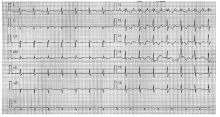
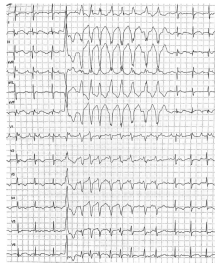
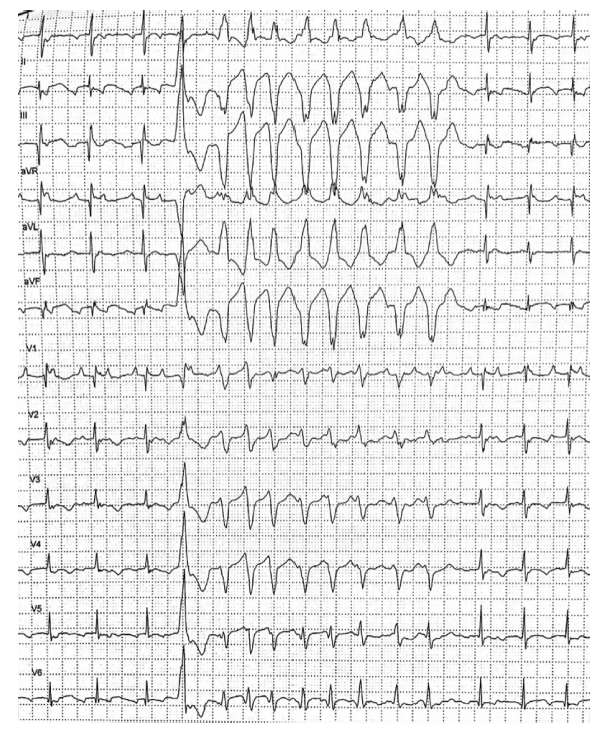
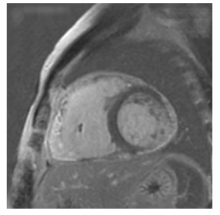
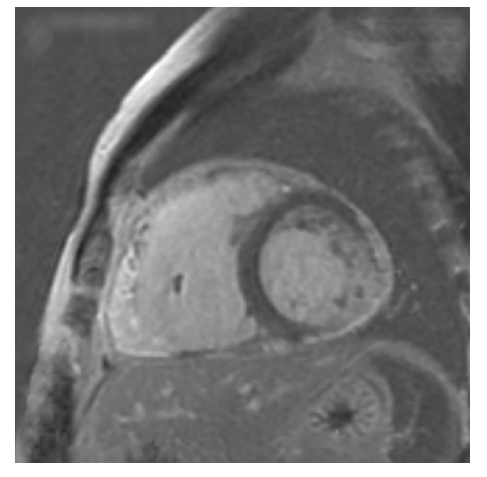
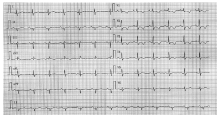
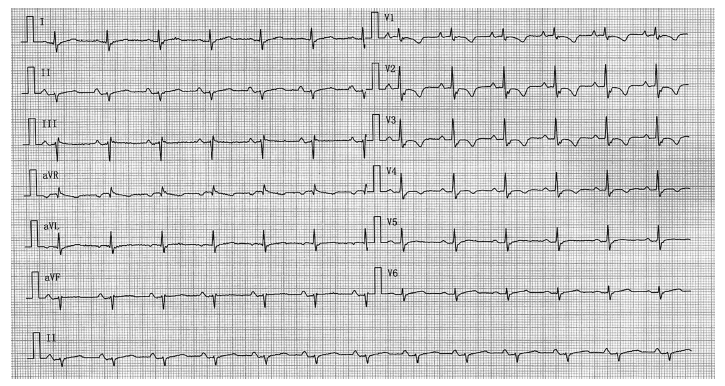
北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (5): 1002-1006. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.05.032
致心律失常型右心室心肌病伴发心律失常性心肌病1例
- 北京大学第三医院心内科、血管医学研究所,国家卫生健康委心血管分子生物学与调节肽重点实验室,分子心血管学教育部重点实验室,心血管受体研究北京市重点实验室,北京 100191
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy associated with arrhythmia-induced cardiomyopathy: A case report
CHEN Shao-min,SUN Chao( ),WANG Xin-yu,ZHANG Yuan,LIU Shu-wang
),WANG Xin-yu,ZHANG Yuan,LIU Shu-wang
- Beijing Key Laboratory of Cardiovascular Receptors Research, Beijing 100191, China
中图分类号:
- R541
| [1] |
Gandjbakhch E, Redheuil A, Pousset F, et al. Clinical diagnosis, imaging, and genetics of arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy/dysplasia: JACC state-of-the-art review [J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2018, 72(7):784-804.
doi: S0735-1097(18)35284-7 pmid: 30092956 |
| [2] | 中华医学会心血管病学分会精准心血管病学学组, 中国医疗保健国际交流促进会, 精准心血管病分会, 等. 单基因遗传性心血管疾病基因诊断指南 [J]. 中华心血管病杂志, 2019, 47(3):175-196. |
| [3] |
Marcus FI, McKenna WJ, Sherrill D, et al. Diagnosis of arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy/dysplasia: Proposed modification of the task force criteria [J]. Circulation, 2010, 121(13):1533-1541.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.840827 |
| [4] |
Morimoto S, Sekiguchi M, Okada R, et al. Two autopsied cases of arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia [J]. J Cardiol, 1990, 20(4):1025-1036.
