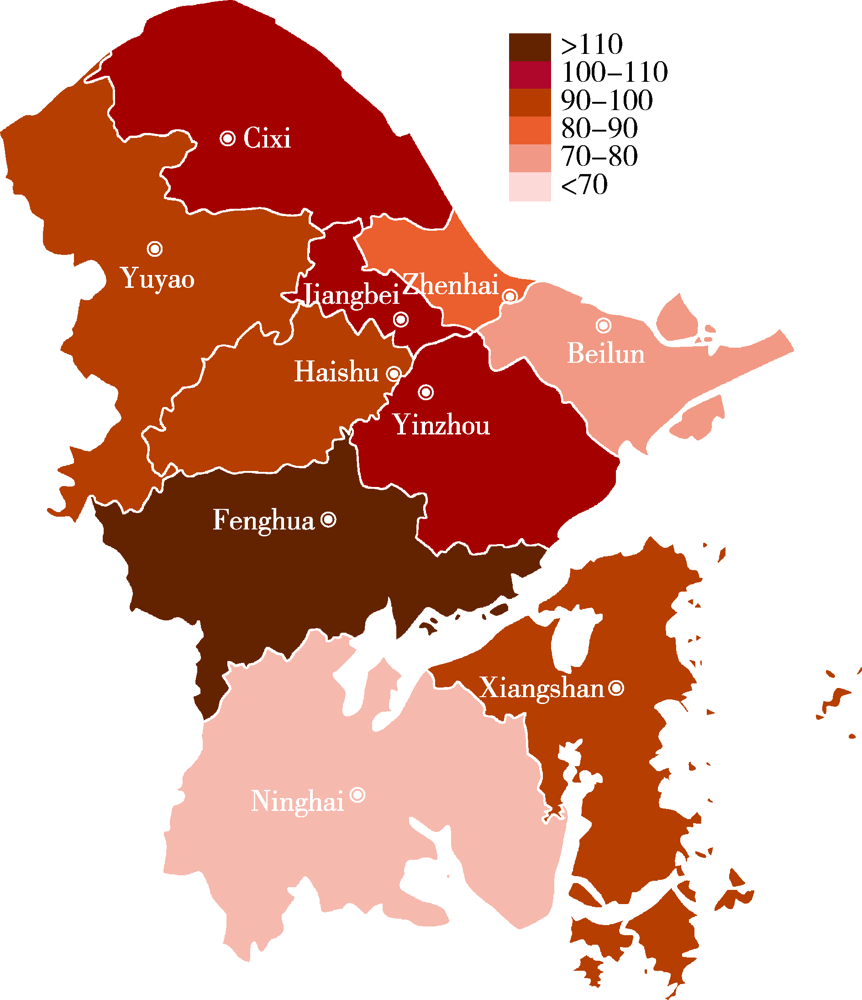
目的: 描述浙江省宁波市0~36月龄婴幼儿癫痫发病的三间分布及其变化趋势。方法: 采用出生队列设计,回顾性收集2015—2019年宁波市全民健康信息平台中本地出生的婴幼儿,以平台内电子病历首次癫痫就诊作为新发病例。采用泊松分布估算癫痫发病密度及其95%CI。结果: 2015—2019年宁波市累计出生29.49万儿童,男性占51.92%,总人年59.53万,中位随访人年2.31年[四分位距(interquartile range, IQR):1.90]。观察期间癫痫新发575例,总就诊人次2 599,平均就诊人次4.52,总发病密度96.59/10万人年(95%CI:88.85~104.82)。中位发病月龄13月龄(IQR:15),0~12月龄发病密度最高(102.18/10万人年),25~36月龄最低(89.68/10万人年),差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。男性发病密度97.58/10万人年,女性95.53/10万人年,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。下辖10个区县中,奉化最高(130.54/10万人年,95%CI:94.47~175.83),宁海最低(66.44/10万人年,95%CI:47.02~91.19), 差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。不同出生年份发病差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。不同日历年0~12月龄发病密度差异有统计学意义(Ptrend<0.05)。该年龄组下, 2015年发病密度最低(69.41/10万人年,95%CI:41.79~108.39), 2019年最高(225.61/10万人年,95%CI:186.10~271.03)。不同日历年13~24、25~36月龄发病密度差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论: 2015—2019年宁波市0~36月龄婴幼儿癫痫发病密度整体较低,年龄组、性别、出生年份等发病密度差异均无统计学意义,0~12月龄婴幼儿发病密度随年份呈递增趋势。
中图分类号:
- R181.32
| [1] | 中国抗癫痫协会. 临床诊疗指南·癫痫病分册(2015修订版)[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2015. |
| [2] |
Hildebrand MS, Dahl HH, Damiano JA, et al. Recent advances in the molecular genetics of epilepsy[J]. J Med Genet, 2013,50(5):271-279.
doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2012-101448 |
| [3] |
Scheffer IE. Vaccination triggers, rather than causes, seizures[J]. Epilepsy Curr, 2015,15(6):335-337.
doi: 10.5698/1535-7511-15.6.335 pmid: 26633955 |
| [4] |
Aaberg KM, Gunnes N, Bakken IJ, et al. Incidence and prevalence of childhood epilepsy: A nationwide cohort study[J]. Pediatrics, 2017,139(5):e20163908.
doi: 10.1542/peds.2016-3908 |
| [5] |
Eltze CM, Chong WK, Cox T, et al. A population-based study of newly diagnosed epilepsy in infants[J]. Epilepsia, 2013,54(3):437-445.
doi: 10.1111/epi.2013.54.issue-3 |
| [6] |
Hernan MA, Logroscino G. Neuroepidemiology: from principles to practice[J]. Am J Epidemiol, 2005,161(5):501-502.
doi: 10.1093/aje/kwi070 |
| [7] |
GBD 2016 Neurology Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders, 1990-2016: A syste-matic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2019,18(5):357-375.
doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30454-X |
| [8] |
Jacoby A, Baker GA. Epilepsy and social identity: The stigma of a chronic neurological disorder[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2005,4(3):171-178.
pmid: 15721827 |
| [9] |
Liu ZK, Zhang L, Yang Y, et al. Active surveillance of adverse events following human papillomavirus vaccination: Feasibility pilot study based on the regional health care information platform in the city of Ningbo, China[J]. J Med Internet Res, 2020,22(6):e17446.
doi: 10.2196/17446 |
| [10] |
Camfield P, Camfield C. Incidence, prevalence and aetiology of seizures and epilepsy in children[J]. Epileptic Disord, 2015,17(2):117-123.
doi: 10.1684/epd.2015.0736 pmid: 25895502 |
| [11] |
Christensen J, Vestergaard M, Pedersen MG, et al. Incidence and prevalence of epilepsy in Denmark[J]. Epilepsy Res, 2007,76(1):60-65.
pmid: 17686613 |
| [12] |
Kim H, Thurman DJ, Durgin T, et al. Estimating epilepsy incidence and prevalence in the US pediatric population using Nationwide Health Insurance Claims Data[J]. J Child Neurol, 2016,31(6):743-749.
doi: 10.1177/0883073815620676 |
| [13] |
Casetta I, Pugliatti M, Faggioli R, et al. Incidence of childhood and adolescence epilepsy: A community-based prospective study in the province of Ferrara and in Copparo, Italy, 1996—2005[J]. Eur J Neuro, 2012,19(2):312-316.
doi: 10.1111/j.1468-1331.2011.03506.x |
| [14] |
Wirrell EC, Grossardt BR, Wong-Kisiel L, et al. Incidence and classification of new-onset epilepsy and epilepsy syndromes in children in Olmsted County, Minnesota from 1980 to 2004: A population-based study[J]. Epilepsy Res, 2011,95(12):110-118.
doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2011.03.009 |
| [15] |
Ngugi AK, Kariuki SM, Bottomley C, et al. Incidence of epilepsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Neurology, 2011,77(10):1005-1012.
doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e31822cfc90 |
| [16] |
Hu J, Si Y, Zhou D, et al. Prevalence and treatment gap of active convulsive epilepsy: A large community-based survey in rural West China[J]. Seizure, 2014,23(5):333-337.
doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2014.01.007 |
| [17] |
Li J, Si Y, Hu J, et al. Enhancing medical compliance of patients with convulsive epilepsy in rural community: A randomized intervention trial[J]. Epilepsia, 2013,54(11):1988-1996.
doi: 10.1111/epi.12382 |
| [18] | 宁波市统计局. 宁波统计年鉴2020 [DB/OL]. (2020-12-03)[2021-01-31]. http://vod.ningbo.gov.cn:88/nbtjj/tjnj/2020nbnj/zk/indexch.htm. |
| [19] |
Hauser WA, Annegers JF, Kurland LT. Incidence of epilepsy and unprovoked seizures in Rochester, Minnesota: 1935-1984[J]. Epilepsia, 1993,34(3):453-468.
pmid: 8504780 |
| [20] |
Sillanp M, Lastunen S, Helenius H, et al. Regional differences and secular trends in the incidence of epilepsy in Finland: A nationwide 23-year registry study[J]. Epilepsia, 2011,52(10):1857-1867.
doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2011.03186.x |
| [1] | 焦莶如, 龚潘, 牛悦, 徐兆, 周宗朴, 杨志仙. 以婴儿癫痫性痉挛综合征为表型的吡哆醇依赖性癫痫[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 781-787. |
| [2] | 李洋洋,侯林,马紫君,黄山雅美,刘捷,曾超美,秦炯. 孕期因素与婴儿牛奶蛋白过敏的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 144-149. |
| [3] | 刘京,陆爱东,左英熹,吴珺,黄志卓,贾月萍,丁明明,张乐萍,秦炯. 儿童急性淋巴细胞白血病合并癫痫发作75例临床特征和预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 948-953. |
| [4] | 贺冰洁,刘志科,沈鹏,孙烨祥,陈彬,詹思延,林鸿波. 2011—2020年宁波市鄞州区炎症性肠病发病的流行病学研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 511-519. |
| [5] | 李玭,赵艾,武薇,张健,王培玉,蓝航莲,张玉梅. 北京市和湖南省郴州市4~8月龄婴儿蔬菜水果添加情况的追踪性调查[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 526-531. |
| [6] | 董彦会,陈曼曼,王丽萍,星一,宋逸,邹志勇,董彬,李中杰,马军. 中国6~22岁学生群体甲乙丙类传染病流行趋势[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 498-505. |
| [7] | 候越,赵旭彤,谢志颖,袁云,王朝霞. 线粒体DNA 8344 A>G突变导致的MELAS/MERRF/Leigh重叠综合征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(5): 851-855. |
| [8] | 朱莎,徐宗胜,夏晴,方筱静,赵丹华,刘献增. 伴杏仁核肥大的颞叶癫痫的临床及病理特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(5): 824-828. |
| [9] | 李秀兰,吴艳,钟晓云,王敏,黄利. 新生儿重症监护室早产儿母乳喂养促进策略研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(4): 711-715. |
| [10] | 卢娇杨,薛姣,龚潘,海坡,杨志仙. 光敏性强直阵挛发作:局灶性及全面性发作的统一体[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(3): 422-429. |
| [11] | 孙智明,陈倩,李明华,马维宁,赵旭阳,黄卓. 小鼠卡英酸颞叶癫痫慢性发作期的磷酸化蛋白组学研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 197-205. |
| [12] | 包菊,刘佳,曲元,穆东亮. 脐动脉血气pH值对剖宫产新生儿住院期间并发症的预测价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(1): 159-164. |
| [13] | 张晓慧,邓雪蓉,李凡,朱颖,张卓莉. 系统性红斑狼疮合并可逆性后部脑病综合征1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(6): 1102-1107. |
| [14] | 龚潘,杨志仙,薛姣,钱萍,杨海坡,刘晓燕,边凯归. 头皮脑电图中高频振荡在癫痫性脑病伴睡眠中持续棘慢波患儿中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(2): 213-220. |
| [15] | 刘园,栾庆先. 北京石景山社区中老年人群慢性牙周炎和颈动脉内膜中层厚度的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(2): 264-270. |
|
||