pmid: 2133713 |
| [5] |
Vila J, Pariaut R, Moise NS, et al. Structural and molecular pathology of the atrium in boxer arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy [J]. J Vet Cardiol, 2017, 19(1):57-67.
doi: S1760-2734(16)30073-X pmid: 27769725 |
| [6] |
Wu L, Bao J, Liang E, et al. Atrial involvement in arrhythmo-genic right ventricular cardiomyopathy patients referred for ventri-cular arrhythmias ablation [J]. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 2018, 29(10):1388-1395.
doi: 10.1111/jce.2018.29.issue-10 |
| [7] |
Cardona-Guarache R, Åström-Aneq M, Oesterle A, et al. Atrial arrhythmias in patients with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy: Prevalence, echocardiographic predictors, and treatment [J]. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 2019, 30(10):1801-1810.
doi: 10.1111/jce.v30.10 |
| [8] |
Saguner AM, Ganahl S, Kraus A, et al. Clinical role of atrial arrhythmias in patients with arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia [J]. Circ J, 2014, 78(12):2854-2861.
pmid: 25327952 |
| [9] |
Camm CF, James CA, Tichnell C, et al. Prevalence of atrial arrhythmias in arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia/cardio-myopathy [J]. Heart Rhythm, 2013, 10(11):1661-1668.
doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2013.08.032 |
| [10] |
Sugumar H, Prabhu S, Voskoboinik A, et al. Arrhythmia induced cardiomyopathy [J]. J Arrhythm, 2018, 34(4):376-383.
doi: 10.1002/joa3.2018.34.issue-4 |
| [11] | Corrado D, Wichter T, Link MS, et al. Treatment of arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy/dysplasia: An international task force consensus statement [J]. Eur Heart J, 2015, 36(46):3227-3237. |
| [12] |
Haugaa KH, Haland TF, Leren IS, et al. Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis [J]. Europace, 2016, 18(7):965-972.
doi: 10.1093/europace/euv340 |
| [1] | 刘园梅, 傅义程, 郝靖欣, 张福春, 刘慧琳. 老年髋部骨折患者住院期间发生术后心力衰竭的列线图预测模型的构建及验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 874-883. |
| [2] | 韦莹,崔鸣,刘书旺,于海奕,高炜,李蕾. 心房颤动患者血清生长分化因子-15的表达差异和临床意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 715-721. |
| [3] | 彭圣嘉,祁雨,孙丽杰,李丹,王新宇,韩江莉,陈宝霞,张媛. 传入压力反射衰竭合并低钠血症1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 357-361. |
| [4] | 许昊,张国栋,范桄溥,陈彧. 冠状动脉旁路移植术后新发心房颤动的血浆预测因子:倾向性评分匹配研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1139-1143. |
| [5] | 刘欢,何映东,刘金波,黄薇,赵娜,赵红薇,周晓华,王宏宇. 血管健康指标对新发心脑血管事件的预测价值:北京血管健康分级标准的初步验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(3): 514-520. |
| [6] | 任川,吴晓月,赵威,陶立元,刘萍,高炜. 心肺适能对动脉粥样硬化性心血管疾病高危患者的保护作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 152-157. |
| [7] | 孙文强,赵舟,高卿,韩增强,杨威,廉波,刘刚,陈生龙,陈彧. 非体外循环冠状动脉旁路移植术中桥血管血流对术后近中期预后的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(5): 851-855. |
| [8] | 张静,李素芳,陈红,宋俊贤. miR-106b-5p在调节内皮细胞基因表达谱中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 221-227. |
| [9] | 赵灿,胡京敏,郭丹杰. 血浆D二聚体临界值联合Wells量表对可疑肺栓塞的除外价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(5): 828-832. |
| [10] | 任书堂,王勇,周建华,龙进,王翠华,李冬蓓,黄云洲. 心下型完全性肺静脉异位连接的超声心动图诊断[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 0, (): 883-888. |
| [11] | 任书堂, 王勇, 周建华, 龙进, 王翠华, 李冬蓓, 黄云洲. 心下型完全性肺静脉异位连接的超声心动图诊断[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(5): 883-888. |
| [12] | 冯琦琛,李选,栾景源,王昌明,李天润. 肾滤过分数评价肾动脉支架植入术对动脉硬化性肾动脉狭窄的治疗效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(1): 158-163. |
| [13] | 刘滕飞,张婧薇,陈夏欢,冯雪茹,柏中胜,刘梅林. CMTM5基因rs723840单核苷酸多态性与阿司匹林治疗下血小板高反应性的相关性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(6): 905-909. |
| [14] | 刘滕飞,张婧薇,陈夏欢,冯雪茹,柏中胜,刘梅林. 尿11-脱氢血栓素B2水平与2型糖尿病合并冠心病患者阿司匹林临床疗效的相关性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(6): 920-924. |
|
||